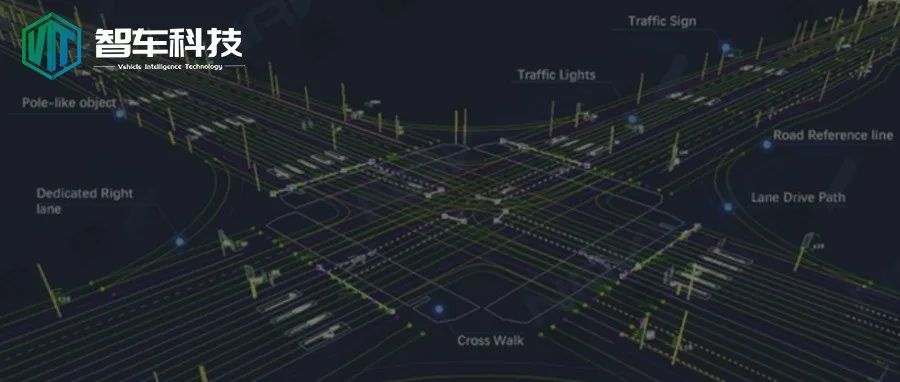
Introduction
For the navigation maps on mobile phones, everyone must be familiar with them and use them almost every day. No matter where you go, you can quickly find the most convenient and fastest route by opening the map on your phone. For drivers, navigation maps are crucial, but for autonomous driving, simple navigation maps cannot meet their needs, and many additional semantic information needs to be added. As the output is directly given to the decision-making and planning module in the autonomous driving algorithm, high-definition maps need to include detailed road models, lane models, road components, road properties, etc. It can be said that with the help of high-definition maps, the decision-making and planning algorithms in autonomous driving can understand the surrounding environmental information more completely and focus more on responding to the traffic and people around, and make more reasonable and safe decisions after mastering more information. This article will lead readers to learn more about the high-precision maps that play a pivotal role in autonomous driving.
What is a high-definition map
High-precision maps (also known as high-precision electronic maps) are actually thematic maps that serve autonomous driving systems as opposed to ordinary navigation electronic maps. High-definition maps, also known as autonomous driving maps and high-resolution maps, are a new type of map data paradigm for autonomous vehicles. The absolute position accuracy of high-precision maps is close to 1 meter, and the relative position accuracy is at the centimeter level, which can reach 10-20 cm.
Accurately and comprehensively representing road features and requiring higher real-time performance is the most significant feature of high-precision maps. In addition, high-definition maps record the specific details of driving behavior, including typical driving behavior, the best acceleration point and braking point, the complexity of road conditions, and annotations on receiving signals from different road sections.
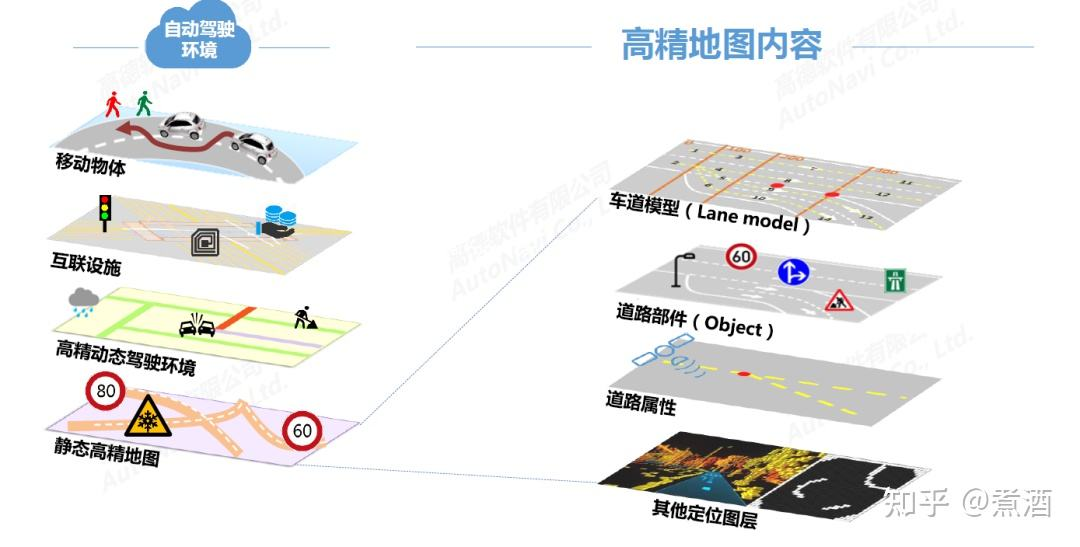
High-precision maps can be divided into two levels: static high-precision maps and dynamic high-precision maps.
Static high-precision maps are at the bottom level and are currently the focus of research and development. It generally consists of three types of vector information containing semantic information of lane models, road components (Object), and road properties, and features (feature) layer for multi-sensor positioning.
Dynamic high-definition maps are built on the basis of static high-definition maps and mainly include real-time dynamic information, including information on other traffic participants (such as road congestion, construction conditions, whether there are traffic accidents, traffic control conditions, weather conditions, etc.), and information on traffic participants (such as traffic lights, pedestrian crossings, etc.).
Why high-precision maps are essential for autonomous driving## High-precision Map
A high-precision map is not only superior in its centimeter-level quantization accuracy, but also in its spatial abstraction level. As an important part of the automatic driving system, high-precision maps focus on the automatic driving scenario and allow the autonomous vehicles to understand the constantly changing real environment in a humanized way. They play an important role in the perception, positioning, decision-making, and planning modules of autonomous driving with multi-layered high-precision map data that is updated in real time through cloud computing. They are an indispensable component of the autonomous driving solution.
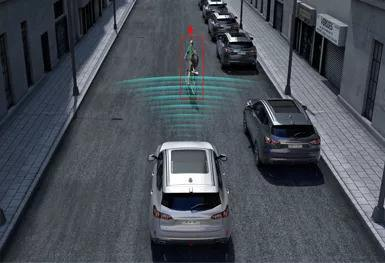
Let’s imagine a typical autonomous driving scenario where we are driving on a road and there is a bicycle riding in front of us. In this situation, there are two decisions to be made for the autonomous vehicle: either following the bicycle or changing lanes. In order to make the decision to change lanes, the autonomous vehicle needs to know a lot of specific information such as:
-
Which lane are we currently in and the specific location of the lane on the map?
-
Does the current lane have a neighboring lane? If there is no other lane, then the vehicle cannot change lanes and can only avoid obstacles in its current lane.
-
Is changing lanes allowed in the current lane? What is the type of lane? Are the lane markings solid or dashed? Is the distance for changing lanes long enough? Will the vehicle be able to reach the destination after changing lanes?
As we can see, the above information is crucial for the autonomous vehicle. However, the perception algorithm of autonomous driving cannot provide such precise and rich scenario information due to its range, computing power, etc. In this case, high-precision maps play an irreplaceable role.
High-precision Map Production Process
Now that we have discussed the role of high-precision maps, let’s take a closer look at how they are made. Generally, the production of high-precision maps involves the following steps:
-
Data collection and acquisition of map information.
-
Data cleaning/aggregation.
-
Automatic recognition, which processes necessary information from the map, including lane markings, traffic lights, crossroads, etc.
-
Manual inspection/annotation because the existing algorithms cannot achieve 100% automatic extraction, so there is still a need for manual inspection and annotation.
-
Post-processing and validation. After the data is generated, it needs to undergo post-processing and validation. The ultimate goal of processing is to ensure that the provided map information is accurate. If a traffic light position is marked incorrectly or automatically recognized incorrectly, it may cause safety hazards during road testing. Therefore, the validation process is an important part.
-
Release. After passing the validation, the data will be published (Data Release) and all data will be integrated into a unified management system. The quality of each version of the released map has been strictly validated. This is a routine release process.
Challenges Facing the Future of High-Precision Maps
After discussing the advantages and necessity of high-precision maps, let’s take a look at the challenges and difficulties that high-precision maps will face when applied to autonomous driving.
First is the issue of cost. High-precision maps require centimeter-level accuracy, which means that the data collection vehicle or person employed by map makers must be equipped with various sensors (LiDAR, cameras, GNSS/IMU). The image below shows Apple’s map collection vehicle, which is clearly costly to manufacture.

Secondly, there is the issue of data storage. High-precision maps contain a large amount of data, and how to store and partition this data for easy use is also one of the difficult points to be solved. The consumption of computing resources is also a concern. Only when these problems can be effectively solved, can high-precision maps be widely deployed on autonomous driving vehicles.
Lastly, there is the issue of updating high-precision maps. Unlike regular maps, the update frequency of high-precision maps needs to be greatly shortened due to the inclusion of a large amount of spatial, temporal, and semantic information. Otherwise, incorrect information could be fatal for autonomous vehicles. Of course, achieving a very frequent update frequency in real life is also unrealistic. Thus, improvements in perception algorithms and computing power are still needed to address the issue of updating frequency redundancy for high-precision maps.

High-precision maps are the key to the successful implementation of autonomous driving in the future. Although there are many problems and challenges that need to be solved urgently, we believe that with the maturity of technology, high-precision maps will play a pivotal role in our daily autonomous travel in the future.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.