New Year’s Preparation on Battery Technology
After returning from the countryside on the second day of the lunar year, work began on preparing for the new year.
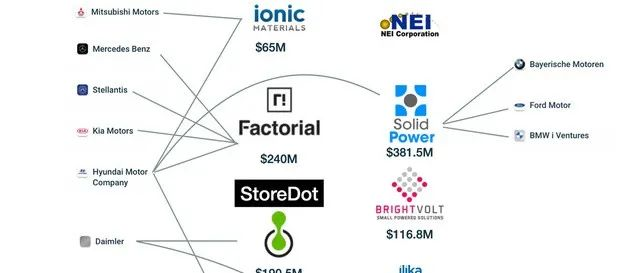
As viewed from an investment perspective, the development of battery technology is no longer solely controlled by individual battery companies and their upstream supply chains. With the continuous trend towards electrification, will vehicle manufacturers need to enter the battery production and design sector? With Tesla being the first to answer this question affirmatively, most vehicle manufacturers are actively or passively investing in cutting-edge battery technology.

Investment Strategies for Vehicle Manufacturers
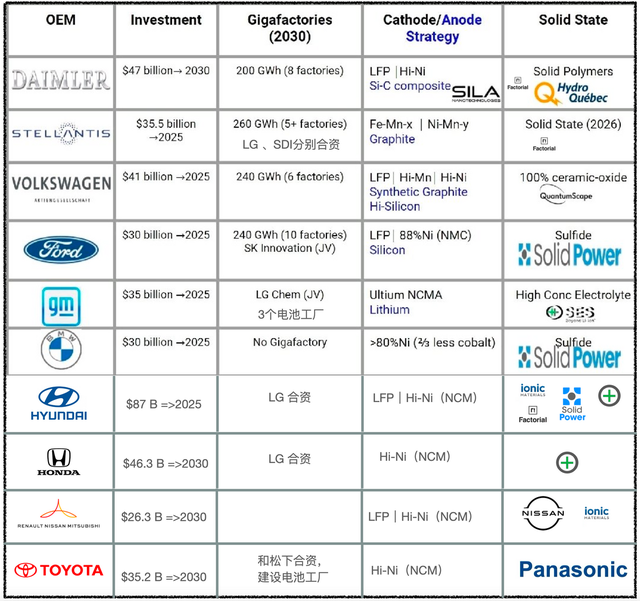
As shown in Table 1, the overall logic behind investing in cutting-edge battery technology this round of investment is primarily due to the substantial investment in electric vehicles (EVs) by major vehicle manufacturers. This includes continuously financing the development of EV platforms and models, all while retrofitting factories to consider battery demand.
Presently, European vehicle manufacturers (from Volkswagen onwards) and American vehicle manufacturers (General Motors, Ford, and Stellantis) are primarily constructing battery companies as part of their efforts to expand.
European Automotive Companies
At present, they can mainly be divided into three camps:
-
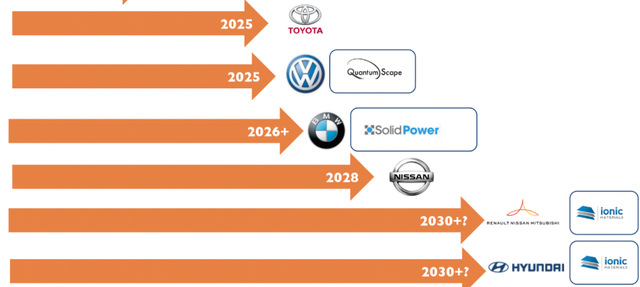
Volkswagen Group is associated with Quantum Scape. Its logic is to continuously assist Quantum Scape in developing production capabilities through investment and capitalization, aiming to mass-produce solid-state batteries by 2025. The resulting joint venture for solid-state batteries would also be packaged into Volkswagen’s overall battery group and eventually offered as a whole to the stock market.
-
Daimler is currently exploring a super battery factory with Stellantis and is constructing a power battery factory (Pack) in Germany. It also invested in Enevate following investments in Stellantis’ affiliate ACC. Previously, Daimler partnered with Hydro-Québec in Canada to develop solid-state batteries, but the overall progress was unsatisfactory.
-
BMW is the only European car company that has not announced plans to build a battery factory. Previously, it discussed investing in Solid Power and has now deepened its cooperation with the company. It plans to test cars equipped with Solid Power’s batteries in 2022, and launch solid-state battery prototype cars by 2025, with a goal to use them in mass production vehicles by 2030.
American Automotive Companies
- Ford has teamed up with SK and invested in American solid-state battery company, Solid Power. It also invested $30 million in Solid Power through SKI and secured the right to use the company’s solid-state battery-related technology and production processes.General Motors is developing solid-state battery research projects on their own, and investing heavily in SES while also collaborating with Honda on the development.
Asian Car Companies
Toyota has lagged behind in solid-state batteries, having put HEVs as their first priority after missing the opportunity to showcase their technology at the Olympics. They have a long way to go to catch up with others.
Hyundai has invested in Solid Power and SES, two American solid-state battery companies, in addition to their previous investments in Envisics and Ionic Materials. They have coverage in investments wider than any other car company.
As for Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi, their investment pace is also different from one another. Nissan is developing their own solid-state battery technology internally while also continuing their investment in Ionic Materials.
In terms of the timing, solid-state battery development is still in its early stages. While most solid-state battery start-up companies have already gone public, they plan to commercialize their batteries by 2025. From the perspective of cooperating car companies, the commercialization of solid-state batteries will start in 2025 (with prices still very high), and from 2025 to 2030, mainly testing and iterations in small quantities will take place. Optimistically, cars equipped with solid-state batteries will begin to be produced on a large scale around 2030. In terms of quantity, Yole estimated that demand for solid-state batteries would be less than 2.5 GWh in 2027, and traditional power lithium-ion batteries will not experience a large-scale leap to solid-state batteries with advanced iterations.
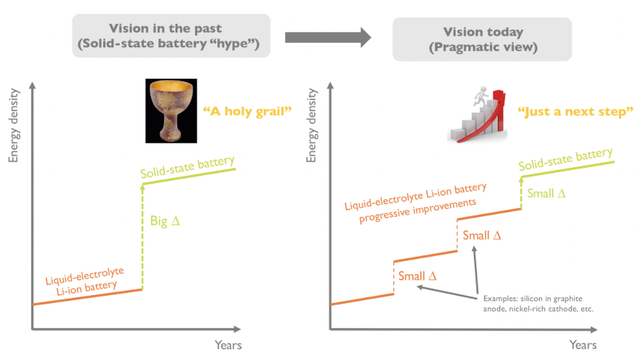
How to View These Investments
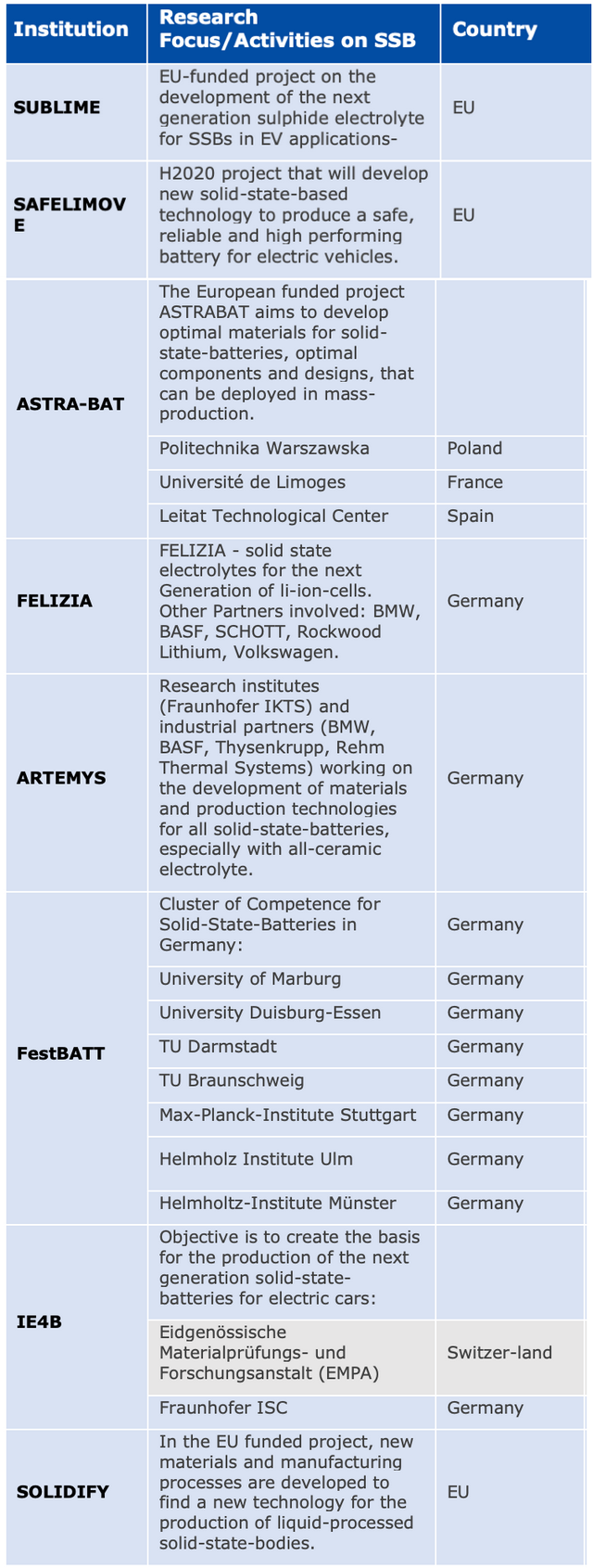
At present, systematic collaboration needs to take place beyond these investments in order to develop advanced and solid-state batteries as seen in Table 2.
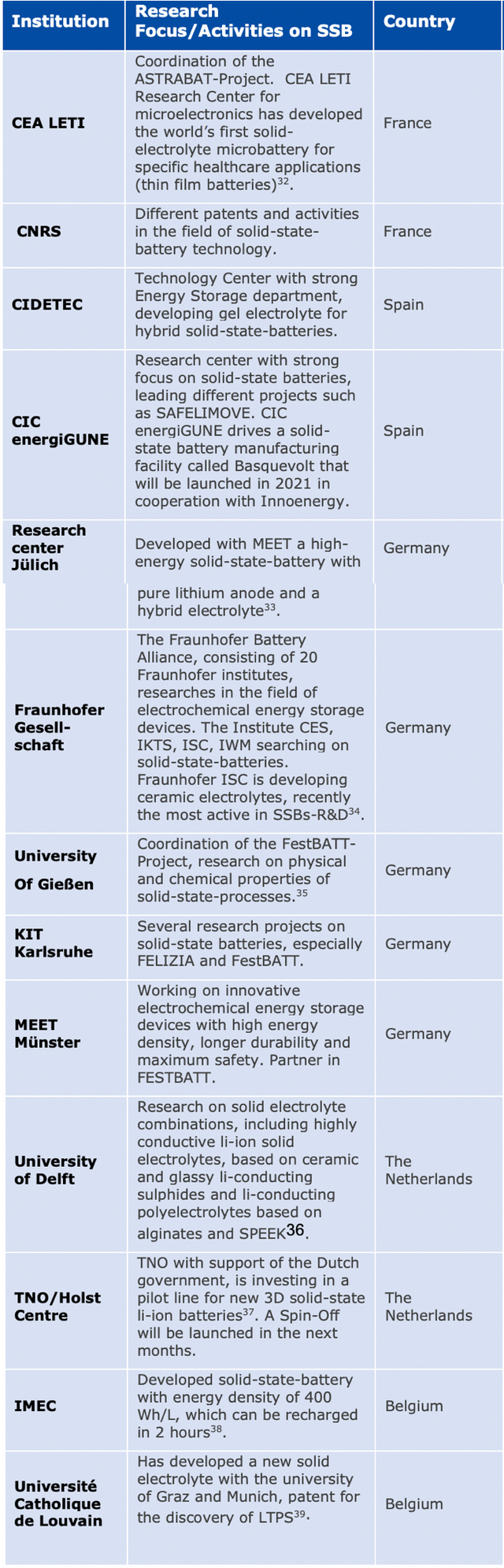 In Europe, the German government has invested €1 billion to support the research and production of solid-state battery technology, as well as to establish a power battery research alliance, focusing on the development of solid-state battery technology. Companies such as Volkswagen Group, BASF, Ford Germany, and Voltabox AG have voluntarily joined this alliance. The EU has also approved a special investment program for European solid-state batteries, with multiple EU countries contributing €3.2 billion (about RMB 23 billion), and an additional €5 billion (about RMB 36 billion) being raised from private investors for the development of solid-state batteries.
In Europe, the German government has invested €1 billion to support the research and production of solid-state battery technology, as well as to establish a power battery research alliance, focusing on the development of solid-state battery technology. Companies such as Volkswagen Group, BASF, Ford Germany, and Voltabox AG have voluntarily joined this alliance. The EU has also approved a special investment program for European solid-state batteries, with multiple EU countries contributing €3.2 billion (about RMB 23 billion), and an additional €5 billion (about RMB 36 billion) being raised from private investors for the development of solid-state batteries.
The US Department of Energy has funded $209 million for 26 laboratory projects to develop solid-state batteries and fast charging technologies. The Japanese government plans to provide billions of yen in subsidies for solid-state battery research and development, and will use NEDO to develop alliance technologies. The Korean government has decided to invest KRW 30 billion in the next five years to support the development of all-solid-state batteries.
Summary: Currently, the investment in the field of power batteries is still in a complex stage when combined with the industry background. With the improvement of the existing power battery capacity, if the investment is not economically viable, this investment may become a dilemma in terms of current production capacity.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.