Author: Turbocharged Little Fatty
This morning, NIO released its unaudited financial performance report for the fourth quarter and full year of 2020. The report shows that NIO’s performance in 2020 has improved as the company focuses on timely risk control, revenue growth and margin enhancement.
Without further ado, let’s take a detailed look at the performance information:
Fourth Quarter of 2020
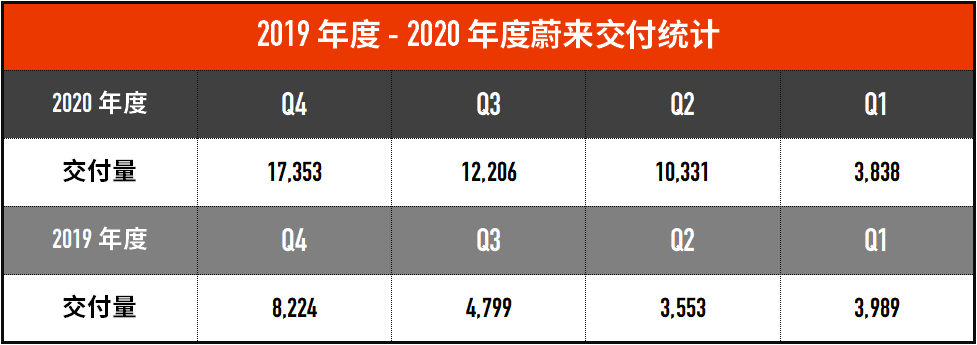
- Deliveries: In the fourth quarter of 2020, NIO delivered 17,353 vehicles, including 4,873 ES8s, 7,574 ES6s and 4,906 EC6s.

- Revenue: NIO’s total revenue for the fourth quarter of 2020 was RMB 6.6411 billion, an increase of 133.2% year-over-year and 46.7% quarter-over-quarter. Automotive sales revenue for the fourth quarter of 2020 was RMB 6.1740 billion, an increase of 130.0% year-over-year and 44.7% quarter-over-quarter.
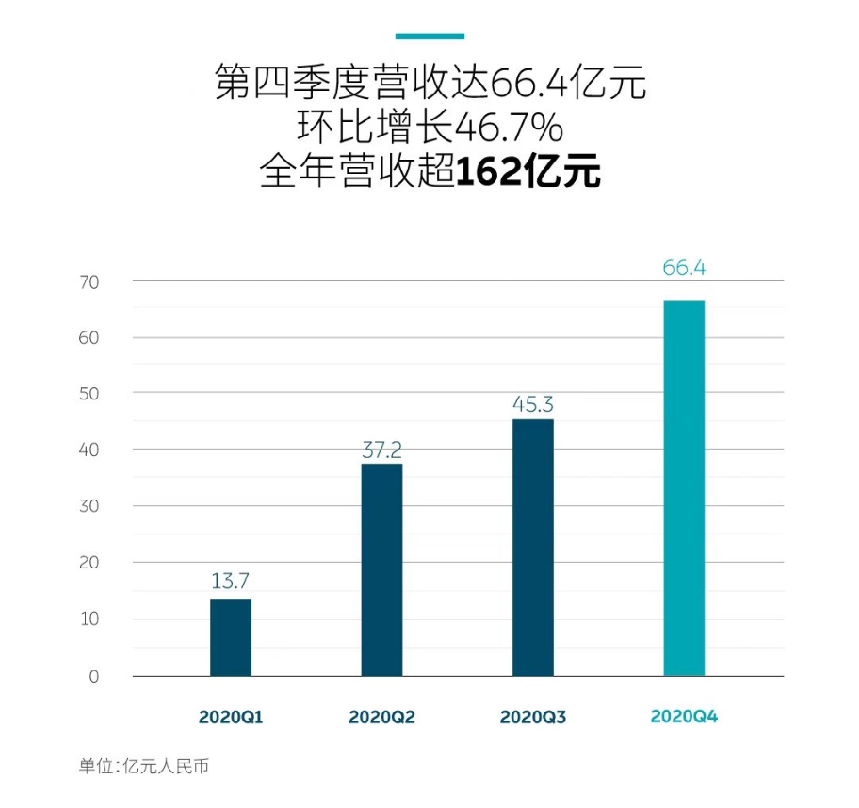
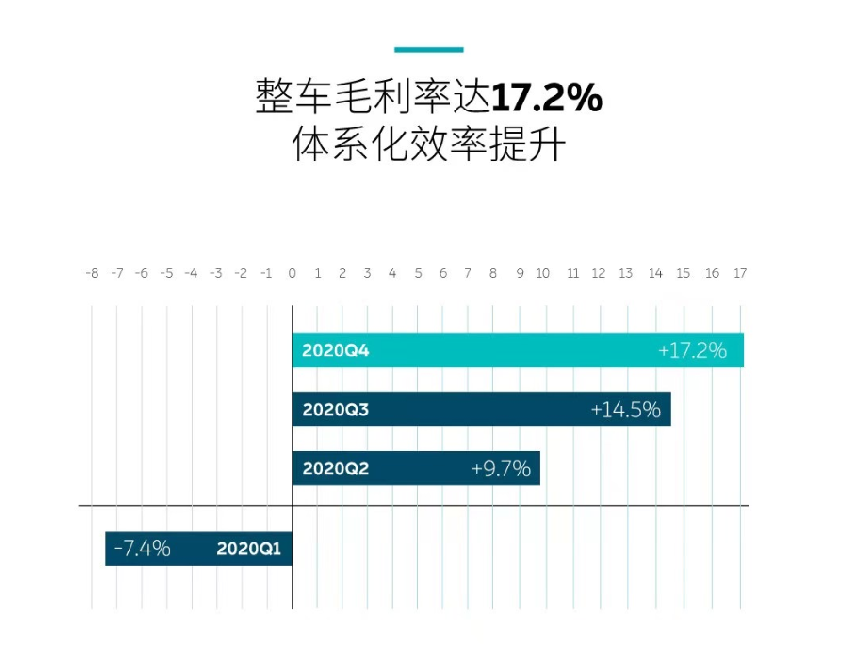
- Gross profit: NIO’s gross profit for the fourth quarter of 2020 was RMB 1.1419 billion, an increase of RMB 0.5561 billion from the third quarter of 2020. The gross margin for automotive sales in the fourth quarter was 17.2%, compared to 14.5% in the previous quarter.
- Loss: NIO’s operating loss for the fourth quarter of 2020 was RMB 0.9314 billion, a decrease of 67.0% year-over-year and 1.5% quarter-over-quarter. The non-GAAP operating loss was RMB 0.8712 billion, a decrease of 68.6% year-over-year and 2.9% quarter-over-quarter. NIO’s net loss for the fourth quarter of 2020 was RMB 1.3886 billion, a decrease of 51.5% year-over-year and an increase of 32.6% quarter-over-quarter. The non-GAAP net loss was RMB 1.3284 billion, a decrease of 52.8% year-over-year and an increase of 33.1% quarter-over-quarter.
Full Year of 2020
-
Deliveries: In 2020, NIO delivered 43,728 vehicles, compared to 20,565 vehicles in 2019. Due to the impact of the pandemic, NIO’s deliveries in the first quarter of 2020 were slightly lower.
-
Revenue: NIO had a total revenue of CNY 16.258 billion in 2020, representing an increase of 107.8% YoY. Vehicle sales revenue in 2020 was CNY 15.183 billion, up 106.1% YoY.
-
Gross profit: The gross profit in 2020 was CNY 1.8734 billion and the gross profit margin for vehicle sales was 12.7% in 2020.
-
Loss: The operating loss in 2020 was CNY 4.6076 billion, a decrease of 58.4% YoY. The non-GAAP operating loss was CNY 4.4206 billion, a decrease of 58.9% YoY. The net loss in 2020 was CNY 5.3041 billion, a decrease of 53.0% YoY. The non-GAAP net loss was CNY 5.1170 billion, a decrease of 53.3% YoY.
-
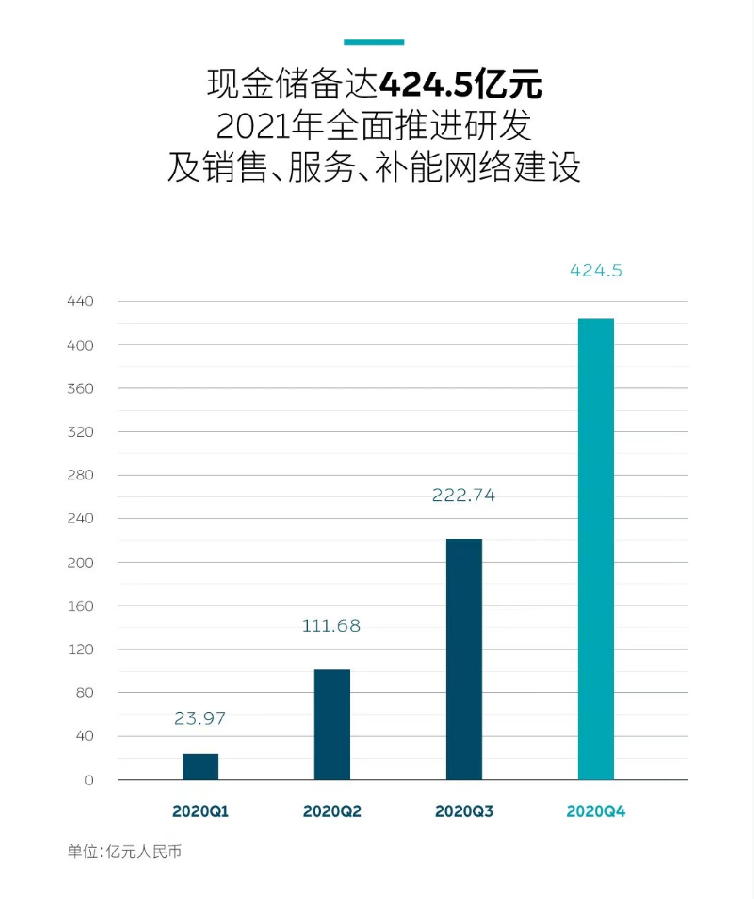
Cash: As of December 31, 2020, NIO’s cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash and short-term investments amounted to CNY 42.5 billion.
The Nightmare is Over, but There’s No Time to Rest
NIO will never forget the nightmare in 2019. When the NIO China headquarters project landed in Hefei with over 10 billion yuan in hand, NIO finally breathed a sigh of relief and regained investors’ confidence. In addition to the funds received, the factor that could continue to stabilize NIO’s progress is the delivery volume.
As of February 28, 2021, NIO had delivered a total of 88,444 ES8, ES6, and EC6. NIO delivered a total of 43,728 vehicles in 2020, up 112.63% from the 20,565 vehicles delivered in 2019.

But according to NIO’s financial report data, the delivery volume of NIO in January 2021 was 7,225, and the delivery volume in February 2021 was 5,578, including 1,327 ES8, 2,216 ES6, and 2,035 EC6.
NIO previously expected to deliver about 20,000 vehicles in the first quarter of 2021, which means NIO needs to achieve a delivery volume of at least 7,200 in March 2021 to meet expectations.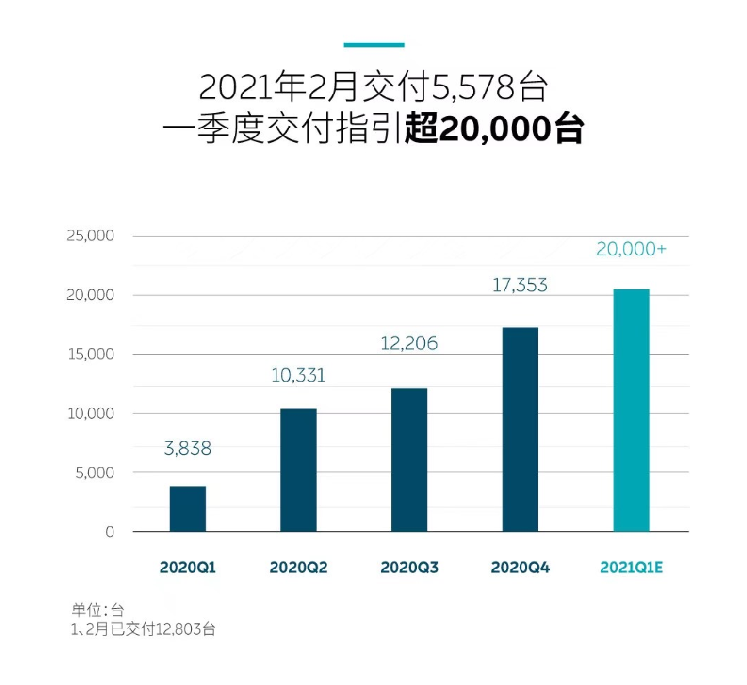
Before the official mass delivery of NIO ET7, NIO currently relies on only three SUV models, ES8, ES6, and EC6 to support the market.

After the pandemic situation stabilized in the second half of 2020, the delivery volume of most automakers showed an upward trend. However, it is difficult for the delivery volume to reach such a level in 2021 with the fading of consumption after the pandemic.
NIO also achieved explosive deliveries in the last three quarters of 2020, and NIO expects the monthly delivery volume in 2021 to remain at around 7,000 vehicles for a long time.
As there is a price difference of up to RMB 100,000/vehicle between ES8 and ES6 and EC6, it is crucial for NIO to maintain the delivery volume of ES8. In the fourth quarter of 2020, the delivery volume of NIO ES8 is comparable to that of EC6.

The hero who achieved this goal is the Battery-as-a-Service (BaaS) plan. For vehicles using the NIO BaaS plan, the cost of the battery is deducted directly at the time of purchase and converted into leasing rent on a monthly basis.
This directly reduces the sales invoice price of the car and lowers the threshold for high-priced car models, which has played a certain role in promoting sales of high-priced car models.
Li Bin revealed during the NIO earnings conference call that the proportion of BaaS in orders added in February reached 55%.
Even though the nightmare of 2019 has passed, NIO in 2020 is still shrouded in the shadow of losses.
Reducing costs and increasing profits is vital
NIO’s net loss in 2020 was RMB 5.3041 billion, a year-on-year decrease of 53.0%. Although NIO’s net loss in the fourth quarter of 2020 decreased by 51.5% compared to the same period of the previous year, it increased by 32.6% on a quarter-on-quarter basis.
Therefore, continuing to reduce costs is vital.
NIO’s R&D expenses for the whole year of 2020 were RMB 2.4878 billion, a year-on-year decrease of 43.8%. Among them, the R&D expenses for the fourth quarter of 2020 were RMB 829.4 million, accounting for 33.34% of the total R&D expenses for the year. The main reason for the high proportion of R&D expenses is for the design and research and development of new models and technologies.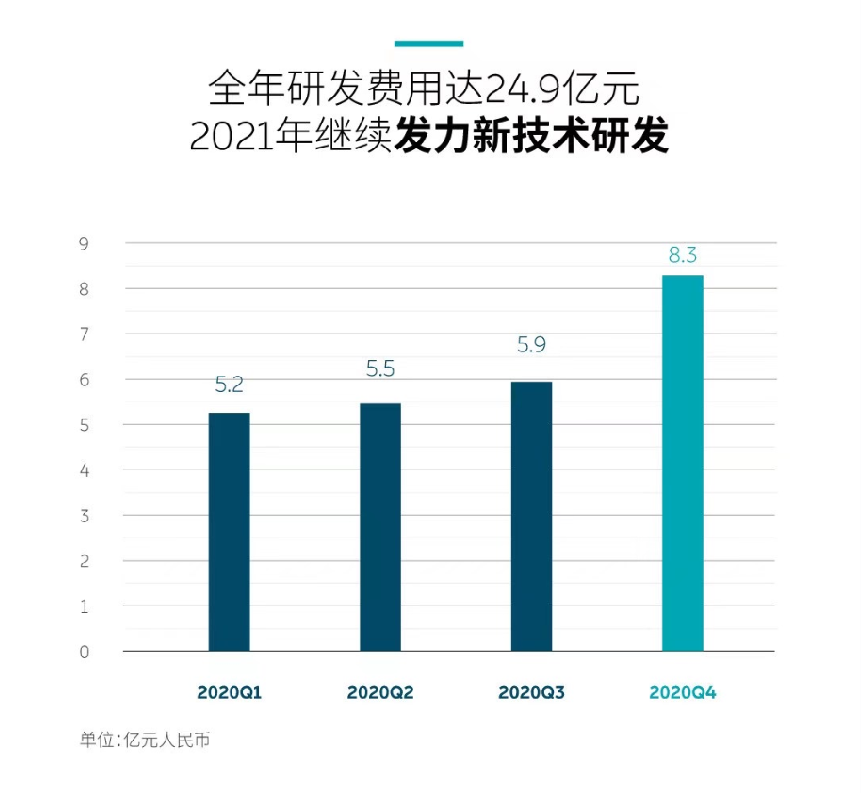
NIO’s full-year sales and administrative expenses for 2020 were RMB 3.9323 billion, a year-on-year decrease of 27.9%. The fourth quarter sales and administrative expenses were RMB 1.2068 billion, a year-on-year decrease of 21.9% and a quarter-on-quarter increase of 28.3%.
From the perspective of R&D expenses and sales and administrative expenses, NIO has made great efforts in cost control compared to 2019. This mainly includes overall cost savings, improved operating efficiency, reduced design and development costs, and employee salaries.
NIO has always pursued “user experience”. Therefore, when faced with the choice between cost and user experience, NIO chose the latter. The reduction in losses in 2020 was mainly due to the cost control that NIO realized after experiencing financial difficulties in 2019.
NIO’s Future
NIO expects total revenue for the first quarter of 2021 to be between RMB 73.823 billion and RMB 75.572 billion, an increase of approximately 11.2% to 13.8% compared to the fourth quarter of 2020.
NIO reached a full supply chain capacity of 7,500 units in January 2021 and has the production capacity of 10,000 cars per month by operating some assembly lines in double shifts. NIO also plans to achieve a single shift capacity of 150,000/double shift capacity of 300,000 by the end of 2021.
NIO plans to double its investment in R&D expenses in 2021 to approximately RMB 5 billion. The main focus will be on NIO ET7, autonomous driving, the second-generation battery swap station, and 150 kWh battery packs.
NIO currently has 23 NIO centers and 203 NIO spaces, covering 121 cities in China. In 2021, NIO plans to add another 20 NIO centers and 120 NIO spaces, expanding its regional coverage.

NIO has built 191 battery swap stations in 76 cities. In 2021, NIO plans to add at least 309 swap stations and start deploying the second-generation swap stations in Q2 2021.
At the same time, NIO also plans to increase the construction of supercharging networks and destination charging piles, from 127 supercharging stations and more than 1,700 destination charging piles to 600 and 15,000 respectively by the end of this year.
During a conference call, Li Bin mentioned two bottlenecks that NIO is currently facing: one is chips and the other is the 100-degree battery pack.
Li Bin said: “The influence of chips on the supply chain is significant, and it will have some impact on NIO in the second quarter. However, it can basically meet the normal production plan, although this satisfies our needs, the risk is very high.
The supply of batteries is also a bottleneck, especially for 100-degree batteries, because the demand for electric vehicles has indeed increased recently. It is expected that the production of batteries will be able to meet NIO’s requirements around July.” (Slightly edited for brevity)
Compared with the financial report released by Li Auto a few days ago:
-
NIO: delivered 43,728 vehicles throughout the year in 2020, with a net loss of 5.304 billion yuan;
-
Li Auto: delivered 32,624 vehicles throughout the year in 2020, with a net loss of 0.1517 billion yuan.
And Li Auto achieved a quarterly profit for the first time in the fourth quarter of 2020. However, the same point is that both NIO and Li Auto may not have significant actions in 2021, especially in the mass production and delivery of new models.
According to the plan, the mass production and delivery of NIO ET7 will be scheduled for the first quarter of 2022. Li Auto’s second model will also be launched in 2022.
Therefore, for these two new forces, 2021 is a year of accumulating strength and biding time, and whether they will break out or not will be revealed in 2022.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
