Introduction
Both Tesla and Volkswagen’s MEB platform have made some improvements in the high-voltage connection system.
We have already analyzed Tesla’s approach, and in this article, we will explore Volkswagen’s attempts to optimize the high-voltage battery system. The main features include:
1) Instead of a common power distribution unit (PDU), Volkswagen uses branch lines to realize the high-voltage power distribution path throughout the entire system.
From the interface perspective, the DC fast charging and rear inverter drive are connected directly, while the on-board charger, DC-DC converter, two PTC units and electrically driven compressor are connected through branch lines, achieving overall modularity of the system.
2) Volkswagen’s high-voltage connection system uses an unshielded approach, shifting the responsibility of EMC control to the various electrical components, and using hardware filtering.
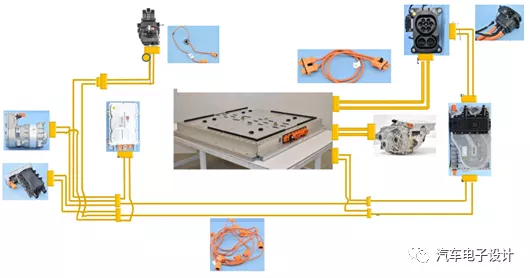
High-Voltage Connection
In the high-voltage connection, all integrable plugs are integrated together at the high-voltage interface of the battery. As shown in the figure below, a rectangular custom interface is designed at the output end of the battery, integrating the DC charging port, inverter, and accessory power. X1, X2, and X3 represent the three high-voltage plugs, respectively.
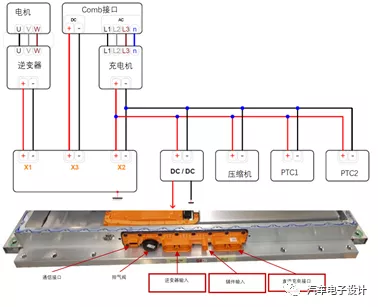
In the external branch equipment, the main auxiliary high-voltage connection is provided. The overall configuration includes a 100A fuse, and the fuse is processed on the branch lines as follows:
-
On-board charger (OBC): Placed in the rear compartment, the high-voltage + / – is connected to the battery pack through a 2-into-1 Oneline interface and connected to another branch splitter.
-
DC-DC converter: Connected through the high-voltage that passes through the Oneline interface and OBC. Front compartment: PTC1, PTC2, and the air conditioning compressor are placed here, and the branch lines are slightly more complex but overall as shown in Figure 1.
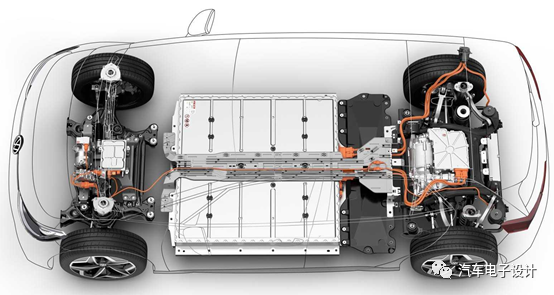 From this perspective, the overall output for the battery is simplified, reducing the need for a general PDU for conversion. Of course, the downside is that five high-voltage accessories and the battery are interconnected using Oneline interfaces, which may create additional issues in terms of distance between high-voltage arrangements, especially with regards to OBC’s spatial location, resulting in complex cable lengths and a weight of roughly 13 kg.
From this perspective, the overall output for the battery is simplified, reducing the need for a general PDU for conversion. Of course, the downside is that five high-voltage accessories and the battery are interconnected using Oneline interfaces, which may create additional issues in terms of distance between high-voltage arrangements, especially with regards to OBC’s spatial location, resulting in complex cable lengths and a weight of roughly 13 kg.
In the long run, the three components of the air conditioning unit may be combined, similar to Tesla’s approach, and integrated directly onto the battery protrusion, along with OBC and DCDC.
As PPE continues to integrate certain components onto the battery protrusion, the overall distribution cable system will be further simplified. External cables for high-voltage components will only need to be connected to the front compartment, with some being covered inside the battery protrusion (where copper connectors may be used), further shortening physical distances and simplifying the connection process into a single plug-and-play interface.

Conclusion
The primary goal of simplifying high-voltage cable connections is to reduce the risk of potential physical short circuits during collisions. With the cancellation of PDU, the overall high-voltage layout will be further simplified and clarified.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
