Author: Wang Lingfang Qiu Kaijun
The lithium iron phosphate battery (LFP) continues to attack the fortress of ternary batteries.
In 2019, the installation rate of LFP batteries was 32%; in 2020, it increased to 35%; and in the first two months of 2021, it has reached 38.6%. Many people predict that the installation rate of LFP batteries in vehicles will likely exceed 50% this year.
One of the core reasons for the decline of ternary batteries is safety concerns.
Just at this time, GAC Aion released its “Magazine Battery System Safety Technology” and declared to the world that the ternary lithium battery system can now withstand piercing without fire.

On March 10th, GAC Aion held an online press conference to announce that the results of the test showed that the ternary lithium (magazine battery) pack made by GAC Aion only exhibited a brief smoke (for 1 minute) after being pierced by a needle, without any fire or explosion.
Based on the fact that battery packs made with the biggest safety challenge of ternary batteries can achieve such a high level of safety, GAC Aion’s magazine battery has become the industry leader in electric vehicle battery pack system safety.
Moreover, the safety technology of the magazine battery system can also support other batteries beyond ternary batteries, such as LFP, and even future fast-charging graphene-based batteries, silicon negative electrode batteries, etc., achieving a battery pack system safety that far exceeds the current level.
Consumers of electric vehicles can now purchase electric vehicles with more peace of mind.
Ternary Battery Pack Now Withstands Piercing without Fire
When it comes to needle penetration testing, industry professionals may most remember BYD and CATL’s cell needle penetration testing last year.
However, cell needle penetration testing is not actually a mandatory test. In the national mandatory standard GB 38031-2020 “Safety Requirements of Power Batteries for Electric Vehicles”, the puncture test for individual cells has been cancelled.
The purpose of the national regulatory body is to consider battery safety at the system level.
Therefore, the national standard has not relaxed the safety requirements for battery systems. Both needle penetration testing and heat diffusion testing are two trigger methods for battery pack overheating. The other one is heating.
The “Safety Requirements of Power Batteries for Electric Vehicles” clearly stipulates that the vehicle should issue an alarm signal within the first 5 minutes before the battery loses control. In other words, to ensure personnel safety, the heat diffusion must be controlled for at least five minutes after the battery pack loses control.

GAC Aion is not satisfied with the national standard and hopes to further improve the safety of the ternary battery pack to the point where individual cell overheating will not cause the battery pack to catch fire.The pin puncture test of battery cells reflects the safety of single battery cells, but the single cells are tightly wrapped in the battery pack and assembled into a part of the whole vehicle as a component of the entire battery system.
In practical applications, the battery pack directly contacts the external environment. Therefore, the pin puncture test of the battery system is more in line with the situations that occur in real life, and thus has more reference value for consumers.
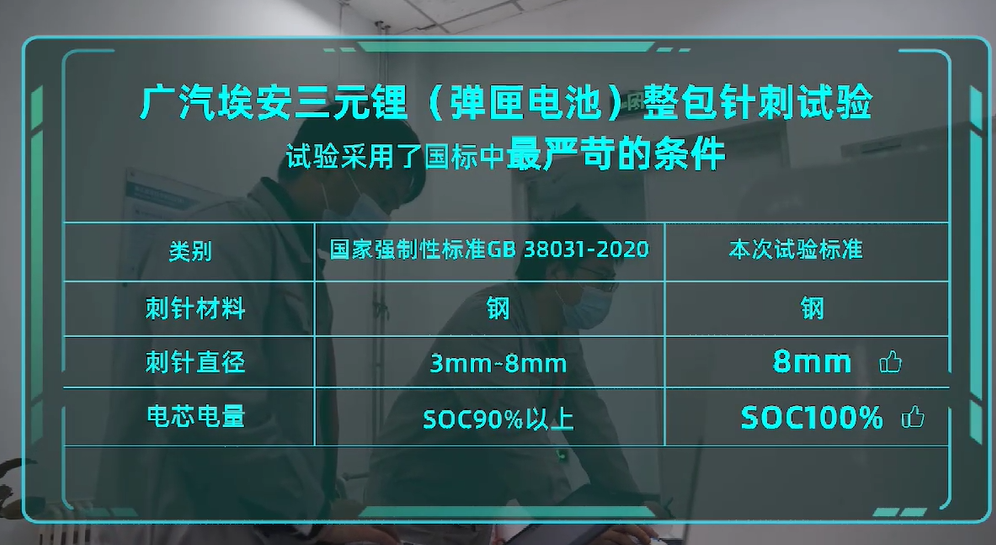
To verify the safety of the magazine battery technology, GAC Aion conducted a pin puncture and thermal diffusion test on a ternary lithium battery pack equipped with magazine battery system safety technology at a third-party institution, the China Automotive Technology Research Center.
Under the most stringent conditions – an 8 mm steel needle and full charge, GAC Aion conducted the test.
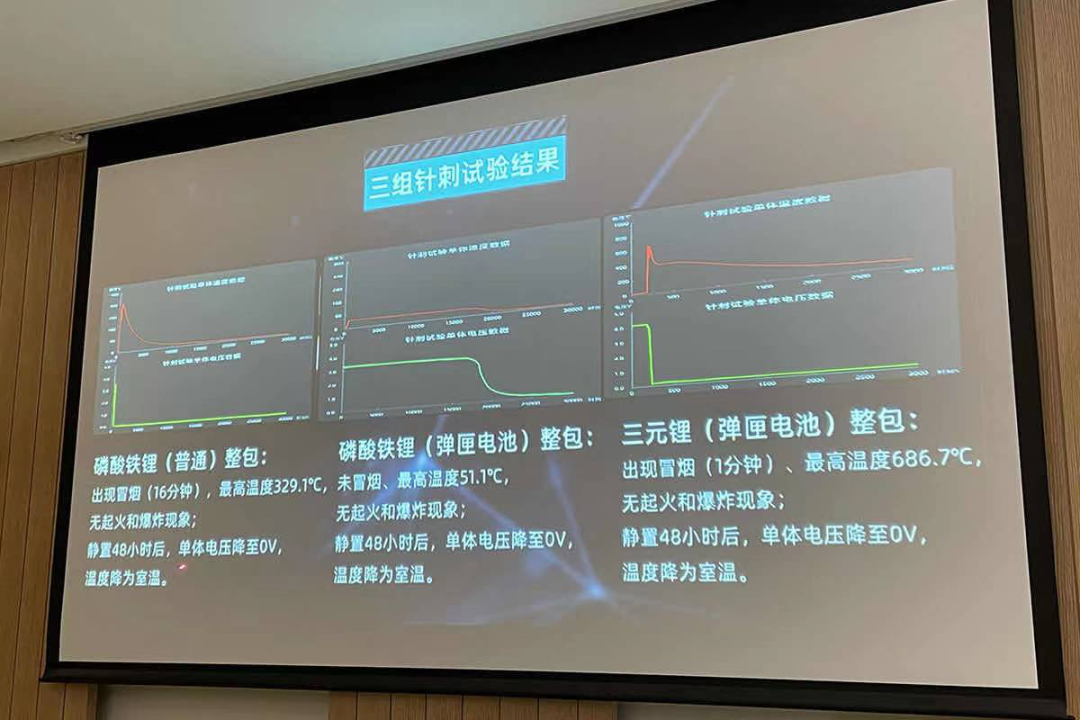
The test results showed that after the thermal incident signal was issued for 5 minutes during the test, the whole pack of GAC Aion’s ternary lithium (magazine battery) only had a brief smoking phenomenon (1 minute) without any fire or explosion.
After resting for 48 hours, the voltage dropped to 0 V and the temperature returned to room temperature. Only the punctured cell module was thermally runaway, and did not spread to other cells. After opening the battery pack, the internal structure was intact.
In other words, GAC Aion’s magazine battery not only survived for 5 minutes, but also remained fire and explosion-free.

Here is a video of the magazine battery pin puncture test:
The performance of the ternary battery pack in the thermal runaway test can be said to be the best in our field of view. After all, due to its high active material content and high electric capacity, when a ternary battery pack experiences thermal runaway, the energy released is extremely high, making it extremely difficult to completely control.
Therefore, the national standard only requires that the ternary battery pack does not catch fire for 5 minutes during the thermal runaway test, and the better ones in the industry can last for half an hour. The Guangqi Aion S three-element battery pack, which has been constantly not catching fire, should be the first one.
Empowering Safety for All Types of Battery Cells
The China Automotive Technology Research Center not only tested the magazine battery pack with ternary batteries mounted on Guangqi Aion, but also tested the magazine battery pack with lithium iron phosphate batteries mounted on it.
The test results were even better.
The lithium iron phosphate battery system that uses the magazine battery pack technology did not smoke or catch fire in the puncture experiment, with the highest temperature only reaching 51.1 ℃. After being stationary for 48 hours, the single-cell voltage dropped to 0, and the temperature dropped to room temperature, completely without any safety threats.
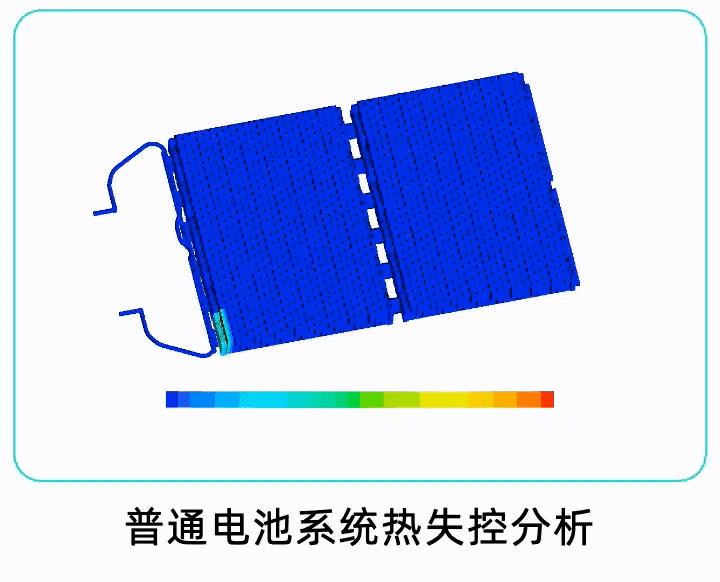
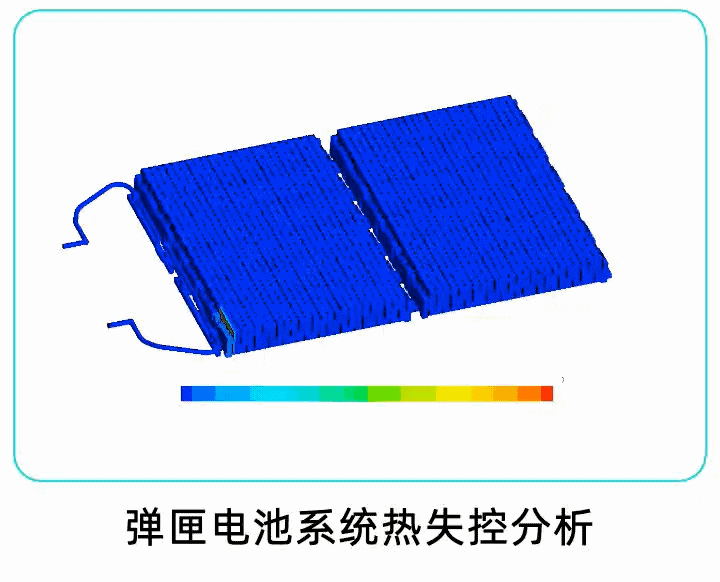
The China Automotive Technology Research Center also compared the results of the magazine battery pack with lithium iron phosphate and the results of the magazine battery pack with ordinary batteries mounted on it. The results showed that the magazine battery pack system significantly improved safety. Even when comparing ternary battery packs with lithium iron phosphate battery packs, the duration of smoking was shorter.

As the test results show, the magazine battery pack can significantly improve safety regardless of whether it uses lithium iron phosphate or ternary battery cells. Moreover, from its principle, it can also significantly improve the system’s safety performance for future exploration by companies such as Guangqi Aion of graphene-based ultra-fast charging batteries and ultra-long-life silicon negative pole batteries.
What is its principle?
In addition to improving the safety of the battery cell itself, the magazine battery pack system embodies a system-level safety concept.
First, it is necessary to control the single cell’s thermal runaway to a degree that will not ignite the surrounding battery cells, so good thermal insulation is required.
In terms of thermal insulation, magazine battery packs use a mesh nano-porous insulation material and a high-temperature-resistant upper cover to construct a safety compartment, like a golden bell, to “shield” the thermally-runaway battery cells and prevent it from spreading.
This material is a mesh nano-porous insulation material which is a soft nanomaterial based on silicon dioxide. The space between the material is about 20 nanometers, and the air does not flow in this space, which means the heat cannot be transmitted to the outside through the air.
Second, it is necessary to rapidly dissipate the heat released by the thermally-runaway single cell, so it requires a rapid cooling system.The magazine battery pack achieves a 40% increase in heat dissipation area and a 30% increase in heat dissipation efficiency through a design of fully fit liquid cooling system, high-speed heat dissipation channel and high-precision thermal path. Once a thermal runaway is detected, the magazine battery system can immediately start the battery rapid cooling system to cool down the battery.
Thirdly, the precondition for a rapid cooling is to rapidly know about the thermal runaway. The magazine battery pack adopts the fifth generation of the battery management system, which is under full-time control. By using the latest generation of vehicle-grade battery monitoring chip, it can achieve 10 times of all-weather data acquisition per second in the 24-hour full coverage full-day patrol mode. When an exception is detected, the pack will immediately activate an abnormal self-rescue and start the battery rapid cooling system to cool down the battery.
According to Li Gang, the Vice President of Guangzhou Automobile Group Research Institute, the signal acquisition frequency of Guangzhou Automobile Aegea is 100 times that of the previous generation technology, which is beneficial for rapid danger detection and adoption of measures.
Looking at the three principles of the magazine battery pack, which prevent stabbing and ignition, it is not directly related to the materials and assembly technology of the battery cores. Therefore, the magazine battery pack can support a variety of material systems and assembly technologies for battery cores.
Under the protection of “magazine”, no matter which type of battery core is assembled into the battery pack of Guangzhou Automobile Aegea’s electric vehicles, its safety performance will exceed the national standard of not igniting or exploding for 5 minutes.
Density Improvement and Cost Reduction
After improving safety, will energy density and cost be sacrificed?
Guangzhou Automobile Aegea states that the magazine battery has been optimized in terms of cooling system, battery core design, and package layout. The energy density of the battery pack equipped with the magazine battery system safety technology is 9.4% higher than that of the same type of ordinary battery pack in terms of volume energy density and 5.7% higher in terms of weight energy density. The cost is also reduced by 10%.
This may puzzle industry insiders, how can both be achieved?
We analyze that the high volume utilization rate of the stackable battery and the higher system integration bring about this effect.
The system energy density of Guangzhou Automobile Aegea’s previous models was already high, ranging from 170-180 Wh/kg, and there are only a few models in the market that can reach 180 Wh/kg.
The magazine battery pack of Guangzhou Automobile Aegea has taken one more step further in energy density-185 Wh/kg.
Many people have not noticed that the battery core of the magazine battery of Guangzhou Automobile Aegea adopts a stacking process.
Generally speaking, compared with the winding battery, the stackable battery can increase the energy density by 5%, the cycle life by 10%, and reduce the cost by 5%, and it is safer.The “hard shell stack” process adopted by GAC Aion has improved the internal space utilization and increased the energy density of the battery cells, while avoiding the durability issue of expansion and wrinkling of the wrapped cell and the insulation risk of aluminum-plastic film after long-term use. At the same time, the internal resistance of the battery has been reduced, improving the safety performance of the battery.
Secondly, the energy density of the magazine system has been further improved mainly because of the higher degree of integration, for example, the independent liquid cooling plate has been simplified.
How to achieve cost reduction?
GAC Aion did not reveal more details. However, we analyze two possibilities.
Firstly, technological cost reduction. As mentioned earlier, the change from wrapping to stacking allows the battery cell factory to make more batteries of the same material. And the increase in system integration can also reduce the material cost of the battery pack.
Secondly, scale cost reduction. GAC Aion sold 60,033 electric vehicles in 2020, which can place orders with one of the top four largest scales in the industry for the power battery factory. Moreover, the future sales of GAC Aion are expected to rise, and battery factories are also willing to exchange price for scale.
Currently, one of the main obstacles to the popularization of electric vehicles is the high initial purchase price, which is due to the high cost of power batteries. The 10% cost reduction achieved by the magazine battery is only a small step towards the popularization of electric vehicles, but it is a solid step.
More Possibilities after the “Magazine”
To replace fuel cars and become the first choice for people’s travel, the current priority is to improve the experience of electric cars. The current core shortcomings are two: cruising range and charging speed.
In terms of cruising range, many vehicles have achieved a cruising range of 600 kilometers under NEDC standard. However, if winter degradation and heating degradation are taken into account, the range is still insufficient.
When there is no good solution for winter performance and heating energy consumption, increasing the absolute amount of electricity is also a solution. Although automakers can also install more lithium iron phosphate batteries, the three-element battery with higher specific energy and less degradation in winter has some advantages.
On the basis of the existing three-element battery, some companies continue to increase the proportion of nickel in the positive electrode, from series 5 to series 6, and even to series 8 or 9. However, due to the safety issues of 811 batteries, many people stopped at series 6.
In terms of the negative electrode, many companies have begun to use silicon-based negative electrodes. The reason for choosing silicon is because the theoretical specific capacity of silicon-based negative electrode material is more than 10 times that of graphite negative electrode, which is 4200 mAh/g. With the current technology level, the silicon-based negative electrode is essential to make the battery reach 300 Wh/kg.
In terms of charging speed, many automakers have turned their attention to high-power charging, so batteries with better charging rate performance are needed.
In this regard, the mainstream thinking in the industry is to modify the surface of the negative electrode material and establish a channel for lithium ions to enter the negative electrode quickly to achieve fast charging efficiency.
In these two aspects, the solutions revealed by GAC Aion are silicon negative electrode batteries for long-range and graphene-based batteries.Along with the increase in driving range and power comes greater challenges to safety. The box-shaped battery developed by GAC Aion provides the optimal solution for balancing performance, safety and cost for electric vehicles, and establishes a framework of safety for the application of new batteries with different materials and performance in the future.
This innovative, easily produced, low-cost and versatile solution for the safety issues of power batteries in the industry is sure to advance the safety of power batteries in the industry!
Thus, we can look forward to electric vehicles with higher performance that provide a better driving experience.
——END——
To communicate with the author, please add WeChat:
skilawang
qiukaijun123
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
