On May 30th, the International Automobile Safety Conference convened. At the conference, Shen Haidong, the Director of Vehicle Safety Integrated Technology at SAIC General Motors Pan Asia Automotive Technical Center, shared the company’s efforts in safety investment.
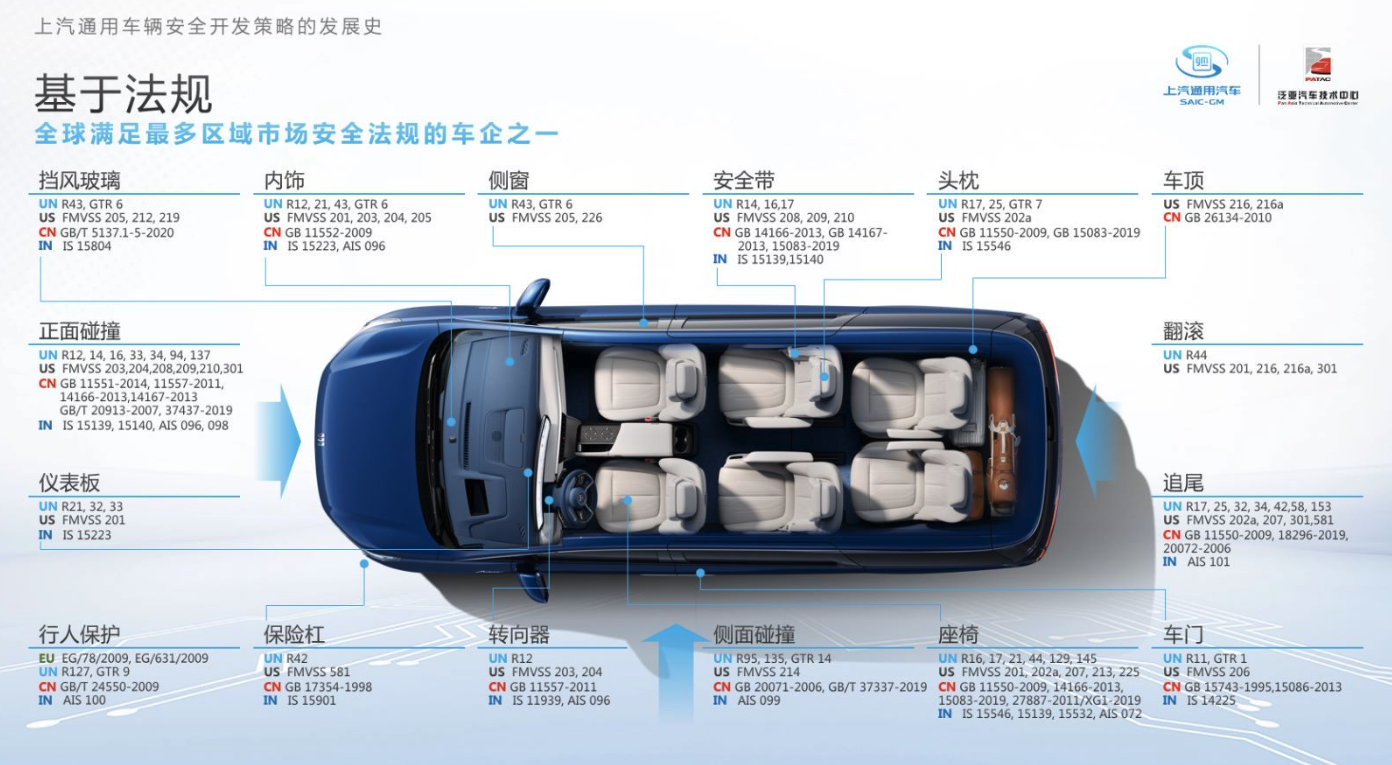
SAIC General Motors’ safety performance in the global market has consistently garnered attention. Not only do their products meet safety regulations in markets like China, the United States, and Europe, but they are also developed in accordance with a third-party evaluation system in China and the U.S and adhere to GM’s global unified GMW standards. This stringent set of standards and regulations ensures the unified safety performance of SAIC General Motors in the global market.

The safety development goal of SAIC General Motors is to ensure all produced vehicles maintain stable safety performance under real-world use. Their safety development covers an entire process including safe driving, accident warning, collision protection, and post-accident rescue. Each year, SAIC General Motors conducts over 150 full-vehicle physical safety tests and accumulates a simulation time that exceeds one hundred million hours annually. These safety development data are rapidly iterated through artificial intelligence algorithms to distill efficient safety development plans.
Addressing “Electrical Safety”, SAIC General Motors has developed an entire suite of development standards, covering scenario definitions, target setting, safety layout, component testing, simulated development, and test verification stages. For high-voltage electrical safety on the Auton platform, the adoption rate of high-strength steel is 61%, ultra-high-strength steel takes up 37.5%, and the battery pack’s crush resistance exceeds the national standard by three times. Upon a potential collision, a PCDD high-voltage power cut can be achieved as quickly as two milliseconds.
PHEV plug-in hybrid models adhere to the same high-voltage safety standards as the Auton platform. Non-contact occurs during battery pack collisions and the battery pack and fuel tank are designed separately without interference. Additionally, SAIC General Motors implements strict low-voltage electrical safety standards. By refining virtual modeling and performing system safeness limit testing, digitized model accuracy is improved to ensure personnel safety. SAIC General Motors also employs an electronic logic workbench to verify low-voltage electrical safety in various scenarios, transcending the limitations of physical tests.
Regarding proactive safety in automation, SAIC General Motors offers a 360° blind-spot-free proactive safety warning function, full-speed range forward and low-speed rear proactive braking functions, and develops proactive safety technology for all-weather conditions. The Super Cruise advanced assistive driving system’s DMS driver monitoring system, through a high-performance infrared camera and infrared lighting, real-time monitors the driver’s condition. When the driver’s line of sight deviates from the road, a warning light will trigger from the steering wheel. Without the driver taking control, the system will sound an alarm and activate seat vibration for double warnings. If the driver still does not reclaim control, the vehicle will slow down and stop in the current lane, with an OnStar representative will call the driver to confirm their condition.
With these multi-dimensional security measures, SAIC-GM not only enhances the safety performance of the vehicles but also offers a more reassuring driving experience to its users.
This article is a translation by AI of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
