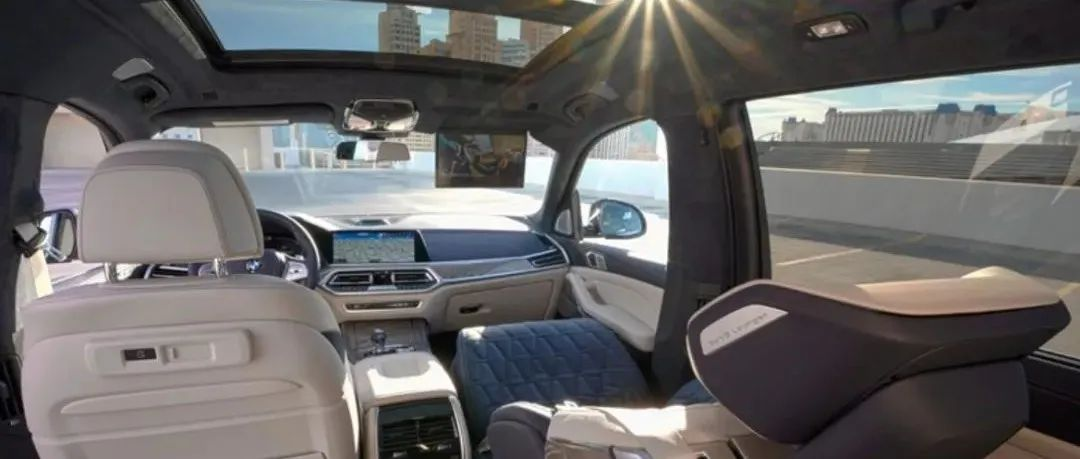
The Concept of Zero Gravity Seats
With the rapid development of intelligent cockpit technology, Chinese consumers have increasingly demanded more comfortable and intelligent cabins. We have noticed that more and more automakers are launching new models equipped with “zero gravity seats,” including NETA S, SAIC MG ONE-β, BAIC BEIJING-X7, and others that will be released in 2022.
Moreover, more and more automakers are collaborating with Tier 1 and innovative companies to develop zero gravity seats, and it is expected that more new cars equipped with zero gravity seats will appear around 2023-2024.
What kind of experience can zero gravity seats bring to consumers, and what are the technological highlights involved? The authors hope to explore this in this article.



The Genesis of Zero Gravity Seats
The core concept of zero gravity seats lies in the “zero gravity posture.” This concept originated from NASA’s study of how the human body naturally positions itself under microgravity conditions. In this natural posture, astronauts lift their arms, extend their shoulders, bend their knees, flex their hips, and curl their feet. NASA believes that this posture requires the least amount of muscular effort for astronauts to stay afloat, so it defines this posture as the zero gravity posture.
However, the academic community has not yet formed a clear definition of the “zero gravity posture.” The posture was defined based on the average measurement of the crew’s body posture indicators during a space experiment, but during subsequent follow-up experiments, NASA found that there was a significant difference in the individual and group differences of the zero gravity posture among crew members. That is to say, the “zero gravity posture” has significant differences between individuals and groups.
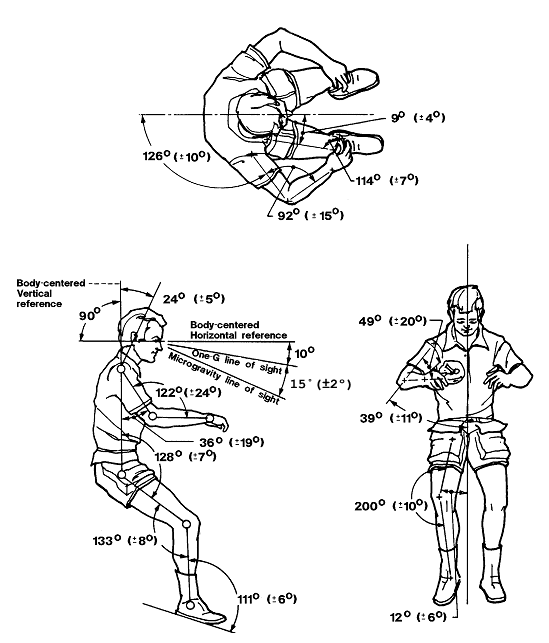
Although no general law of zero gravity posture has been truly deduced from an experimental perspective, the concept of “zero gravity” that brings comfort to the human body by minimizing muscle contraction has received increasing attention in the subsequent development of the automotive industry.
The application of the zero gravity concept in the automotive industry began with Nissan Motor, which in 2005 designed 14 different pressure points for seat support, providing reasonable support from the lower back to the shoulders to ensure that the spine of the occupant always maintains its natural position, thereby reducing pressure and muscle fatigue and avoiding back discomfort caused by long-term sitting.
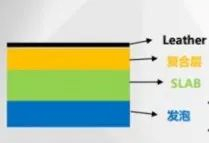
Based on these studies, Nissan Motor equipped the “Zero Gravity Seat” in the 2013 Altima by optimizing the seat’s comfortable section to ensure that the seat fits the occupant’s body curve as closely as possible, providing better riding support for the occupant. Through the application of SLAB height-damping foam materials, the resilience and hysteresis losses of the foam body were improved, providing occupants with a softer and more durable seating feel, effectively suppressing vibration transmission during driving. The comfort of the “Zero Gravity Seat” received very good market feedback at that time, and the concept of the “Zero Gravity Seat” originated from this.
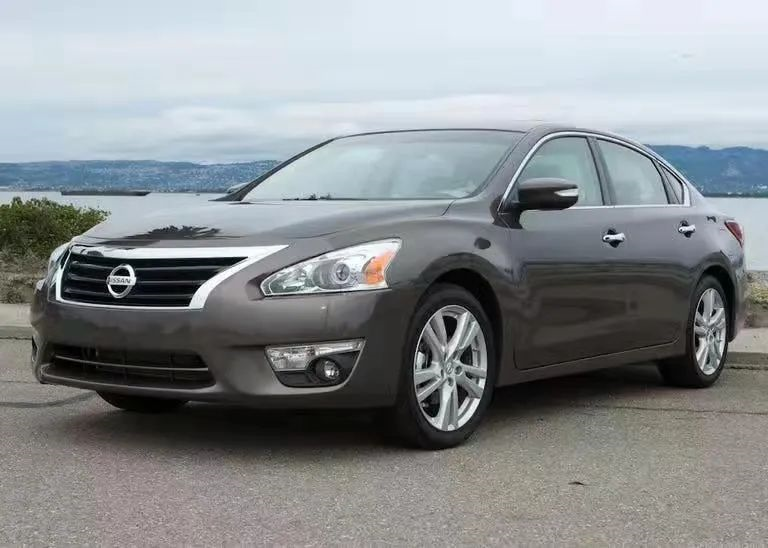

Development status of Zero Gravity Seats
With the rise of intelligent cockpit technology, the concept of the zero gravity seat has ushered in a new development. According to our observation and summary of the Chinese automobile market in 2021-2022, the automakers that currently equip “zero gravity seats” in addition to SAIC Motors, BAIC Motor, and NIO mentioned earlier, also include FAW Hongqi, Changan, and so on.
Among them, Changan’s UNI-K, SAIC’s MG5, and Hongqi H9 all adopt a zero gravity design concept similar to Nissan, combining high-elasticity seat foam, zero gravity filling layer, and leather composite layer sponge to balance the pressure distribution on the contact part of the driver and the seat, improve the riding comfort of occupants.



At the same time, we see the “zero-gravity seats” equipped in these models. On the premise of upgrading the foam technology, improvements and developments have been made in both driving comfort and seat adjustability, making the comfort of the zero-gravity seats further enhanced.
“Driving comfort” refers to the optimization of riding comfort through support point design, surface design, and vibration filtering design. For example, Changan UNI-K is designed for the spinal curve of Chinese people, with the shoulders, the middle of the back, and the lower part of the lumbar vertebrae designed, and the entire seat surface is designed by defining the comfort section and its parameters. The SAIC MG5 also balances the support of the hips by setting elastic support springs, balances the body pressure distribution between the driver and the seat contact surfaces, and avoids discomfort caused by high pressure from a single contact surface due to prolonged sitting.
In addition, the side support of the seat also enhances driving comfort from another perspective. In cornering, good side support can reduce the displacement of the driver and passengers caused by centrifugal force, reduce pressure changes between the body and the seat support, and maintain a good driving state and riding experience for the driver and passengers.


The adjustability of the seat range includes the adjustment of the backrest angle and the support of the leg rest/footrest. Through adjustable angles and leg support, the optimization of joint angle parameters of the human body can be achieved so that the spine can be in a naturally relaxed state in different riding postures. For example, BMW officially released the ZeroG Lounger zero-gravity seat at the North American CES exhibition. It can tilt the backrest backward 40° or 60° according to personal comfort needs, allowing passengers to experience the comfort of a nearly lying position. With the configuration of a cocoon-shaped airbag, passengers can also experience the comfortable feeling of a large tilt angle while driving.
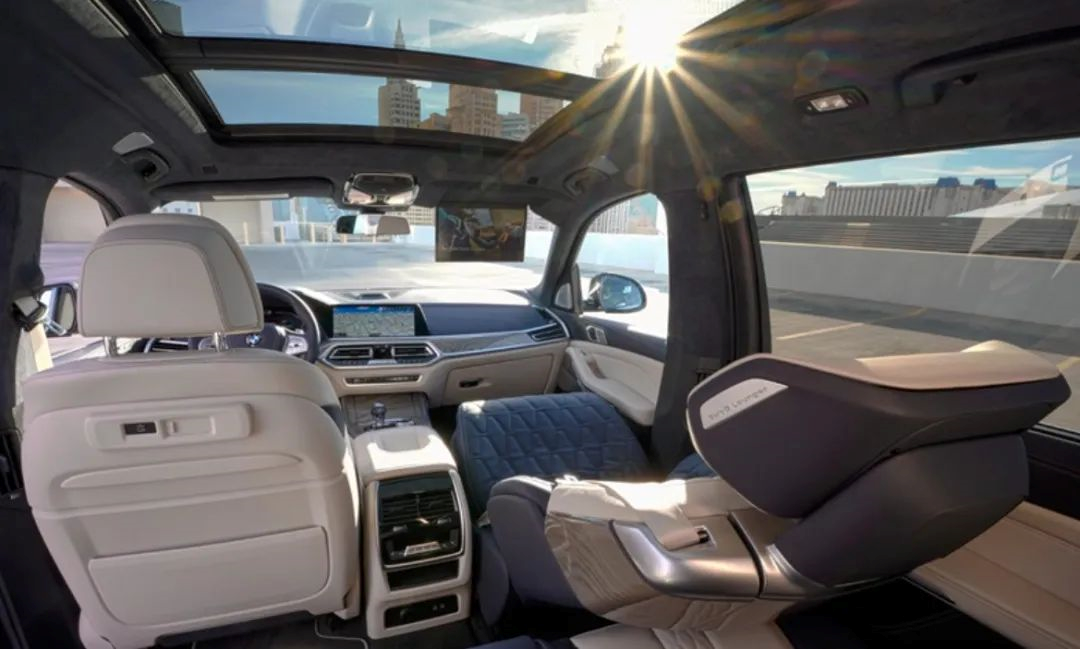

Development prospects of zero-gravity seatsThrough the research on the existing “Zero Gravity Seats”, we believe that improving riding comfort is an endless process. There is still a long way to go in terms of technology to achieve true “zero gravity” riding under existing technological conditions.
There are significant differences in group and individual comfort experiences. Optimization of comfort cross-section and foaming technology can indeed improve comfort to a certain extent, but limited by the boundaries of material properties, it is clearly impossible to meet everyone’s needs in all application scenarios, and can only satisfy the comfort needs of the majority of the population as much as possible. The optimization of adjustment range can indeed provide passengers with more possible choices, but limited by the overall cabin space layout and driving regulations, its usage scenarios are also greatly restricted. Therefore, the current “Zero Gravity Seats” are more of a directional guidance for optimizing the comfort of car seats, rather than a clear technical definition.
However, it can be foreseen that the development of “Zero Gravity Seats” technology is highly convergent with the development of autonomous driving technology. With the further development of autonomous driving technology and intelligent cabin technology, the improvement of computing power will play a greater auxiliary role in improving riding comfort. On the basis of fully expanding the adjustable range of seats and extensively adopting adjustable comfort components, by automatically analyzing the sensory reactions of passengers in different scenarios, the seat can create a “personalized zero-gravity experience” for each individual based on their body condition and usage habits, thus achieving a higher dimension of riding comfort and allowing passengers to experience a “zero gravity riding experience” that is close to breaking away from gravity constraints.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
