The development of assisted driving functions up to today has given birth to two divergent paths. One focuses on urban intelligent driving, and the other is about elevating abilities to L3. Urban intelligent driving is currently the hottest sector in the competition of intelligent driving, with many models supporting urban intelligent driving available for consumers to choose from. As for L3 intelligent driving, it generally stagnates at the Robotaxi stage. Does that mean L3 is far from ordinary consumers?
In fact, around the world, L3 has been in use for some time. In Germany, the first country to allow L3 on the roads, Benz introduced DRIVE PILOT with L3 capabilities in 2022. BMW also announced last November that the new 7 series will support L3. However, there are certain issues and limitations with L3 under current German policy, such as explicit delineation of circumstances where car companies are responsible, speed limitation at 60 km/h, mandatory operation within closed sections, no lane changes are allowed, and mandatory takeover when encountering emergency vehicles and so on.
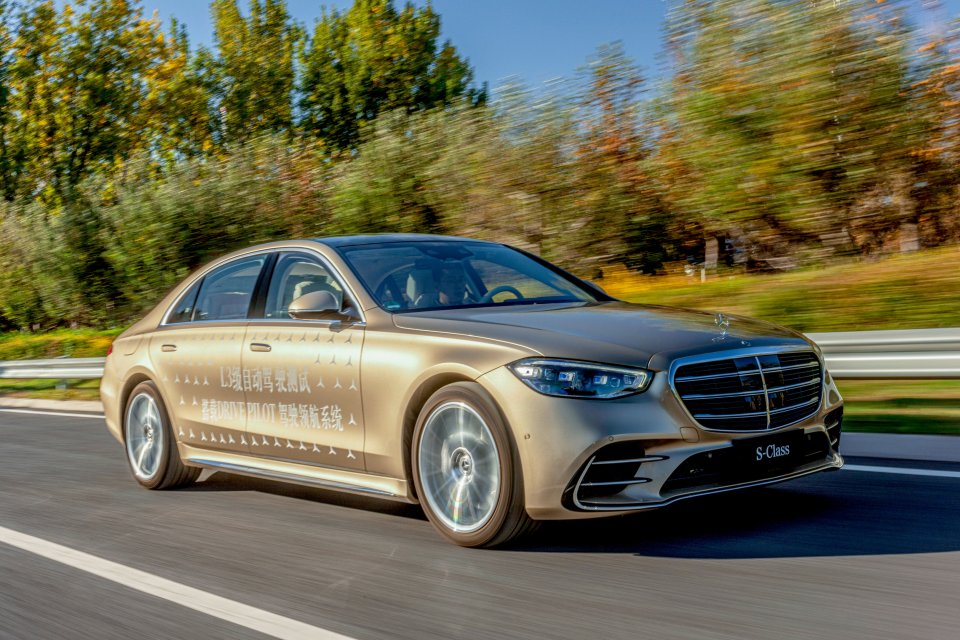

Domestically, as of November 17, 2023, the national level policy for trial applications of L3 intelligent connected vehicles finally came into effect. Along with Benz and BMW that are already operational in Germany, Hyper, IM, and General Motors among a group of car manufacturers have also obtained autonomous driving test licenses.
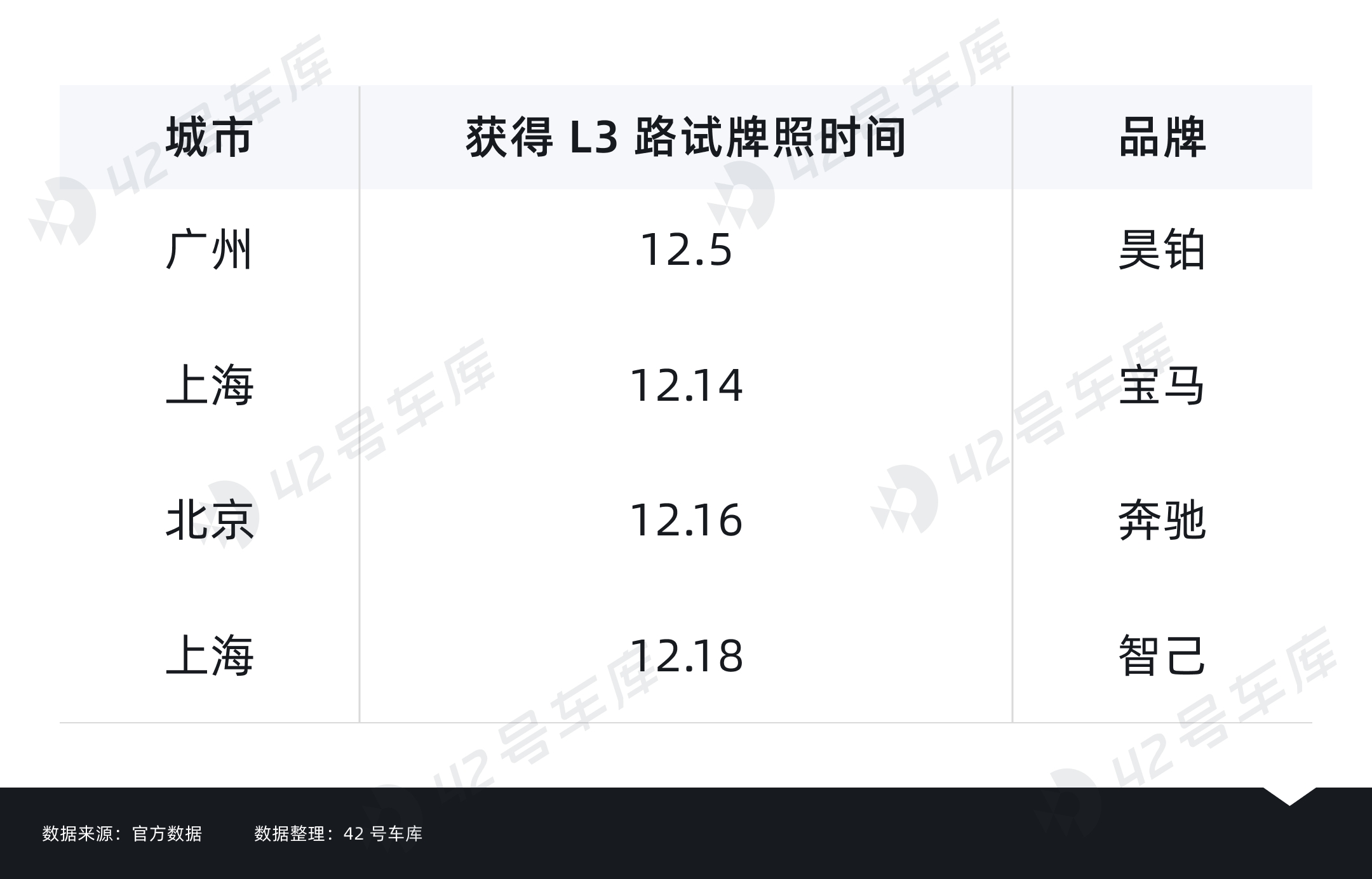
These brands can be considered the first batch to obtain the domestic L3 test license, yet when the first car will land in consumers’ hands still remains a mystery.
Is 3L 3 Lidar or L3?
On February 27, Hyper released the Hyper GT 710 Rear-Drive Advanced Intelligent Driving 3L version, with an official guide price of 259,900 RMB. The title of the Advanced Intelligent Driving 3L version naturally brings to mind L3’s intelligent driving capabilities, or perhaps the implication of 3 Lidar systems.

Primarily from the hardware perspective, the Hyper GT 710 Rear-Drive Advanced Intelligent Driving 3L version utilizes 3 variable-focus lidar sensors on its perception hardware, which are responsible for front and side perception – an apt embodiment of 3L. This combination of three lidar sensors grants a 300-degree perception sphere, effectively covering blind spots compared to a single lidar model, providing faster recognition and responses in scenarios with sudden cuts. In addition, 2 front-facing 8-megapixel cameras are used for visual perception, comprising one wide-angle and one telephoto lens; 4 side-looking 8-megapixel cameras; rearview perception employs one 1-megapixel camera, along with 6 millimeter-wave radars for redundancy.
The parking gear comprises 4 panoramic cameras with a resolution of 1 million pixels each, coupled with an infrared camera. It adapts the MDC 610 autonomous driving chip by Huawei, which has a computing power equivalent to 544 TOPS.

The Hyper GT upper-level IntelliDrive 3L version features 34 perception sensors identical to those on L3-class autonomous road test vehicles. In terms of functionality, high-speed navigation NDA and automatic parking can currently be achieved. Support for urban navigation will also be accommodated later, in conjunction with national laws and regulations, for timely launch of the L3 function. Guangzhou Hyper had forethought in this regard when laying out this hardware.
What can the Hyper GT’s L3 do?
We’ve previously experienced the Hyper GT’s high-speed NDA function on the same hardware. The system is quite comfortable and easy to use in terms of lane changing logic, speed regulation, interaction, etc. It was unfortunate that during testing, we were caught in a long thunderstorm, but even in harsh weather, the stability could reassure the driver. Moreover, the NDA’s driver monitoring system was pretty sensitive.

However, the L3 IntelliDrive capabilities differ from high-speed high-rail navigation assistance. China’s current admission regulations haven’t clearly defined the usage scope. If it’s based on existing overseas laws, the vehicle can only enable the function under limited conditions, such as within enclosed roads and at speeds less than or equal to 60 km/h. The usage scenarios are somewhat single, as it doesn’t perform lane changes or overtaking like navigation assistance, but only brakes even in the presence of obstacles ahead. Under the aforementioned conditions, if the vehicle is the main responsible party in an accident, it is only then the automakers take responsibility. Therefore, the current application conditions of L3 lean more towards congested high-rail conditions.
_20240229183340.jpeg)
Therefore, the L3 function of the Hyper GT upper-level IntelliDrive 3L version, is referred to as TJP Traffic Jam Assistance. It’s activated in the same way as typical IntelliDrive. When the vehicle is in high-speed NDA mode, and the vehicle ahead slows down to below 80 km/h, with more than 5 seconds of following, the system can enter the TJP mode. When the L3 IntelliDrive conditions are not met, the IntelliDrive system seamlessly downgrades to the NDA status.
Upon activation of the TJP feature under the L3 Intelligent Driving, the vehicle maintains center-lane positioning and follows the vehicle ahead, capable of handling various congested road conditions and sudden events. During the operation of L3, the driver can take their hands, feet, and eyes off. In other words, it allows the driver to shift focus onto other matters, such as replying to messages, working, or keeping an eye on their children.

Confidence in Bearing Responsibility Ensures Safety
According to the law, if a traffic accident occurs after activating the TJP function under the L3 Intelligent Driving, the responsibility will fall onto the car manufacturer. Thus, safety is paramount for L3, and redundancy is key to ensuring this. This redundancy also forms the demarcation line between L2 and L3. The Hyper GT Advanced Intelligent Driving 3L version implements useful hardware redundancies and software algorithms in its structural design, ensuring driving stability.
The hardware redundancy of the Hyper GT Advanced Intelligent Driving comprises 8 redundancy systems. Intelligent driving-related systems include a redundant intelligent driving domain control system and 13V6R3L perception redundancy. Driving-related redundancies include dual IPB and RBU braking systems and multiple turning torque redundancies. Lastly, the car itself has a dual battery power supply redundancy, communication redundancy, parking redundancy, and a Star-based + Ground-based fusion positioning system to ensure the safety of intelligent driving in remote areas with inferior signal quality. These 8 redundancies, coupled with safety monitoring, ensure that the advanced intelligent driving system can function normally even when a single point of failure occurs.
In terms of software, the Hyper GT utilizes the popular BEV + Transformer + OCC network perception algorithm, combined with intelligent driving hardware, can meet the demands of urban intelligent driving and L3. Furthermore, Hyper GT incorporates ONE MODEL artificial intelligence algorithm in developing L3.
Concerning the decision-making abilities of the intelligent driving system, Hyper has adopted a fusion, path enhancement, and human-learning algorithm at the software level. Under the ONE MODEL fusion algorithm, the overall operation is more decisive, avoiding problems such as multiple conflicting steps, frequent irregular exits, and steering wheel jitters. Simultaneously, the enhanced path algorithm allows for better recognition in complex environments. During testing and training, the system can optimize its learning from a human perspective through a fully data-driven algorithm.## Final Thoughts
In retrospect, ever since 2019 when foundational assistance driving just started to enter the majority’s field of vision, assistance driving has evolved dramatically. From the initial stage of adaptive cruising, to the development of lateral control and lane-keeping, and up to now when domestic smart driving has reached L3 and urban smart driving.
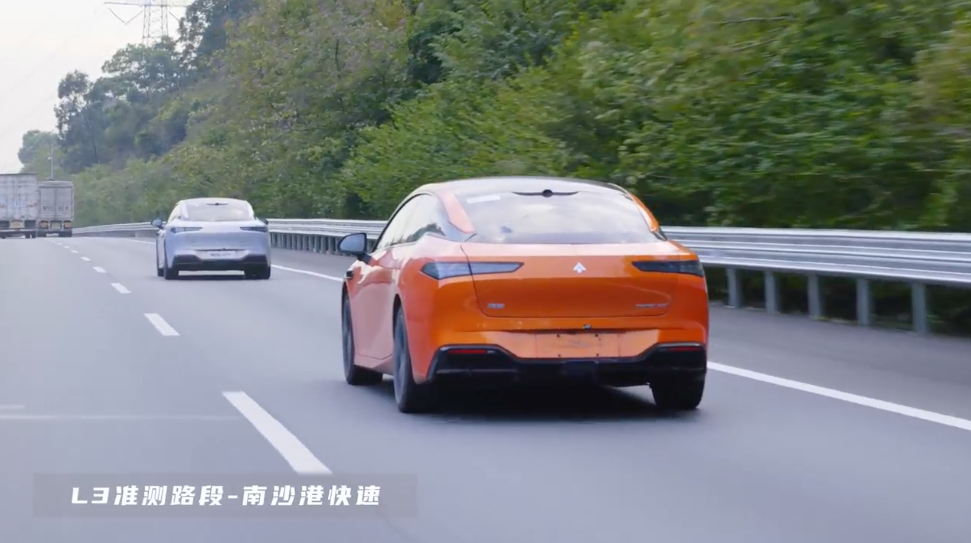

Previously, we felt that L3 was far from conventional use, perhaps only existing in modes like Robotaxi. With the onset of pilot programs, it indicates that L3/L4 level smart driving cars on our roads now have a definitive, unified top-level policy support. Globally, China will follow Germany and the United States, becoming another major country to introduce L3 pilots.
Now Hyper GT advanced smart drive 3L version is armed with the same hardware as that of L3 level autonomous driving road test vehicles, in which the hardware redundancy can provide a significant guarantee of safety during the smart driving process. Thus for consumers, the launch of the new car brings us one step closer to obtaining L3 level smart driving. We can foresee that in the not too distant future, with the establishment of laws and regulations, it will unlock more traveling scenarios for consumers.
This article is a translation by AI of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
