Author: Zhu Yulong
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a considerable impact on General Motors’ operations in China. However, the good news is that SAIC-GM’s first pre-production Cadillac LYRIQ has officially rolled off the Cadillac factory.
From 2021 to 2022, General Motors faces great pressure in increasing production of electric vehicles, even being outstripped by Ford in North America. As a result, GM CEO Mary Barra stated that a portion of executives’ shares will be tied to the company’s electric vehicle targets – the number of electric vehicles in North America and their launch dates and quality – up to 2 million units by 2025 and whether or not the company can launch $30K vehicles by 2027. This is truly related to the lifeblood of General Motors.
The interesting thing is that the company is planning to develop various car models around its battery cell and subsequent module and pack designs, covering entry-level FWD models (small cars), RWD models (mid-size cars), and long-wheelbase luxury car models, as well as CTC-designed pickups and SUVs, and low-roof electric sports car designs. Due to the complexity of the plan, this article will only expand on two important aspects of the product line available in China.

As I understand it, General Motors initially focused on soft pack design and then used a module design approach to meet the demands of China’s shell batteries. The company integrated battery production into three categories: sedans, mid-sized SUVs, and sports cars (Low Roof) – this was in line with the current US economic and industrial policies towards making long-term, large-scale investments in transformation.

Battery Capacity and Module Planning
Due to the use of a single cell mode, the company has configured battery systems with the same width and different lengths and thicknesses. The following capacities are calculated based on a planned 1/3C capacity, which differs from the Chinese 1C shell battery for charging and discharging.
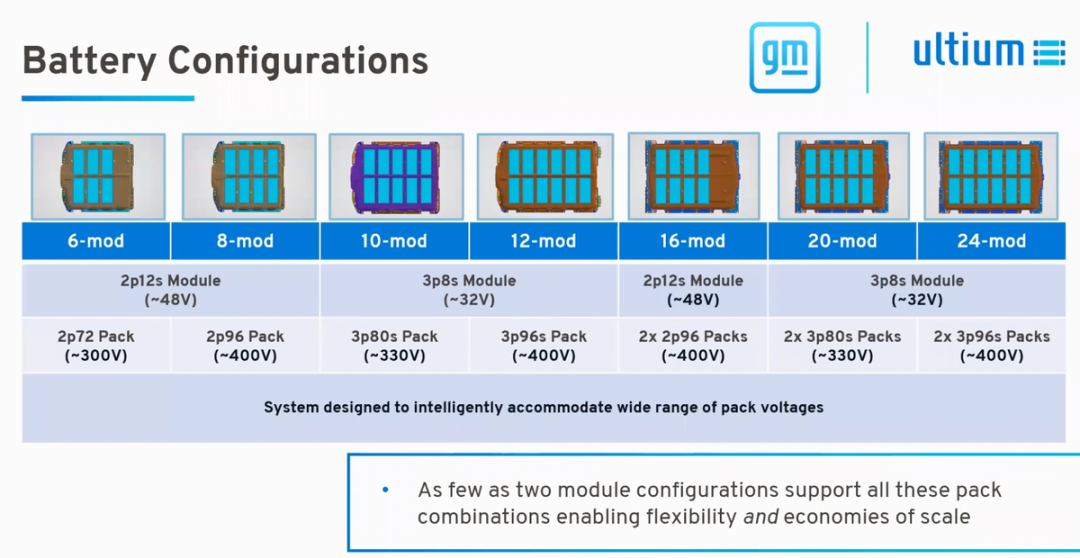
Note: If we use the 4680 single cell mode, these configurations will be easier to implement and will be more optimized in terms of capacity and voltage balance.
- Low capacity mode (shortest length L1, thickness H1)# Battery Configuration
There are two minimum configurations for 50kWh battery: 6 modules and 8 modules using 2P12S modules (voltage 48V), which form a 2P72S 300V battery pack and a 400V model, respectively. Both of these battery packs are designed for low-cost applications.
- Medium power mode (L2 length and H1 thickness)
10 modules (84kWh), configured with 3P8S 32V battery modules forming a 330V battery for mid-size SUV.
- Standard power mode (L3 length and H1 thickness)
12 modules (100kWh, 95.7kWh in China), configured with 3P8S 32V battery modules forming a 3P96S 400V high-efficiency battery pack for luxury cars.
- 10 and 12 modules are designed for front-wheel drive and rear-wheel drive applications (including four-wheel drive), considering the difference in wheelbase. It is difficult to further increase the energy of front-wheel drive.
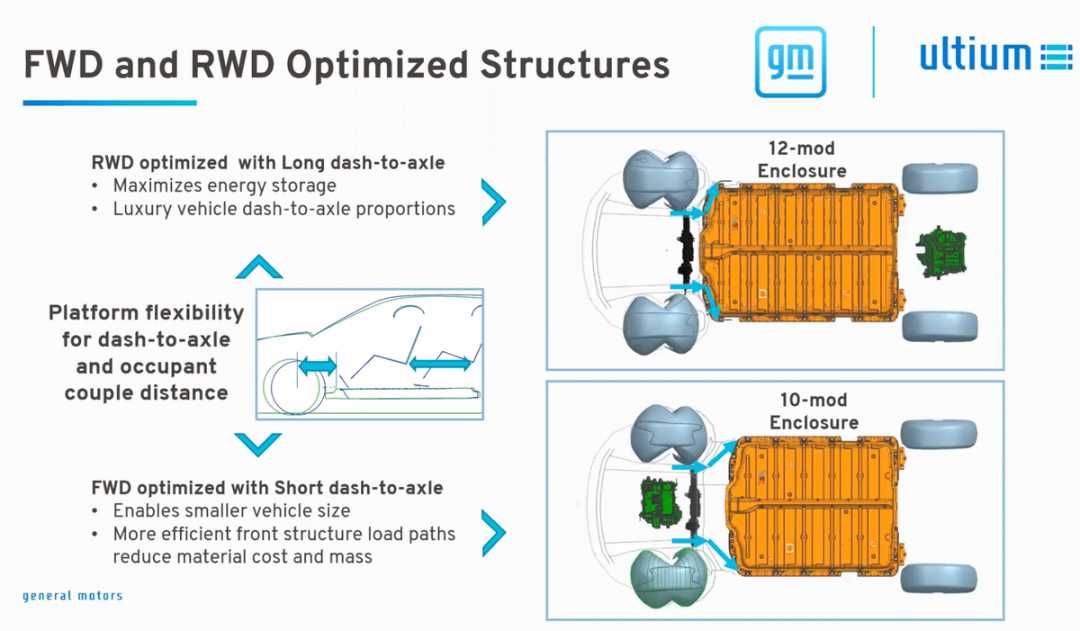
- 16, 20, and 24 modules (L4 length and H2 thickness)
These three use CTC mode and are used in mid-size SUVs and pickup trucks, with 400V and 800V platforms available.
- Others include a battery pack with a length of L5 and a thickness of H3 of 110mm, designed for sports cars, which we will introduce tomorrow.
As shown above, a battery platform has many battery configurations, which can be quite complex.
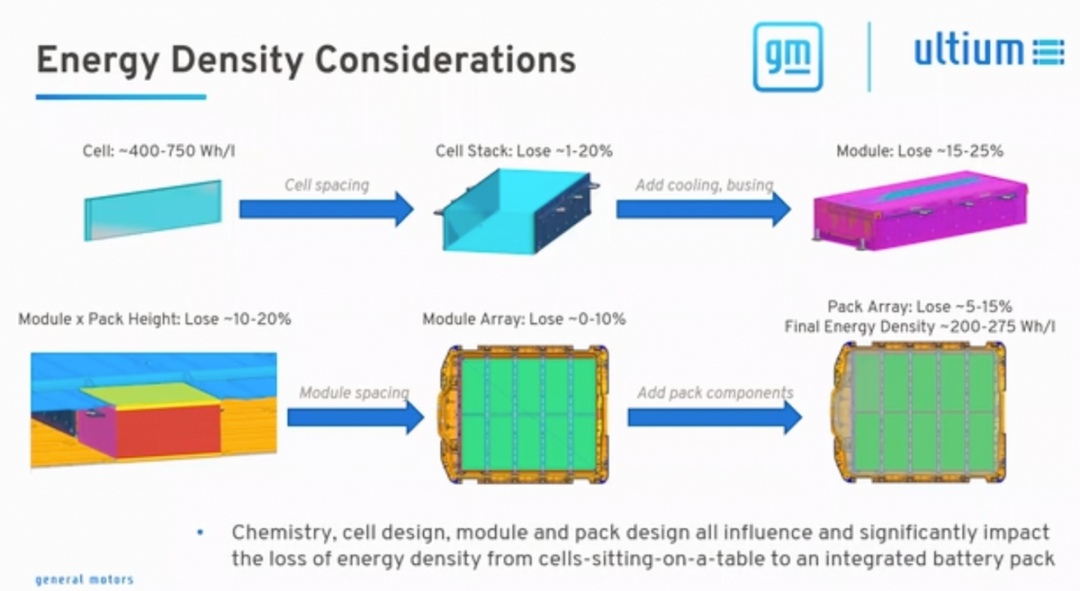
Due to so many changes, the energy density of battery cells has been reduced from 400-750Wh/L to 200-275Wh/L, with a 15%-25% reduction when modules are stacked, a 10-20% reduction in module and battery pack height, and a 10% loss in overall XY layout efficiency. Frankly speaking, compared with the Chinese Chang Dao, Duan Dao, and Qi Lin batteries, at least in terms of layout efficiency and cost structure, there is not much advantage.
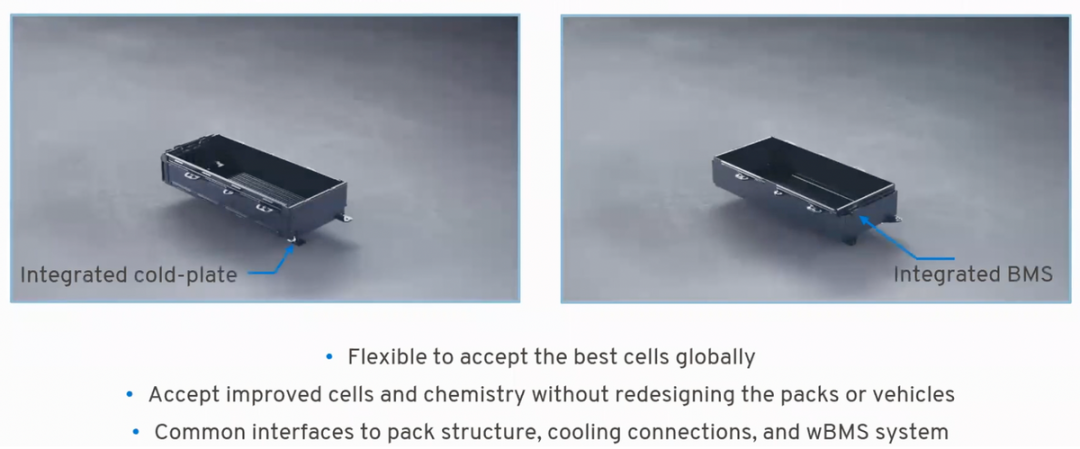
Interestingly, wireless wBMS objectively enables GM to change its battery modules. Removing the communication lines and integrating CMUs brings good grouping effects.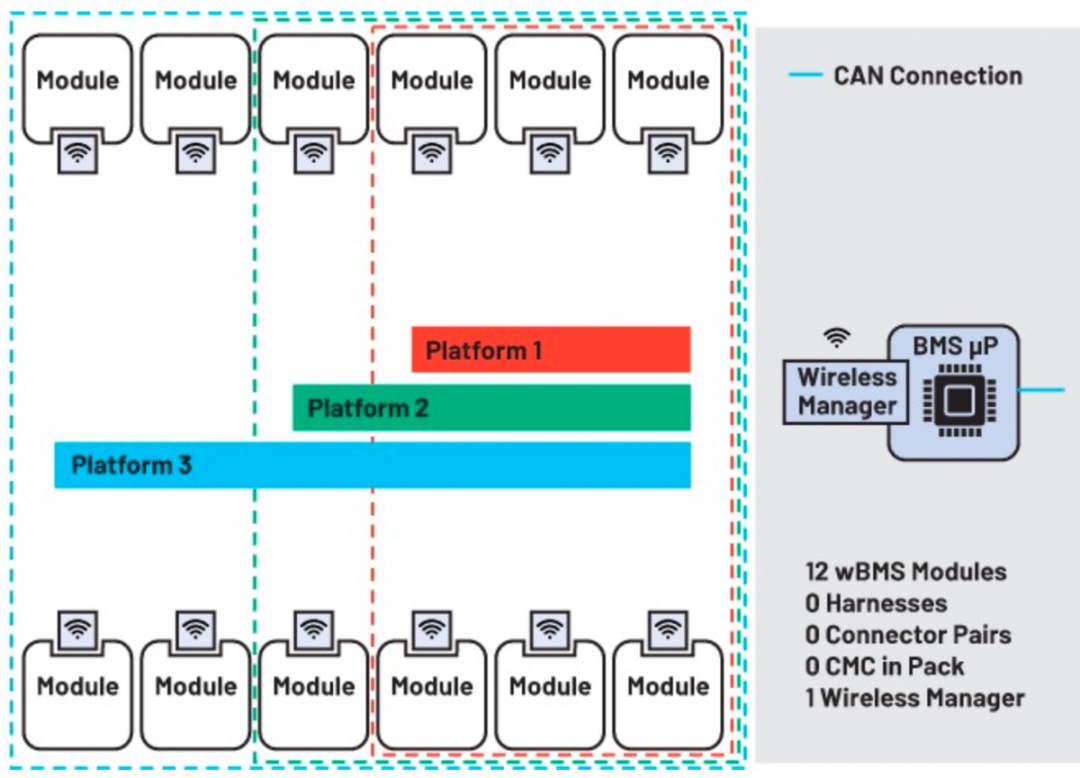
Comparison between General Soft Pack and Square Shell
The main reason for using square shell is due to the uniqueness of China, where they must have it. However, in the United States, they are determined to crush the four battery soft pack factories.
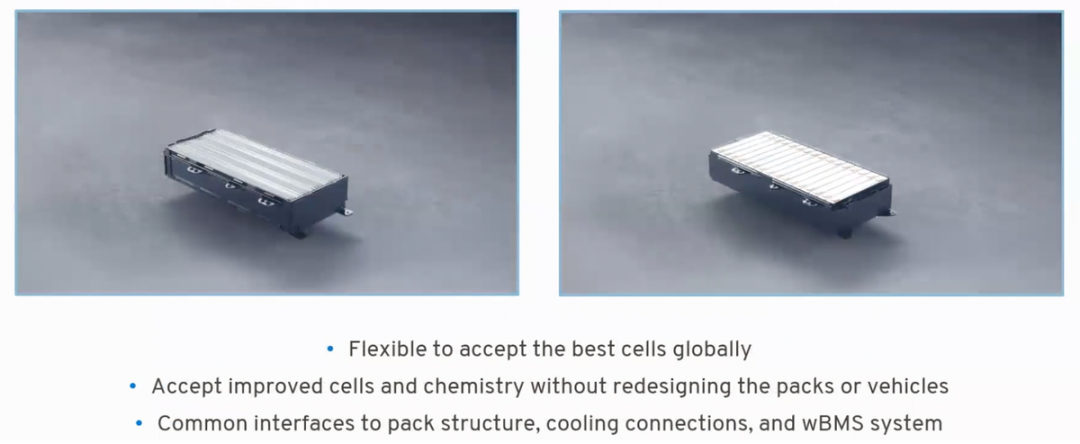
The most valuable comparison is shown in the figure below, in terms of overall package arrangement, cooling, and wireless connectivity compatibility.
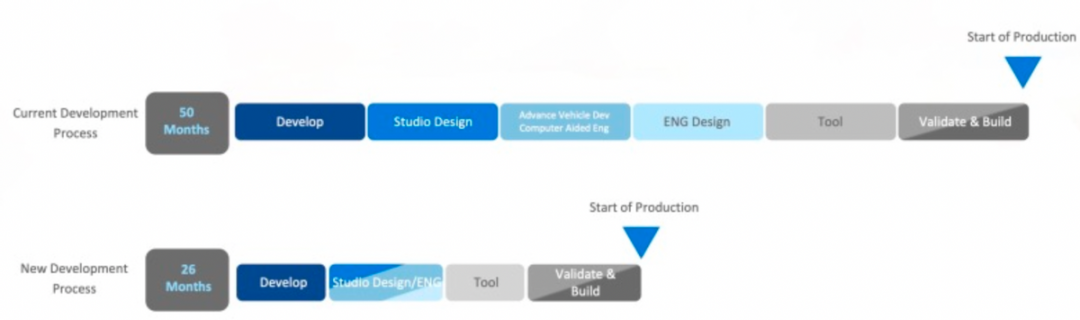
Since the design and development goal is shortened from 50 months to 26 months, it is still worth paying attention to whether any vehicle models will emerge in the future. The reduced steps are the vehicle model and engineering development, both of which are completely shortened.
Since GM has set a very low price expectation for the battery, requiring the cell to be under 100 US dollars per Wh, it remains to be seen whether they can hold up under the current battery material system.
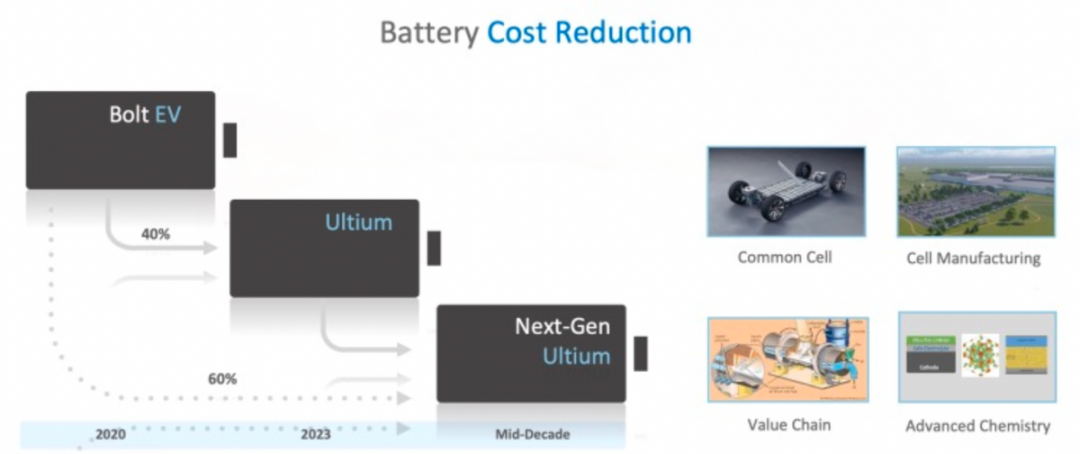
Because the investment and upstream of this battery have received support from the US government, the transformation and investment in North America are very smooth.

Summary: Really hope that GM can make a difference. Based solely on the group efficiency and other data currently available, it can only be said that they have achieved their initial goals, and compared with the Chinese coil kings who are pursuing the ultimate, they are still not ruthless enough towards themselves. They should directly use soft pack CTP.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
