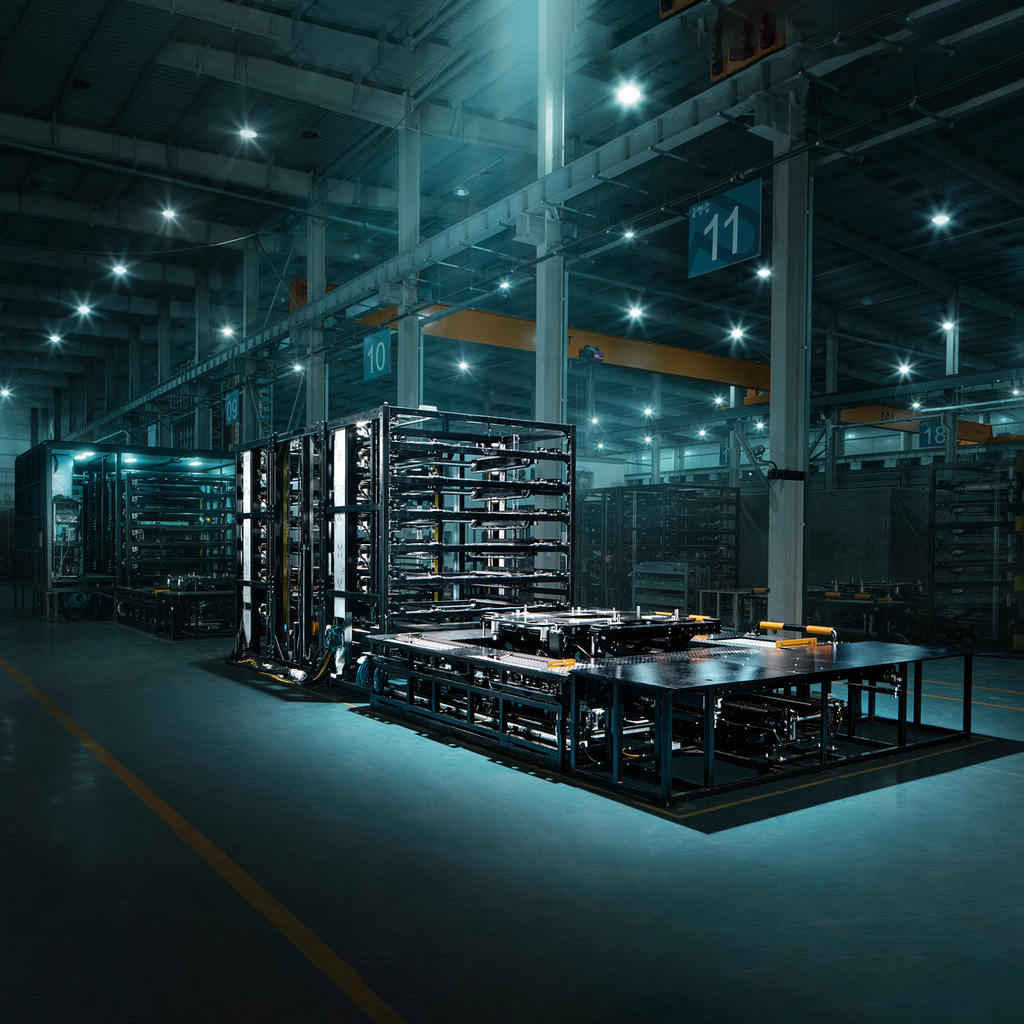
Recently, NIO released the unique technology and internal pictures of its second-generation battery swapping station. As a technology enthusiast, I have long been studying its internal workings. This is a great opportunity to take a closer look at the black technologies of NIO’s second-generation battery swapping station.
How does the swapping station recognize NIO’s three existing models?
Currently, NIO’s ES6, EC6, and ES8 models are available for sale, and more models will be added to the swapping lineup soon. Therefore, the first problem that NIO must solve is how to make the swapping station compatible with multiple models.
According to NIO’s official App post, the second-generation swapping station uses a brand-new SAP (Self-Adqptive Platform) swapping platform, which can automatically identify the wheelbase, adjust the position of the wheels, and adjust the vehicle posture accordingly. This is the first step in making NIO’s entire lineup compatible with battery swapping.

About the Bayobolt bolt and its secrets
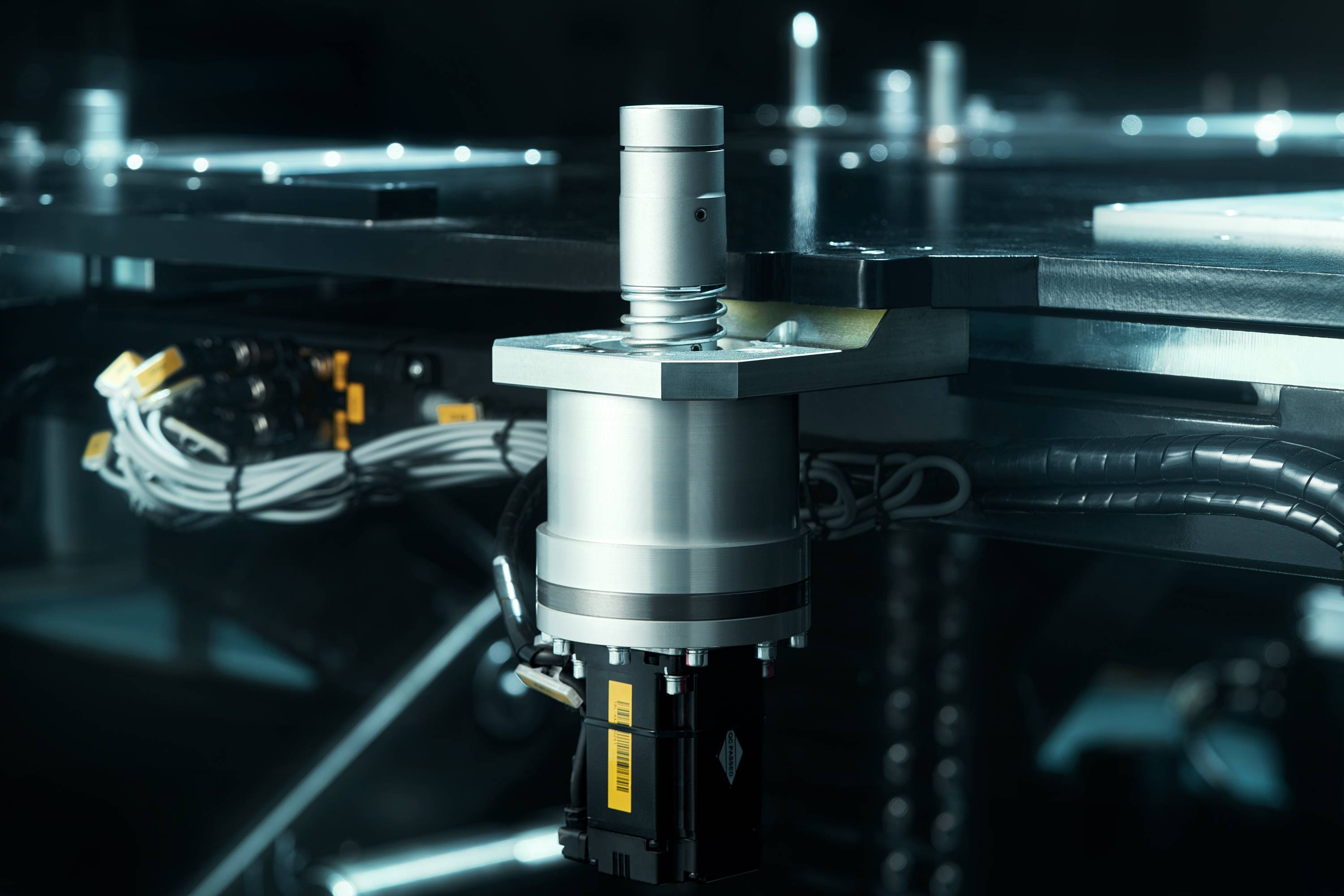
Supporting battery swapping means that the vehicle’s battery pack will inevitably undergo very frequent disassembly and assembly. Friends who have tinkered with toy cars know that screws that have been tightened too much can become stripped. So, how does NIO overcome this issue? How to avoid safety hazards?
To solve this problem, NIO has developed the Bayobolt bolt for connecting the battery to the vehicle body. Simply put, the Bayobolt is NIO’s patented technology, which has the characteristic of ensuring the connection strength while allowing a certain degree of float. Its design concept is similar to that of the docking device used by the Chang’e-5 lunar probe to dock with the lunar orbit. It will not damage the battery while ensuring the reliability of repeated separation, and a single screw can provide 3 tons of tightening force.
According to NIO’s official introduction, the Bayobolt bolt can achieve 2,000 lossless locking and unlocking cycles. Taking the 70 kWh battery pack with the largest inventory currently available on the market as an example, replacing the battery every 300 kilometers, a lifespan of 2,000 cycles means a range of 600,000 kilometers. It can be said that this lifespan is sufficient to support driving until the scrap stage.
In addition, each swapping station’s swapping robot RGV is equipped with 10 unlocking devices, and the visual recognition device can accurately position the screw holes of the battery pack under the vehicle. The 10 unlocking devices can automatically control the unlocking nuts in 31 seconds.

More Changes Besides Batteries and Increased Speed for the Second Generation Battery Exchange Stations
Two Sets of Water Cooling Systems
Similar to the first generation battery exchange stations, the exchange stations use a 22-degree Celsius water cooling system to ensure fast and safe battery charging with no seasonal limitations.
After embarking on a journey to Norway on July 7th, the second generation battery exchange stations now offer quick energy replenishment for local users during the long winter months. Compared to the first generation’s capacity for up to 5 batteries, the second generation battery exchange stations can accommodate up to 13 batteries. As a result, each station is equipped with two sets of battery liquid cooling and temperature control systems to ensure that the battery vitality is not affected by the environment.
Synchronously Delivered Battery Pack
As is well-known, the second generation battery exchange stations are faster than the first generation, mainly due to higher efficiency in internal coordination.
During battery exchanges, the first generation would only send out new fully charged batteries after the original batteries were collected. In contrast, the second generation battery exchange stations utilize dual-track entrance and exit compartment designs. In short, this means that fully charged batteries are sent out from the battery compartment while the original batteries are collected, thereby further shortening the time required for battery exchanges for an ultra-fast swapping experience.


NIO’s battery exchange technology can avoid battery wear and tear that would reduce the value of automotive products. Additionally, the technology offers unique advantages such as fast energy replenishment, high battery utilization rates, and the ability to quickly assemble batteries of different energy capacities. Whether it is the development of fast charging technology or the advancement of battery exchange technology, these improvements are worth looking forward to for users.
🔗Source: Official NIO website
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
