Let’s first take a look at a chart that shows the levels of autonomous driving technology among various leading car manufacturers, to get a general idea of which company is ahead in terms of commercialized autonomous driving technology.
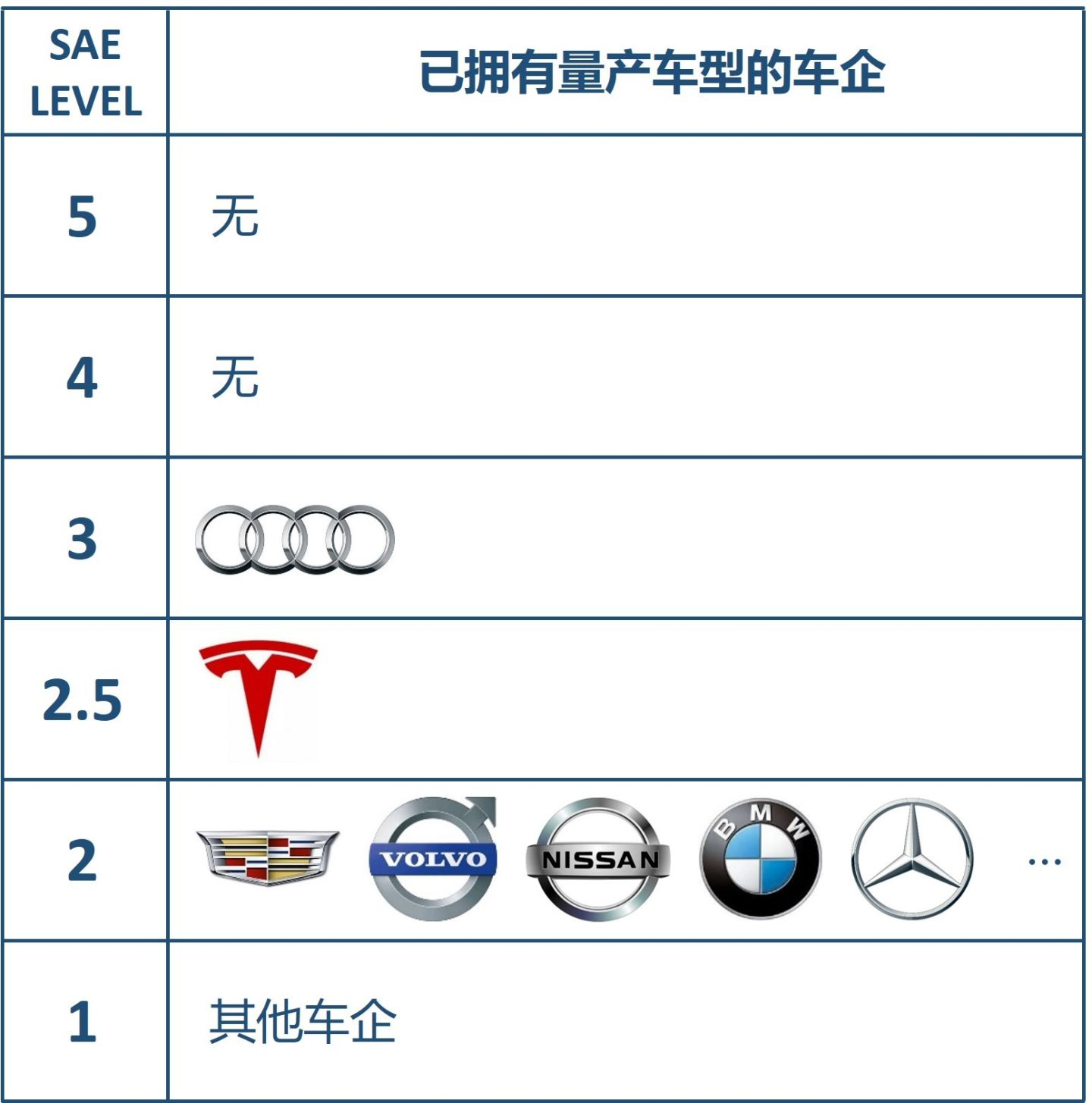
Mercedes-Benz: It’s a bit crowded here…
Volvo: Hey, buddy next door, you’re stepping on my foot…
Tesla: Sigh, it’s lonely at the top.
Audi: Tesla, you know nothing about power.
The road to autonomous driving from Level 2 to Level 5 is a relatively long process. Among currently available commercialized car models, Audi A8 is at Level 3, Tesla is at Level 2.5, and Cadillac CT6 is at Level 2.
So, what are the specific differences and challenges that need to be overcome between each level? Let’s take a closer look level by level.
According to international conventions, when discussing autonomous driving levels, we must refer to the SAE classification chart.
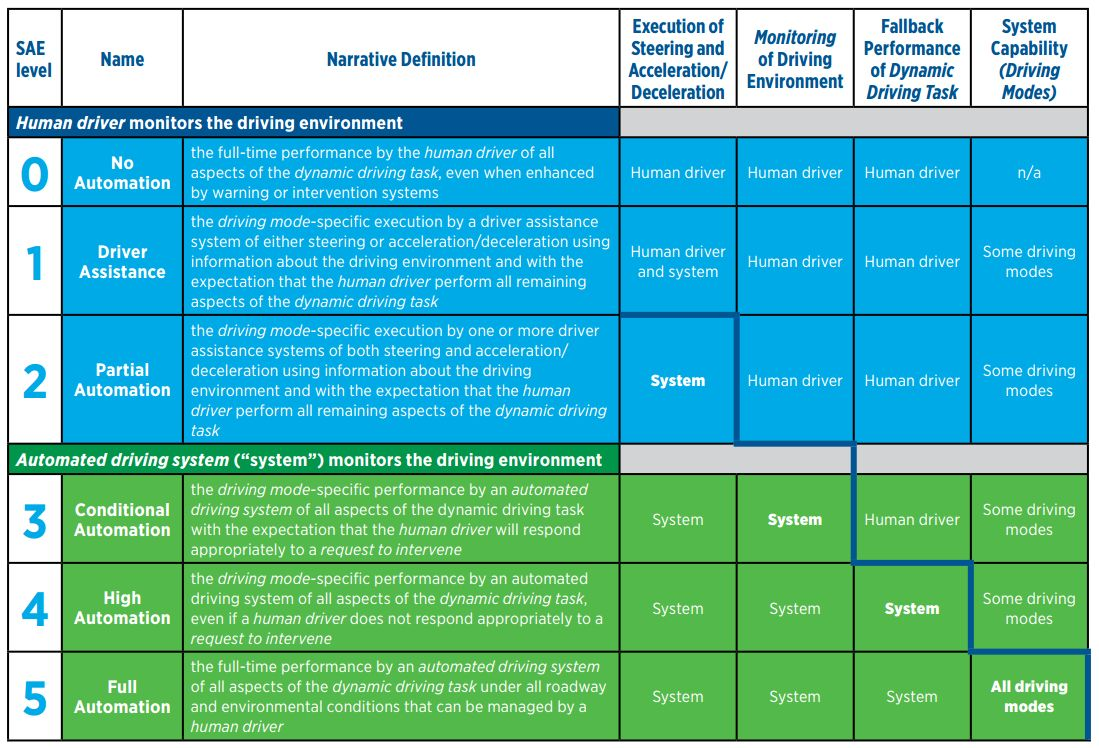
Image source: LEVELS OF DRIVING AUTOMATION ARE DEFINED IN NEW SAE INTERNATIONAL STANDARD J3016
Next, I’ll explain three questions for you below:
- What kind of technology does each level represent?
- What indicators can be used to immediately differentiate which level a car belongs to?
- Why the higher the level, the higher the requirements for technology?
SAE Level 0: No Automation
To be precise, it is now very difficult to see Level 0 cars on the road. They have either been scrapped or are prohibited by regulations from being on the road.
No Automation means that even the most basic configurations, such as ABS (automatic anti-lock braking), are not available.
To put it more extremely, you can think of a Level 0 car as simply four wheels and a couch. \@[Geely]
SAE Level 1: Driver Assistance
Most common cars on the road today belong to Level 1.Level 1 is called driver assistance system, and any function that intervenes in the driving state during the driver’s driving process is called driver assistance, which belongs to Level 1. For example, the most basic ABS, ESP upgraded from ABS, and the commonly used cruise control, ACC adaptive cruise control function, and LKA lane keeping assist on highways. All the English abbreviations seen in the chassis function introduction when buying a car are more or less defined as Level 1 according to SAE regulations.
SAE Level 2: Partial Automation
The most significant difference between Level 2 and Level 1 is whether the system can control the vehicle in both lateral and longitudinal directions simultaneously. If a vehicle can simultaneously achieve ACC+LKA (adaptive cruise control + lane keeping assist), then the vehicle has crossed the threshold of Level 2. The semi-automatic driving system “Super Cruise” on the 2018 Cadillac CT6 is a typical Level 2 system. Let’s take a look at a video: Cadillac CT6,SuperCruise automatic driving system demonstration
In the video, it can be seen that the car does not have the function of active overtaking. That is to say, the current Super Cruise can only achieve acceleration and deceleration within a single lane.
Now let’s talk about Tesla, which cannot be ignored when it comes to automatic driving. As I mentioned in “Which one do you think is more promising: Internet companies or car companies developing automatic driving technology?“, Tesla has exaggerated the capabilities of its system excessively.
Why is Tesla’s AutoPilot currently called Level 2.5? Because Tesla has a lane changing function. When the driver ensures safety, the vehicle can change lanes according to the signal sent by the turn signal lever. That is to say, Tesla’s lane changing operation is not fully automatic, but it outsources the demand for environmental perception to the driver. Tesla will judge whether it is safe to change lanes after receiving the lane change signal. For example, if the distance between the front and rear vehicles is too close or there is a solid line, it will not change lanes.
Difficulty: Level 1 ~ Level 2- Comfort of the coordination between lateral and longitudinal control in cars While individual lateral control (lane keeping) or longitudinal control (ACC, etc.) technologies are already mature, the current challenge is how to achieve the highest comfort level when both are operated simultaneously.
- Selecting the timing to notify the driver to take over control of the vehicle Level 2 systems do not have higher-level autonomous driving functions, and require the driver to monitor in real time and be prepared to take over control. Human-machine interaction engineers need to devise the most friendly and appropriate way to notify the driver to take over control without affecting their mood.
SAE Level 3: Conditional Automation
Conditional automation refers to the use of autonomous driving technology in specific scenarios. For example, the all-new Audi A8 limits its Traffic Jam Pilot function, which is used in a very common scenario – traffic congestion, to the situation where the vehicle speed is less than or equal to 60 kilometers per hour. In situations where local laws permit, the system will take over the driving task completely until the user is notified to take over again. This is currently the highest level of autonomous driving capability achieved in mass-produced vehicles worldwide.
Reference: Audi AI behind the world’s first mass-produced autonomous driving car, Audi A8
Upon careful consideration, the features of Level 3 can also be achieved by upgrading software for Tesla. Why is only the Audi A8 able to claim to have achieved Level 3? Because the biggest improvement of Level 3 over Level 2 is that the driver no longer needs to monitor the current road conditions in real time, but only needs to take over the vehicle when prompted by the system. This is a huge leap forward for autonomous driving technology and means that the autonomous driving system replaces humans as the driver and monitor. The driver becomes a passenger who does not need to monitor the current road conditions in real time.
Challenge: Level 2 ~ Level 3- Sensor Sensing Technology Recently, NTSB released the verdict of the May 2016 fatal accident involving a Tesla colliding with a truck, stating that the limitation of Tesla’s Autopilot feature was the main cause of the accident, due to the deficiency in sensor sensing technology. AutoPilot 1.0’s hardware configuration had difficulty handling special situations, like intersections, for example. The image below shows an accident caused by Tesla’s sensor sensing deficiency, which led to it failing to correctly recognize the truck.
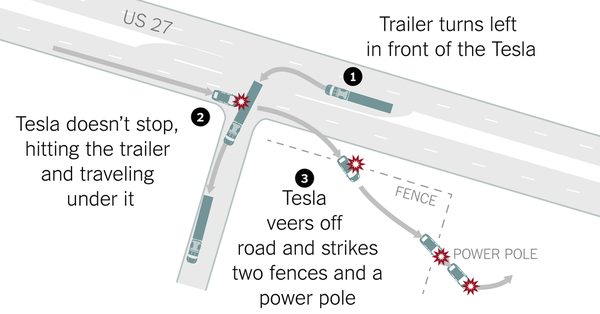
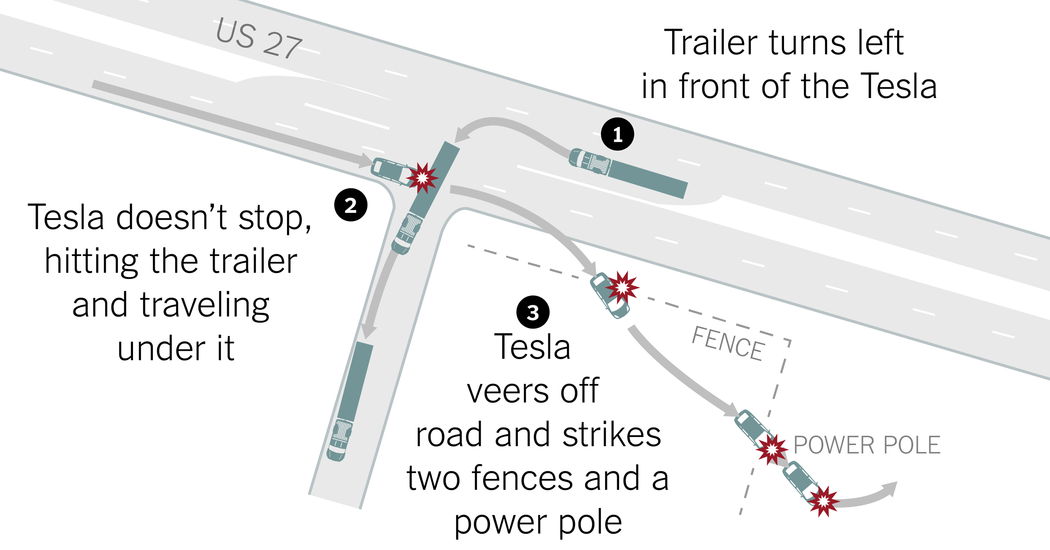
Image source: Inside the Self-Driving Tesla Fatal Accident
Due to the presence of this objective factor, the entire vehicle industry has become particularly conservative when it comes to developing autonomous driving technology. They either add sensors to enhance perception ability, such as the four-line lidar added to the all-new Audi A8, or they monitor the driver’s facial expression to ensure that the driver is observing the road conditions in real time, such as in the Cadillac CT6.
- Regulations At the last Apollo press conference, Baidu announced the testing of its autonomous driving technology on open roads in front of the whole of China, and was subsequently visited by law enforcement. Currently, China does not allow testing of autonomous driving vehicles on open or high-speed roads, so testing can only be conducted in enclosed testing facilities, with other countries leading the way in autonomous driving regulations.
SAE Level 4: High AutomationThe research of Level 4 autonomous driving technology is done by companies such as Waymo, Uber, and Baidu L4 department. One obvious common feature of their autonomous vehicles is a bulky LIDAR on top, like the one shown below.


LIDAR provides extremely accurate and rich perception information, which enables autonomous vehicles to handle extreme situations with ease. With LIDAR as the primary sensor, supplemented by vision and other redundant sensors and high-precision maps, Level 4 autonomous driving from point A to point B on open roads is no longer distant.
Challenge: Level 3 ~ Level 4
-
Sensor Cost The cost of LIDAR cannot be reduced in the short term, which is one of the important reasons why L4 autonomous driving vehicles are not yet popular. Waymo announced earlier this year that it hopes low-cost LIDAR sensors will arrive soon by reducing the cost of LIDAR by 90%.
-
Highly Robust Autonomous Driving Algorithms and Stable Computing Platforms The accuracy and precision of Level 4 autonomous driving algorithms need to meet or even exceed human cognitive levels, which requires highly robust algorithms and stable computing platforms to ensure that autonomous vehicles can react well even in unexpected situations.
-
High-precision Map Acquisition Qualifications This challenge does not exist in foreign countries but is a big obstacle in China due to national defense reasons. Apart from well-known companies such as BAT having map surveying and mapping qualifications, there are very few mapping companies with qualifications in China. In recent years, with the development of autonomous driving, mapping companies may become a scarce resource for those who want to develop autonomous driving technology in China. If possible, it is recommended that people conduct their own research on a few mapping companies with qualifications in China, buy their stocks, and look forward to their success. This is also one of the reasons for our company’s cooperation with mapping companies, as reported in SAIC collaborates with GuanTing Information to develop high-precision maps, intelligent driving helps auto leader “shift up.”– Acceptance of passengers Now imagine you’re getting into a car with no steering wheel that you can’t take over at any time, you may feel a little nervous. Therefore, the acceptance of humans is also a major difficulty in the popularization of autonomous driving, which takes time to establish trust.
Level 5: Full Automation
Many people may feel confused about L4 and L5, but they are actually easy to distinguish by observing their driving ranges. Take a look at the figure below. The large arc in the figure represents the area limited by Level 4 autonomous driving, and the small circle represents the perception range of the car. At time t, the car is still within the large arc, and the autonomous driving system is working properly; at time t+1, it is close to the boundary, and the autonomous driving system is about to fail and issues an alert; at time t+2, the car has driven out of the boundary, and the autonomous driving system has completely failed and stops safely.
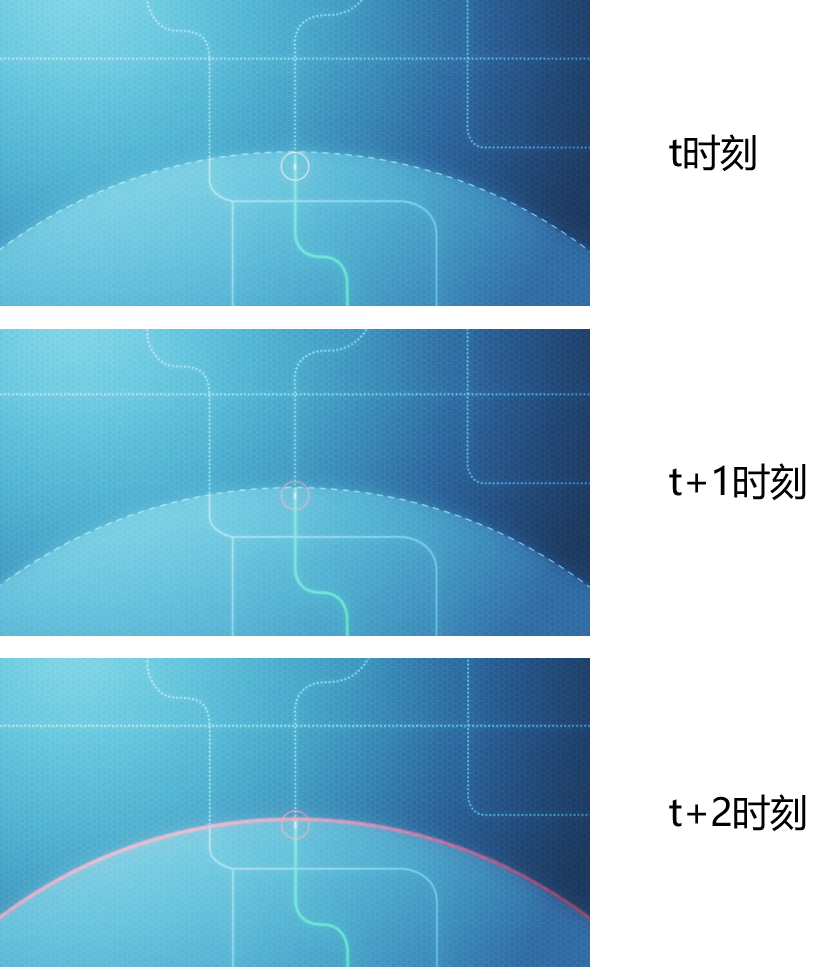
Image source:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av12429465
So, how to describe the functions of L5? Just give a GPS coordinate point, and the L5 autonomous driving car can take you to the designated place, regardless of whether the regulations there are driving on the right or left, the autonomous driving car can easily deal with it. It is fully automated driving in all conditions and all areas.
Difficulties: Level 4~Level 5
High-precision map crowdsourcing and updating ecosystem Autonomous driving technology relies heavily on high-precision electronic maps, and the electronic maps used must ensure real-time and easy updating. In the future, every autonomous driving car on the road will not only be used for normal commuting, but will also be a vehicle for collecting map information, and will provide the current map information to the cloud in real time for other autonomous driving cars to use.
These are the difficulties that the autonomous driving research needs to overcome. More will be added in the future.
When will we achieve Level 5?In this era where predictions can be proven wrong at any moment, let’s make a conservative estimate: L4 autonomy will be popularized before 2025. As for L5, it may not exist because building a car that can run anywhere in the world is not cost-effective. L4 is already sufficient for users. Do you really care if a car can travel freely in China but not in the United States?
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
