2020 was supposed to be a good year for the automobile industry, but the sudden outbreak of the pandemic disrupted the work arrangements of all industries, and as a pillar industry, the automobile manufacturing industry was affected significantly. After experiencing a two-year decline in 2018-2019, the automobile industry will suffer another blow.
How much impact will this epidemic have on the automobile industry? Although there is no clear number, Mercedes-Benz recently announced that if it cannot resume work in a timely manner, it will suffer a loss of 400 million yuan per day. If this applies to other multinational car companies, who can escape it?
The epidemic is also a cruel magnifying glass, highlighting each automaker’s strengths and weaknesses. For multinational joint venture companies and independent traditional automakers with strong supply chain management, strong cash reserves, and a complete system of supply chain, research and development, manufacturing, marketing, and after-sales service, even if affected, they can pass through it safely.
To be honest, for most car companies, although there are losses that can be sustained, I believe they can hold on. However, for China’s new car making forces, this epidemic may be a matter of life and death. So what are the other challenges that new car manufacturers need to overcome after surviving the “virus”?
-
How long can new car manufacturers continue to spend their cash reserves during the difficulty in resuming work?
-
Financing is becoming increasingly difficult. How can new car manufacturers continue to push forward their delivery plan, even if it has not been achieved after the epidemic?
-
How can new car manufacturers withstand the competition from domestic Tesla (cars)?
-
How can new car manufacturers withstand the competition of multinational joint venture companies’ new energy vehicles in 2020?
-
The demand end is unclear. How can (new car manufacturers) proceed with the next sales plan for the cars that have already been delivered?
Each of the above challenges requires urgent solutions for new car manufacturers.
How long can new car manufacturers continue to spend their cash reserves during the difficulty in resuming work?
Having money is the foundation for survival, but making cars is not easy. For new car manufacturers, the early stage of research and development, sales, and management costs are high. Under the circumstances where most companies are in huge losses, they have to rely on capital to mass produce, deliver and generate sales revenue.
Lack of money has always been a problem for new car manufacturers, and the epidemic has significantly affected their cash flow. How can new car manufacturers support future development? It should be noted that the use of existing financing funds has already been planned before the epidemic, and the capital consumption caused by the sudden outbreak of the epidemic was not planned for, which will inevitably affect the existing work arrangements.Although some of the new car manufacturers completed a financing in 2019, it seems that the money has been mostly spent up until now.
Data shows that in Q3 of 2019, NIO’s total revenue was RMB 18.368 billion, up 21.8% from the previous quarter and 25.0% year-over-year; its automotive sales revenue was RMB 17.335 billion, up 22.5% from Q2 of 2019 and 21.5% year-over-year. The gross margin for vehicles was -6.8%. NIO’s net loss in Q3 of 2019 was RMB 25.217 billion.
Combined with a net loss of RMB 32.858 billion in Q2 and RMB 26.236 billion in Q1, NIO has a total net loss of RMB 84.311 billion for 2019.
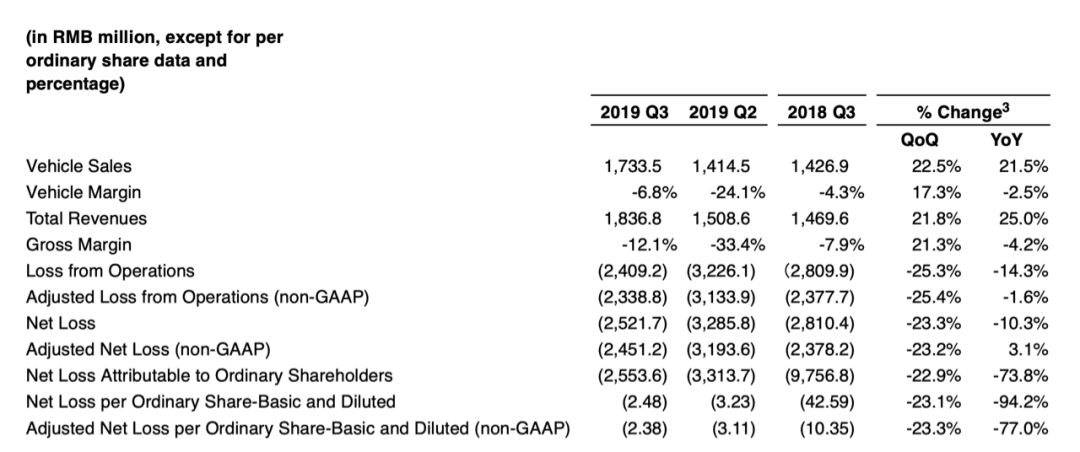
According to its Q3 financial report, as of September 30, 2019, NIO’s cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash, and short-term investments amounted to RMB 19.607 billion, a decrease of RMB 1.5 billion from the end of Q2. NIO stated that its cash balance is insufficient to support ongoing operations for the next 12 months.
As the delivery process accelerates and the industry deepens, new carmakers face increasing challenges. As a bulk commodity, the demands on a company’s overall service capability are extremely high, as are the financial requirements.
However, according to published data, WM Motor delivered a total of 16,876 new cars in 2019, with annual deliveries of 16,810 for the EX5, ranking first among new car manufacturers in terms of single-vehicle annual deliveries.
Xpeng delivered a total of 16,608 cars in 2019, and Hozon Auto delivered a total of 10,006 cars in the same year, which can ease companies’ cash flow pressures to some extent, but large-scale deliveries also mean increased capital outflows.
New car manufacturers such as Byton, Skywell, and Qidian have not yet achieved deliveries, while Aiways and IDEAL achieved only about 1,000 deliveries by the end of the year, and the revenue from overall deliveries cannot support a positive cash inflow for the companies. Thus, although new car manufacturers have different cash reserves, they all face multiple pressures.
This is why NIO chose to disclose two new convertible bond financings totaling $200 million at this time, and more importantly, this financing can boost market confidence. For new car manufacturers that need more capital inflows, especially under the epidemic, the situation is even more serious.
How to Promote Delivery Plans When Future Financing is Challenging?The sudden outbreak of the epidemic has led to factory shutdowns, causing delays and setbacks in existing deliveries and marketing activities. The impact on the consumer end may be even more far-reaching, as conservative consumer sentiment further strengthens. Moreover, whether the new round of financing can arrive as scheduled after the epidemic will be the key to the life and death of new forces, and capital institutions will also re-evaluate the new energy vehicle market and adjust their investments, which is a potential risk for the next step of financing for new carmakers.
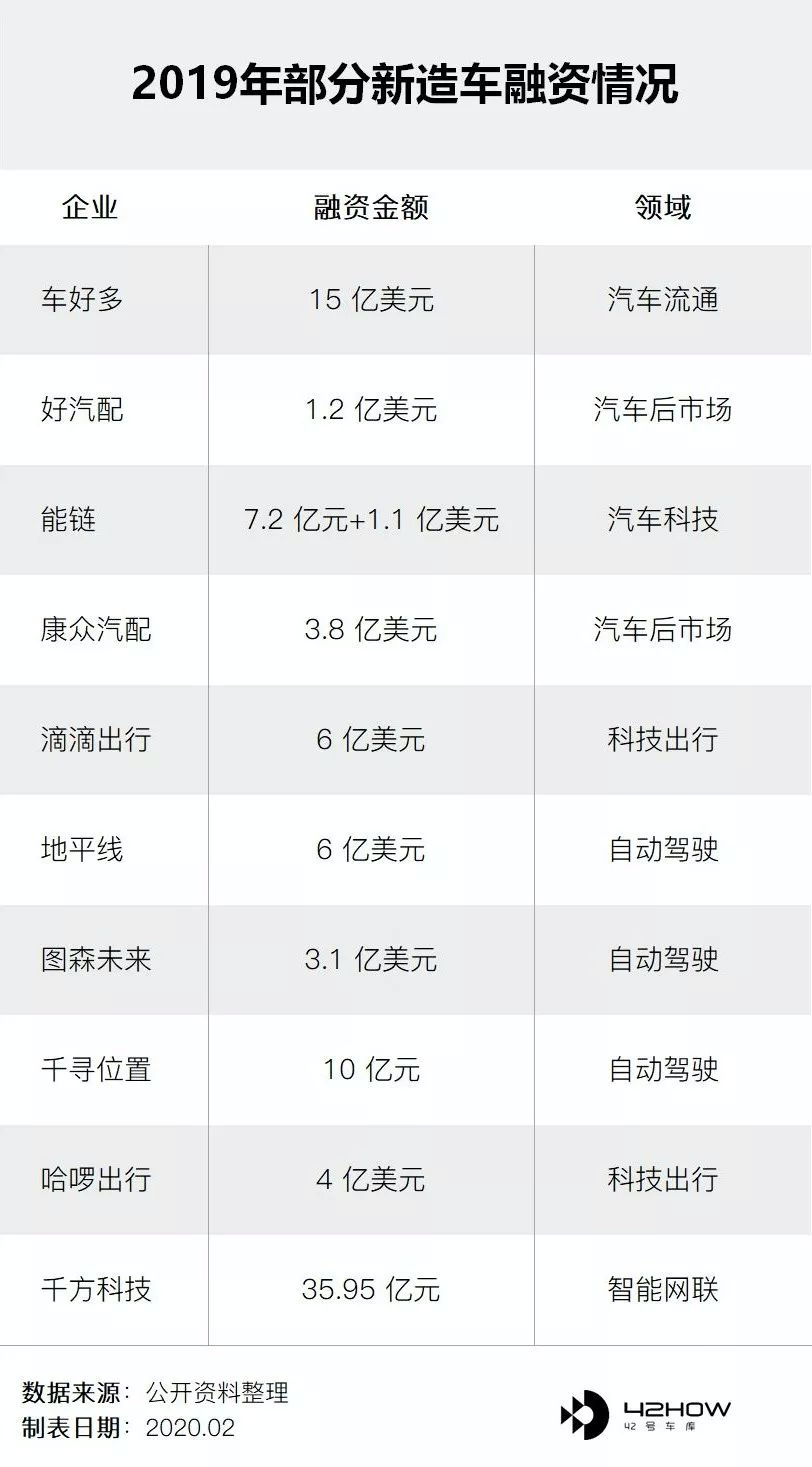
From the financing situation in the automotive industry in 2019, the proportion of the automotive industry chain is the largest, and the proportion of new forces as the main manufacturers is significantly higher. Therefore, the overall financing capability of new forces in 2020 will decrease unless there are unexpected factors.
For instance, Byton’s C-round financing has not yet been fully disbursed, and the original M-Byte production plan may be shelved due to the impact of the epidemic. The key is that the money is still being spent, but it is not known when the next round of financing will arrive.
Of course, there are also two camps in the new forces, one is the delivered and listed NIO, and the other is the new forces that have not yet delivered. It should be noted that for enterprises that have realized deliveries, the pressure of investment outflows based solely on financing funds can be alleviated, as revenue is the fundamental basis for enterprise development.
The patience of capital with new forces is decreasing, and some institutions predict that new carmakers will complete their reshuffle before 2025. However, based on the current situation, this time frame may be reduced. Stocking up for the winter will be an important measure in 2020, and new forces may collectively apply for IPOs.
How to withstand Tesla?
Tesla is a hurdle that every new carmaker must face, especially the domestically produced Tesla, which has further reduced its price. Faced with Tesla products that are of similar price to the new carmakers, how many consumers will stick to the new forces’ products?
In terms of products, Tesla has a relatively complete product layout. The Model 3 has been delivered domestically, and the other heavyweight model, Model Y, is scheduled for foreign delivery in March, and the domestic version is expected to be released in the second half of 2020.
Tesla has started accepting reservations for the Model Y model on its official website. The starting price for the long-endurance version is USD 52,990, equivalent to RMB 3.72 million (the Chinese official website price is RMB 4.88 million), and the starting price for the Performance version is USD 60,990, equivalent to RMB 4.28 million (the Chinese official website price is RMB 5.35 million).
Thus, Tesla’s products basically cover the price range of 300,000 to 1,000,000 RMB, forming a complementary relationship between sedans and SUVs.
Moreover, the most critical thing is that as Tesla’s volume models, these two models still have room for price reduction after the localization rate gradually increases. According to the research report on Tesla’s localized supply chain released by CICC previously, the production cost of domestically produced Model 3 is 20%-28% lower than that of the US version. With Tesla’s supply chain gradually achieving localization, there is 27%-34% room for price reduction in the future.
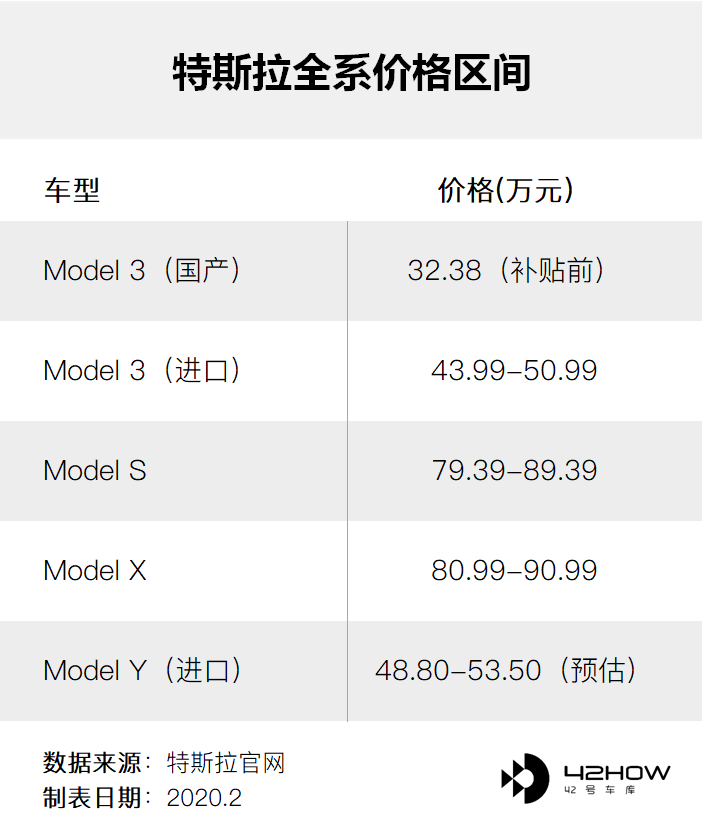
Even after the subsidy reduction, Tesla still has enough room for price reduction to cope with potential price competition in the market.
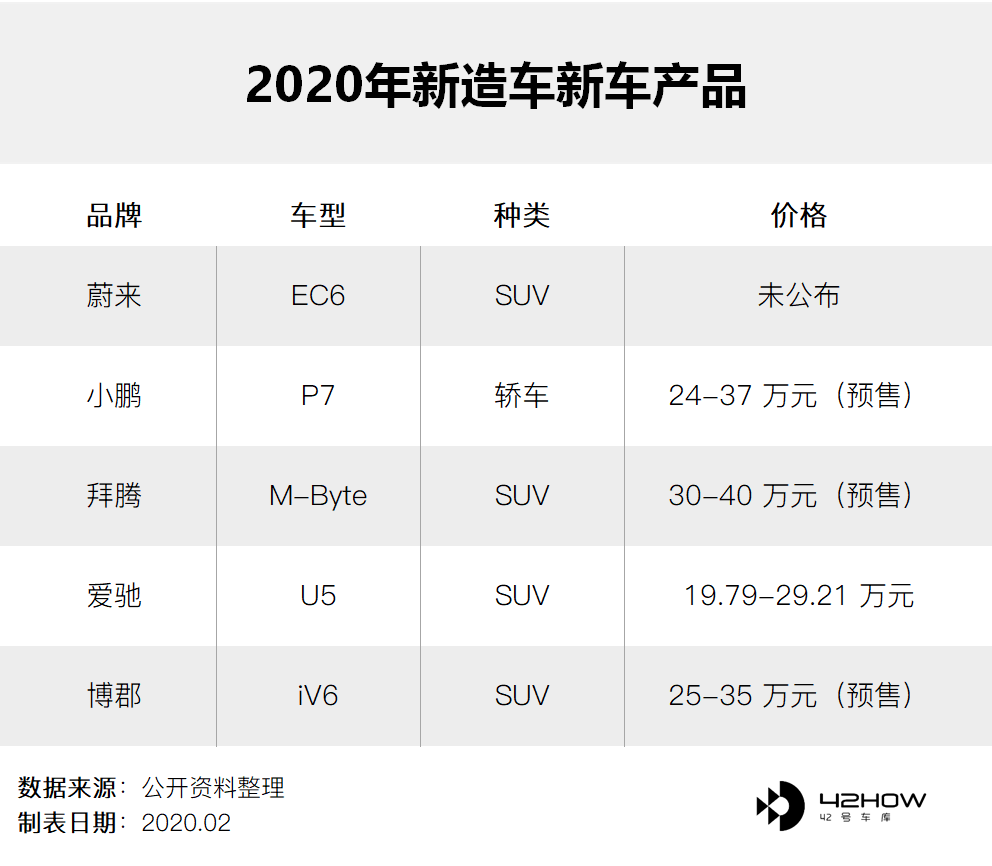
In contrast, NIO EC6 did not announce its price and is waiting for Tesla’s pricing strategy. And the prices of models such as Xpeng, Byton, Aiways, and Borgward, which will soon be produced and delivered, will fall within Tesla’s price range.
If the prices of Model S and Model X can allow new car manufacturers to find their own user groups through prices, positioning, and services, then when Tesla’s products are also sold at 300,000 yuan and are about to be less than 300,000 yuan, new car manufacturers obviously need to spend a greater price to convince those consumers who ask, “Why not buy Tesla for 300,000 yuan?”

In the latest batch of enterprise-declared models announced by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the “domestic long-endurance rear-wheel drive version of Model 3” is among them. From the 1745 kg curb weight and 202 kW motor power, it can be seen that this is the long-endurance rear-wheel drive version of Model 3 (the standard endurance upgrade version of Model 3 has a curb weight of 1614 kg).
The domestically produced version has a curb weight 8 kg lighter than the imported version, and the battery is a ternary lithium battery. It should use the 2170 battery cells supplied by Nanjing LG Chemical. The tail of the car is still a combination of “Tesla” + “Model 3”. Facing these, it is unlikely that anyone will believe that new forces are not nervous.
How to survive the joint venture with multinational enterprises“Fast” seems to be a knot for new car manufacturing. Faced with Tesla’s speed, transnational car companies are now investing heavily in electric vehicles. What chance do new car manufacturers have? In 2020, the electric vehicles invested in by joint venture brands will basically land in the Chinese market. At Volkswagen’s new brand night in 2019, Volkswagen officially stated that its first MEB-platform electric car will be put into production in 2020.
Audi China’s Executive Vice President Lu Yi stated: “By 2021, the number of new energy vehicle models will increase to 9, half of which will be pure electric.” Toyota’s TNGA architecture electric car will also be launched, and companies including General Motors, Honda, and Nissan have electric car products that may be launched.
However, as industrialization deepens, joint venture brands are strengthening the perfection of related services, technologies, and experiences, and if they can break through traditional brand thinking, the crisis for new car manufacturers will truly arrive. Because brand trust has a great impact on consumer behavior, when the “road rights” advantage of new energy vehicles from new players disappears, the brand trust of joint ventures may directly determine purchasing behavior.
Moreover, the risk of new car manufacturers being acquired has increased again. “Shortage of money” is the lifeblood of new car manufacturers, but traditional automakers have money. For new car manufacturers with a lack of funding but new technology reserves, strategic investment is likely to evolve into acquisitions.
The impact of the epidemic on demand is most directly reflected in sales. Small and medium-sized enterprises suffered heavy losses during the epidemic, and the income of frontline manufacturing workers was greatly affected. After the epidemic, as white-collar workers, they will certainly be cautious in spending money. This suggests that the sales decline may continue for a long period of time.
Summary:
The impact of the epidemic may even be more profound. The cruel reality is that new energy vehicle manufacturing must be faced. Relying on capital and support, can new car manufacturers support themselves in moving to the next stage? In comparison, streamlining the supply chain and reducing costs is a more core problem at present.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
