Recently, we had the opportunity to test drive a Cadillac CT6 equipped with Super Cruise on the Shanghai Ring Road, providing us with a comprehensive experience of the system. Since the vehicle was not an official one, we are unable to provide data from the manufacturer, but we will do our best to share our experience.
The Little-Known Super Cruise
As we enter 2019, competition in the field of assisted driving has intensified with numerous automakers showcasing their accomplishments in L2 assisted driving technology on their product launch PPTs. However, General Motors’ Super Cruise, which was officially unveiled in CES Asia 2018, has not achieved much recognition. Although those who have heard of Super Cruise may recall a promotional image of hands-free driving, it is generally unfamiliar due to high production costs. Super Cruise is only available on Cadillac CT6’s top-of-the-line model, the CT6 40T Platinum, priced at 699,900 RMB. This model, already a limited production of the Cadillac line, experiences even more limited distribution due to the additional expense. Consequently, few people have actually experienced Super Cruise. Another significant reason for its low profile is left to readers to ponder.
The Unique Route of Super Cruise
Super Cruiser deploys a totally different ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance System) from forward sensing cameras that surround cars. Here are two examples:
Tesla’s Autopilot: Autopilot utilizes forward camera to identify road lines and maintains the vehicle within the lane, while utilizing eight surrounding cameras to identify and detect vehicles and obstacles around.
Bosch’s System: Currently, a large number of automakers’ ADAS systems utilize Bosch’s solution, which similarly uses the forward camera to identify the road lines and keep the vehicle in the center of the road, but the difference is that the sensors that detect surrounding cars for Bosch use millimeter wave radar.
These two solutions have a high reliance on lane markings. Once the lane markings are unclear or missing, the assisted driving function will be disabled. The system’s algorithm determines how many unclear or missing markings are required to automatically exit, which is dependent on the manufacturer. This is the downside of camera-based recognition.
Cadillac’s Super Cruise, on the other hand, relies entirely on high-precision maps and high-precision positioning. In other words, wherever there are high-precision maps, this Super Cruise set can automatically keep the vehicle in the lane for assisted driving. If there are no high-precision maps, this ADAS system cannot achieve assisted driving. Obstacle detection around the vehicle and vehicle detection are still done using millimeter-wave radar.

Assisted Driving that Makes You Feel Safe, but with Limited Use
After understanding the general logic, let’s talk about the experience. Super Cruise is an automatic driving system for highways. The concept of a “highway” here can be understood as a relatively closed loop or expressway.
Since foreign manufacturers do not have the right to collect high-precision maps in China, General Motors uses high-precision maps provided by Amap. At present, high-precision maps cover most of the overpasses, loops, and expressways, but the coverage area is still very limited. Some sensitive areas cannot collect road curvature, so assisted driving cannot be achieved, such as the Nanpu Bridge in Shanghai.
Activating the Super Cruise system also has two conditions. First, it must be in a high-precision map coverage area, and second, it must be driving in the center of the lane and not riding along the center of two lanes.
Once these two conditions are met, a gray steering wheel logo will appear on the top right of the instrument panel.
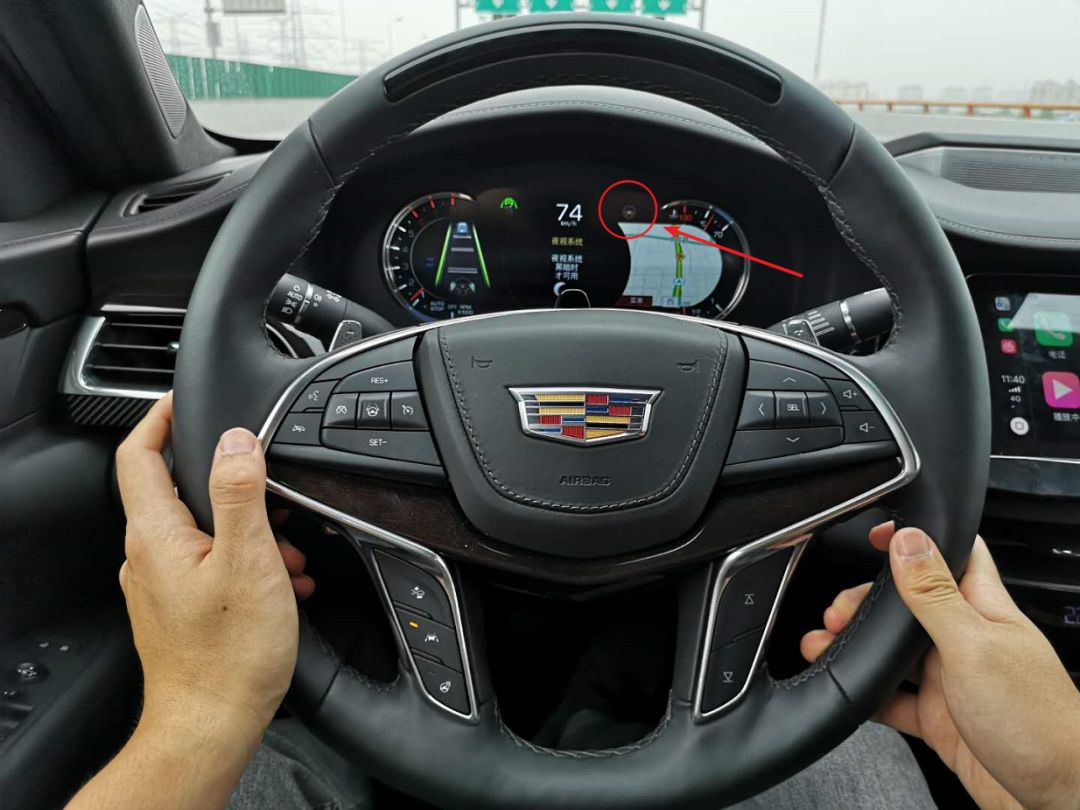

After pressing the button in the middle left of the steering wheel, the Super Cruise can enter the state.
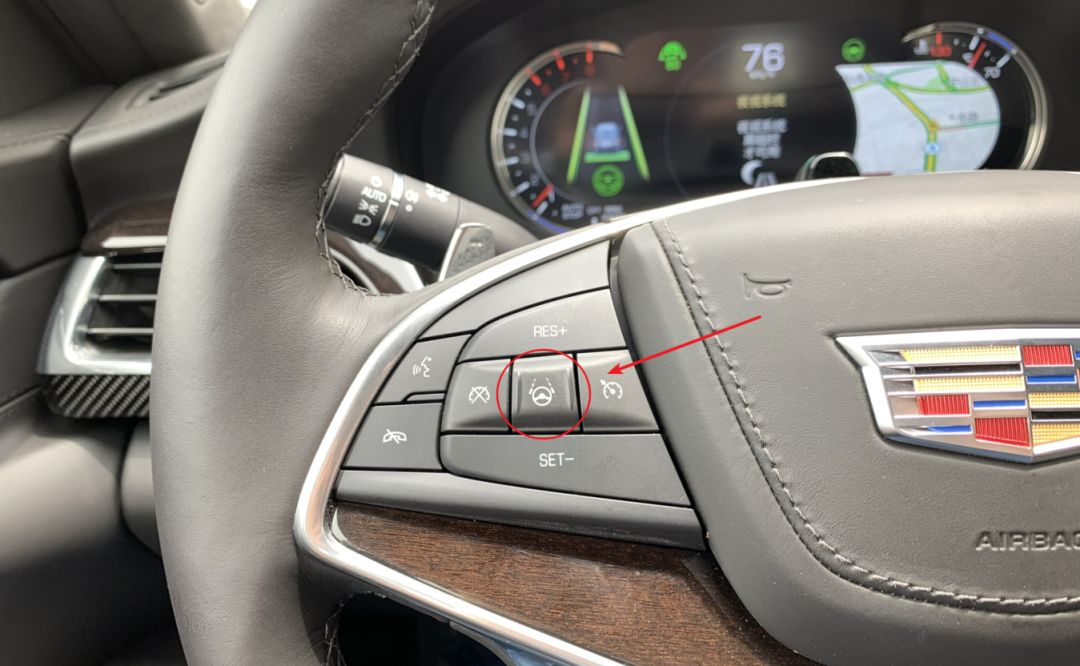

After entering Super Cruise mode, the gray logo on the instrument panel will turn green, and the indicator light immediately above the steering wheel will turn green as well. At this point, the vehicle takes over acceleration, braking, and steering.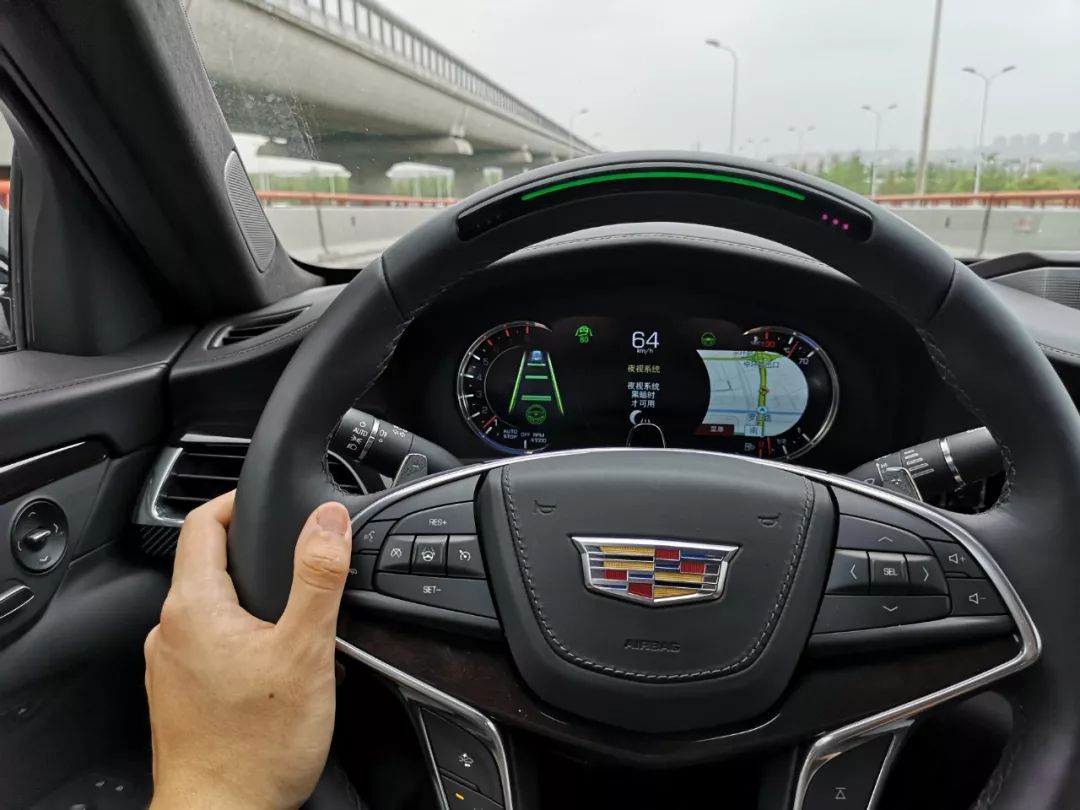
Unlike other advanced driver-assistance systems, Super Cruise uses an infrared camera above the steering wheel to detect the driver’s visual direction and eye status to judge whether there is any distraction, instead of detecting whether the driver’s hands are on the steering wheel by setting a torque sensor on the steering wheel to judge whether there is any distraction.

When my gaze is away from the front for more than 5 seconds, the system will remind me to take over the steering wheel by flashing the indicator above the steering wheel. If I continue to look forward, the system will automatically return to Super Cruise mode.
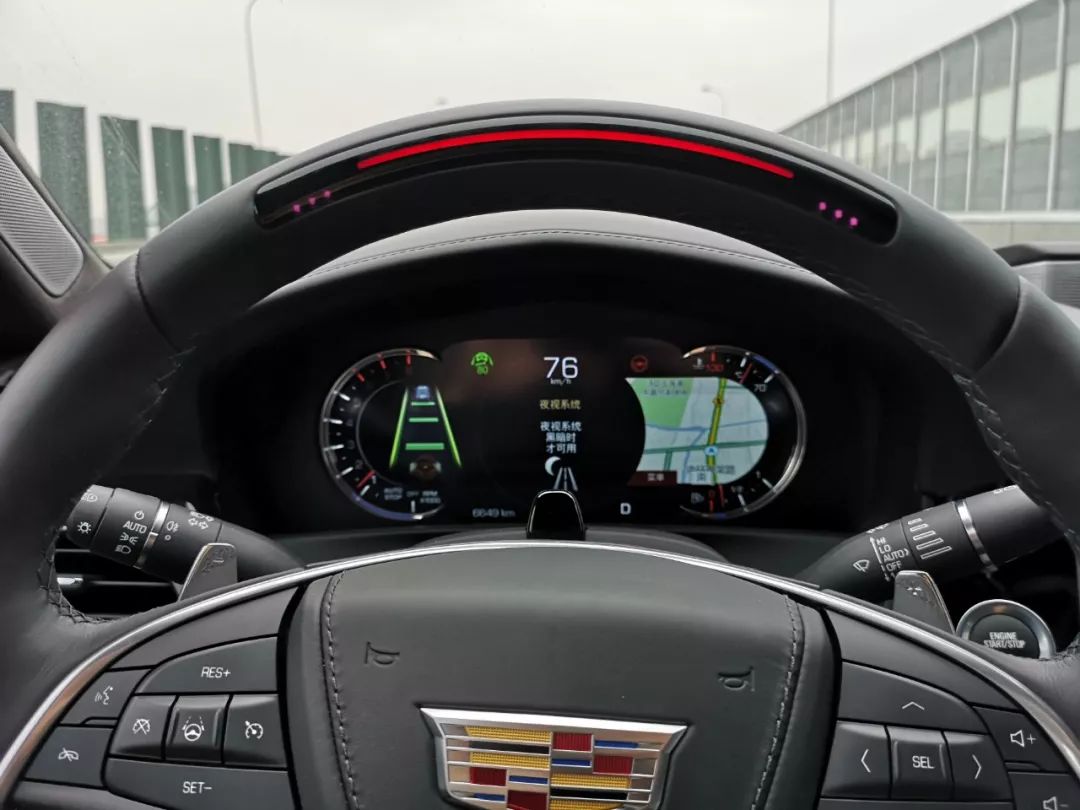

If I still don’t look ahead, the indicator on the steering wheel will blink red and the seat will vibrate. At this point, I need to take control of the vehicle. After taking over, Super Cruise will automatically exit and need to be re-enabled (ACC still works).
If I still don’t take over, the system will judge that the driver may have passed out, and the vehicle will automatically slow down and alert the OnStar system.
What if I want to change lanes while driving?
Super Cruise does not support automatic lane change. To change lanes, the driver does not need to exit the cruise function. The driver can simply take control and turn the steering wheel to change lanes. During the lane change process, the indicator on the steering wheel will turn blue. After staying in the center of the lane for a short while, Super Cruise will resume control and the indicator will turn green.
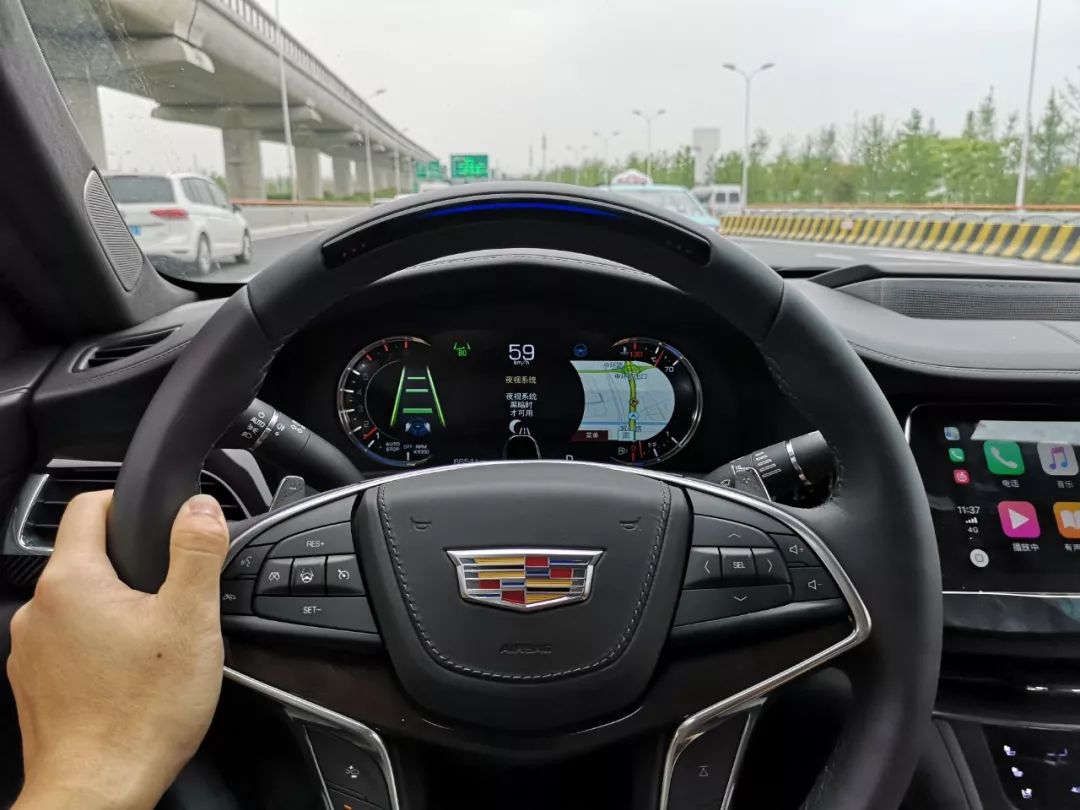

This is also different from Tesla Autopilot. When AP is in control, if the driver wants to turn the steering wheel, they need to overcome a certain amount of force, which creates a feeling of “competing” with AP. If the driver wins, AP will exit. There is no such feeling with Super Cruise. When turning the wheel, only a very small resistance needs to be overcome, which can be ignored.
Does it affect driving in traffic?As long as you are in the coverage area of high-precision maps, Super Cruise can intervene regardless of the speed.
Can I rely on Super Cruise to finish driving on the entire high-speed road covered by high-precision maps?
The answer is no. Although the high-precision map covers the entire high-speed road, the system will remind the driver to take over the vehicle when approaching the ramp because the road conditions near the ramp will be much more complicated and there is no high-precision map coverage in the ramp. Therefore, the use of Super Cruise is still very limited.
How does the automatic steering feel? Linear!
It is more linear than Autopilot, and much more linear than Bosch’s system, especially in larger turns. The linearity comes from its assisted steering logic. Because Super Cruise relies completely on high-precision maps, the system knows whether there is a turn and what the turning angle is. It can calculate the required steering angle based on the known information and high-precision positioning. Therefore, it can be very linear.
Reliance on visual recognition will always be a passive adjustment. The recognition of the turn, calculation of the required turning angle, and execution all occur in the process of turning. Therefore, the driver might feel like they need to constantly adjust the direction. To achieve a linear feeling, excellent algorithms are required.
How about acceleration and deceleration control?
The core steering has been discussed. The remaining function is actually the full-speed range ACC function, which detects surrounding vehicles using five millimeter-wave radars around the vehicle.
The acceleration and deceleration control under the following status is comfortable enough, but occasionally when someone cuts in, the system may have a strong braking operation. There are three adjustable distance settings, which maintain a relatively large following distance.
Super Cruise is worth looking forward to
To summarize, Super Cruise provides me with a very strong sense of safety in its working state. This sense of safety comes from its limited usage scenarios, which do not involve too many system decisions or uncertainties. The system has already memorized all the information regarding turns. Once it reaches the ramp or an area without high-precision map coverage, the system will prompt me to take over.
The disadvantages are also very obvious. The usage range is too limited, which is also the difference between China and the United States. American highways are often dozens of kilometers or even longer straight roads, so there are still many scenarios where Super Cruise can be used, while the road conditions in China are much more complex.I hope that in the future, Super Cruise can make more optimizations for the Chinese market. At the same time, by utilizing the hardware sensing devices on the vehicle layout and cooperating with high-precision maps, Super Cruise can be achieved even in areas without high-precision map coverage, expanding the usage scenarios of Super Cruise.
Furthermore, I hope that GM can quickly lower the cost of Super Cruise and deploy this function to more mid-to-low-end Cadillac models, so that more Cadillac users can experience the convenience brought by Super Cruise.
Lastly, there is a fatal problem with Super Cruise on this vehicle. It cannot be updated over-the-air (OTA), meaning that it cannot continue to evolve and update in this rapidly developing era. Without continuous updates, it will soon be surpassed by its competitors.
Tesla’s Autopilot Chip Production: A Well-planned Attack
In-depth Analysis: Tesla’s Autopilot and Self-driving Architecture vs. Systems Based on Lidar


This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
