Introduction
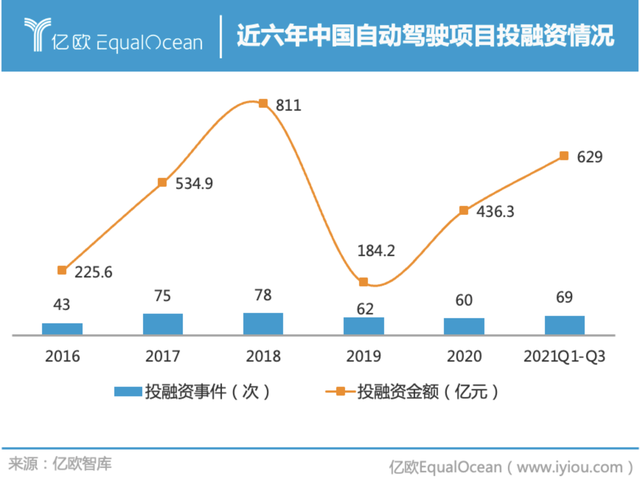
In 2021, the autonomous driving industry as a whole has experienced a financing boom. After the downturn in 2019, the industry has started to recover. By the third quarter of 2021, there have been 69 financing events in the field of autonomous driving, with a total investment of 62.9 billion yuan. According to the prediction of EO Intelligence, the financing amount of autonomous driving projects is expected to surpass the new investment peak of 81.1 billion yuan in 2018 this year.
Li Kaifu, Chairman and CEO of Innovation Works, once said that under the catalysis of the COVID-19 pandemic, the deployment of autonomous driving has accelerated. It can create value not only in scenarios such as autonomous driving taxis, autonomous driving trucks, and unmanned handling in factories or warehouses.
The key to helping the Autonomous Driving industry to emerge from the downturn and rebound is twofold. Firstly, investors have realized the difficulty of the industry and given more opportunities and patience. Secondly, self-driving companies have gradually reached a consensus and seized their areas of expertise by starting with specific scenarios. Autonomous driving, which has found the right scenarios, has finally experienced explosive growth this year. In this article, the author will discuss the top companies in the Autonomous Driving industry from five major mainstream application scenarios to observe their technical paths in 2021 and prospects in 2022.
Unmanned Delivery
For the unmanned delivery scenario, it should be one of the scenarios with the lowest landing difficulty and higher profit potential at present. Representative enterprises in this area include Meituan, Alibaba’s Cainiao, and JD.com, all of which are companies that are closely related to their own businesses. On the other hand, these internet companies have a unique and leading understanding of autonomous driving technology. For them, connecting low-speed unmanned driving in closed scenarios in parks is not difficult. Moreover, the prospects for unmanned delivery are very broad. According to the research report on the terminal unmanned distribution track by Chengtao Capital, the terminal delivery market size in China will exceed RMB 300 billion in 2021. Facing such an attractive market, Internet giants will certainly not miss the opportunity. From Meituan’s Magic Bag 20, Alibaba’s Xiaomanlv, to JD.com’s fourth-generation unmanned delivery vehicle, enterprises have launched their most proud unmanned delivery products and achieved commercial landings in closed parks.
 In the future, the use of autonomous driving technology in the logistics industry, including unmanned delivery, loading and unloading, transportation, warehousing, and shipping, will gradually become unmanned and mechanized. This will promote the entire logistics and distribution industry to reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve. Safety officers can remotely monitor the real-time status and surrounding environment of vehicles on a daily basis, reducing labor costs. When a vehicle has an abnormal status or malfunction, safety officers can assist in decision-making and processing through remote monitoring functions, such as restoring the vehicle to autonomous driving mode or switching to remote driving mode.
In the future, the use of autonomous driving technology in the logistics industry, including unmanned delivery, loading and unloading, transportation, warehousing, and shipping, will gradually become unmanned and mechanized. This will promote the entire logistics and distribution industry to reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve. Safety officers can remotely monitor the real-time status and surrounding environment of vehicles on a daily basis, reducing labor costs. When a vehicle has an abnormal status or malfunction, safety officers can assist in decision-making and processing through remote monitoring functions, such as restoring the vehicle to autonomous driving mode or switching to remote driving mode.
As one of the most promising scenarios for autonomous driving to land and achieve profitability, unmanned delivery has undoubtedly attracted great market attention. With the gradual relaxation of subsequent policies and regulations, we can also see unmanned delivery vehicles on public roads in the future, which will greatly facilitate our daily lives.
RoboBus
For public transportation, fixed routes, slow speeds, and dedicated lanes make it a natural landing scenario for autonomous driving. Robobus can not only help alleviate traffic pressure on main roads but also flexibly respond to emergencies by detecting pedestrians and vehicles, slowing down, emergency stopping, avoiding obstacles, changing lanes, and automatic station stopping.
Currently, autonomous driving companies, including Baidu, EHang, and Volcanic Islands, have a rich layout for this scenario. On February 27, 2021, Volcanic Islands’ Dragon Boat ONE increased peak period capacity on Q1 Road of Suzhou Robo-Bus to cover peak travel; In August of this year, Baidu Apollo Ⅱ was officially launched, and the new car has made further improvements in computing power, sensor configuration, redundant safety (vehicle-road collaboration + 5G cloud driving), cockpit interaction, etc. The Operational Design Domain (ODD) has also expanded from a closed or semi-closed park to an open road, allowing it to safely cope with complex traffic scenarios on open urban roads such as unprotected left turns, traffic flow selection to change lanes, and intersection crossings. The unmanned driving microcycle minibus jointly developed by EHang and Yutong also went offline in batches in April this year and is currently undergoing routine testing in Guangzhou, Nanjing, Zhengzhou, and other places.
In the near future, more and more cities will see the appearance of Robobuses and autonomous driving will usher in reality. According to relevant data, as various places have expressed their intentions to promote autonomous driving buses, by 2022, the number of unmanned bus lines in China will exceed 60, with 300 boarding and alighting stations and a total length of 300 kilometers, bringing transformative change to public transportation.
Port Scene
For autonomous driving technology, port autonomous driving is a typical closed and low-speed operation scene. Autonomous driving container trucks with speeds below 30 km/h can travel between cranes and yards and are responsible for transporting containers. For ports, autonomous driving can also achieve automated horizontal transportation of existing containers through economically feasible solutions, effectively solving problems such as imprecise driving routes, blind spots in turning sightlines, and driver fatigue driving during traditional manual driving, making it an ideal cost-reducing and efficiency-increasing technology.
Currently, the main ports in China with implemented autonomous driving projects include Shanghai Port, Qingdao Port, Tianjin Port, Ningbo-Zhoushan Port, and other companies participating in autonomous driving application projects. On the one hand, there are port autonomous driving companies that have emerged in China in recent years, including Westwell Technology, ControlWorks, etc. On the other hand, automotive industry companies such as SAIC Motor, FAW Group, Sany Heavy Industry are also actively deploying.

In the future, thanks to the sharing of hardware such as commercial vehicle chassis by the two parties, the engineering standardization of port autonomous driving can also be shared. Port autonomous driving is expected to extend to long-haul logistics with point-to-face, and scaled commercial operation can quickly accumulate and iterate algorithm capabilities, engineering capabilities, operational capabilities, and commercial capabilities, and extend to the outside container trucks and long-haul logistics.
Long-haul Logistics
Long-haul logistics refers to the logistics operation process of transportation, receiving, warehousing, and delivery utilizing unmanned driving. Long-haul logistics can achieve point-to-point transportation of goods, with a travel speed of up to 80-120 km/h, and China will lay smart roads specifically for it. Such a high travel speed is due to the fact that in long-haul logistics scenarios, the running routes of motor vehicles and non-motorized vehicles are segregated, which can reduce the perception and decision-making difficulties of autonomous driving vehicles. Therefore, this scenario has become a battleground for major enterprises, especially e-commerce express companies, since the beginning of the autonomous driving industry.
This year, long-haul logistics is undergoing the development route of evolution from L2/L3 to L4/L5. In this development route, L3-level autonomous driving has already begun to create commercial value in the field of long-haul logistics. FAW Jiefang, Dongfeng Commercial Vehicle, China National Heavy Duty Truck all released L4-level unmanned electric truck trial operation landing in April 2018. The 5 unmanned container truck fleet of TuSimple also officially entered the commercial trial operation stage at the same time. Since then, e-commerce companies such as Suning, JD.com, etc. have successively announced the completion of unmanned driving logistics operation tests and commercial deployment trials. Internet companies such as Baidu, Meituan have also launched unmanned driving logistics and delivery vehicles.
 In the future, thanks to the rapid development in China’s logistics and express delivery industry, unmanned vehicle delivery in trunk logistics will attract more attention from the market. At the same time, the evolution of policies and regulations for high-speed public roads will affect the progress and trend of relevant companies in the future by setting restrictions on unmanned delivery in high-speed logistics.
In the future, thanks to the rapid development in China’s logistics and express delivery industry, unmanned vehicle delivery in trunk logistics will attract more attention from the market. At the same time, the evolution of policies and regulations for high-speed public roads will affect the progress and trend of relevant companies in the future by setting restrictions on unmanned delivery in high-speed logistics.
RoboTaxi
When it comes to autonomous driving, the ultimate goal, RoboTaxi, cannot be ignored. Unlike other application scenarios, RoboTaxi faces the most complex road conditions, high speed, and the highest safety requirements. As the ultimate test for autonomous driving, whoever can achieve the normalization of RoboTaxi operations first will firmly establish themselves as China’s leader in autonomous driving.
In this regard, Baidu, China’s autonomous driving industry leader, and Pony.ai, the representative of the new generation of autonomous driving, are at the top of the industry. Beijing granted licenses to these two companies at the end of the year, making them the first companies authorized to operate RoboTaxi businesses within a fixed range in Beijing, which shows their position in China’s autonomous driving industry. As the first companies to enter the field of autonomous driving in China, Baidu’s investment in RoboTaxi is undoubtedly huge. This year, Baidu has created an “automaker-government-technology company” model in Changsha — Changsha providing 45 testing licenses for the Apollo Go project, thereby forming an intelligent driving ecosystem in the area, FAW Red Flag providing RoboTaxi pre-installed production lines, and Baidu Apollo providing autonomous driving and vehicle-road collaborative software and hardware systems.

However, for RoboTaxi, which still requires safety personnel to help avoid driving risks, the cost of both personnel and vehicles is high, which makes large-scale vehicle deployment difficult for all companies that enter the RoboTaxi field. But even so, there remain companies willing to make effort to continuously advance China’s autonomous driving technology. We must give enough respect to these companies solely for this point.
Summary
In 2021, when autonomous driving revives, enterprises taking the route to break through the bottleneck of autonomous driving technology with the approach of scenario fragmentation seem to be on the right track. Although the day when autonomous driving technology can bring us surprises like in the movies may be far away, it cannot be denied that there will be more autonomous driving vehicles entering our daily lives in the future, bringing convenience to our travel, shopping, and daily routines. This requires us to have more trust and patience for the industry as a whole, while autonomous driving companies need to follow relevant laws and regulations and prioritize safety at all times. Only when both sides complement each other can we promote the further development of the industry in the future.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
