Ten years ago, online shopping wasn’t as popular as it is now, and many users were switching from QQ to WeChat for online chatting. Short videos and food delivery platforms were still in the conceptual stage and had not yet become products.
Meanwhile, Baidu, founded as a search engine company, chose to look to the future and fully embrace the autonomous driving industry. Baidu’s goal as a technology company was to achieve full autonomous driving in one fell swoop. Therefore, Baidu purchased a batch of BMWs and installed a series of sensors around their bodies for testing and training on public roads. This can be called Baidu’s first Robotaxi.
Today, after nearly a decade of laying the foundation for autonomous driving, Baidu is recognized as a talent incubator for autonomous driving in the industry. As a company that aimed to explore the uncharted territory of autonomous driving before the establishment of the new competitive powers, Baidu’s strong foresight cannot be overlooked.
At the 10-year milestone of Baidu’s autonomous driving business, Apollo has entered a new phase of competition.
What Everyone Was Talking About This Year
At this time last year, new competitive powers were vigorously negotiating with lidar suppliers. XPeng set its sights on Livox, while NIO chose Tusimple, in which it had invested.

In the view of new competitive powers, lidar can act as a redundant sensor, playing a complementary role while also increasing the “coolness” of the vehicle. Moreover, the cost of lidar has already been reduced, so why not do it?
As a result, XPILOT 3.5 followed closely behind, and as the flagship, the NIO ET7 shone with a dazzling light. After this wave of publicity, user expectations were raised, and so we call 2021 the year of autonomous driving.
But the reality is that the development speed cannot keep up, and it’s all empty talk. Even calling 2021 the year of lidar would be a stretch, let alone the year of autonomous driving; because if we count, there was only one vehicle delivered this year equipped with lidar — the XPeng P5, and its lidar has not yet been put into use.
Looking back at the whole year, what really surprised and impressed me were only three companies: Tesla, Huawei, and Baidu.
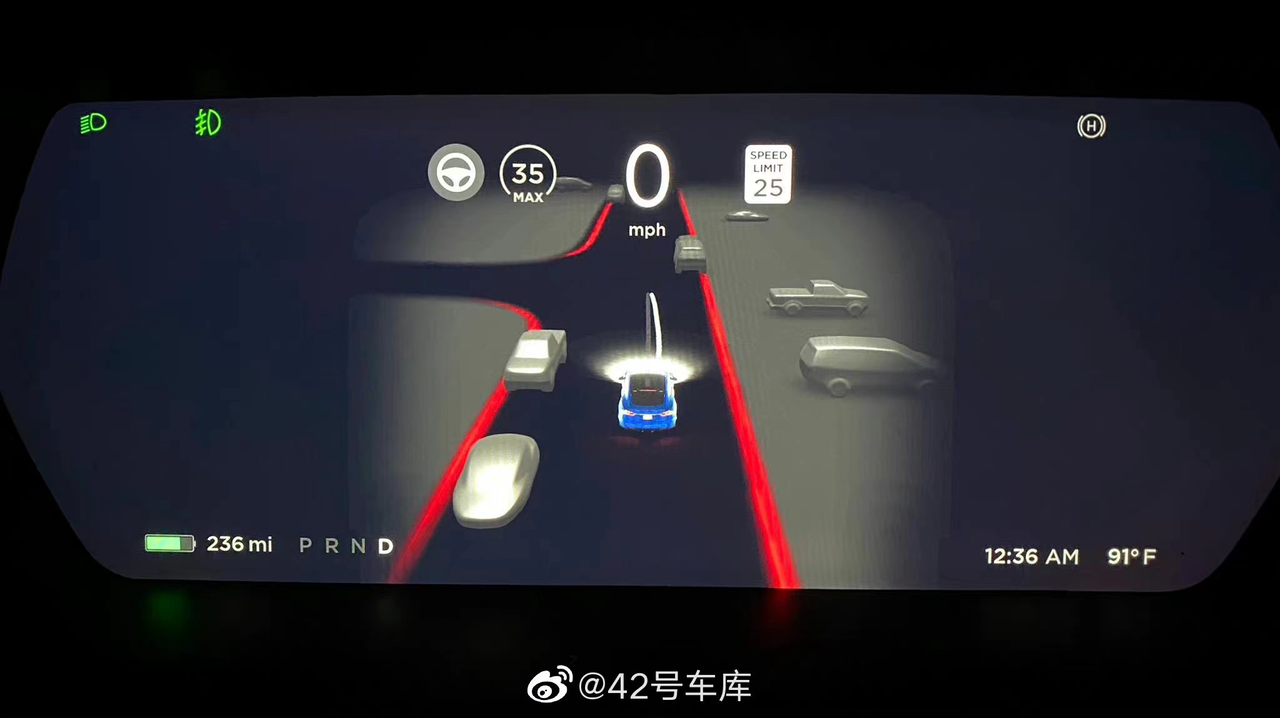
Tesla pushed FSD Beta in North America, and the v10.1 version launched public beta testing. In the United States, Tesla’s FSD Beta had basic L4 level urban autonomous driving capabilities, and after rewriting all the underlying code, Tesla demonstrated their powerful AI capabilities.However, in China, FSD Beta seems to be a distant dream, and Tesla’s NoA navigation-assisted driving strategy in enclosed scenarios has yet to be resolved. Without solving these tricky localization issues, Tesla’s core competitiveness is difficult to break through the bottleneck.
In April of this year, Huawei held a dedicated event in Shanghai, where Huawei ADS demonstrated its abilities in specific scenarios, exceeding everyone’s expectations. However, since then, Huawei has not produced any other road test videos for other segments, leading to doubts and criticism.
Another technology company that competes with the above-mentioned companies is Baidu. Many people compare Baidu and Google since both are technology companies and both have been involved in the autonomous driving industry for a long time. While Google has invested billions of dollars annually for many years, they have not been able to achieve substantial results. Therefore, Baidu’s main competitive issues are localization advantages, scene generalization capabilities, and commercialization.
Although Baidu has made many products over the past few decades, it has paid significant amounts of tuition fees. Ultimately, when differences arose, Baidu chose to pursue a strategy of parallel development with multiple solutions.
What has Baidu done?
This year is crucial for Baidu, whether in the research and development of autonomous driving or in entering the field of car-making.
By 2023, the Company’s JD Plan will be in mass production and delivery, while intelligent driving software is being concurrently developed. No other new entrant or batch of automotive players can match the speed of JD Plan entry.
In the field of unmanned vehicles, Baidu officially launched the fifth-generation Robotaxi, and also released the ARCFOXxing, WM Version, and Guangqi Aion versions. Additionally, Apollo has reduced the cost of Robotaxi to an unprecedented 480,000 yuan, which is almost equivalent to the cost of a human ride-hailing driver when in daily use.
Moreover, Apollo has achieved routine operations of unmanned vehicles, 5G cloud co-driving fully scaled landing, Apollo Moon’s mass production officially launched and put into operation, and has been granted approval to start a paid riding Robotaxi commercial model.
An essential point not to be ignored here is that Apollo’s Robotaxi has achieved commercialization with full autonomy in limited areas, making it the only autonomous Robotaxi with a full-autonomy main driving system in commercial operation currently.
This move not only demonstrates Apollo’s confidence in its abilities but also reveals the government’s recognition of Apollo. This is an important step in the history of Robotaxi development because only by being fearless and autonomous can Robotaxi realize its true value.It is regrettable that the commercial operation of unmanned driving currently only limits to the SG Park area, which has a relatively small range. Moreover, the distance that can be experienced on-site during our actual experience is also relatively short. But as the saying goes, a journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step.
Standing at the subtle time node of 2021, the competition of autonomous driving has shifted from technical accumulation to product competition. Although Baidu has made significant breakthroughs in unmanned vehicles, it is not enough to expand the volume quickly solely relying on the Jidu and unmanned vehicles driving in a limited area.
Baidu will speed up the landing of ANP (Autonomous Navigation Platform) in the next few years. The ANP architecture is downsized by the only L4-level pure visual unmanned driving technology Apollo Lite in China. With the independent ANP base, adding only one customized LiDAR and corresponding hardware can enable the vehicle with the ability of advanced level assisted driving.
Apollo Lite is a pure visual system of light perception equipment, but it also has high customizability. Customers can add other hardware based on their own needs based on this perception foundation. Robotaxi has been a key focus of Baidu’s efforts for decades, and ANP becomes a product to enable vehicle companies by combining the two.
Technical downsizing data feedback
It is obviously unrealistic to directly transplant the Robotaxi system to civilian vehicles if you want to provide a packaging plan for vehicle companies. Baidu’s first step is to cut down on hardware. When Apollo Lite was first born, Baidu hoped to reduce reliance on LiDAR. To achieve L4 in urban areas, it is possible to achieve it with 12 cameras covering a 360-degree perception range.
The second step is the architecture shift. Robotaxi adopts X86 architecture, which is difficult to meet the vehicle regulation level requirements of civilian cars. Therefore, Baidu shifted the architecture to ARM. After the architecture shift, computing power is directly reduced by half. Baidu must improve the visual perception model while reducing computing power and delay to ensure model accuracy.
The last point is that depending on high-precision maps on closed roads is feasible. However, it is not realistic to rely on high-precision maps for open urban roads. ANP must reduce the demand for high-precision map elements while maintaining precision and freshness at the same time.
In the autonomous driving competition where data is king, Baidu has a innate advantage. As of this month, Baidu’s real-world road tests have reached 21 million kilometers, and these data can help feedback ANP to eliminate more corner cases and maintain long-term progress.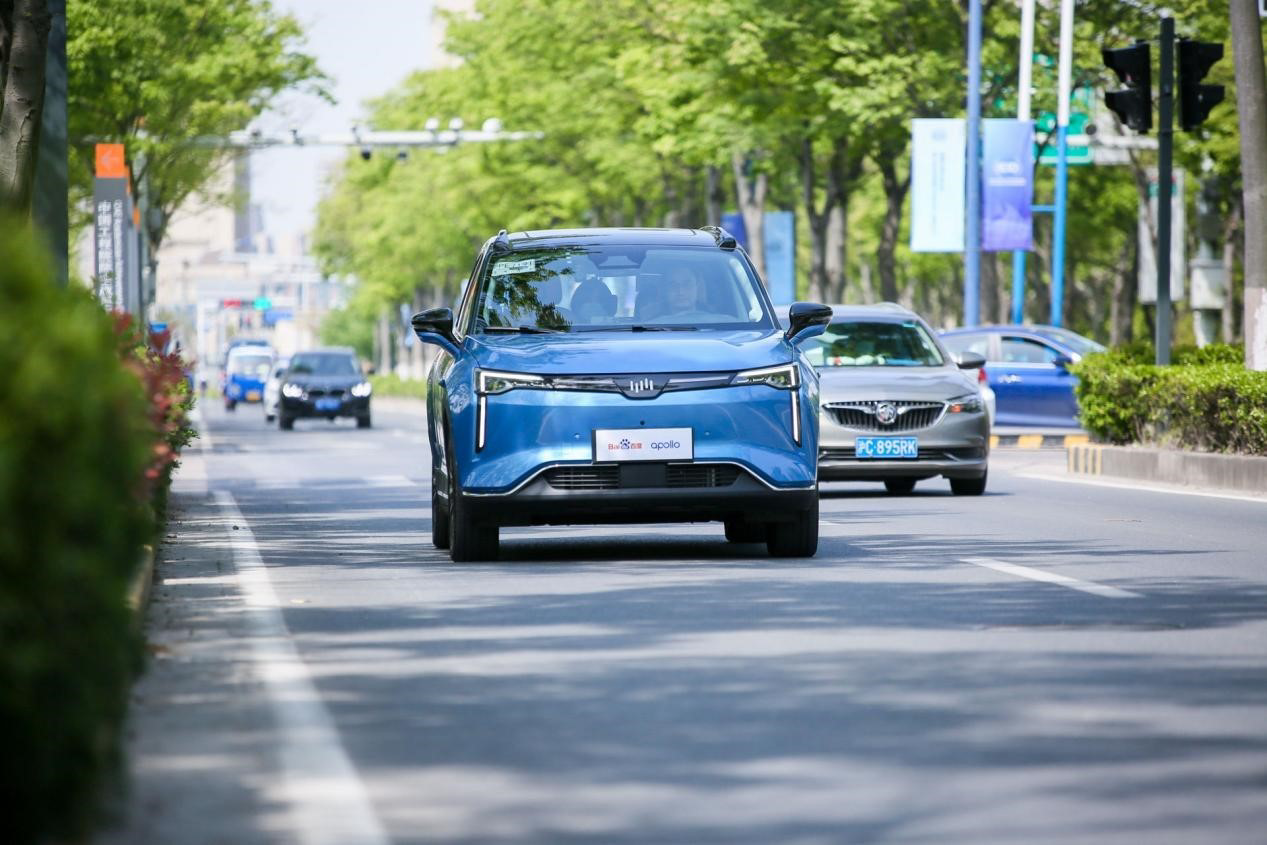
Previously, we thought that Baidu Apollo was the Chinese equivalent of Waymo, but now it seems that the diversified development of Baidu Apollo resembles a localized combination of Mobileye and Waymo.
Competition Upgraded
Regarding Robotaxi, Baidu’s newest generation of self-driving car, Apollo Moon, not only reduces the costs to 480,000 yuan, but also launched three new models in succession. This breakthrough price point of 480,000 yuan is crucial for commercial mass production in the future because Robotaxi was previously considered too expensive, and now Baidu has lowered the price to be on par with civilian vehicles.
The three new models lay the groundwork for future large-scale commercialization, offering more vehicle options for consumers.
In addition, government support is also an important driving force for the commercialization of Robotaxi. While each company has launched their “demonstration operation with passengers” and “unmanned testing”, Baidu’s larger number of testing licenses demonstrates comprehensive advantages in technology, products, and operational capabilities.
Looking Back at Baidu’s Ten Years
Ten years ago, self-driving technology was not yet popular in China, and was considered remote by many. Among BAT (Baidu, Alibaba, Tencent) technology companies, only Baidu chose to enter the AI self-driving field. Nowadays, this decision is seen as very courageous.
However, self-driving technology is not something that can be done just with money and determination. Even Waymo could not overcome all obstacles after decades of research and development to achieve full self-driving.
Valuable products will continue to dynamically adjust with the advancement of technology, and the commercialization of products depends on the development of the industry. There wouldn’t be the current prevalence of short videos without 4G or the smart home industry without the IoT.
Over the past decade, Baidu has continuously explored and ultimately confirmed its development path, even entering the car manufacturing industry itself. This is all due to considering its market position and its own strategic goals.
Therefore, for Baidu, the past decade was just the beginning, and the present competition is in the form of advanced driver assistance systems and Robotaxi services that serve the general public. Now, Baidu Apollo enters a new era of competition.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
