Translation in English:
Article length: 1,445 words
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
Future Tesla is a company that engages in vertical integration in car manufacturing, energy production and charging network, and travel technology.
Continuing from the previous article, let’s talk about why Tesla is a vertically integrated car manufacturing company and its value.
Recently, it was reported that the production capacity of the Shanghai super factory has increased continuously to a level of 14,000 vehicles per week, which means an annual production capacity of 700,000 vehicles. What does this mean? The production capacity of Tesla’s headquarter Fremont factory in the United States is approximately 10,000 vehicles per week. The production capacity of the Shanghai super factory has reached 140% of that of the Fremont factory, with almost the same area enclosed in the red box for comparison purposes. Hats off to the Tesla team and to Chinese manufacturing.

The upcoming factories that are marked with asterisks in the figure are the Texas super factory in the United States and the Berlin super factory in Germany, both of which are much larger than the Shanghai super factory.
Currently, Tesla is in the stage where demand exceeds production capacity, and delivery time for cars is 6-10 months in North America, 2-3 months in China, 3-4 months in most parts of Europe, and 3 months in most parts of the Asia-Pacific region, according to daily observations and data analysis.
Moreover, globally, the new energy vehicle penetration rate is in the fast-rising stage of early adopters, and is expected to enter the early majority stage as a whole within the next two years.
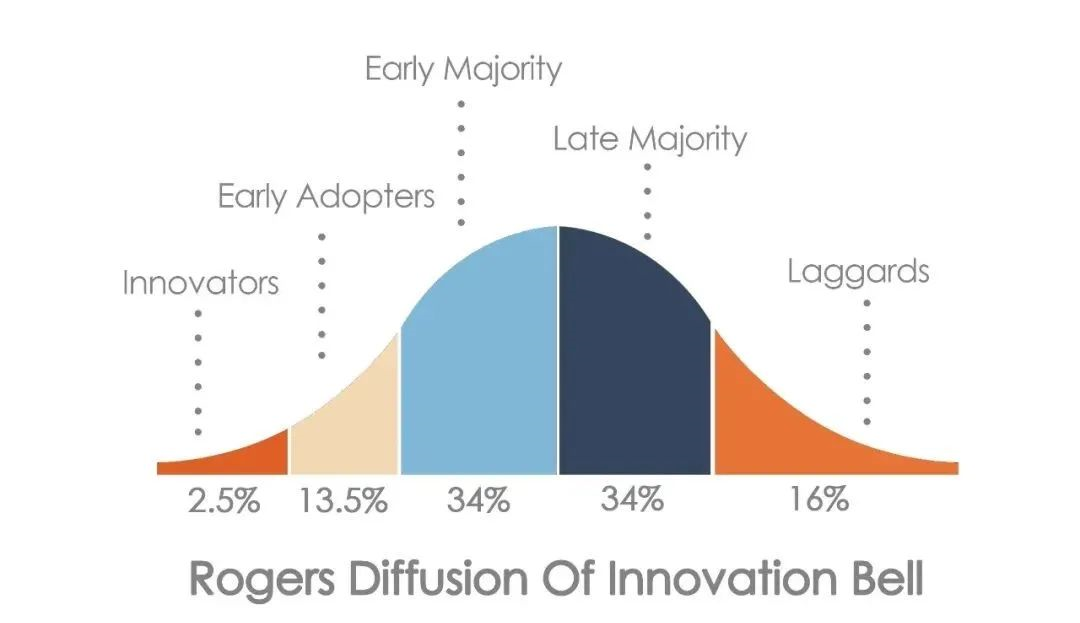
To break it down, the main players in global electrification are North America, China, and Europe, with essentially an equal share of the market. Europe has the highest level of electrification and has already entered the early majority stage, China is next but is also crossing the boundary between early adopters and early majority, while the United States has just entered the early majority stage and is rapidly improving.In the next few years, the demand for new energy vehicles in China and North America will be stronger than in the past few years. Demand from Europe will remain at current levels with slight growth until the overall penetration rate reaches the Late Majority stage, then it will slow down.
The three major players in the world are experiencing rapid growth, growth, and slow growth, respectively. Therefore, combining them means that demand for new energy vehicles will show a high-speed growth trend in the next few years. Therefore, the currently booming new energy market is actually still in a relatively early stage, which means that there is still a lot of room for growth in the future.
Now, back to Tesla’s production capacity. Going around such a big circle is just to explain that Tesla is already facing a supply shortage. In this high-speed development situation in the future, the situation of supply shortage will continue.
Therefore, we will use demand as the basis for a quantitative measurement to see the value of Tesla as a vertically integrated car manufacturer.
Tesla sold 360,000 cars in 2019, 500,000 cars in 2020, and is expected to sell 900,000 cars in 2021, with a compound annual growth rate of about 35% for three years. According to this compound growth rate, the annual sales volume after 10 years (2031) is approximately 18 million cars. This number has some differences with Elon Musk’s sales expectations of 20 million cars for Tesla in 2030, but we still use 18 million cars/year as the basic data for simulation.
Tesla’s current average vehicle price is about $50,000 (calculated based on the sales ratio of S/3/X/Y models), and 18 million cars is $18,000,000 x $50,000 = $900,000,000,000 (900 billion US dollars), with a gross profit margin of about 28%, which is a gross profit of approximately $252 billion. In my previous Q3 earnings review, I analyzed that Tesla’s current operational costs are about $6,800 per car (including all operating and R&D expenses), so the operating expenses are $18,000,000 x $6,800 = $122,400,000,000 (122.4 billion US dollars), and the net profit is $12.96 billion.
What is the level of this net profit? Apple’s net profit in the 2021 fiscal year was 95 billion US dollars.Translated English Markdown text with HTML tags preserved:
However, what does selling 18 million cars per year mean? In 2020, the global total automobile sales were at the level of 72 million units, which means Tesla will account for 1/4 of global vehicle sales. Of course, this sounds crazy. Up until now, no automaker has been able to account for a quarter of global vehicle sales. The closest is Toyota, which only sells approximately 10 million cars per year, meaning Tesla would have to double that number.
It sounds difficult, but who knows, has Tesla ever failed to achieve something beyond people’s imagination?
(to be continued)
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
