Differences between Chinese and foreign car companies in the new energy sub-markets
1) Previously, I broke down the penetration rate at the price end and if further refined by grades, it will reflect the overall pattern and status: A00 is still dominant, while there has been a breakthrough in the B-class.
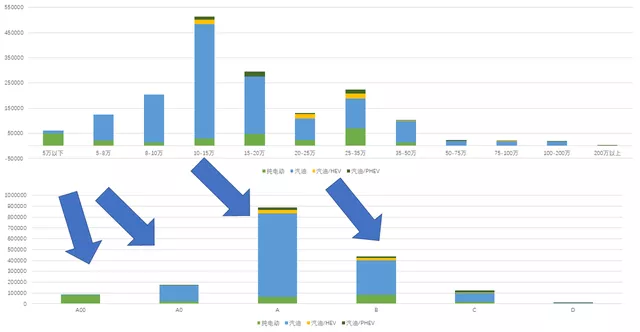
2) Vehicle segment market status
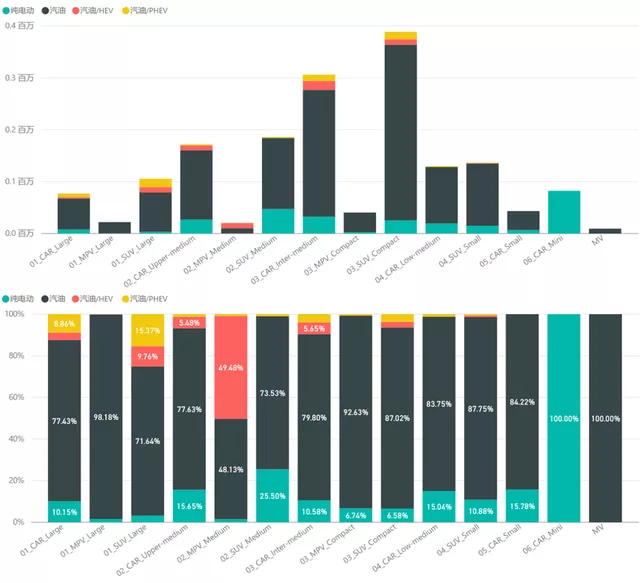
In the electric vehicle market, there has always been a question as to why foreign traditional car companies have not put up their efforts in electric vehicles like experts, even if they have invested huge sums of money, the overall volume of electric vehicles is still weak. Especially, when we see these traditional auto giants, such as Volkswagen, plan massive production capacity; their brand effect has not been replicated in the electric vehicle race track. I want to try to answer this question, there are many complex factors involved.
There are several characteristics in the domestic market:
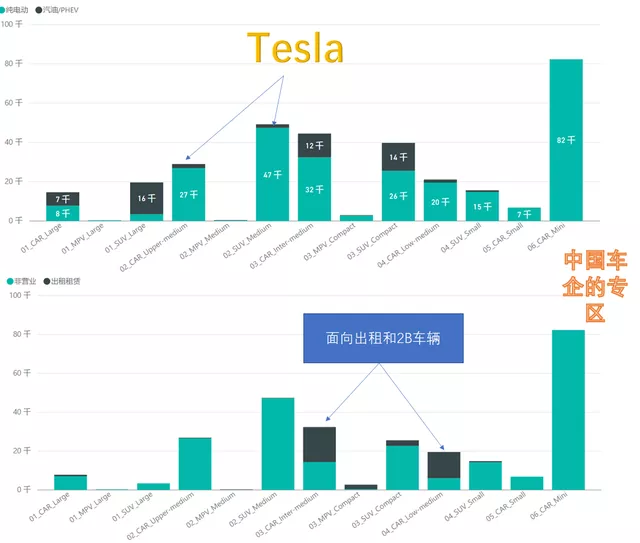
The most successful strategy of Chinese car companies, and currently the largest market of pure electric models, is Mini Car; this is something that foreign car companies cannot do. Sales of these models reached 83,200 units last month, accounting for 30.7% of the pure electric vehicle market.
Apart from this, the largest sub-market is where the Model Y is located, with 47,000 units sold. After Tesla reduced the price, the Model Y has become extremely competitive. Another major sub-market is the medium to high-end sedan market (28,000 units), where Model 3 sales are forcing joint venture car companies to lower profits.
The traditional joint venture automakers are more dominant in the sub-market of medium and compact sedans (44,000 units and 20,000 units respectively), which has the largest demand in the B2B travel market, which has also limited the potential of joint venture car companies.
The remaining identifiable sub-markets are the compact SUV market (40,000 units), where the German brands have performed relatively well, and the small SUV market, which is currently not yet covered.
The mid-to-large SUV market is currently based on PHEVs, in which joint venture car companies have not made much progress.
 The overall market penetration is reflected in the following figure, and increasing penetration currently requires popular car models to drive it, which depends on both the characteristics of the car model and advanced thinking.
The overall market penetration is reflected in the following figure, and increasing penetration currently requires popular car models to drive it, which depends on both the characteristics of the car model and advanced thinking.
Looking at foreign brands, Tesla has achieved 65%-67% market share in the Model 3 and Model Y market segments respectively, forming a repressive trend, while German brands rely on their presence in the large PHEV sedan market, and the compact and large SUV market.
In my personal opinion, joint venture car companies have relatively few actual demands in this booming market, and apart from Tesla, foreign brands as a whole have had a hard time familiarizing themselves with the Chinese market.
Therefore, currently, other car models are struggling except for the ongoing efforts of Model 3 and Model Y, and Volkswagen lets JAC-VW produce the Sihao to make low-priced products.
What is the reason?
Firstly, traditional car companies, especially foreign vehicle manufacturers, have relied primarily on powertrain (transmission and engine) barriers to success, and any new entrants or competitors need to follow development experience, which matches to a long development cycle. However, the development of electric vehicles perfectly circumvents this barrier, coupled with the fact that consumer groups focus more on smart interactions and autonomous driving, while many traditional car companies’ barriers in manufacturing and quality are not highly regarded within this emerging consumer group. Foreign traditional car companies have had a certain strategic misjudgment in this regard. Although they have spent a lot of effort to solve the problem in the traditional development manner, the focus of attention cannot be effectively conveyed to consumers.The characteristics of pure electric vehicles are rapid iteration. From the perspective of battery technology, the development of battery technology promotes the rapid improvement of pure electric vehicles’ endurance, which makes new car manufacturers iterate quickly in other areas. However, in the eyes of customers, this approach seems slow and outdated, consequently many customers regard new electric vehicles as trends and the future.
According to the traditional mindset of automobile enterprises, a lot of data needs to be considered in determining design concepts, overall testing and verification procedures, and overall consideration needs to be given to safety, cost, lifespan, performance (including energy density and fast charging characteristics), and adaptability to high and low temperatures, as well as maintenance and recyclability. Given the many factors to consider in this regard, there will inevitably be a longer confirmation cycle, leading to certain disadvantages.
Times are changing, and consumers are beginning to diverge. As shown in the figure below, we see various consumer groups who have undergone changes in their expectations of cars after owning their first, or even second car. They have expectations for the development of the next generation of cars, similar to the way smartphones have changed their lives. There is an expectation for cabins and automatic assisted driving. Over the past 10 years, there have been changes in the mentality of Chinese consumers during the mobile internet era, and with the traditional mindset of automobile enterprises in holding on to long development cycles and safety concerns, updates have been relatively slow.
At the same time, we can also see changes in sales patterns. This generation of consumers is faced with a flood of products coming at them from all over the world, making choices difficult. From a service perspective, looking at the entire sales process chain, customer data is very important. New car manufacturers still follow the complete internet service model. For the vast majority of new energy vehicle owners, many things remain unknown, so selling electric vehicles requires a complete answer key: how to deliver products to consumers, how to buy, how to use, and how to repair them. Many of the experiences gained by traditional automobile enterprises have led to a gap between the mode of handling dealerships by 4S shops compared to the importation of electric vehicles into the internet service model, resulting in a disadvantage.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.