Introduction:
Recently, there was an unexpected power outage in Dresden, the capital of Saxony, Germany, and one of the largest semiconductor clusters in Europe. The abnormal power supply situation lasted for two hours. According to Bloomberg, Infineon’s factory was closed until Tuesday night, and Bosch managed to resume operations on Monday afternoon, but Bosch said it is still evaluating the damage to its €1 billion factory. GlobalFoundries Inc. stated that the impact of the Dresden factory is limited due to the energy supply of the energy storage system.
Earlier, during the outbreak of the pandemic in Malaysia, which is known as the global “semiconductor packaging and testing capital”, STMicrelectronics, a global chip giant, experienced collective infections in its factory in Malaysia, causing multiple production shutdowns. This has led to a shortage of chip supply issues that have spread to the automotive industry. Malaysia is an important part of the global semiconductor industry, and its packaging and testing capacity accounts for 13% of the global market.
Why does the lack of chips have a significant impact on the automotive industry?
Automotive chips are the basis of automotive electronics. Generally speaking, automotive electronics refer to the general term for all electronic devices installed in vehicles. To take a simple car door as an example, if it wants to achieve the functions such as automatic locking, remote locking and unlocking, and automatic glass rolling down at a certain speed, it cannot do without chips. Chips are usually present in three types of components, including sensors, electronic control modules, and actuators.
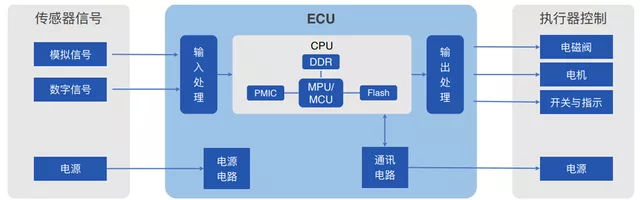
From the perspective of the classification of automotive electronic functions, automotive electronics mainly include basic components such as sensors, controllers, and actuators (including external mechanical structures).
1) Sensors (similar to human five senses): Its main function is to convert physical quantities into recognizable electrical signals, usually to collect the required object information and status for the controller. At present, it is also an important chip in cars. From the perspective of physical quantities, sensors help cars to collect useful information such as temperature, pressure, vehicle speed, acceleration, etc., and then transmit this information to the electronic control module.
2) Electronic control module (similar to human brain): It is the brain of information processing in the car, with MCU and SOC chips as the core, including various power supply circuits, communication circuits, input processing circuits, and output power circuits.
3) Actuators (similar to human limbs): The actuators in the car are used to execute the control signals issued by the electronic controller and are a load for the electronic module.With the development of the automotive industry and increasing expectations from consumers, manufacturers are increasingly focused on improving car safety, reducing energy consumption, improving comfort, and adding entertainment and auxiliary functions to increase the competitiveness of their automotive products. Therefore, the smarter a car is, the more intelligent control modules and sensors it requires, and the more chips it needs. For microcontrollers, a single car often requires 40-80, and with various sensors and chips for specific functions, the main large chips on a single car can have over 1000, not to mention various discrete devices (diodes and transistors) and passive components (such as resistors and capacitors). Typically, a car needs 4000 diodes, 1200 transistors, 50,000 resistors, and 60,000 capacitors.
It can be said that automotive chips make our vehicles smarter and more comfortable to use, but they have also become a very important part of cars. In extreme conditions, chip supply becomes the Achilles’ heel of automotive supply chain management.
Why are chips in short supply?
Overall, the shortage of automotive chips is mainly due to a supply-demand imbalance, with supply being tight due to various natural disasters and man-made incidents. This has made the bullwhip effect in the supply chain increasingly severe, with all companies in the supply chain needing to increase their inventory, exacerbating the shortage of chips.
First, let’s review the shortage of automotive chips. In December last year, Volkswagen Group, Continental, and Bosch began to report the first shortage of chips in the automotive industry from the perspective of supply chain shortages. From December last year to February 2021, the shortage of automotive chips was mainly due to a mismatch between supply and demand. The sudden outbreak of the pandemic in 2020 caused a sharp drop in automotive production in the second quarter of 2020, which led to a sharp drop in demand for chips in the second half of 2020. When global automotive production rebounded in the third quarter of 2020, a large demand for automotive and consumer electronics together put huge pressure on chip suppliers upstream, triggering a short-term imbalance between supply and demand.As the recovery time gets longer, the automotive industry has found that the main shortage of chips is in MCU microcontrollers. As previously mentioned, automotive control modules use a large number of MCU microcontrollers, which require a fabrication process of 40 nm or smaller due to the demand for chip miniaturization and high frequencies. Most IDMs outsource chip production to foundries such as TSMC. TSMC produces about 70% of all automotive MCUs on the market. As the automotive MCU chip market is highly concentrated, the top 7 MCU suppliers account for about 98% of the demand. At the time, the bottleneck was TSMC, which had its own considerations regarding processing other chips or automotive MCU microcontrollers, as the automotive business accounted for only 3% of its total revenue. However, with the mediation of governments and automakers worldwide, the bottleneck at TSMC has gradually been overcome, and the shortage has gradually eased after April.
During this process, there were also rare snowstorms in Texas, a production hub for semiconductor manufacturing, which caused power shortages and forced several major chip companies to shut down and conserve electricity. In addition, one of the world’s largest automotive chip companies, Renesas Semiconductor, experienced a factory fire. Then, in July, the exacerbation of the Southeast Asian pandemic forced a certain automotive chip supplier centered in Malaysia to close some production lines until August 21, after previously shutting down for several weeks. This directly led to the deterioration of chip supply, and the shutdowns of chip manufacturers also caused difficulties in supplying products such as Bosch’s ESP/IPB, VCU, and TCU. As Bosch is the world’s largest automotive supplier, the supply gap of chassis and safety components has caused significant damage to all global automakers.
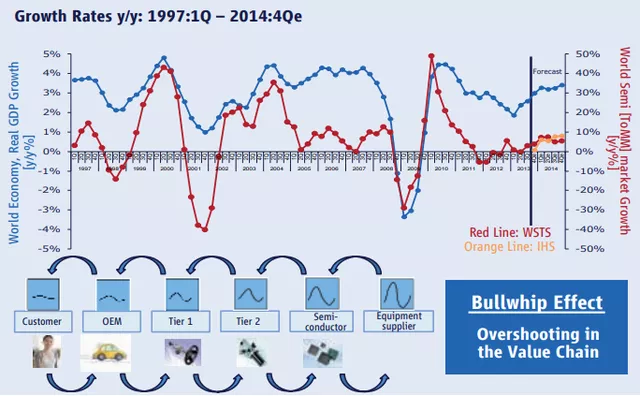
Due to the ongoing background, the automotive chip supply has experienced a very obvious bullwhip effect. The bullwhip effect is the phenomenon where demand information is amplified step by step during the transmission process. This is the most typical case in the automotive industry. The end customer is the car owner, the dealer is the well-known 4S store, and the manufacturer is the automaker that produces the car. The supplier who directly supplies the automaker is called a first-tier supplier. The process of supply chain information distortion mainly includes three key words:
-
Demand information, including orders and forecasts;
-
Transmission process, passing through multiple dealers and suppliers;
-
Amplification step by step, the amplitude of the supply chain tail is the largest.
Due to the continuous shortage of automotive chips, all automakers and suppliers have been forced to abandon the zero-inventory strategy. The demand for chips is very high, which has led to chip companies receiving a large number of orders and demands that are impossible to fulfill.
In fact, the production of automotive chips is also affected by the following issues:The long production chain leads to insufficient supply: including the four major links of materials, design, manufacturing, packaging, and testing, the production chain is finely divided and factories are scattered around the world. Any problem in any link will affect the chip production capacity. Shortages of automotive chips have various reasons in wafer fabrication, manufacturing, and packaging testing.
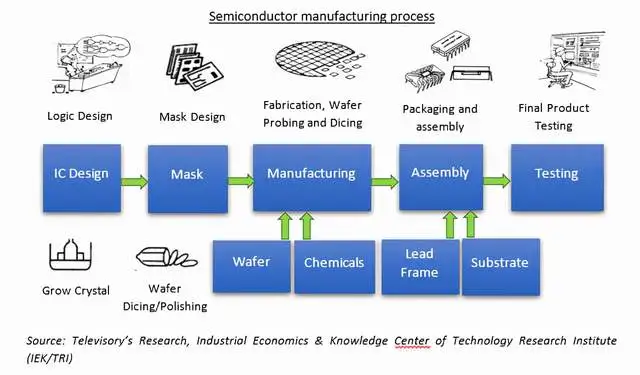
Long production cycle: Due to the length of the industrial chain of chips, it generally takes 24-26 weeks from raw materials to chip products. When supply chain disruptions increase, the supply time is constantly elongated.
Automotive chip production has high requirements and low profits: Compared with consumer-grade chips, automotive-grade chips have lower profit margins and its production value only accounts for about 10% of the entire industry. The chip manufacturer would prefer to produce consumer-level chips with higher profit margins in the case of increased demand for consumer-level chips and overall insufficient production capacity.
Therefore, from this logic, the shortage of automotive chips also has a certain inevitability under the current environment.
What is the industry layout of automotive chips?
As mentioned earlier, the four major links of chip production include design, manufacturing, packaging, and testing, and only a few companies can independently complete all four links. In order to pursue higher profit margins, the automotive chip industry has adopted a large number of outsourcing services. The top 10 automotive chip suppliers include Infineon, STMicroelectronics, and NXP Semiconductors, among which these giants have design capabilities and layout the low value-added packaging and testing links in labor-intensive regions. At the same time, with the experience accumulation of automotive parts suppliers, they have designed proprietary automotive chips, such as Bosch has incorporated a lot of knowledge into its design and developed its own dedicated chips.
Conclusion: From the current situation, the shortage of automotive chips will persist for a period of time, and many forces are working hard to improve the supply of chips. This period is indeed a difficult time for the automotive industry. For consumers, insufficient supply of automobiles also leads to an increase in prices of automotive products. With the efforts of various parties, chip supply will gradually improve.
Reference:
1) Guideline Supply Chain Management in Electronics Manufacturing
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.