Author: Wang Lingfang
“By the end of 2025, NIO will have over 4,000 global battery swap stations, with approximately 1,000 of them located outside of China. 90% of NIO users in China will be within 3 kilometers of a battery swap station.”
This was the latest plan announced at the NIO Power Day on July 9th.
NIO Co-founder and President, Qin Lihong, broke down this goal into yearly targets: In 2021, NIO’s battery swap station construction target has been increased to over 700 sites, up from the previously announced goal of 500 sites at NIO Day. From 2022-2025, NIO will add 600 new battery swap stations per year in the Chinese market.
In addition, NIO also announced the full opening of its NIO Power charging and swapping system and BaaS services to the industry, and will share its achievements with the industry and intelligent electric vehicle users.
800 Battery Swap Patents
The industry has always believed that operating vehicles require more frequent battery swapping.
In the view of NIO’s Vice President of Energy, Shen Fei, this conclusion was reached by thinking from the perspective of battery swap operators: Drivers of commercial vehicles have more regular driving patterns, and the arrangement of battery swap stations for them is relatively easier.
Shen Fei believes that private car users have a greater need for battery swapping, but the difficulty lies in the construction of stations. Private car user behavior is irregular, they tend to travel further, and they are not willing to wait at a battery swap station for long periods of time. There are also private car users who don’t have a designated parking space in the city, so the demand is higher. In addition, the stations need to be located in convenient places for users and not too far away. Shen Fei gave an example of his own experience, he lives more than 4 kilometers away from the nearest battery swap station, and it takes 12-15 minutes for a round trip. He believes that is too far. If the distance is reduced to 3 kilometers, it will take about 10 minutes or less to reach it in a big city, which is the most suitable distance.
NIO users who live within 3 kilometers of a battery swap station are called “Electric Zone Households” by Shen Fei.
Shen Fei found that currently only 29% of users in China live in “Electric Zone Households”. He believes that this is far from enough, and his goal is to have 90% of NIO users become “Electric Zone Households” by 2025.
In order to achieve this goal, NIO is accelerating the construction of battery swap stations. Qin Lihong stated that by the end of July 2021, NIO will add around 50 new swap stations, and by the end of Q3, they will add 200 more. The goal is to increase the total number of battery swap stations to 700 by the end of the year. In terms of high-speed battery swap stations, the number by the end of 2021 will be more than double that of the beginning of the year.
Shen Fei also considered safety and reliability issues, which are reflected in the technology and over 800 patents related to battery swapping held by NIO.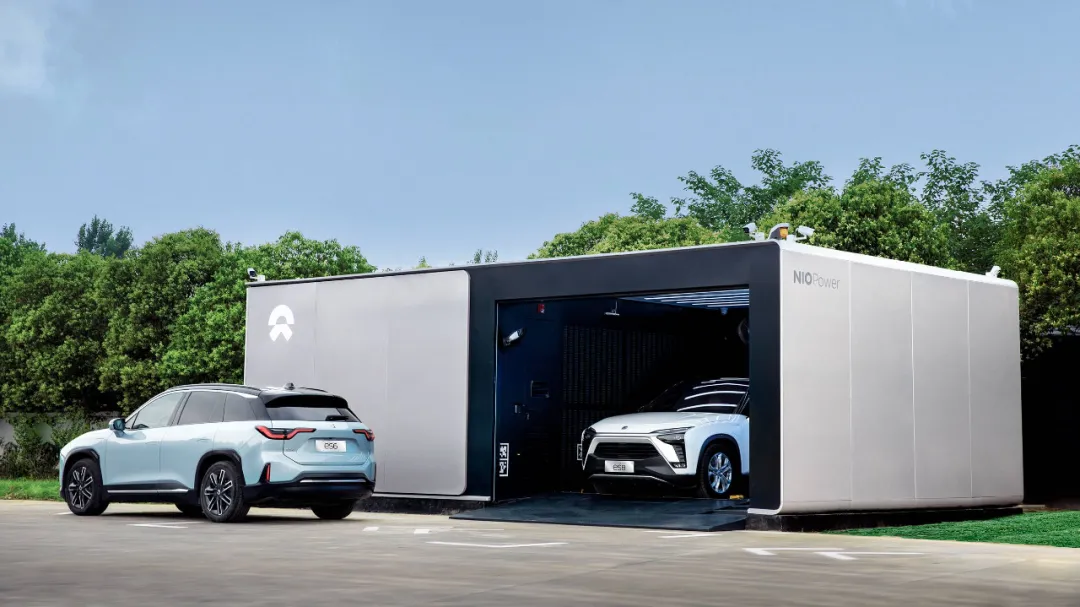
Shen Fei used the example of a locking bolt to illustrate the bayobolt, Nio’s patented solution for connecting its batteries to its chassis. The design concept is similar to that of the lunar orbit docking device used on the Chang’e 5 lunar probe, achieving a stable and reliable connection, repeatable separation, ensuring both the rigidity and strength of the connection, and allowing for a certain degree of docking floatation tolerance. The complete unlocking process with the lock and unlock gun is done within 31 seconds, with 1 second for visual judgment, 10 seconds for calibration and alignment, and 20 seconds for unlocking, all using automatic control.
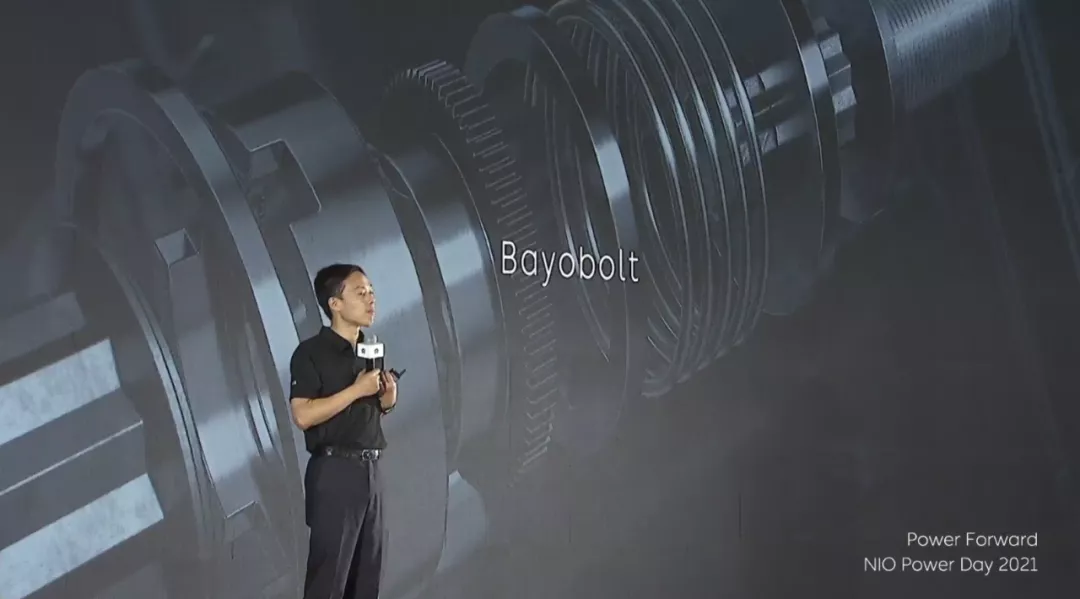
In Shen Fei’s own words, even in the most extreme case, if only 2 of the 10 bolts that connect the battery to the chassis are fastened, it can still be locked in place, ensuring extreme reliability.
Additionally, it is worth mentioning that Nio’s battery swap station has also officially expanded overseas. On July 7th of this year, Nio’s battery swap station was shipped to Norway for deployment. These two battery swap stations will be launched in Norway at the end of the third quarter of this year, and have already undergone EU certification regulations and interface changes, as well as modifications to suit European users.
More than just battery swap
Nio is not only focusing on battery swap, but also keeping up with the charging business.
Nio has already built 204 supercharging stations and 382 destination charging stations, providing users with more than 2.9 million battery swaps and more than 600,000 one-click quick charges.
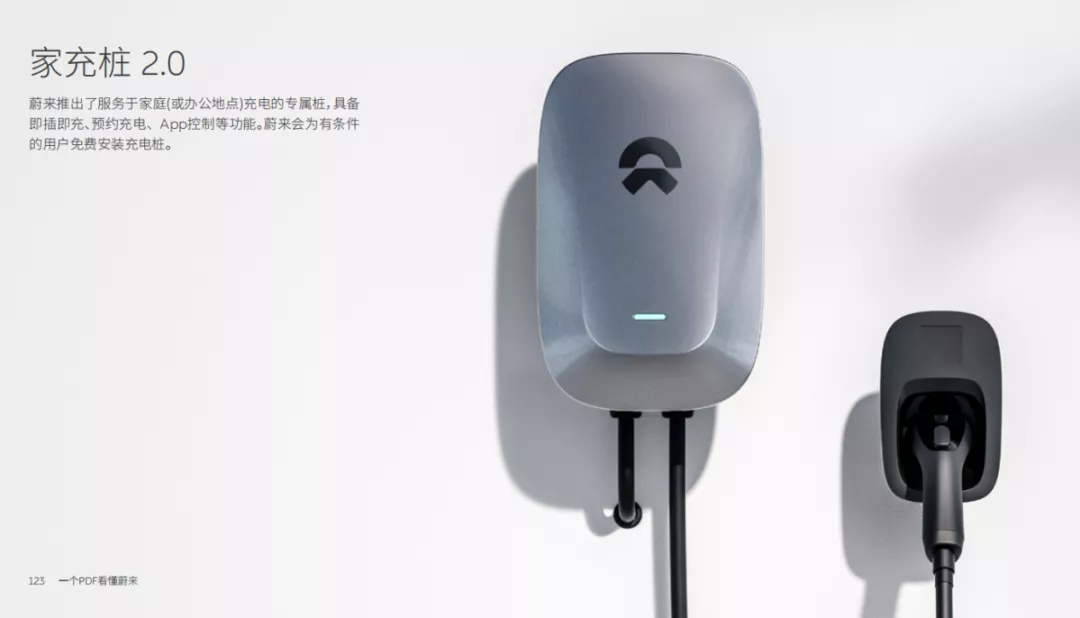
In the charging domain, Nio has launched four types of chargers, including 7 kW Home chargers 1.0 & 2.0, 20kW fast chargers, and 180kW superchargers. Currently, Nio has installed a total of 75,360 home chargers. Qin Lihong said that according to incomplete statistics, the installation proportion of Nio’s home chargers is probably the highest in the industry.

This is because they have a dedicated team to communicate with vehicle owners and property owners about the installation of charging facilities. “Of the 120,000 Nios on the road, 3,205 have more than 99% of their power coming from their own home chargers. Although the proportion is small, for them, charging is already more convenient than refueling,” Qin Lihong said.NIO is also accelerating the deployment of public charging stations. Since the end of last year, after connecting 16 groups of charging piles to the 318 national highway, destination charging piles have been built rapidly. On March 18th of this year, NIO deployed destination charging piles throughout southern Anhui; on May 11th, destination charging piles in the Xisha Islands were completed; on May 20th, destination piles were laid out in the Beidaihe Anaia area; and on June 1st, destination piles were connected along the Sichuan-Tibet-Qiang loop.
This year, NIO will also complete the layout of destination charging piles in locations including Qinghai-Tibet Highway, Duku Highway, Kanas, Hexi Corridor, Lugu Lake Ring Road, Changbai Mountain, and Mohe North Pole Village.
As NIO’s earliest well-known energy replenishment method, the mobile charging car has been deployed in more than 500 units. The mobile charging car was once NIO’s main energy replenishment method. So far, NIO’s mobile charging cars have provided more than 10,000 energy replenishment services for more than 30 other brands of vehicles.
Whether it is battery swapping, charging, one-click charging, or mobile charging cars, NIO strives to achieve the ultimate user experience – worry-free travel.
Scientific Management: NIO Power Cloud
To achieve worry-free travel, it is not just about having a large number of energy replenishment network stores; it also requires scientific scheduling and management to ensure the best user experience.
To this end, NIO has upgraded its soft power and built the NIO Power Cloud platform, which includes 4 major components: Athena, PowerGo, Power Prime, and Shield.

Athena intelligent algorithm platform is a simulation-assisted decision-making system that assists in planning and deploying electric vehicle charging and swapping networks. The system accesses massive data, can automatically analyze operational service capabilities and resource bottlenecks, and provides optimal deployment plans for adding new resources to ensure user experience and overall operational efficiency of the system.
①Based on spatio-temporal distribution data of user charging demands, the system can predict user charging behavior through built-in machine learning algorithm models.
②Based on predictions, the system can provide more accurate and reasonable service planning, respond more quickly to user service demands, provide better service experience, and improve the systematic efficiency of operations.
③Based on analysis of these historical orders, the system will continue to improve resource deployment and service scheduling strategies, providing users with better charging services.
PowerGo is a one-stop charging and swapping operation platform.This is a platform specifically designed for long-distance electric car travel, which was the earliest to be developed and applied in the industry. NIO’s system integrates charging station data, real-time traffic information, vehicle range, and user charging strategies from all over the Internet. It can conduct personalized route planning and recommend charging resources along the way. It also combines NIO Power’s comprehensive energy replenishment methods, including battery swapping stations, mobile charging cars, and one-click charging, which allows for route planning even in areas with few or no charging stations, ensuring worry-free long-distance travel for electric vehicles.
Power Prime refers to the high-performance IoT platform connecting vehicles, charging stations, battery swapping stations, and personnel, forming the foundation of the all-scenario charging service.
Power Prime is a high-performance IoT platform independently developed by NIO, which not only connects to various charging stations and battery swapping stations owned by NIO but also integrates more than 80% of the charging resources on the market. It is compatible with almost all mainstream protocols in the IoT and electric vehicle industries, making it easy for various devices to access. With powerful data processing capabilities, it can support real-time processing of millions of devices at the second level.
Utilizing digital twin modeling, Power Prime can monitor and manage the status and operation of connected devices in real-time. Based on the stream processing engine and artificial intelligence algorithms, it can detect abnormalities in IoT device data, generate alerts in the cloud, and remotely control, configure, and upgrade devices, realizing fault detection, diagnosis, positioning, and recovery of physical devices.
Shield refers to real-time monitoring of battery status and intelligent scheduling of battery flow.
The Shield battery management platform can provide all-round intelligent operation and management of batteries, including intelligent diagnosis of faults and hazards, health status assessment, operation analysis, and business decision-making. It can achieve accurate battery status assessment, online real-time health check of batteries, and intelligent scheduling of the battery circulation system. Behind it are three black technologies independently developed by NIO: battery health monitoring technology, State of Health (SOH) evaluation technology, and battery intelligent scheduling technology:
① Online real-time health check of batteries: significantly improves the safety and reliability of batteries and greatly reduces after-sales maintenance costs.
② Battery SOH evaluation system: can combine battery portraits and operating characteristics to calculate battery capacity, Ohmic impedance, polarization impedance, and charge consistency, thereby accurately evaluating battery status.
③ Battery intelligent scheduling technology: based on a distributed charging and swapping network, it can implement intelligent circulation, abnormal interception, precise maintenance, emergency energy replenishment, and other operational measures for batteries. It achieves large-scale equilibrium for tens of thousands of battery blocks, ensuring that batteries always operate in the optimal operating range, effectively delaying the decline in battery life, fully tapping into the full life cycle value of batteries, and providing ample technical support for the development of BaaS business.
NIO connects battery swapping stations, charging stations, mobile charging cars, battery packs, vehicles, NIO personnel, and users into a smart energy Internet, ultimately providing users with more efficient charging services.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
