Author: Let’s talk about automotive electronics
Standard Overview
Time
When the AUTOSAR organization was newly established in 2003, there was only one AUTOSAR standard and no differentiation between AP (Adaptive Platform) and CP (Classic Platform).
In 2005, the AUTOSAR organization released the first version 1.0 of AUTOSAR.
In 2017, the AUTOSAR organization released the first version R1703 of AP AUTOSAR. This was the first time that the outside world saw AP AUTOSAR, and AUTOSAR was divided into AP and CP from this point onwards. At the same time, the CP AUTOSAR version was named R4.x.x.
To the outside world, the differentiation between AP and CP happened in 2017, but the AUTOSAR organization had already made the differentiation internally in 2015.
Another time point is in November 2019, when the version numbers of AP, CP, and FO (Foundation) were unified named: AP AUTOSAR R1911, CP AUTOSAR R1911, etc.
Release Content
The AUTOSAR organization generally only publishes the CP AUTOSAR standard.
For AP AUTOSAR, the AUTOSAR organization provides APD (Adaptive Platform Demonstration) for AUTOSAR members in addition to releasing relevant standards. APD contains only for reference AP AUTOSAR tools, code packages, etc.
Goals
Whether it is AP AUTOSAR or CP AUTOSAR, the overall goal is the same:
-
Better manage the increasing number and complexity of automotive ECUs
-
Improve ECU software quality and reliability
-
Enhance product upgrade flexibility and shorten the time to market for products
-
Scalable architecture solutions
Initiative Content
The initiative content for both CP AUTOSAR and AP AUTOSAR is the same:
-
Automotive software architecture standard design
-
Detailed design of underlying software modules
-
Standardized data description of various automotive product domains
-
Process definition and software toolchain applicable to this architecture
Hardware
Chip Types
CP AUTOSAR generally runs on 8-bit, 16-bit, and 32-bit microcontrollers (MCUs), such as Infineon’s TC3xx and Renesas’ RH850.AP AUTOSAR can run on high-performance processors (MPUs), CPUs, etc. with a 64-bit architecture, such as Renesas’ H3 and NVIDIA’s Xavier, among others. Additionally, AP AUTOSAR can run on virtual hardware.
Note: Some companies may port a particular POSIX OS to a platform like TC3xx and then use AP on it. These cases are rare and not recommended, so we won’t go into detail here.
Chip Performance
The chip performance required for CP AUTOSAR is generally below 1000 DMIPs, while AP AUTOSAR can run on chips with performance higher than 20,000 DMIPs. Here, the term “chip performance” refers to logical performance measured in DMIPs, as opposed to TOPS, which is another metric for AI chips that generally refers to matrix operation computing power.
OS
OS Types
CP AUTOSAR OS is based on the OSEK standard.
AP AUTOSAR OS is a POSIX OS and should at least include the PSE51 subset.
Developers
CP AUTOSAR OS is generally developed by CP AUTOSAR suppliers such as AUBASS and VECTOR.
The OS that comes with AP AUTOSAR is usually developed by specialized OS manufacturers such as eSOL’s eMCOS and BlackBerry’s QNX.
CP vs. AP
Architecture
CP AUTOSAR has a layered software architecture with clear upper and lower layer relationships, as shown in the figure below:
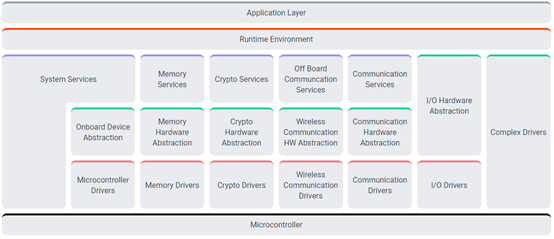
From bottom to top, these layers are:
-
Microcontroller Layer (HW)
-
Basic Software Layer (BSW)
-
Microcontroller Abstraction Layer
-
ECU Abstraction Layer
-
Service Layer
-
Complex Driver
-
RTE Layer
-
Application Layer
AP AUTOSAR generally refers to ARA (AUTOSAR Runtime for Adaptive Applications). It has two main components (Foundation and Service), as shown in the figure below:
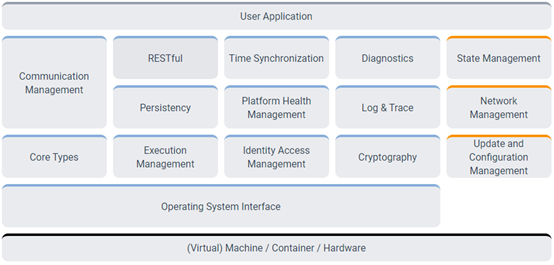
In the figure above, all modules are referred to as Functional Clusters (FC).The architecture design principles of CP AUTOSAR are:
- Define hardware-related and general system functions as BSW modules
- Define application functions as independent software components (SWC)
- Separate SWC and BSW with RTE
- Configure BSW and reuse it in multiple product lines’ ECUs
- Not open-source
The architecture design principles of AP AUTOSAR are:
- Follow the SOA (Service-Oriented Architecture) design paradigm
- Reuse mature software components from other areas and software market to shorten the development cycle
- Fully utilize various open-source software
In terms of development process, both CP and AP mainly include the following three stages:
- Design stage: design ARXML
- Code generation: generate code based on ARXML
- Integration: integrate application, compile and debug, etc.
The main differences are as follows:
- In the design stage of AP AUTOSAR, Service and Manifest need to be designed, while CP does not. CP needs to design ECU configuration, which is not a design item for AP.
- During code generation, CP generates code related to basic software modules, while AP generates code and Manifest related to FC. It should be noted that not all FCs in AP will generate relevant code and Manifest.
- During integration, AP AUTOSAR needs to consider OEM Application Cloud, while CP does not.
The development process of CP and AP is shown in the following figure:
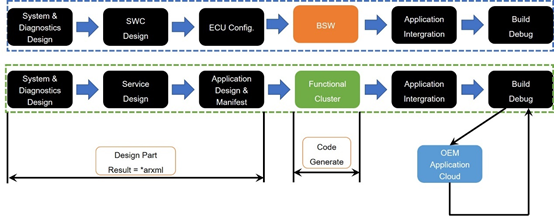
The blue dashed box represents the development process of CP AUTOSAR, and the green represents the development process of AP AUTOSAR.
It should be noted that the figure is a simple arrangement and does not cover all the contents that need to be designed in AUTOSAR.
Interface Types# CP AUTOSAR uses commonly-used interfaces such as Sender-Receiver and Client-Server.
AP AUTOSAR uses commonly-used interfaces such as Service Interface.
When designing communication between CP and AP AUTOSAR, a signal-to-service conversion design is necessary. Currently, only a company from Japan provides this function, which has been used in concrete projects.
Communication Method
CP AUTOSAR is signal-based communication, mainly including CAN, Lin, FlexRay.
AP AUTOSAR is a service-oriented communication, supporting IPC/RPC based on Ethernet.
Although SOME/IP is available in CP AUTOSAR, it merely converts the CAN communication of Sender-Receiver into Ethernet communication of Client-Server. The entire communication link is still statically configured and not truly service-oriented communication.
This is also why the AUTOSAR official claims that AP AUTOSAR is SOA, but never says that CP AUTOSAR is SOA.
Scheduling Method
CP AUTOSAR OS adopts a fixed configuration of task scheduling, which schedules BSW Main Functions and SWC’s Runnable Entities in the OS Task and executes them in the specified rule order. It also collaborates with BSW Modules and App SWC mode switching.
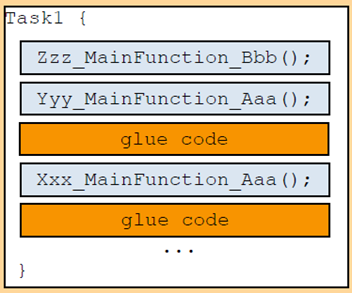
AP AUTOSAR supports various dynamic scheduling strategies, which are completed during runtime and reflected in the Manifest file.
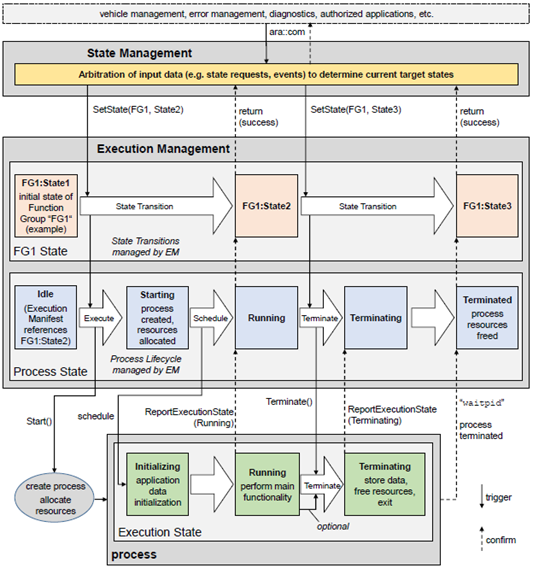
In AP AUTOSAR, modules related to scheduling include Execution Management (EM) and State Management (SM), and the application runs in Processes and Threads.
The scheduling cycle in CP AUTOSAR can reach the microsecond level. In contrast, AP AUTOSAR is generally in the millisecond level (usually tens to hundreds).
State Management
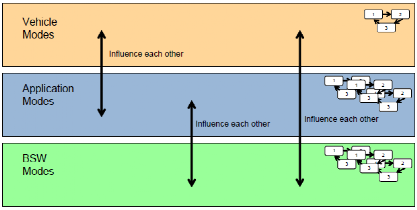
CP AUTOSAR processes different states through Mode Switching Components:
-
BSW Mode (Network Online, Offline)
-
Application Mode (Normal, etc.)
-
Vehicle Mode (Active, Inactive)Translate to English:
AP AUTOSAR mainly manages its states in the following three ways:
- Function Group (FG) State: The state of the function group.
- Machine State: The machine state is a unique state of the function group.
-
Process State: The process state is changed by the Function Group via EM.
-
Execution State: The execution state of the process.
Safety
According to the official statement of AUTOSAR, CP AUTOSAR can support system development up to ASIL-D in terms of functional safety, while AP can support up to ASIL-B in system development.
Of course, this does not mean that when using AP, the system maximum can only be designed to be ASIL-B. For more in-depth functionality safety information, it is recommended to refer to the documents related to ISO26262, CP & AP AUTOSAR with functionality safety.
The Safety mechanism in CP AUTOSAR mainly includes:
- Safety mechanism related to the OS:
-
Memory protection
-
Timing protection
-
Hardware protection
- E2E protection, as shown in the figure below:
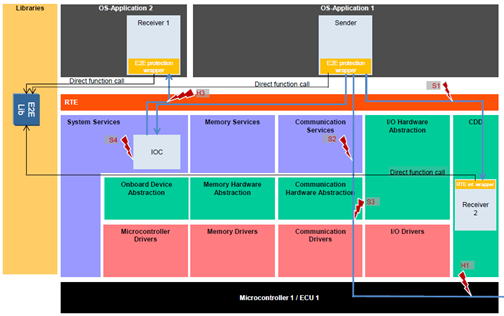
- Watchdog Manager
-
Alive monitoring
-
Deadline monitoring
-
Logic monitoring
- Hardware diagnosis
-
Core Test
-
RAM Test
-
Flash Test
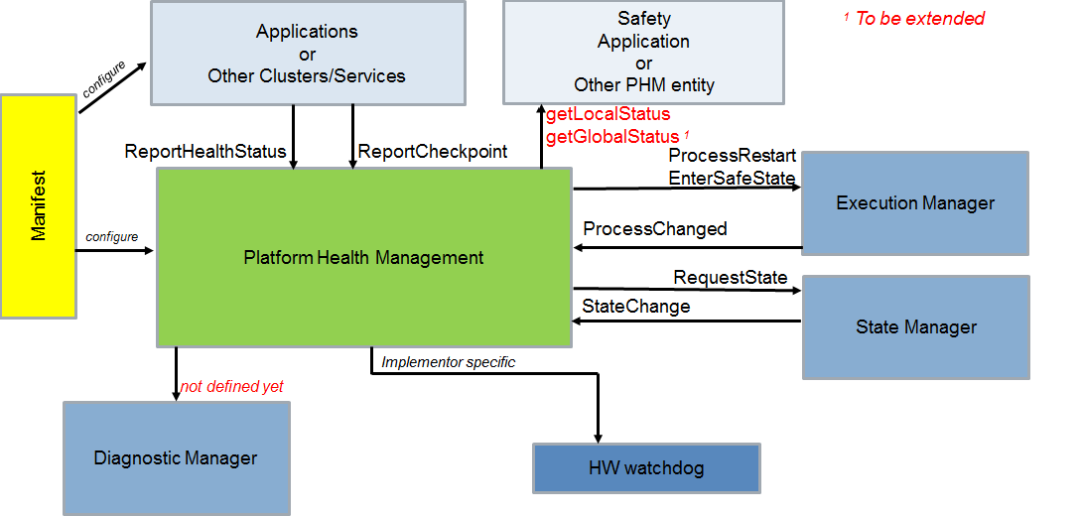
AP AUTOSAR supports E2E in ara::com. At the same time, the following recovery measures are provided in ara::phm:
-
Request to switch to a specified Function Group state by SM
-
Request EM to restart the specified process
-
Forward error messages to the application
-
……
SecurityThe Security solution in CP AUTOSAR mainly includes:
-
SecOC: Secure Onboard Communication
-
CSM: Crypto Service Manager
The process of using Security solution in CP AUTOSAR is shown in the following diagram:
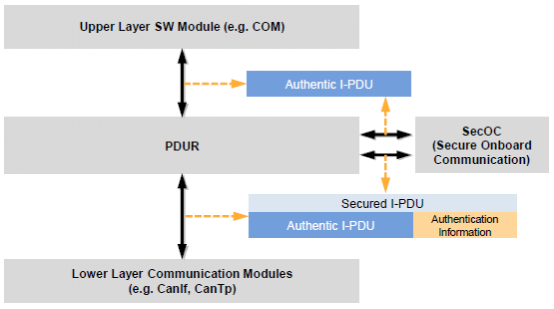
The main process is:
-
Add/verify authentication information (for/from lower layers)
-
Implement interfaces between upper and lower modules
-
Solved by PduR routing configuration
-
Maintain buffers to store and modify secure I-PDUs
The modules related to Security in AP AUTOSAR mainly include:
-
ara::iam: Identity and Access Management
-
ara::crypto: Used for generic encryption operations and secure key management
The main functions of ara::crypto are:
-
Provide interfaces for Adaptive Applications, responsible for constructing and supervising encryption primitives
-
Provide basic structures for accessing encryption algorithms through standardized interfaces
-
This specification does not impose any restrictions on the internal architecture and implementation of the encryption stack.
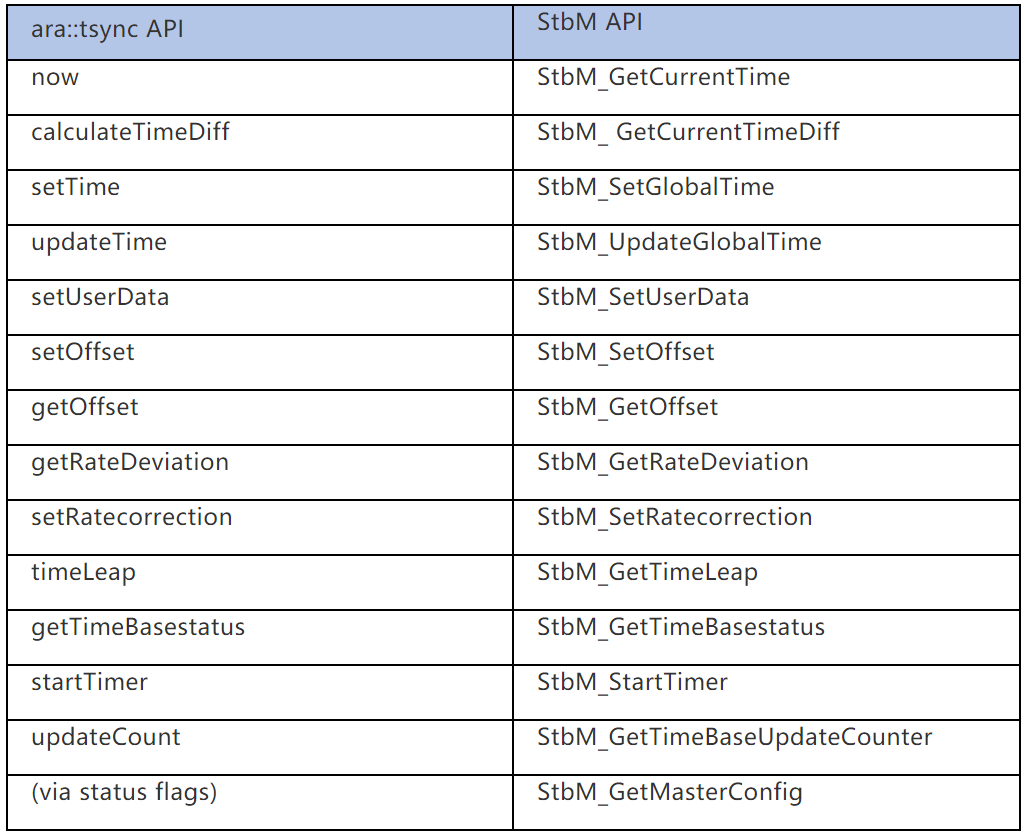
Time Synchronization
The modules related to time synchronization in CP AUTOSAR is StbM.
The modules related to time synchronization in AP AUTOSAR is ara::tsync.
CP AUTOSAR and AP AUTOSAR use the same time synchronization protocol, so the API functions provided by StbM in CP and ara::tsync in AP are functionally similar. The specific API functions of StbM and ara::tsync that have the same function are shown in the following table:
Application Layer
Development Language
CP AUTOSAR mainly uses C language, and the relevant standard is MISRA C. Of course, both application software and basic software use C language. This is explained in the Application Layer section for article structure, but it does not mean that only the application layer is C language. AP AUTOSAR is also the same, but it is just explained here for the sake of article structure.# AP AUTOSAR
AP AUTOSAR mainly uses C++ language, and the relevant standard is ISO/IEC 14882:2014. Currently, it supports C++11, C++14, and some C++17.
It should be noted that according to 1003.13-2003, the operating system interface (OSI) in AP must provide OS functions through the POSIX PSE51 interface. These POSIX PSE51 are C interfaces. This means that when using AP AUTOSAR, C++ should be used to develop applications. However, these C++ applications need to be combined with the PSE51 C interface and C++ libraries (including the C++ standard library) for use.
Code Execution
Applications on CP AUTOSAR directly execute code from ROM.
Applications on AP AUTOSAR are loaded from persistent memory into RAM to run.
Address Space
All applications on CP AUTOSAR have the same address space, and their safety is mainly supported by the memory protection unit (MPU).
On AP AUTOSAR, each application has its own (virtual) address space, which is supported by the memory management unit (MMU).
Update
CP AUTOSAR itself does not support OTA, which means that to update the application running on CP AUTOSAR, the code of this ECU must be updated. Updating a controller running CP AUTOSAR from another controller does not count as OTA for CP AUTOSAR itself.
AP AUTOSAR supports OTA by itself. AP AUTOSAR can delete/update/add individual applications, and it can also update the code of a functional cluster (FC) (although this use case is less common).
Application Scenarios
The main difference between CP AUTOSAR and AP AUTOSAR lies in application scenarios.
CP AUTOSAR is generally used in scenarios where high real-time requirements, high functional safety requirements, and low computing power are required, such as engine control, brake systems, etc.
AP AUTOSAR is generally used in scenarios where there are certain real-time requirements, certain functional safety requirements, and high computing power is required. These include:
-
Sensor fusion processing, runtime dynamic updates
-
Automatic driving:
-
Communication with traffic infrastructure
-
Communication with cloud servers
- Vehicle architecture of Domain Controller
-
Body domain
-
Entertainment domain
-
Power domain
-
OTA
-
Cross-domain computing platform, integration with smartphones, and so on.The following is a simple comparison between CP AUTOSAR and AP AUTOSAR. There are many other aspects that can be compared, such as calibration, diagnosis, deployment, and so on. Please refer to the relevant standards.
In summary, AP AUTOSAR is a supplement, not a replacement for CP AUTOSAR!
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.