Author: Xuan Wang
Currently, the trend of electrification in the global automotive industry is irreversible. Battery safety is not only an important factor for consumers to consider when purchasing electric vehicles, but also the core cornerstone of the healthy and sustainable development of the new energy automotive industry.
On March 10th, GAC Aion released a new generation of battery safety technology – the Magazine Battery System Safety Technology (referred to as the “Magazine Battery”), which was the first time in the industry to achieve no ignition when a puncture occurs in a ternary lithium battery pack.
Ternary Lithium Battery First Achieves No Ignition when Punctured
Currently, lithium iron phosphate batteries and ternary lithium batteries are the two mainstream battery technology routes in the global electric vehicle industry. Lithium iron phosphate batteries are widely used in medium- and low-range models because of their longer life and lower cost, while ternary lithium batteries are mainly used in medium- and high-range models due to their high energy density and low vehicle energy consumption.
According to the current market situation, these two technology routes will still develop in parallel for a long time in the future.

Prior to the release of GAC Aion’s Magazine Battery, BYD’s Blade Battery was the leading technology in the industry. Although the Blade Battery can achieve no smoke and no fire after being punctured, this technology is based on lithium iron phosphate batteries, while the safety of ternary lithium batteries is still a recognized pain point and difficulty in the industry.
The Magazine Battery safety technology released by GAC is currently the only technology that can prevent ternary lithium batteries from catching fire in a puncture experiment within the known scope. To verify the safety of the Magazine Battery, Dr. Liu Shiqiang, a leading expert of China Automotive Technology Research Center and one of the drafters of the national battery safety standards, led a team to carry out a puncture and heat diffusion test on a ternary lithium battery pack equipped with Magazine Battery System Safety Technology.
The test results showed that the ternary lithium (Magazine Battery) pack of GAC Aion emitted a thermal accident signal only 5 minutes after the experiment, and only a brief smoking phenomenon occurred, with no ignition or explosion. After being left idle for 48 hours, the voltage dropped to 0V and the temperature recovered to room temperature. Only the punctured battery cell module lost control, without spreading to other battery cells. After opening the battery pack, the internal structure was intact.

The reason why the Magazine Battery can achieve no ignition when punctured is because it has the following four core technologies behind it:## 1. A highly heat-resistant and stable battery cell
The battery cell utilizes nano-coating and doping technology for the positive electrode material, which effectively improves its thermal stability and prevents thermal runaway. The application of a new electrolyte additive achieves self-repair of the SEI film, thus improving the battery cell’s lifespan and reducing the risk of short-circuits. The high safety electrolyte uses special additives that cause a high-impedance polymer film to form on the surface of the active material through spontaneous aggregation when heated above 120℃, which significantly reduces the amount of heat generated during a thermal runaway reaction. The application of these key technologies has increased the battery cell’s heat resistance temperature by 30%.

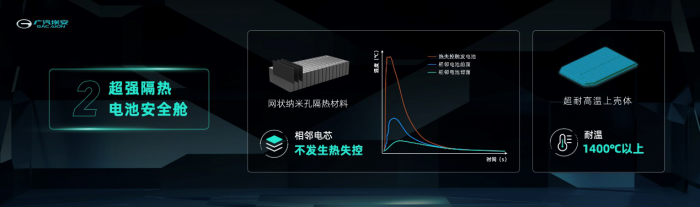
2. An ultra-high-temperature-resistant battery safety compartment
By using net-like nanoporous insulating materials and high-temperature-resistant upper shell, the magazine-type battery has built an ultra-strong heat-insulating safety compartment, ultimately achieving thermal runaway of the ternary lithium battery cell that cannot spread to adjacent battery cells. At the same time, the upper shell of the battery pack can withstand temperatures above 1400℃, effectively protecting the entire battery pack.
3. A high-speed cooling system for fast cooling
Through the design of a full-coverage liquid cooling system, high-speed heat dissipation channels, and high-precision heat conduction paths, the magazine-type battery has increased the heat dissipation area by 40% and the heat dissipation efficiency by 30%, effectively preventing thermal propagation.

4. A fifth-generation battery management system with continuous monitoring
By using the latest vehicle-grade, fifth-generation battery management system chip, the system can achieve all-weather data collection ten times per second, which is an improvement of 100 times compared to the previous generation system. The battery status is monitored through a 24-hour, full-coverage patrol mode. When an anomaly is detected, the battery cooling system is immediately activated to cool down the battery. The application of the continuous patrol mode and self-rescue from anomalies has redefined the active safety standards of the ternary lithium battery.

What do “Blade” and “Magazine” reflect about the electric vehicle industry?
The “Blade” battery of BYD and the “Magazine” battery of GAC Aion have made significant breakthroughs in the safety performance of lithium iron phosphate and ternary lithium batteries, respectively.In the era of electric vehicle competition, battery technology has become an important battleground for car manufacturers and battery suppliers to win the market, and there are only two paths to the high ground: energy density and safety. Regardless of which road is taken, it can be widely publicized and attract potential consumers.
However, it is very difficult to improve energy density, because it is linked directly to the range of electric vehicles in the eyes of consumers, and it is difficult to convince consumers through range tests. Everyone now knows that the real range of electric vehicles is discounted in the NEDC range test data.
In contrast, safety testing results are more intuitive, and consumer acceptance is higher, which also reflects why everyone is making technological breakthroughs on battery safety.
If BYD releases the “Blade Battery” as both a battery supplier and a host manufacturer, it is acceptable, but Guangzhou Automobile Group’s direct entry into the battery field as a host manufacturer only proves that the current electric vehicle market is still dominated by those who have battery capabilities.
However, there are barriers between the host and battery industries, and the host’s work is aimed at battery packs, integrating industry chain technology to achieve integrated innovation, and actually improving cell throughput and volume utilization through structural optimization. Heat monitoring and prevention of heat diffusion by physical insulation, cooling, and software monitoring are in line with the core technology of the “Magazine Battery”, but they do not have the ability to participate directly in the underlying technology.
Although it has been experimentally verified that the “Magazine Battery” is puncture-resistant and does not catch fire, I have reservations about Guangzhou Automobile Group’s mention of increasing battery density at the press conference. The relationship between safety and energy density is a dilemma under the current technological conditions.
Finally, it is reported that the “Magazine Battery” will be gradually equipped on all AION models starting this year. The puncture-resistant “Magazine Battery” marks a new height of battery safety, especially the historical breakthrough in the safety of ternary lithium batteries, which redefines the safety standard of ternary lithium batteries.
I believe that “Magazine Battery” technology will also break down the barriers in the hearts of consumers who hold skeptical attitudes towards the safety of electric vehicles.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
