Author: Zhuyulong
In the automotive industry for a long time, I increasingly feel that the development of the industry often results from the collection of resources. This publicized “National Strategy for Advanced Manufacturing in 2022,” also indicates that China is transitioning from the low-end manufacturing field to the advanced manufacturing field that we were not familiar with in the industry.
This report was developed by the US National Security Agency after extensive public promotion, containing America’s vision of taking a leading position in the field of advanced manufacturing. Manufacturing is a driving force for the economic strength and national security of the United States, playing an important role in almost every sector of the American economy (from aerospace to biopharmaceuticals, etc.). The progress of manufacturing increases economic growth because new technologies and innovations improve productivity, create conditions for producing next-generation products, support our ability to respond to the climate crisis, and create new, high-quality, and high-paying job opportunities.
Note: As my current work focus is in the field of advanced manufacturing, this report is worth my personal repeated study. Here are some excerpts, and I will interpret and quote this material later.
The development of advanced manufacturing in the United States is also built on three pillars. Here we will focus on pillars one and two.

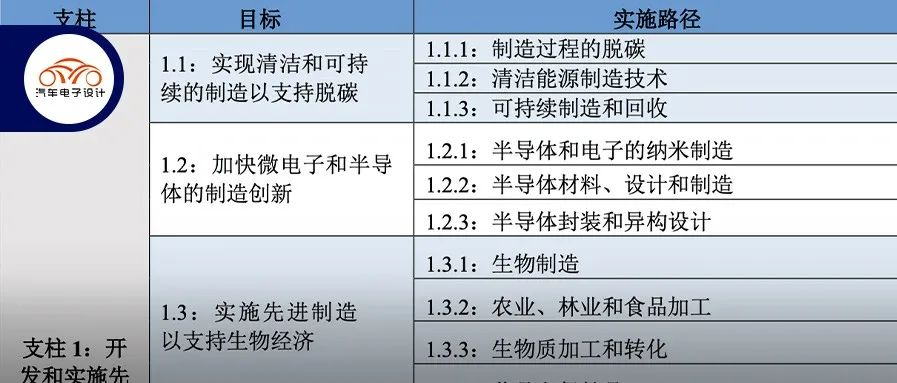
Pillar 1: Develop and Implement Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
It is mainly divided into low carbon, microelectronics, bioeconomy, innovative materials, and intelligent manufacturing. The two main parts related to us are low carbon technology and microelectronics.
Low Carbon Technology
-
Decarbonization of the manufacturing process: Develop and demonstrate advanced manufacturing technologies that improve energy efficiency, electrify industrial processes, use low-carbon raw materials and energy in the manufacturing process, apply new chemical reactions to avoid direct greenhouse gas emissions in industrial processes, separate and store industrial CO2, and create alternatives to greenhouse gas-intensive industrial products. Create and disseminate verification tools and procedures to help integrate electrification and efficient technologies into manufacturing. Publicize advanced materials and processes with lower energy and carbon footprints.
-
Improved materials, manufacturing processes, and product designs for clean power generation and storage; Use zero-emissions transportation, buildings, and industry to achieve decarbonisation of the economy. Strengthen the production of equipment and materials through the development of advanced conductive materials, processing technologies, and machines to make power conversion and transmission more efficient. Manufacture advanced batteries with high energy density and provide new sustainable materials for low-voltage and high-voltage applications. This is directly related to the direction of advanced batteries in the power sector.- Sustainable manufacturing and recycling: Developing economically viable manufacturing technologies to separate valuable materials from waste streams and developing alternatives for energy or pollution-intensive materials. Research and development in the fields of sorting, purification, and deconstruction techniques. Expanding sustainable material design and manufacturing, recycling and circular methods for multiple material categories, and scaling pilot projects and facilities. Improving data and methods to evaluate life cycle impacts and identify areas for improvement. This branch is significant for battery recycling, rare earths in motors, and so on.
These areas can be focused on as the starting point for the promotion of a well-developed industrial chain, alongside subsidies and technological advancements in the electric vehicle and battery industry. In terms of the requirements of the IRA, the US has the potential to achieve this.

Semiconductor technology
Implementation paths for semiconductor manufacturing innovation include:
-
Nanomanufacturing of semiconductors and electronics: Investing in nanomanufacturing capabilities for integrated photonics products, additive and direct printing electronics products, unique sensor formats, and mixed electronic manufacturing to leverage the power of nanomanufacturing. Develop physical, chemical, and biological methods to accurately place atoms and combine them into desired molecules and structures.
-
Semiconductor materials, design, and manufacturing: Develop advanced manufacturing capabilities that can create and test new devices, materials, and structures. Provide convenient design tools and microelectronic foundries for domestic firms and universities to offer accurate information and skilled labor. Provide efficient and sustainable operations for microelectronic devices and components.
-
Semiconductor packaging and heterogeneous design: Introduction of new materials, tools, designs, processes, assembly, and testing to make packaging activities more dense, productive, and reliable. Strengthen research and development and prototype design to increase production efficiency and reliability. Develop national facilities for heterogeneous packaging integration research and development.
Pillar 2: Strengthening the advanced manufacturing workforce: This section is relatively abstract, so I will skip it.

Pillar 3: Enhancing supply chain resilienceThis part is actually very well explained. The manufacturing supply chain in the US (and globally) is a complex ecosystem connecting raw material and component producers, logistics companies, integrators, and business support services. These interdependent entities design, manufacture, and assemble parts and final products, with the supply chain ecosystem creating and benefiting from product and process innovation. A critical area for improvement is the resilience of the supply chain and ecosystem.
Resilience refers to the ability to recover from unexpected shocks and includes visibility, agility, and redundancy, which can be enhanced through better management and advanced digital models. Lack of digital infrastructure and transparency makes our supply chains brittle, unable to adapt to shocks and pressures. Supply chain resilience will mitigate risks through interdependent systems that can withstand various external shocks, such as geopolitical conflicts, cyber attacks, energy interruptions, financial crises, natural disasters, and pandemics.
Three key goals:
-
Strengthen supply chain connectivity
-
Increase efforts to reduce manufacturing supply chain vulnerabilities
-
Strengthen and revitalize advanced manufacturing ecosystem
Strengthen supply chain connectivity
Strong collaboration between manufacturing enterprises can offer benefits such as cost reduction, increased innovation, and adaptation to supply chain disruptions. However, due to a large number of offshore and outsourced activities, cooperation within the industry is weak, and industry actions are isolated. Therefore, small US manufacturers lag behind large enterprises in technology investment, partly because dominant enterprises focus only on easily measurable costs such as unit price reduction. Small and medium-sized manufacturers suffer from technological backwardness, and their large customers are also affected. The implementation path of the goal is:
-
Foster collaboration within the supply chain: Promote public-private cooperation, enhance technological applications in manufacturing supply chains, and promote environmental emission reduction. Establish trust and transparency among supply chain stakeholders.
-
Promote innovation in the digital transformation of the supply chain: Efforts to realize the vision of a digital supply chain highway (digital backbone/digital twin) for critical sectors’ entire process, from raw materials to product lifecycle termination to waste recycling and reuse. Private and public sectors can use and analyze supply chains vertically and horizontally.
Increase efforts to reduce manufacturing supply chain vulnerabilitiesThe resilience of the supply chain is a top priority, and government agencies have begun to map, monitor, and analyze critical sectors of the supply chain. These efforts include examining all aspects of the product lifecycle, from raw materials for manufacturing and distribution to product maintenance and repair, and ultimately to disposal. Supply chain resilience depends on innovative manufacturing processes and advanced technologies. The pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in the supply chains of multiple industries, highlighting the urgency and necessity for evaluating and adopting new technologies, continuously improving the efficiency and effectiveness of logistics processes, reducing risks, and maintaining a highly skilled workforce. Research must objectively evaluate existing frameworks and processes to determine the lifecycle costs and value, and develop and monitor supply chain indicators, such as the cost of resilience value and lead time. By integrating logistics and supply chain management research from government and private sectors, stronger insights, trend analysis, and decision-making tools can be gained.
The implementation path of this goal is as follows:
-
Track information and products on the supply chain: Cultivate awareness, promote common data sharing, improve reporting, and advance standardized network security integration to help identify and quickly reduce risks. Develop tools and practices to help larger supply chain partners identify vulnerabilities and improve network security measures.
-
Increase supply chain visibility: Develop and implement supply chain mapping strategies, digital tools, and standards to increase supply chain visibility while protecting privacy, especially for companies and industries that provide input to many individual supply chains and have significant spill-over effects. This includes energy production, semiconductor or transportation companies and industries, as well as companies and industries that are of critical importance to national security such as climate and health safety. Use artificial intelligence systems and economic analysis to prioritize monitoring of critical nodes in order to provide advance notice of shocks and pressures faced by the supply chain.
-
Improve supply chain risk management: Improve risk management of external factors in the supply chain by improving predictions of decision consequences in uncertain environments. Consider testing the pressure exerted on the supply chain by these events and develop and promote technologies that help businesses measure, evaluate and improve their supply chain resilience.
-
Increase supply chain agility: Develop technologies to support adaptive manufacturing and shorten delivery times in cases where the supply chain experiences shocks and pressures.
Goal 3: Strengthen and revitalize the advanced manufacturing ecosystem
The ecosystem of advanced manufacturing is composed of various types and sizes of manufacturing enterprises. All of these enterprises play important roles in promoting innovation in the creation of new products, new processes, new business models, and new markets. Economic development plans should promote clustering programs around specific sector assets and successfully establish a manufacturing ecosystem. Collaboration organizations for advanced manufacturing innovation should focus on the dissemination, adoption, and commercialization of advanced manufacturing technology.
Summary: To summarize, based on what the US is currently doing, I will create some extensions according to this outline. From a top-level design perspective, we have no reason to believe that the US manufacturing industry will continue its previous outsourcing strategy under global competitive pressure. People are forced to come out, and so are enterprises. Countries also have development pressure and resilience. How we view the changes in the external world is particularly important.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.