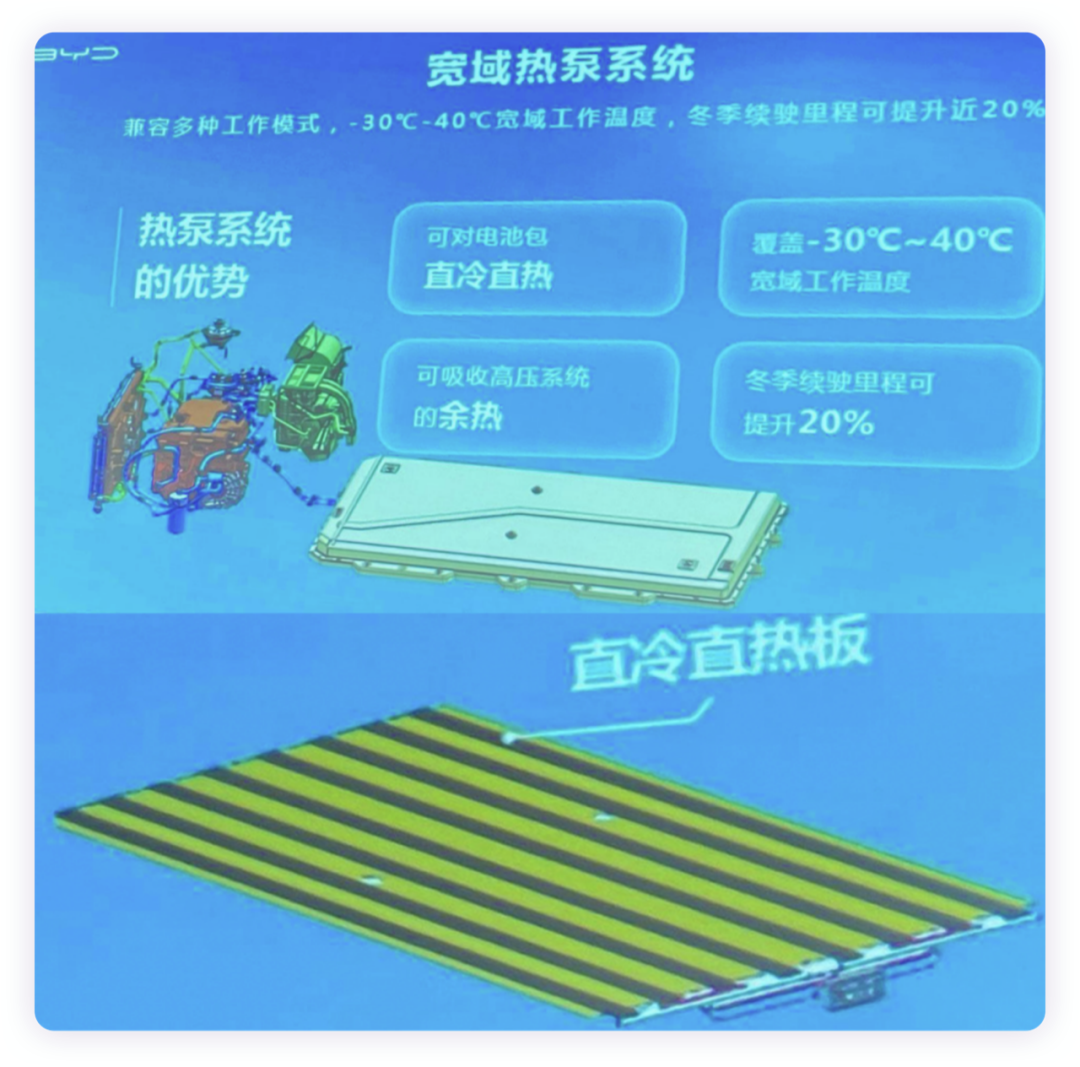
In the field of thermal management, BYD has made attempts on the Dolphin E3.0 by integrating heat pump technology. On the blade battery, the direct cooling and heating technology (direct cooling and heating plate is covered on the blade battery), which uses refrigerant instead of traditional coolant, is also adopted just like the PHEV battery, directly cooling and heating the battery (with reserved film heating).
In terms of design, this thermal management system is similar to Tesla’s integrated valve island scheme, with the refrigerant circuit being extensively integrated. The valve island structure integrates most of the control components of the refrigerant circuit, which is divided into three main parts: the electric compressor, the front-end module, the thermal management integrated module, and the in-car condenser and evaporator, which are controlled by software with the electric drive system.
The battery size is quite large.
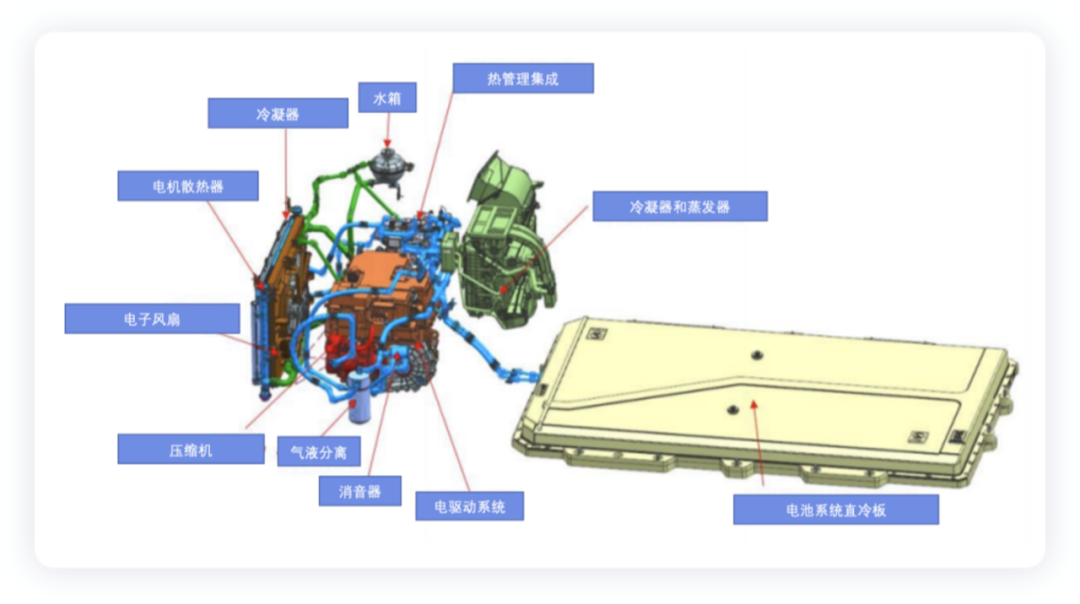
Components of the Vehicle Thermal Management System
From the perspective of composition, this system mainly includes battery direct cooling and refrigeration (internal direct cooling plate) and electric drive heat dissipation (motor radiator). Therefore, the entire system revolves around the refrigerant system, coolant system, and coolant circuit exhaust pipe.
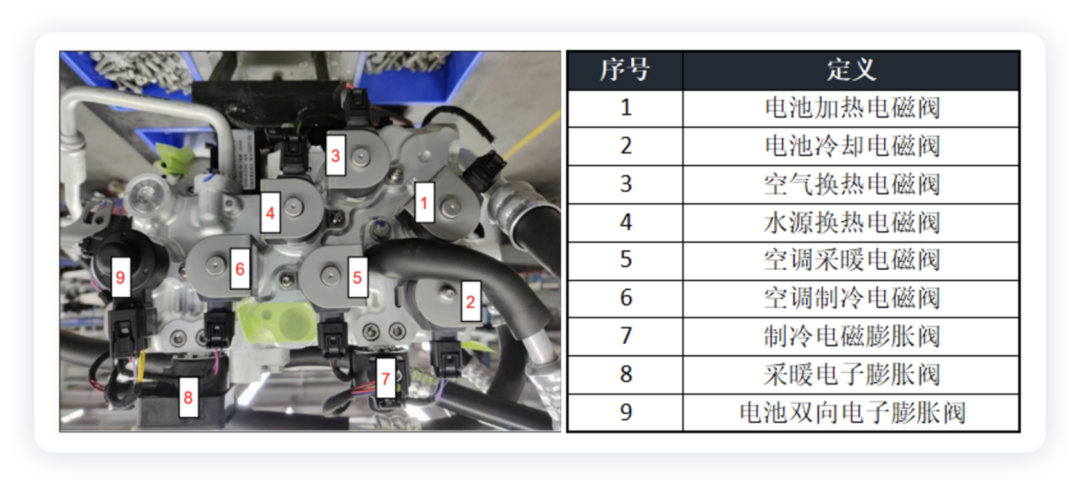
The refrigerant architecture is complex, with battery direct cooling and heating, 6 solenoid valves and 3 electronic expansion valves in the system. As shown in the following figure, this integrated valve body mainly includes battery heating, battery cooling, air heat exchange, water source heat exchange, air conditioning heating, air conditioning refrigeration, and expansion valves 7-9.
Thermal Management System Operation Mode
- Air Conditioning Heating
The heating electronic expansion valve and the air conditioning heating solenoid valve are open, including low temperature driving and idle conditions. When there is a heating demand in the passenger compartment, the heat pump air conditioning system starts the electric compressor, absorbs the residual heat of the high-pressure system for direct refrigerant heating, and can start the PTC fan heater of the HVAC assembly.
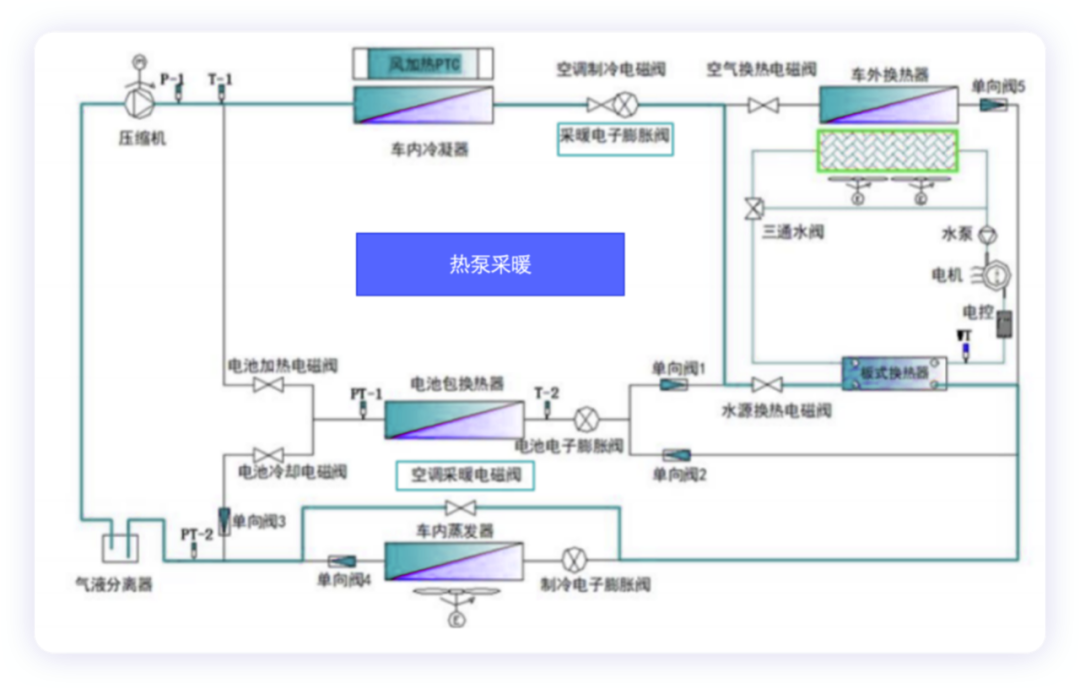
- Battery HeatingThe battery is a crucial component. BYD uses a hot pump air conditioning compressor and high-pressure heating system to directly heat the refrigerant to the battery pack under two conditions: low-temperature driving and idle.
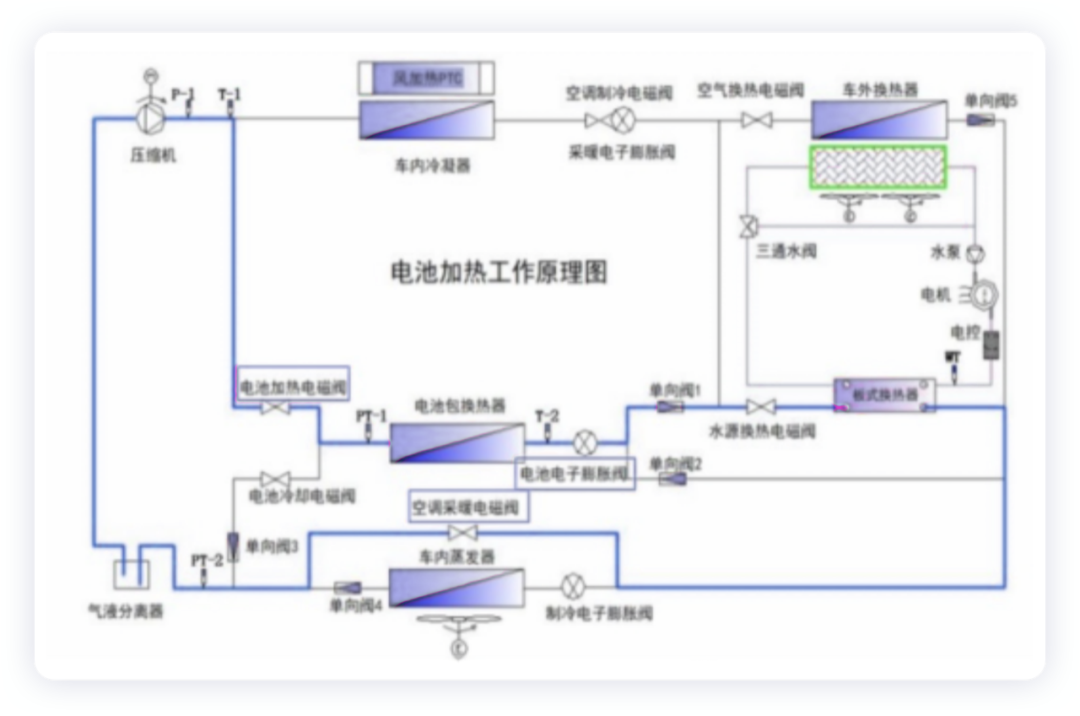
- Heating the battery with the hot pump air conditioning system
To provide heating for the passenger cabin and the battery, the hot pump air conditioning system turns on the electric compressor to absorb the excess heat generated by the high-pressure heating system to directly heat the refrigerant and battery, and when necessary, turns on the PTC wind heater of the HVAC assembly.
Note: the battery electronic expansion valve and heating electronic expansion valve operate; the battery heating solenoid valve and air conditioning heating solenoid valve are open.
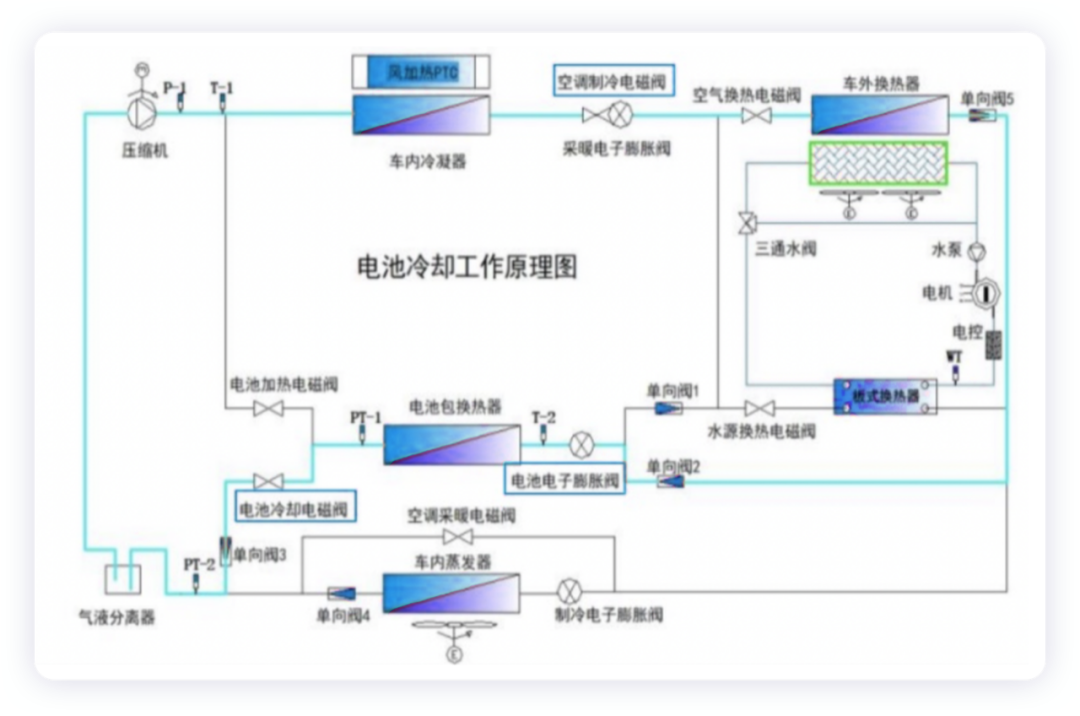
- Battery cooling (fast charging condition)
When charging the battery with high power, to keep the battery at the optimal working temperature and avoid overheating, the charging power must be restricted. The hot pump air conditioning system uses refrigerant to directly cool the battery pack.
Note: the battery electronic expansion valve operates, the battery cooling solenoid valve and air conditioning refrigeration solenoid valve are open.
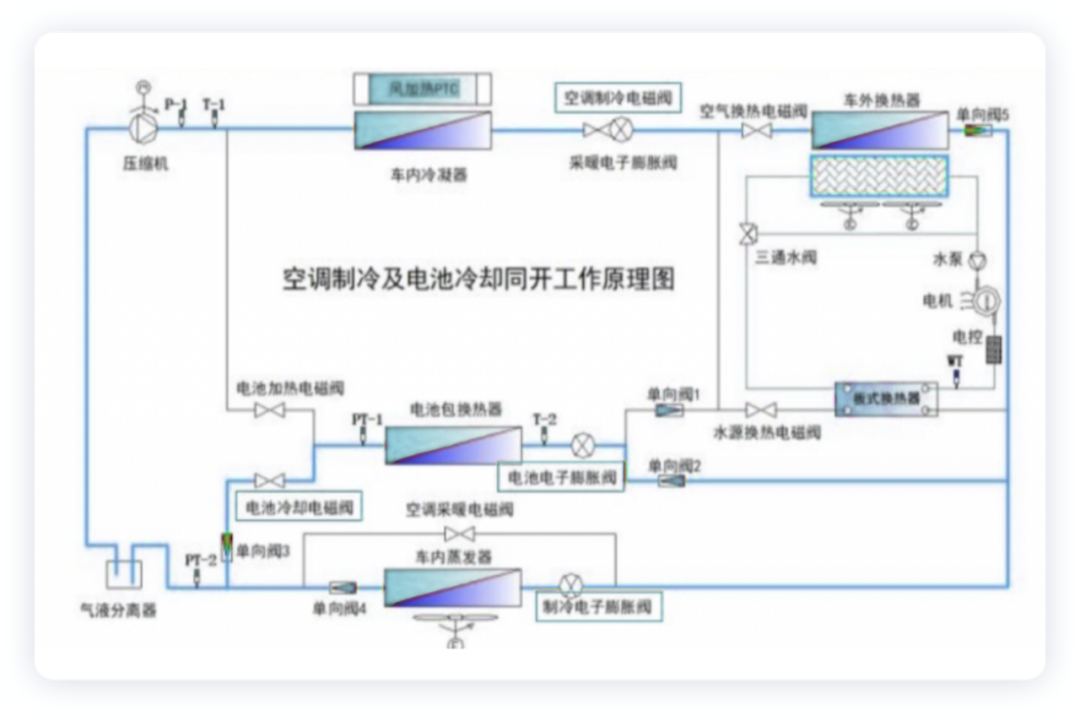
- Air conditioning refrigeration and battery cooling (charging, idle, and driving conditions)
When there is a need for air conditioning refrigeration and battery cooling, the hot pump air conditioning system uses refrigerant to directly cool the battery pack and the passenger cabin to ensure the battery pack can charge under the optimal working temperature.
Note: the battery electronic expansion valve and refrigeration electronic expansion valve operate; the battery cooling solenoid valve and air conditioning refrigeration solenoid valve are open.
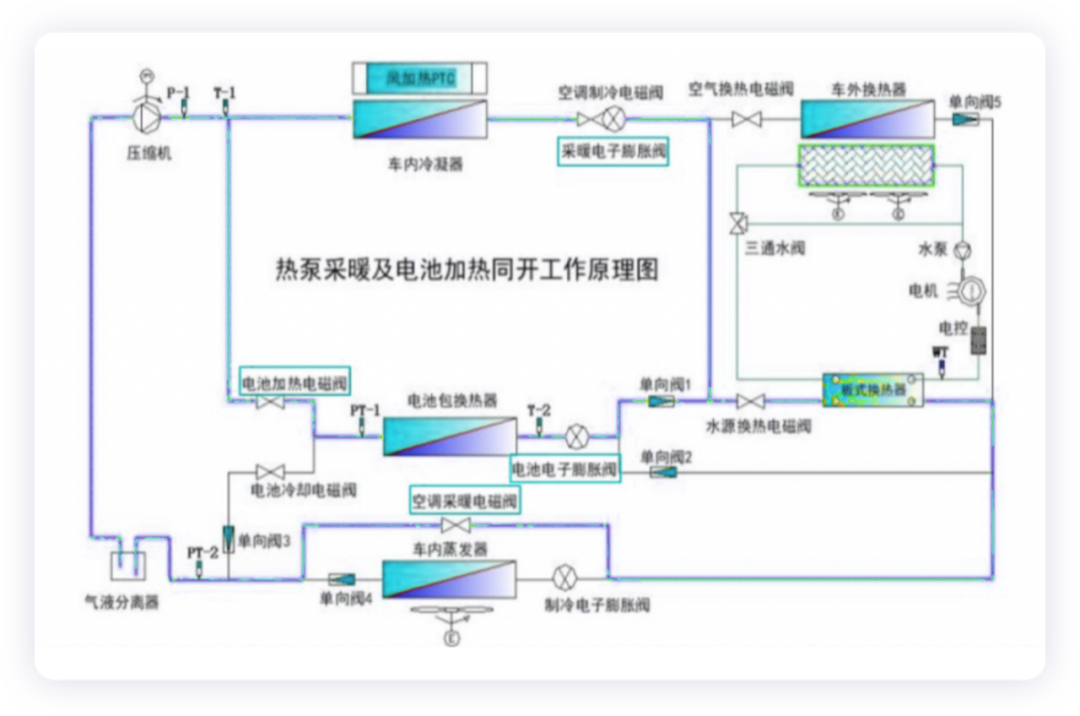
- Air conditioning heating + battery cooling (charging and driving conditions)
When there is a need for air conditioning heating and battery cooling, the hot pump air conditioning system uses refrigerant to directly cool the battery pack and the passenger cabin to ensure the battery pack can charge under the optimal working temperature.
Note: the battery electronic expansion valve operates; the heating solenoid valve and battery cooling solenoid valve are open.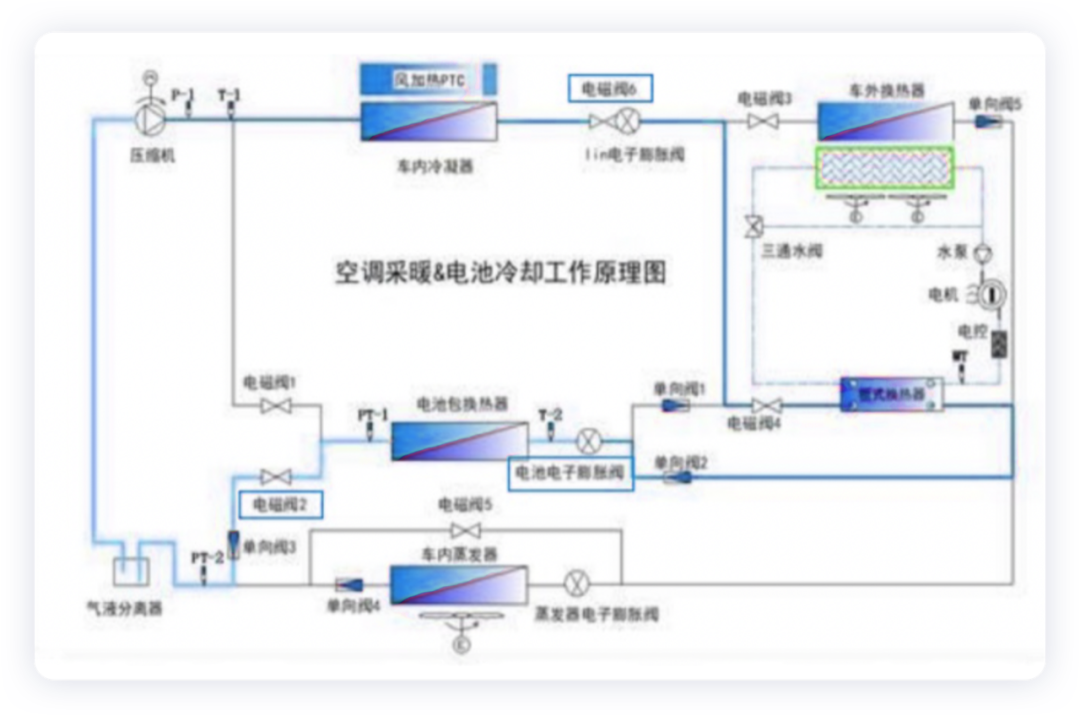
Conclusion: Overall, this wave of heat pump integration mainly softwareizes the demand, different refrigeration needs on different A0-B platforms, especially with different batteries, different electric drive systems, and different heating and cooling demands in the passenger compartment. To make this system work well, a lot of software development and debugging are needed.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
