Author: Zhu Yulong
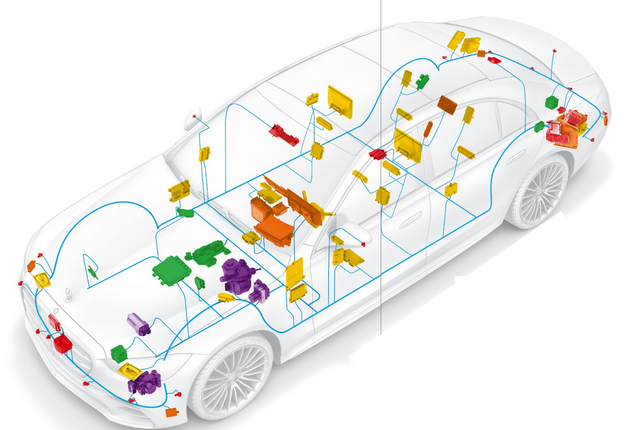
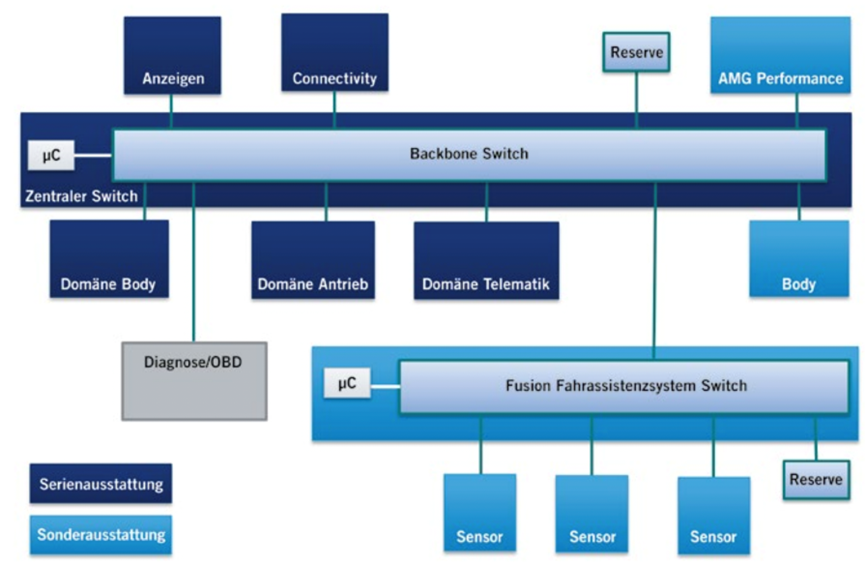
Traditional automotive companies, under the Domain architecture, have replaced CAN networks with Ethernet backbone networks, which revolve around two major components: remote information systems and automated assisted driving systems. With the increasing number of software components in the entire vehicle, following the original design, the demand for communication bandwidth of the backbone network is constantly increasing.
With the help of automotive Ethernet, the concept of service-oriented communication is entering the vehicle network (SOME/IP, C/S communication), which is a necessary path for the expansion of automotive software functions and the increase of flexibility.
Car Ethernet inside STAR 3
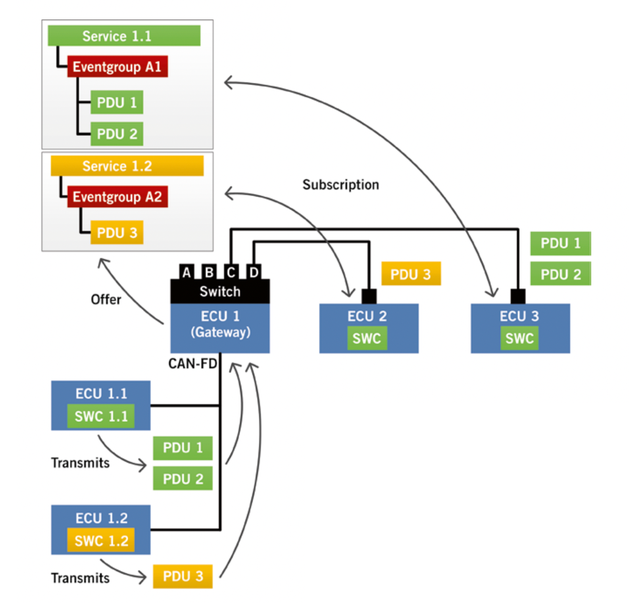
Signal-oriented communication is reaching its limit (transmitting signals). For example, if node B needs certain information from node A, node A directly packs the signal with other signals into a message and sends it to the bus. After receiving it, node B can obtain the signal, as shown in the left half of the figure below.
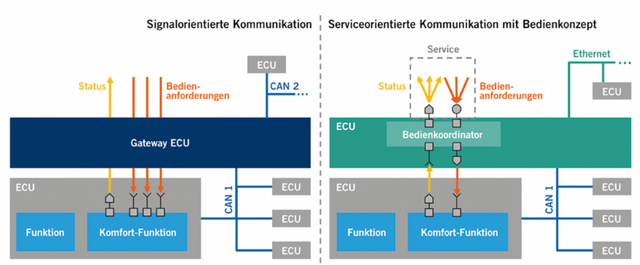
With the help of automotive Ethernet, service-oriented communication is entering the vehicle network (SOME/IP, C/S communication), mainly to flexibly handle more and more requirements, thereby reducing complexity and dynamics.
C/S creates a well-defined interface as a representative service environment, and software components are connected through middleware called the “service bus”. The middleware mediates between service providers and service consumers, so it can achieve loose coupling between service roles in the system. It is more flexible than the original software architecture, has higher reusability, and better integration of new service components. The middleware regulates communication between service providers and service consumers, including establishing this communication. It usually defines the serialization of data in Ethernet messages, and the serializer determines how to serialize the data into a serial bit stream on the sending side and how to deserialize it on the receiving side.
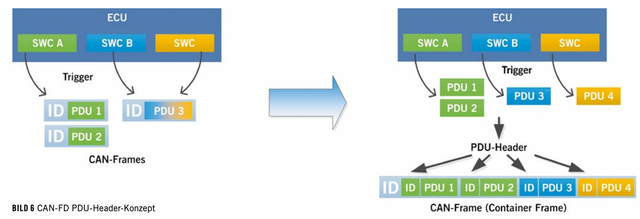
SOME/IP service discovery protocol is the core function of SOME/IP and has the following main tasks:
(1) The SD protocol manages the dynamic search for functional entities and can configure their access rights.(2) The requirement of SD protocol management is to send event messages to the network and send event messages to receivers who need them.
(3) Check whether the service instance is running.
In order to let the client know which services are currently available, SOME/IP-SD provides two mechanisms. Offer Service allows the server to provide the services it can offer to the network on which it is located. Find Service allows the client to request available services.
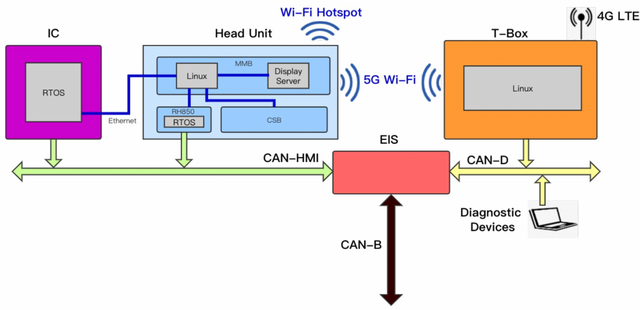
Information Security Mechanism
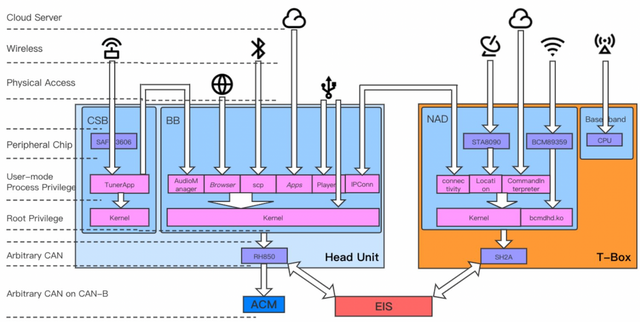
Later, I carefully thought about it, in terms of integration considerations, Europe generally still relies on traditional information security models. Due to the entire software development cycle and the complexity of information security management, it is quite necessary to have a layered approach.
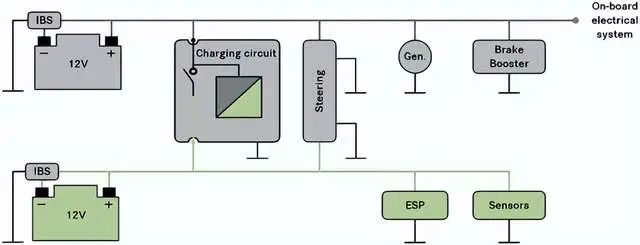
Currently, from the perspective of the 12V power supply, automakers tend to focus on the dual 12V battery model, which is divided into different power backup mechanisms. A balancing unit is formed between the power sources to schedule between them. In other words, even if two batteries or one charging unit fail, the overall performance impact is limited.
Conclusion: For the software and communication parts, I just have a general idea and provide them for your reference.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.