Author: Zhu Yulong
My friends and I have been closely following the overall structural design of the 4680 battery. There are also many online friends who have asked me to confirm a few issues:
-
How is the top-level water-cooled plate arranged?
-
How is the busbar processed?
-
How is the exhaust channel of the battery cell designed: upward or downward spray?
After collecting information from Mr. Munro and some online visits, I want to make a video and write down my thoughts.
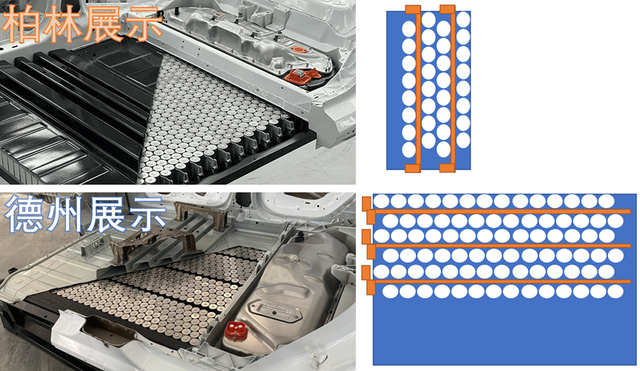
By carefully comparing the 4680 battery systems released in Texas and Berlin, two different layouts are sorted into two modes: horizontal and vertical, each corresponding to different water-cooled plates installed in different directions of the vehicle’s X and Y axes.
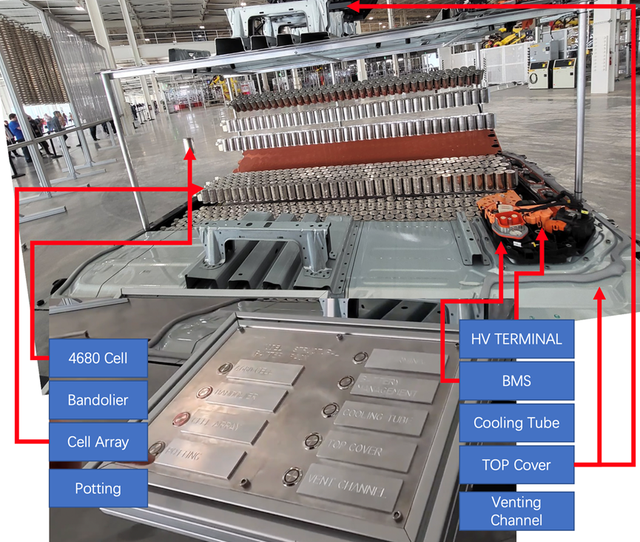
Battery Display Area
In the battery display area, Tesla suspended different parts separately, including:
-
4680 battery cell
-
4680 battery array
-
Bandolier (unclear)
-
Potting (unclear)
-
High-voltage terminal (similar to the entire high-voltage interface)
-
BMS (lights up in the video)
-
Exhaust channel
-
Top cover
To facilitate understanding, I have reorganized this structure as follows:In Tesla’s own video, we saw the structure of a battery array where the bottom battery is supported by insulated plastic. As shown in the well-prepared video, we can see that there is a certain gap in the design of the base. From a manufacturing perspective, this achieves the rationality of cell production to battery array assembly, and the cell array can be directly stacked into the battery pack through mechanical handling.
The leaked photo in the figure below actually matches the horizontal design that appeared in Berlin, and I understand that there is no significant difference in the busbar connection between the two designs.

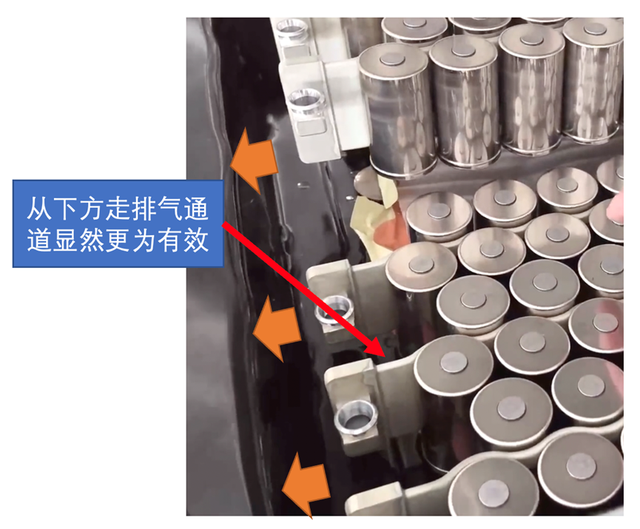
From the design concept, during the CTC stage, the cell’s venting needs to be downward, and the water-cooling plate is placed on top, which has the advantage of being able to isolate the top. From the actual design concept, this water cooling plate is more aimed at the increase in 360kW supercharging and current cell inner resistance. At the beginning, there might not be this component, where single-side cooling could be compatible with the current fast charging power. As the cell’s internal resistance decreases, it is easier to remove this water-cooling plate and put it on top.


In fact, this battery pack is designed with four vent valves, so there should be a larger venting channel than the previous 21700. The upper area directly interacts with the vehicle occupants. Once heat rises, it can cause panic for the consumers.

Structural characteristics of 4680 battery
In the battery system, I think Deloitte’s judgment is very interesting. But the ways of using casing for prismatic, blade, and cylindrical cells are different. The first two can achieve 200-300Ah, while the latter only has 25Ah, corresponding to 100-120 cells for a 100kWh battery pack. Therefore, in the structural design, clever use of vent design, grouping cells into arrays through vent channels, and integraing with low-density adhesive during assembly can achieve significant tactical value.
Summary: I understand that cylindrical batteries have great flexibility in design, and the water cooling design can be added or removed, the overall cost of the entire pack is not high, and there is room for improvement.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
