In the first half of 2020, Tesla officially equipped all its models with HW 3.0 hardware, marking the beginning of the “3.0 era” for Tesla. But only a few months later, we began to see leaks about HW 4.0.
On February 16th, Green, a Twitter account known for leaking Tesla hardware information, once again brought us high-definition photos of the HW 4.0 hardware, allowing us to get a closer look at Tesla’s next-generation hardware platform.
What makes HW 4.0 better than HW 3.0?
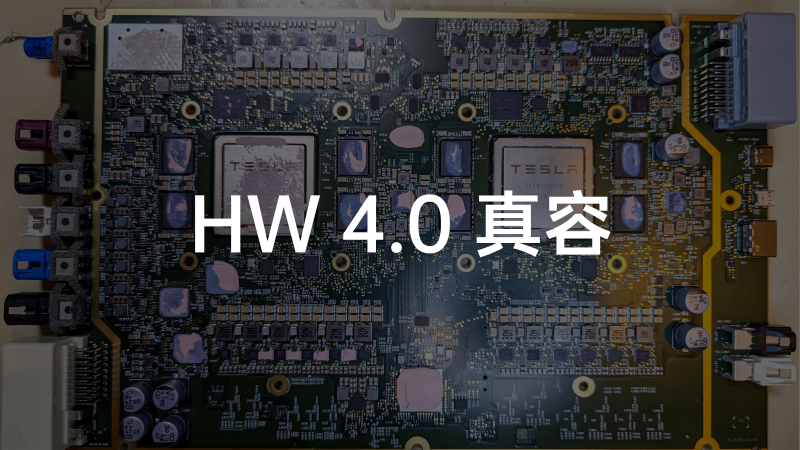
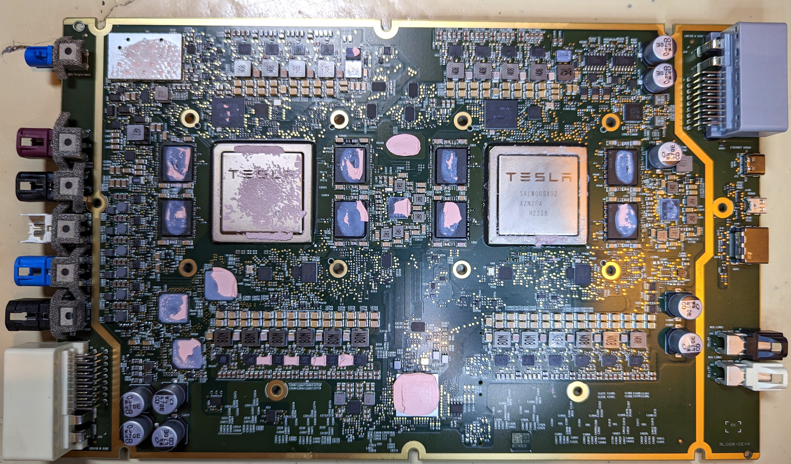
Green obtained the complete computing hardware module, and the above picture shows the dismantled HW 4.0 computing core motherboard, while the two pictures below show what HW 4.0 looks like before dismantling. From the appearance, it can be seen that HW 4.0 is significantly larger than HW 3.0 in terms of computing hardware, which has now been upgraded for MCU performance.
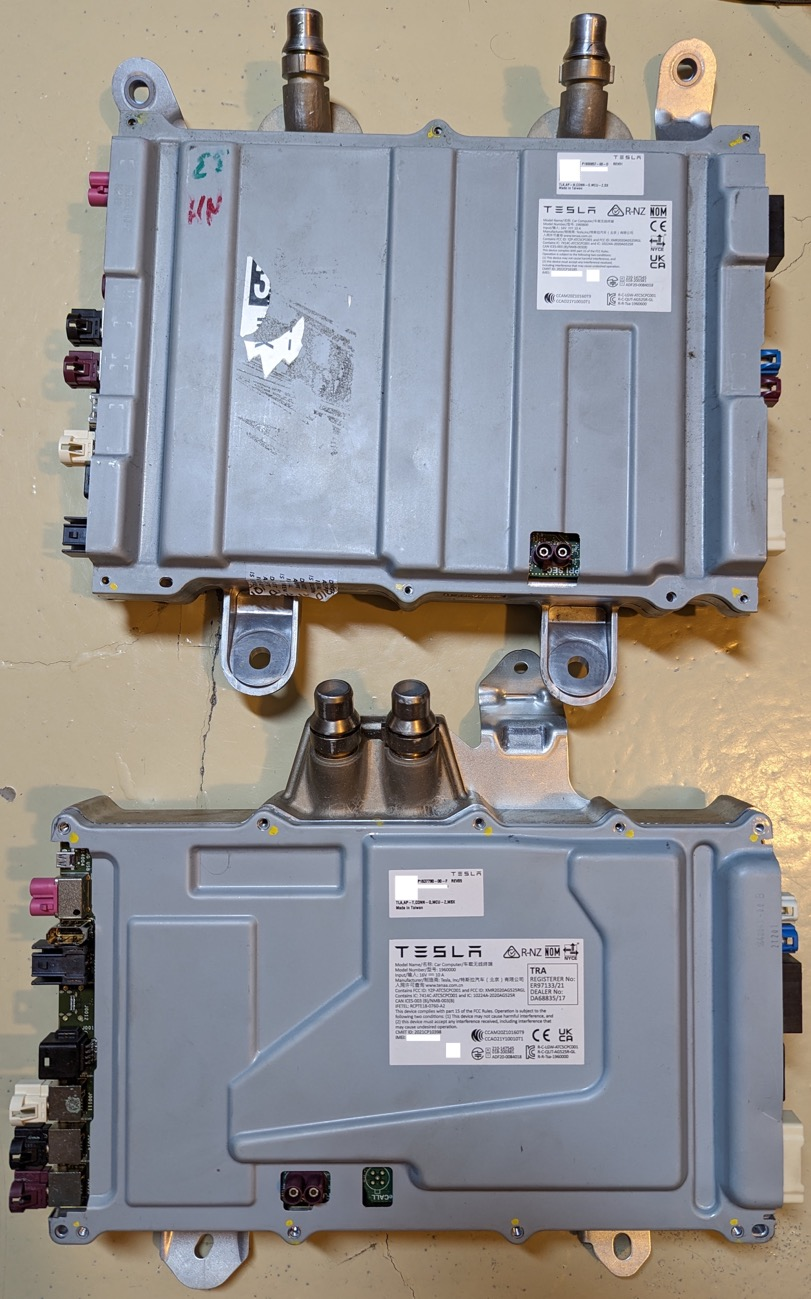


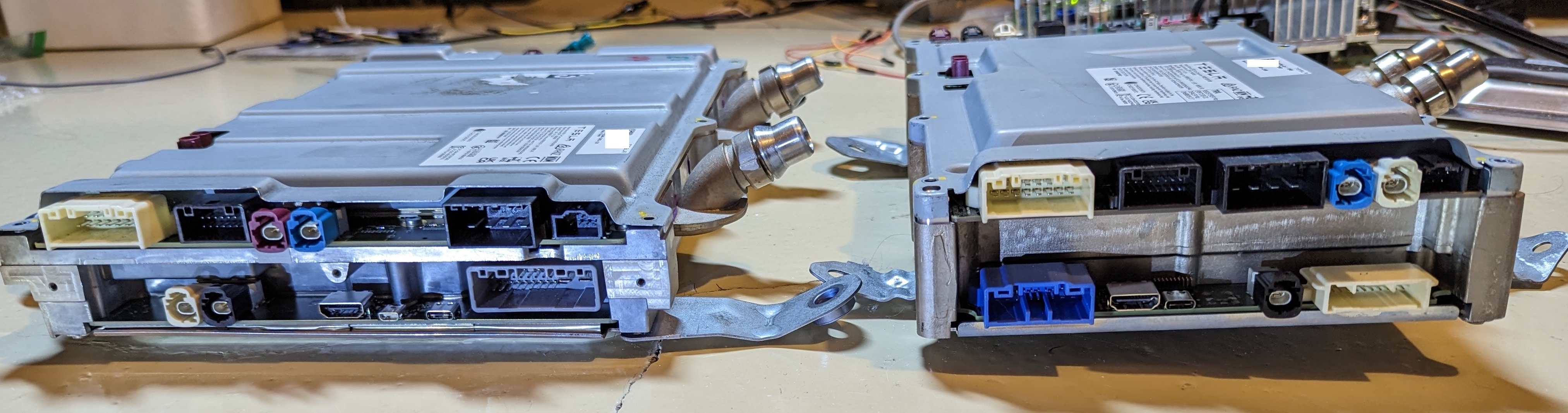
Combined with the interface comparison of the two hardware sets below, it is not difficult to understand why Musk stated that due to the high cost and difficulty of the upgrade, existing models could not be upgraded to HW 4.0. The completely different sensor layout makes it impossible to change the peripheral sensor layout of existing models, although this hardware can be fitted into them.
The following are two comparisons of the front and back of the HW 4.0 and HW 3.0 motherboards, showing the significant differences in their circuit layout.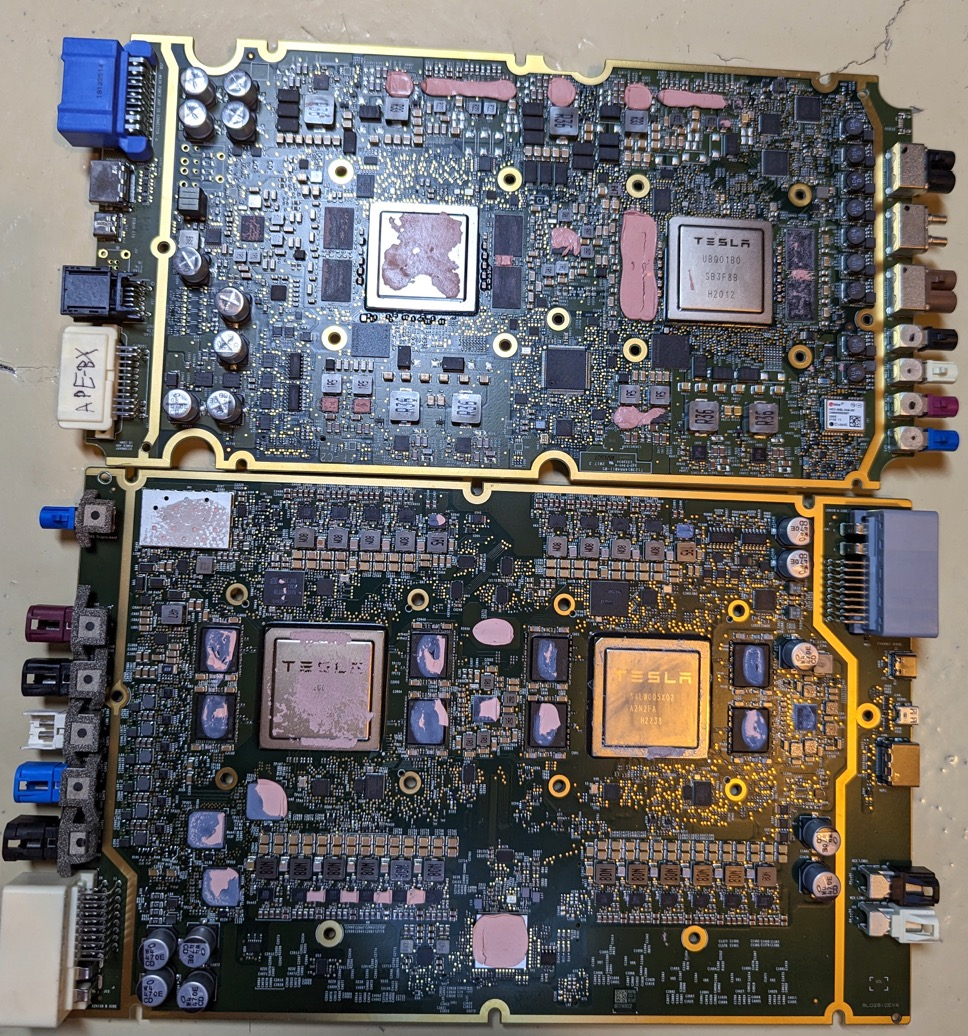
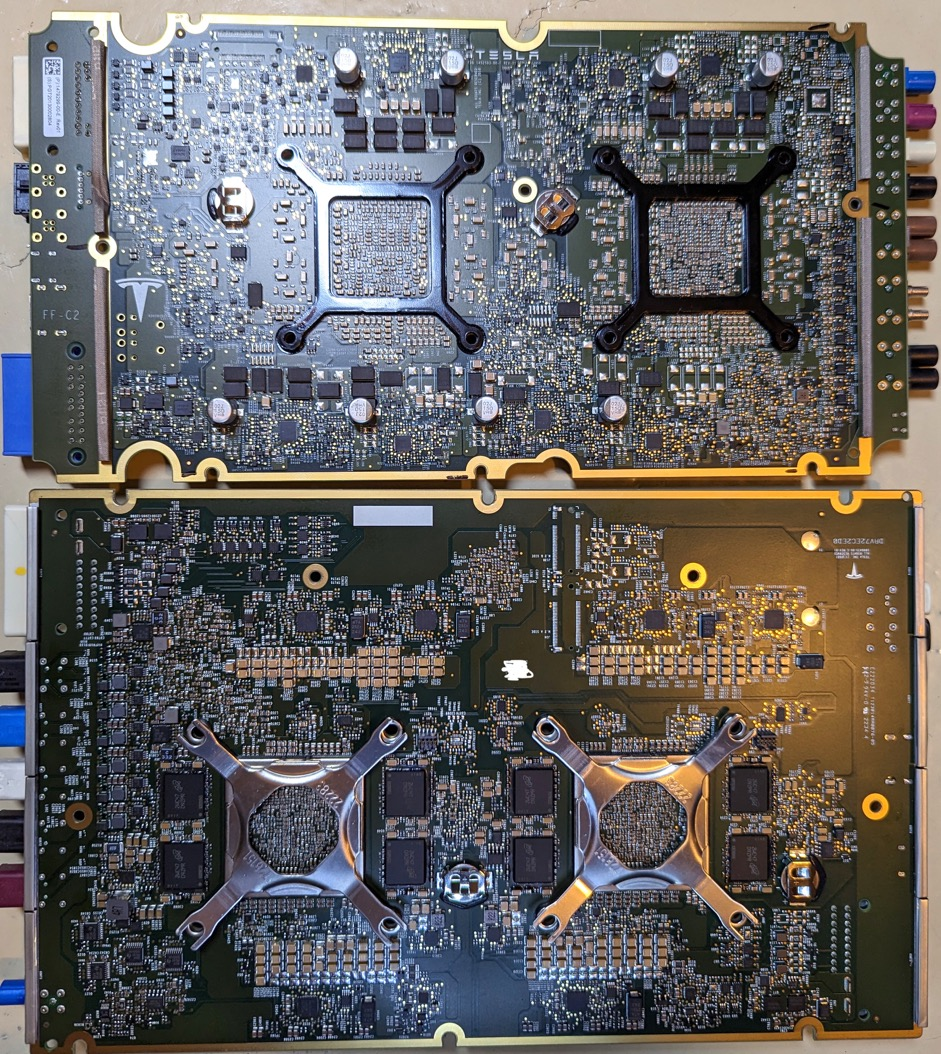
Firstly, the most obvious difference with HW 4.0 is that the GPU is no longer a separate small board like in HW 3.0, but is directly integrated onto the main board with the CPU. This increases the integration level of the entire main board and frees up space for autonomous driving related chips, allowing for more flexibility in the design of the main board.
In terms of MCU, HW 4.0 uses exactly the same hardware as HW 3.0:
- Same model of AMD CPU and GPU;
- 16 GB RAM;
- 256 GB NVMe solid-state flash storage;
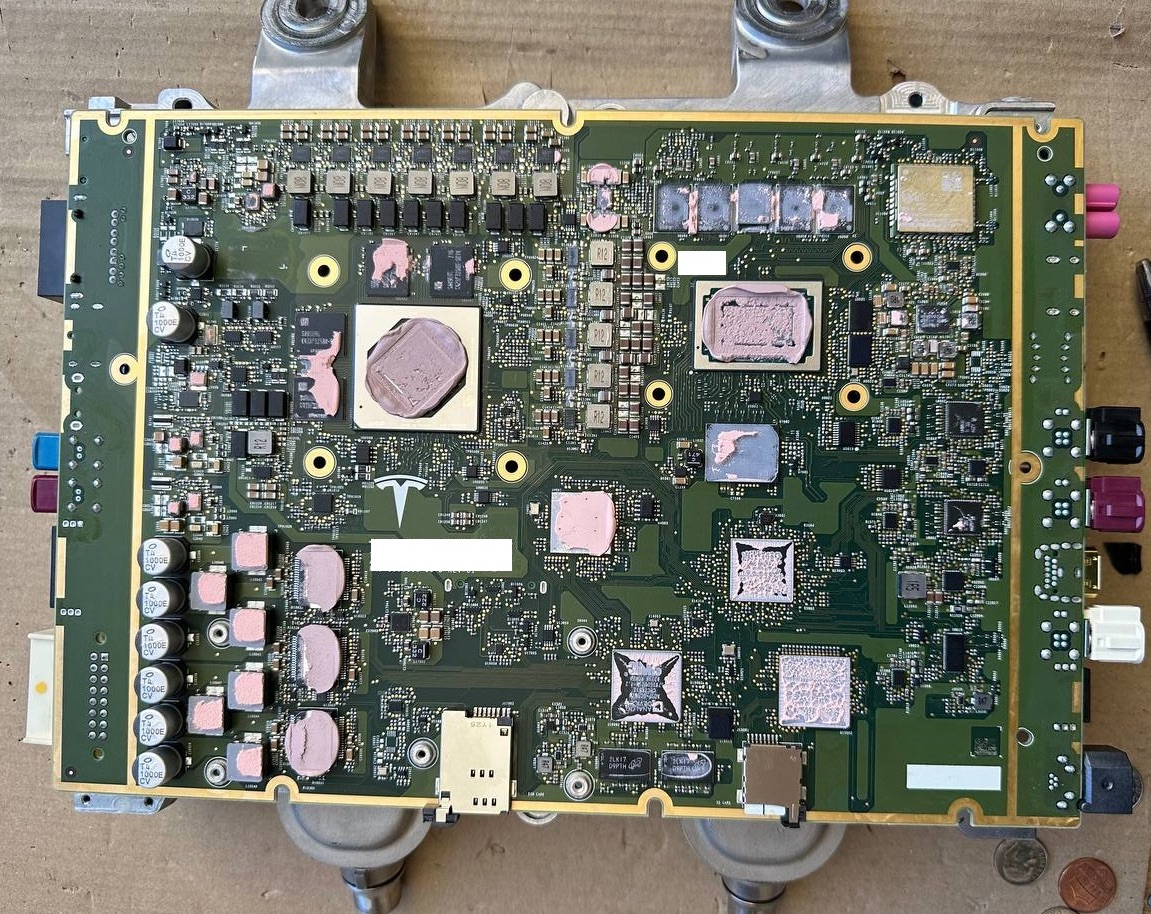
Perhaps due to Jim Keller’s departure, the brand new FSD chip seems to have had to “squeeze toothpaste.” The chip is still based on Samsung’s Exynos architecture, with the number of CPU cores increased from 12 to 20, with a maximum frequency of 2.35 GHz and a low-power frequency of 1.37 GHz. The number of TRIP cores has increased from 2 to 3, with a maximum frequency of 2.2 GHz. The expected total computing power will be between 300-500 Tops.
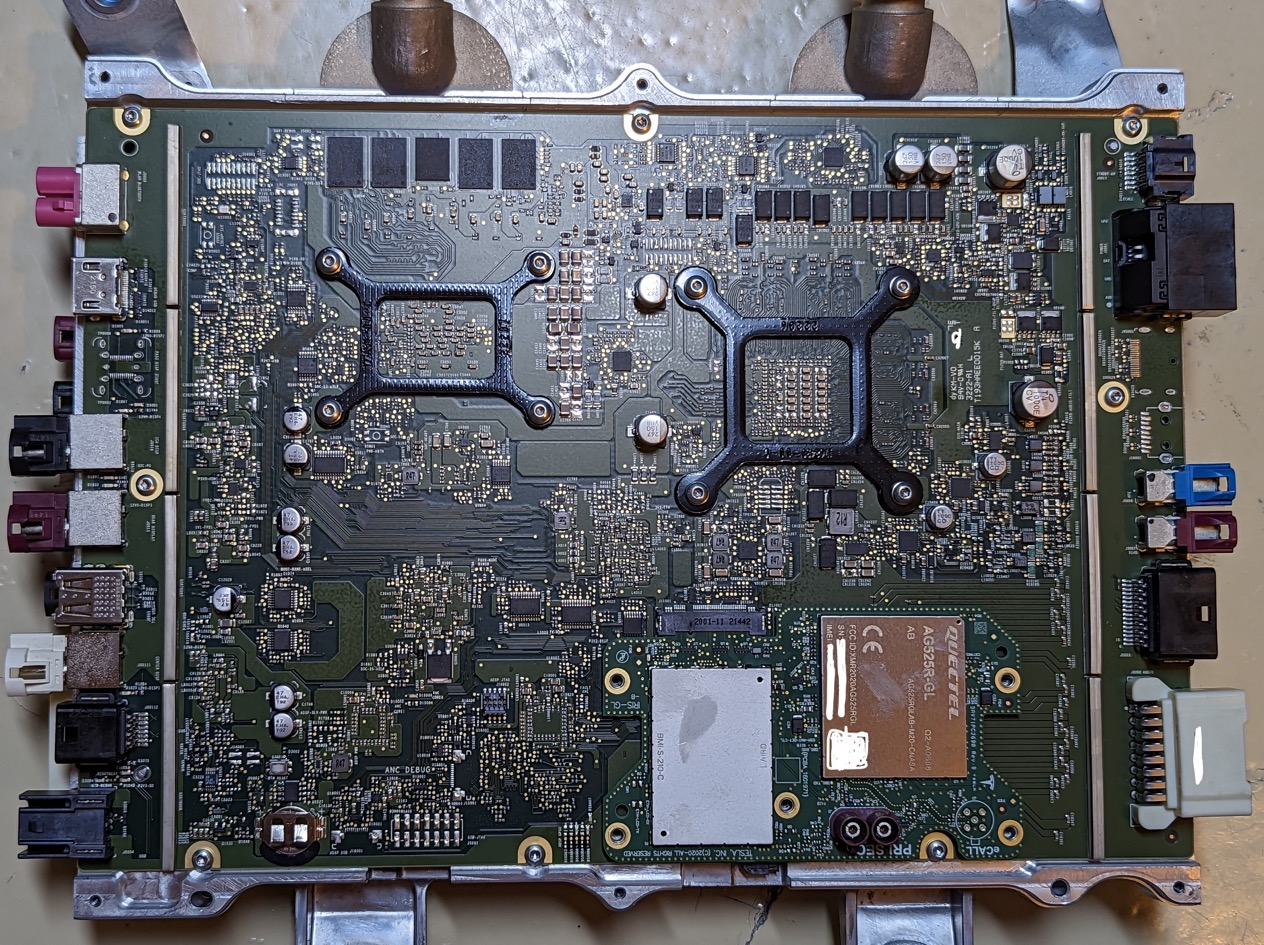
 HW 4.0 provides two FSD chips for each car, which double the computing power and one of which can serve as redundant computing power. However, currently, HW 4.0 cannot achieve true redundancy. If one side’s power fails, the data connection of the entire system will still be affected. The entire PCB presents a symmetrical state, with the same power interface on both sides and two MCU connection modules.
HW 4.0 provides two FSD chips for each car, which double the computing power and one of which can serve as redundant computing power. However, currently, HW 4.0 cannot achieve true redundancy. If one side’s power fails, the data connection of the entire system will still be affected. The entire PCB presents a symmetrical state, with the same power interface on both sides and two MCU connection modules.
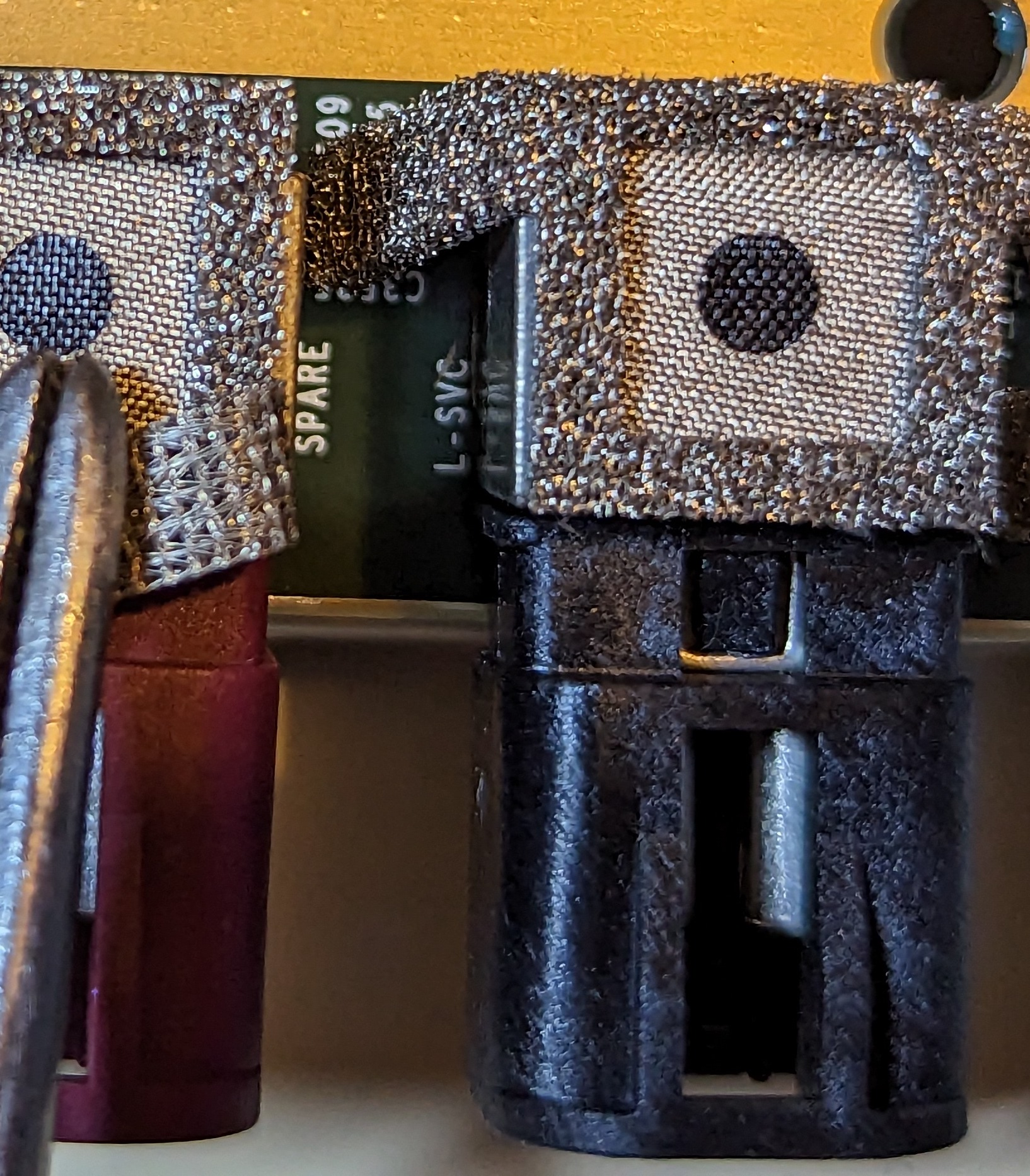
This time, HW 4.0 can support 12 camera inputs, but it can only support 11 cameras in reality, as one position is reserved for a spare camera.

The position of the camera is marked on each interface. From the picture, we can see F-SVC, L-SVC, R-SVC, L-FF-Rear, and R-FF-Rear.
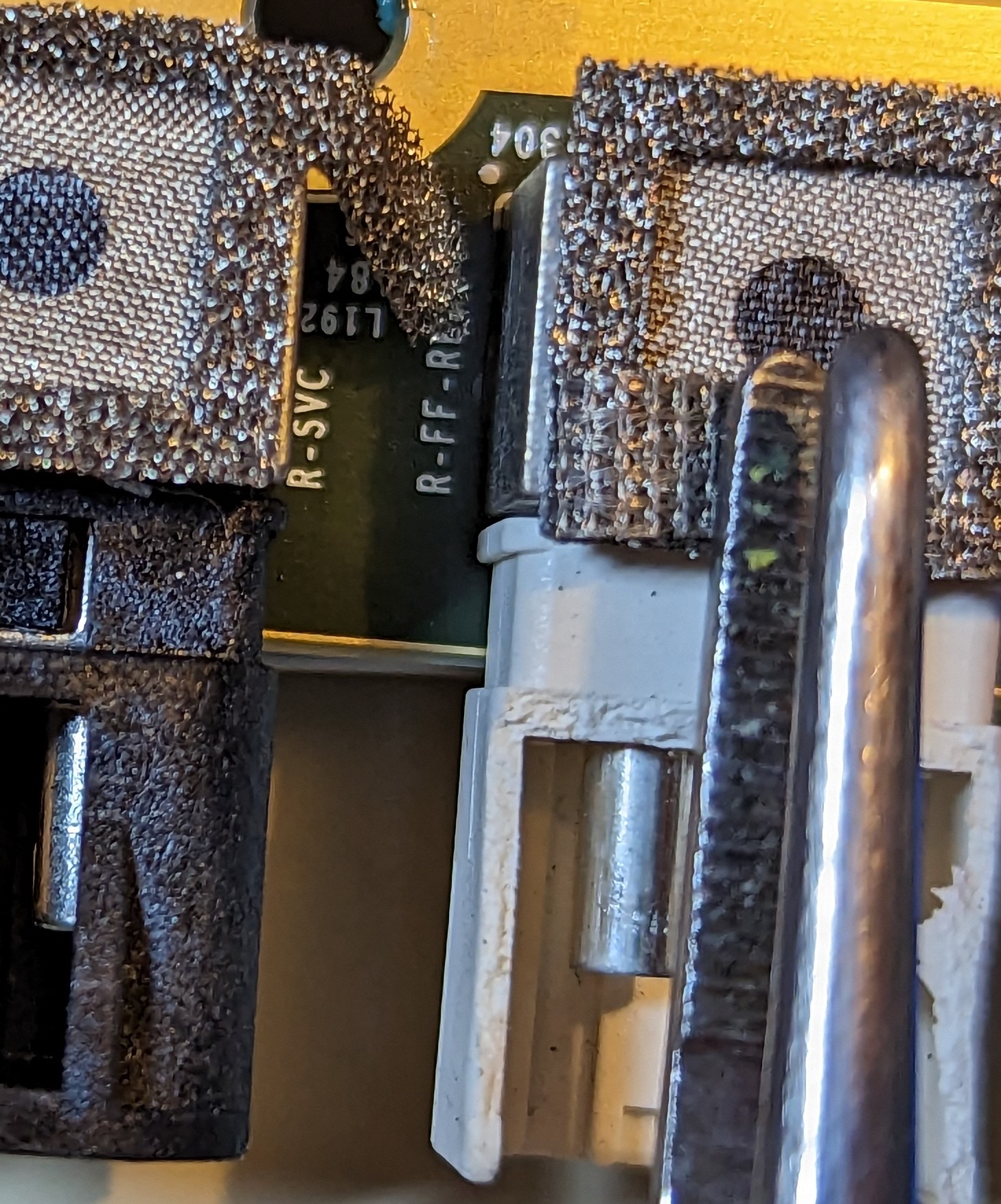
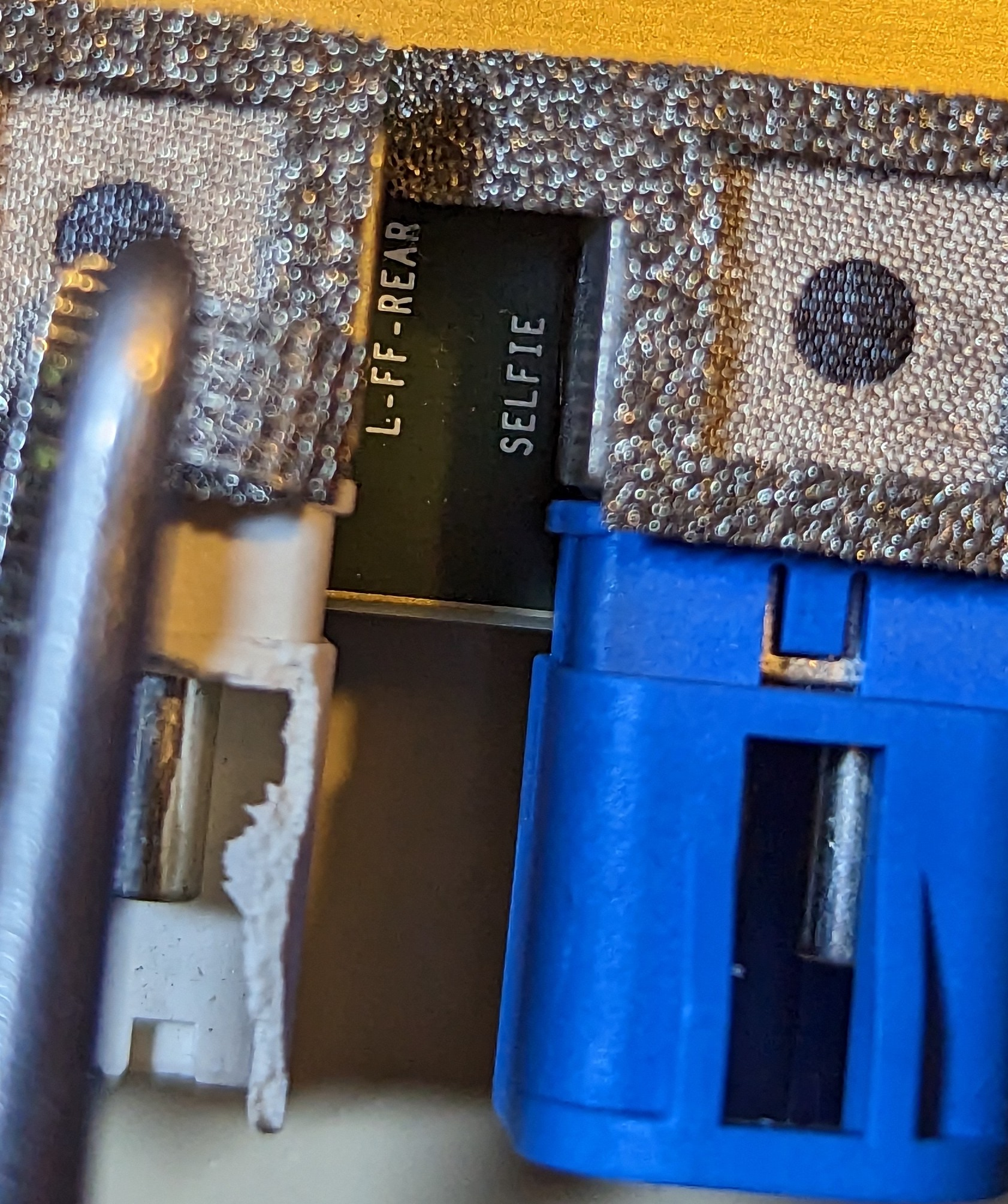



According to the spyshot of the modified Model 3 taken previously, the front camera has changed from the original three-eye scheme to a two-eye scheme. As per previous leaks, HW 4.0 uses a 5.4 million-pixel, 2,896 x 1,876 resolution front camera, while HW 3.0 only has a 1.2 million-pixel camera. The addition of a higher-pixel camera means that Tesla no longer needs a telephoto camera for forward perception. In addition, the car still has a DMS camera to detect the driver.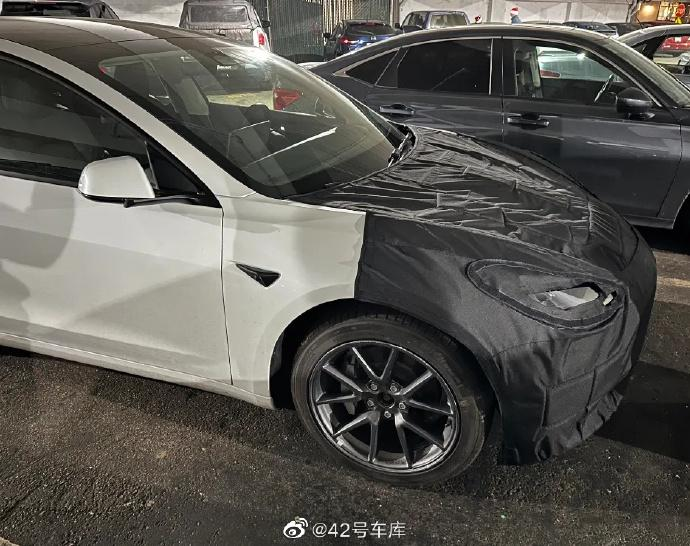
In addition, Tesla has added an SVC camera. According to Tesla’s EPC (Electronic Parts Catalog), the SVC code corresponds to the vehicle’s bumper. Coupled with the black spot on the top of the headlight that appeared in the spy photos earlier, it can be basically confirmed that Tesla has added a blind spot camera at this position. With these two cameras, Tesla can effectively solve the blind spot problem in the left and right front parts of the car, and even truly achieve a 360-degree panoramic view.
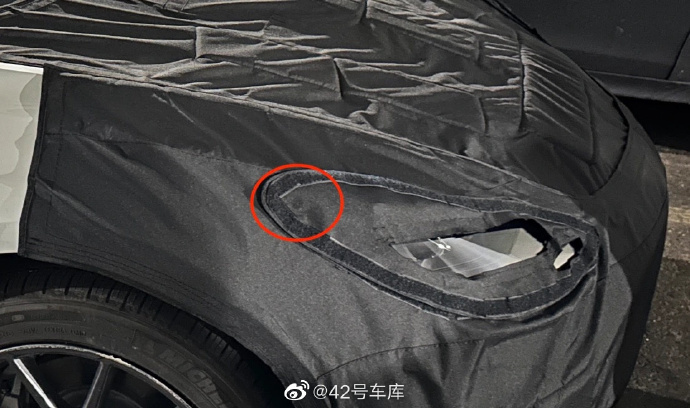

Tesla has also updated the GPS module and uses a more powerful and accurate triple-frequency GPS antenna. This was mentioned in the declaration documents for Europe. The new positioning module not only enhances the ability of GPS positioning but also strengthens other global positioning system standards.
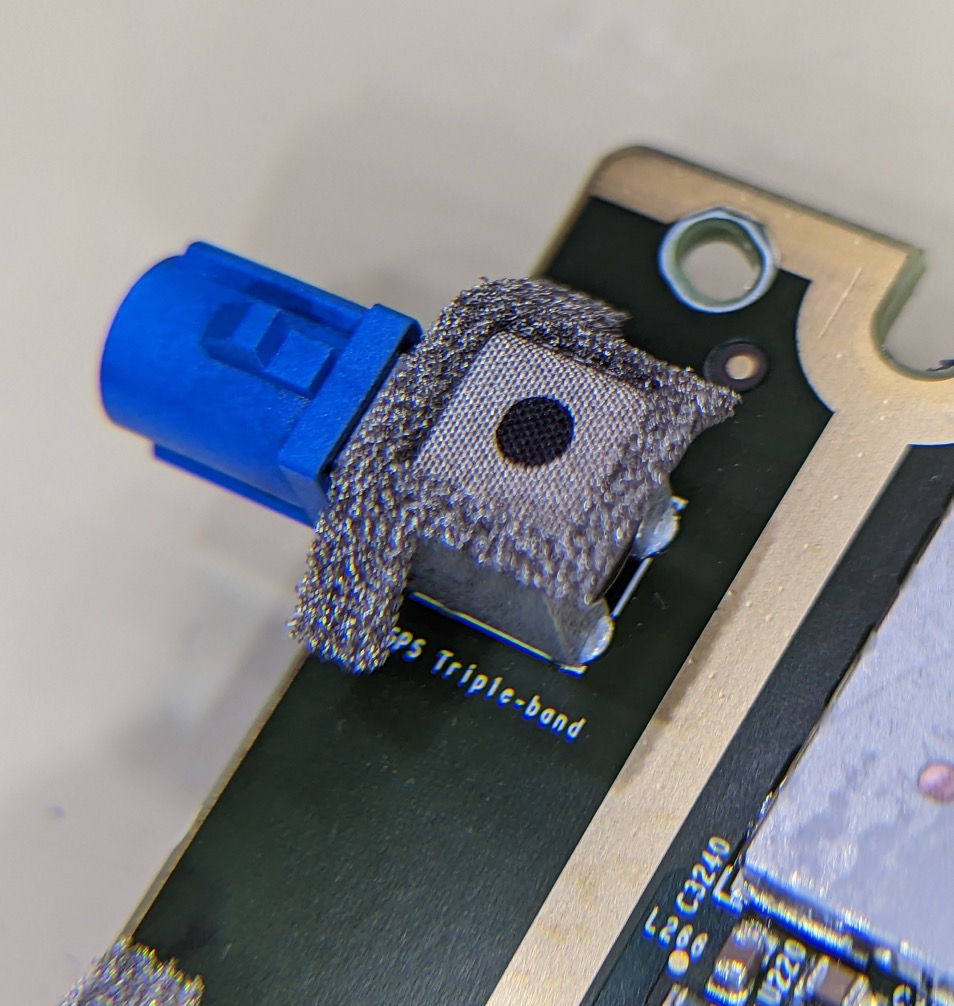
The heavyweight news is that in the software interface exposed by Green, a forward-facing radar with the code name “PHOENIX” has appeared, and it is equipped with a heater! Just a few months ago, Tesla removed the ultrasonic radar on the Tesla Model 3 and Model Y sold in several overseas regions, leaving only eight visual cameras.
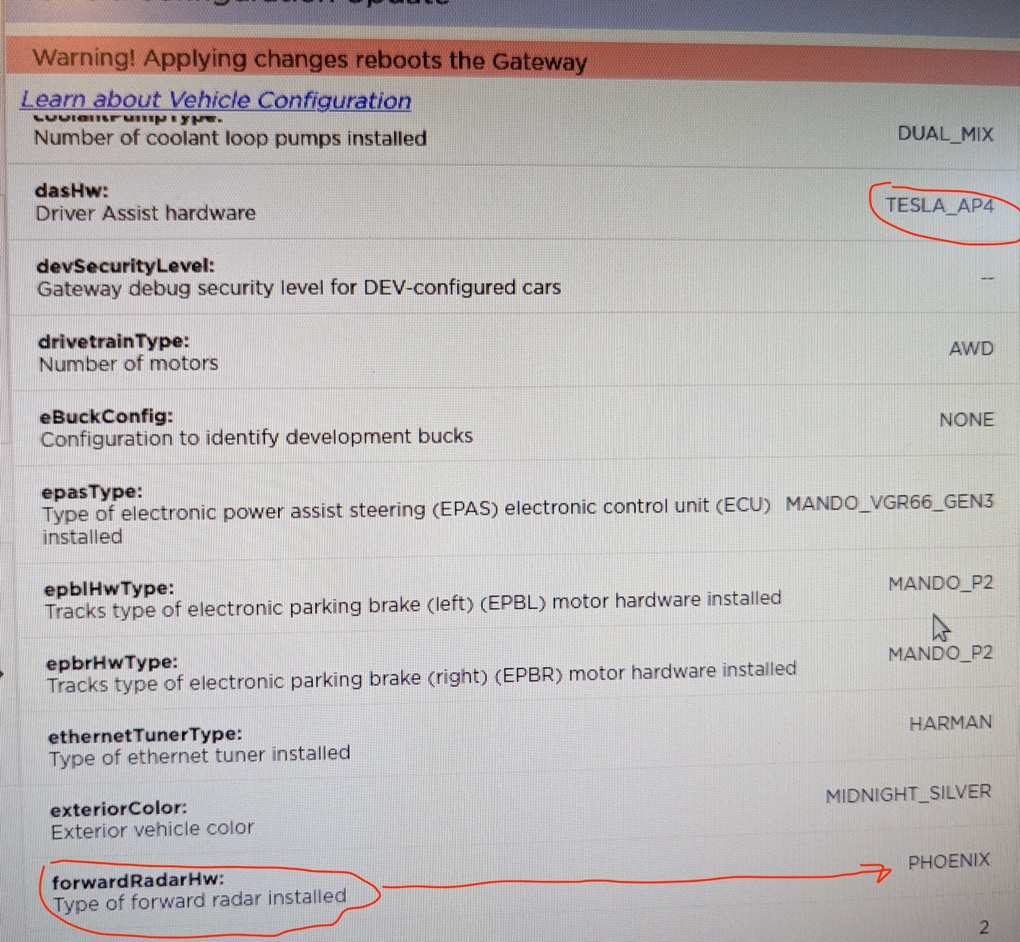
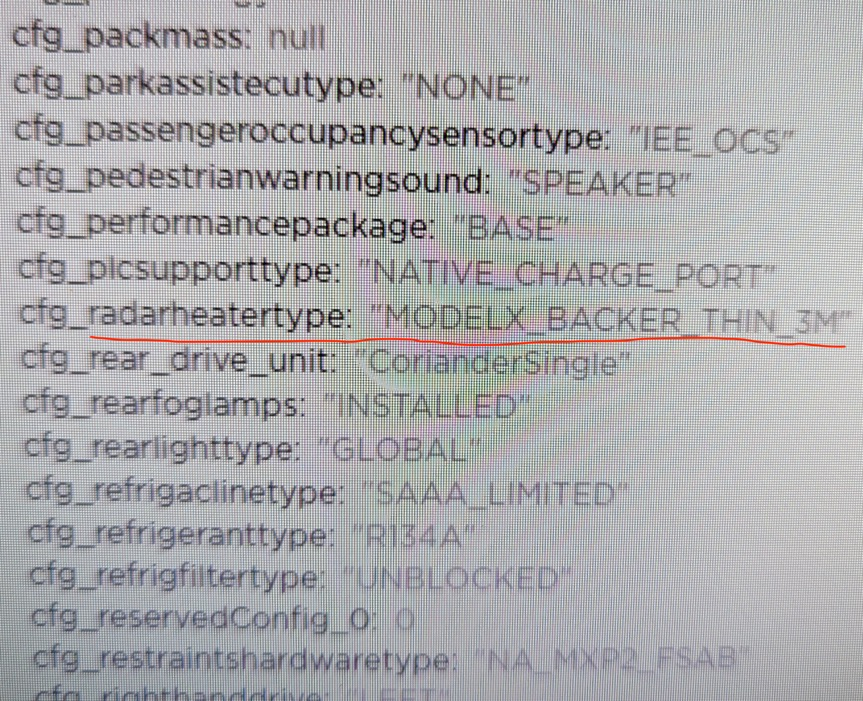
According to Musk’s statement “not opposed to using radar, but won’t use it unnecessarily,” this forward-facing radar with the code name “PHOENIX” will most likely be a 4D millimeter-wave radar.
With the improvement of performance, the power consumption of the entire hardware also increases. Green represents that the power consumption of HW 4.0 is approximately twice that of HW 3.0, and the idle power consumption can reach 80 W. It is currently unclear what impact the new hardware will have on the vehicle’s endurance. Therefore, Tesla has adopted a new power interface on HW 4.0, which supports higher power.
How far is HW 4.0 away from mass production?
At Tesla’s fourth quarter earnings conference, Musk clearly stated that HW 4.0 will first be installed on Cybertruck. However, Cybertruck is still in the sample production stage, and the probability of mass production this year is not high.

According to the documents submitted by Tesla to the European regulatory agency that were previously exposed by foreign media, Tesla is also adding HW 4.0 related hardware to Model S and Model X.
It seems that if Cybertruck cannot achieve mass production this year, we may experience the changes brought by HW 4.0 hardware on the next generation of Model S and Model X. As the 3.1 Tesla Investor Day approaches, Tesla should announce more information about HW 4.0.
Conclusion

When HW 3.0 was released, 144 Tops computing power had few opponents at that time. With last year’s comprehensive public testing of FSD in North America, Tesla has entered a new stage in autonomous driving. The FSD software is becoming stronger and stronger, which also makes me look forward to whether FSD can go further with the support of HW 4.0.
In China, the situation for Tesla is somewhat pessimistic. Due to various reasons, FSD has been unable to go online in China, and domestic new energy manufacturers have used 2 or even 4 Orin-X chips with maximum computing power of 1,016 Tops while Tesla is still at a standstill. Coupled with powerful perception hardware such as LIDAR, the hardware can be said to have surpassed Tesla comprehensively.Although Tesla has achieved an extremely stable basic assisted driving experience with powerful software algorithms, the performance of NOA navigation assisted driving is not outstanding. In our latest 42Mark test, Huawei’s HIHI series and NIO have already achieved nearly hands-free high-speed assisted driving with excellent experience.
At present, I cannot assert whether Tesla models equipped with HW 4.0 can achieve the top-level capability of domestic manufacturers in advanced assisted driving. But if FSD can enter China one day, I look forward to seeing Tesla competes head-on with domestic manufacturers again on the stage of 42Mark.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.