Author: Tian Xi
On July 5th, the “Regulations on the Management of Intelligent Connected Vehicles in the Shenzhen Economic Zone” (hereinafter referred to as “the regulations”) was officially released, with a total of 9 chapters and 64 articles, providing detailed provisions on multiple issues such as the registration of intelligent connected vehicles, on-road driving, rights and responsibilities determination, and commercialized operations.
This regulation, which has caused a stir in the intelligent automobile industry, officially came into effect today.
It is worth noting that this is the first regulation on intelligent connected vehicles in China, which means that autonomous driving, which previously hovered in the regulatory “gray area,” now has a legal basis for normal on-road operation. Many industry insiders cheered for this, believing that the era of urban autonomous driving is coming.
In order to have a deeper understanding of the current development of the industry, Car News Hub came to YRXC, an L4-level autonomous driving company located in the Futian Border Free Trade Zone in Shenzhen, and test-rode the robotaxi under the company’s name. The overall experience was just as good as human drivers.
However, meeting the technical requirements is just the prerequisite for competition in the autonomous driving market; the real challenge lies in commercialization. With the release of the “regulations,” various players have rushed to the streets of the city. The sense of urgency for autonomous driving companies to “survive” has increased, making people curious about who will be the first to run out of this quietly-brewing commercial competition.
YRXC Autonomous Driving: With the Shadow of “Experienced Drivers”
One sentence to describe the riding experience of the YRXC Robotaxi: “Radically innovative yet conservatively practical,” with a balance between flexibility and safety.
The first obvious change one would notice when stepping into the car is that the safety officer has been moved from the driver’s seat to the passenger seat, and their role of “taking over the steering wheel at any time” has been weakened. To comply with safety regulations, only the brake device is equipped in the passenger seat.
Regarding this change, YRXC CEO Zhou Guang explained that the release of “the regulations” allows autonomous driving companies to conduct fleet tests under different conditions according to their own technical progress.
It should be noted that YRXC not only achieves “driverless operation,” but also “completely unmanned operation.”The test route of this time is located in the CBD of Futian District. Starting from the Bonded Area, it goes through Yitian Road, Fuhua Road, Fuhua San Road, Fuoqiang Road, etc., and finally returns to the Bonded Area, passing through multiple traffic lights, corners, and construction sections. Overall, the performance of YUAN RONG QI XING’s Robotaxi is very close to that of human drivers.
For example, YUAN RONG QI XING’s Robotaxi can accurately identify traffic lights and smoothly perform left and right turns at intersections. When encountering a 180-degree bend, it can also smoothly follow the traffic flow through it.
In addition, when encountering vehicle convergence, pedestrians crossing the road, or non-motorized vehicles approaching, YUAN RONG QI XING’s Robotaxi can slow down in advance to avoid them and adjust the steering wheel to the side farthest from the target, creating a bigger safety zone.

YUAN RONG QI XING’s Robotaxi’s flexible lane-changing function is also impressive based on actual road conditions. When encountering parked vehicles occupying the lane or slow-moving vehicles ahead, it can perform timely lane-changing and overtaking.
If the target lane’s situation is too complicated or the traffic flow is too fast, it can also probe by adjusting the steering wheel and wait for the right opportunity to change lanes.
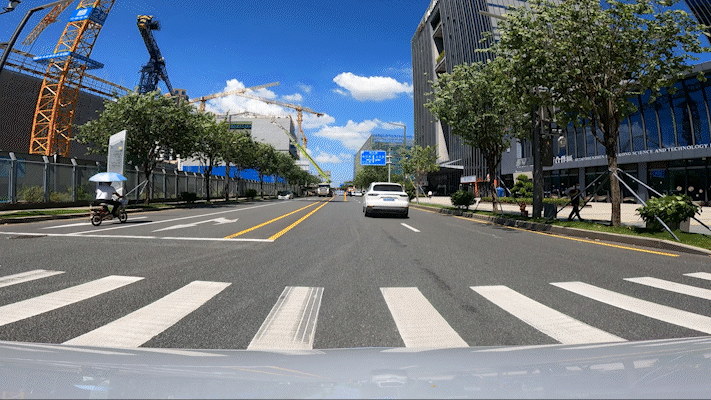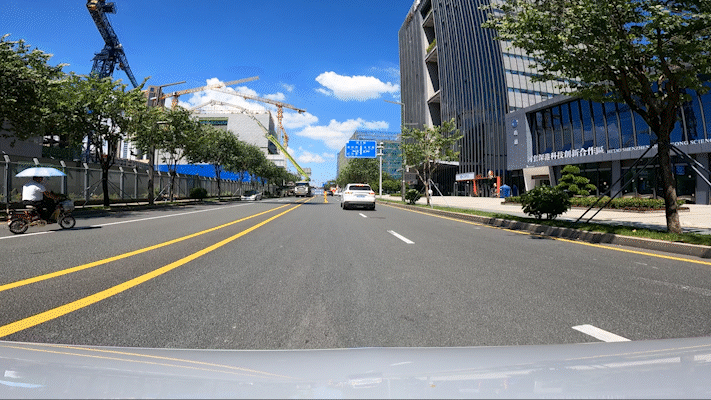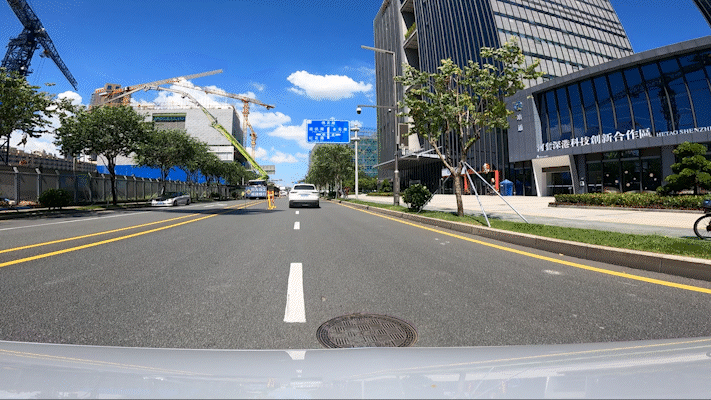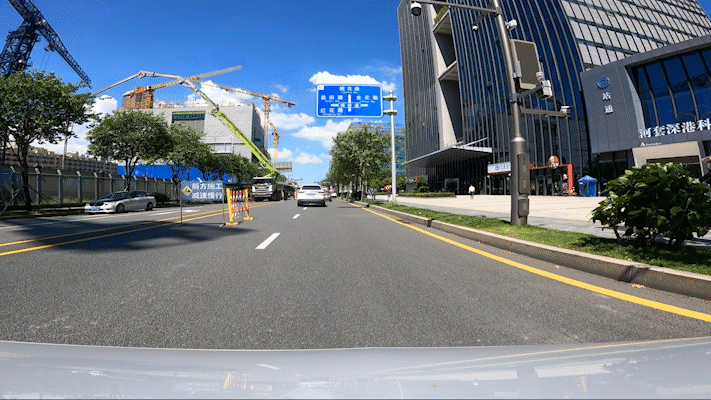
Passing through a construction section is a big test for autonomous driving technology. During this test, workers were constructing not far from the current lane, and a roadblock sign was set up ahead. YUAN RONG QI XING’s Robotaxi quickly detected this situation and executed a strategy to change lanes and bypass it. After passing through, it turned on the turn signal and returned to the original lane.
Overall, YUAN RONG QI XING’s Robotaxi can easily deal with most driving scenarios in cities and respond flexibly and quickly without stuttering. Of course, YUAN RONG QI XING’s autonomous driving is not perfect. If we examine the details closely, there are still areas for improvement.

For example, some obstacle avoidance and braking require further optimization by YUAN RONG QI XING. During this test, an electric delivery bike was coming towards from the opposite lane and moving between two lanes. When YUAN RONG QI XING’s Robotaxi detected this situation, it directly stopped. After the electric delivery bike passed, it started to move again.
At that time, the speed of the vehicle was relatively low, so it did not affect the following car. However, such a response method can cause a rear-end collision when the vehicle speed is fast. Moreover, it reduces the riding experience to some extent.From the response and handling of the retrograde electric bicycles, Yuanrong Qixing generally adheres to the principle of “safety first”, but compared to human drivers, it is slightly conservative.
Of course, Yuanrong Qixing also has a “radical” side, especially in changing lanes. It can be said to have the shadow of a taxi “old driver”.
When driving on a three-lane section of road, Yuanrong Qixing Robotaxi initially drove in the leftmost lane. When detecting the vehicle ahead, it quickly changed lanes to the middle lane.
In less than 25 seconds, Yuanrong Qixing changed lanes 3 times, which is enough to show its agility.
Overall, Yuanrong Qixing’s autonomous driving test in Shenzhen Futian CBD is commendable. With the release of the “Regulations”, Shenzhen will expand the scope of autonomous driving from specific areas to the whole city. Yuanrong Qixing plans to expand the test range to Shenzhen Bao’an District and Nanshan District.
Behind the unmanned main driver is the L4 level multi-safety redundancy
From having a human main driver to having an unmanned main driver, this change not only reflects the improvement of autonomous driving regulations but also the progress of autonomous driving technology.
“When the safety officer is sitting in the main driver’s seat, he can take over the steering wheel, throttle, and brake in a timely manner. However, when sitting in the co-pilot position, the control power is weakened,” said Yuanrong Qixing CEO Zhou Guang. “This change can be compared to a driving school instructor sitting in the co-pilot position. They can ensure safety in very sudden situations, but the main driving is still basically completed by the main driver throughout the journey.”
To achieve this, autonomous driving companies first need to give the vehicle hardware and software capabilities that meet vehicle-level standards and greatly improve the algorithms, reduce the takeover rate of the vehicle, and ensure safety by providing some auxiliary measures that can take over the vehicle in some difficult-to-solve long-tail scenarios.
In fact, this is exactly Yuanrong Qixing’s development strategy. Its test vehicle is equipped with the L4-level autonomous driving solution DeepRoute-Driver 2.0 for forward installation, which was first released on December 8, 2021.On the hardware side, the DeepRoute-Driver 2.0 solution utilizes 2 to 5 solid-state LiDAR devices, including the OneWay MEMS solid-state LiDAR ML-30S, the RoboSense second-generation intelligent solid-state LiDAR RS-LiDAR-M1, and the Mobvoi QiHeng self-developed 8 high dynamic range cameras, which can be adapted to different types of sensors and vehicle models.
For computing power, DeepRoute-Driver 2.0 employs the NVIDIA DRIVE Orin automotive-grade chip, combined with self-developed inference engine technology, to control the overall power consumption of the computing platform within 150 watts. This allows the autonomous driving algorithm to run efficiently and stably on low-cost, low-power hardware platforms and achieve six times higher inference speed than mainstream deep learning frameworks.
With self-developed multi-sensor fusion technology, DeepRoute-Driver 2.0 has a precise perception distance of more than 200 meters. To ensure safety, Mobvoi QiHeng has designed a redundant vision-based perception system that can adaptively perform autonomous driving according to safety policies even when certain sensors fail.
In addition, the solution is also equipped with cloud-based and data protection systems for safety redundancy. When the autonomous vehicle encounters situations such as damaged traffic lights or lane changes, remote safety personnel can provide auxiliary system decision-making information to ensure safe driving.
Mobvoi QiHeng focuses not only on safety but also on improving the comfort of riding in autonomous vehicles. Its game-based planning and control technology makes the vehicle’s driving behavior closer to that of humans.
This technology considers the historical traveling information, current status, and future motion trends of surrounding traffic participants to determine the mutual influence between the vehicle itself and other traffic participants, so as to make efficient and comfortable driving decisions while ensuring safety.
As for commercialization, Mobvoi QiHeng has achieved a low production cost of less than $3,000 for its front-loading system.On the other side of the ocean, Waymo, the leading self-driving company, has provided a template for others to follow. After investing over 11 years and more than 30 billion dollars, Waymo’s valuation has decreased from its peak of 175 billion dollars four years ago to only around 30 billion dollars, a decrease of over 480% due to its failure to commercialize.
Turning to the domestic market, many self-driving companies are also facing this challenge.
Zhou Guang, the CEO of YunRongQiXing, introduced their strategy of “walking on two legs” in commercial and passenger vehicles prior to the release of the “Regulations on Navigation and Control of Intelligent Network-connected Vehicles”.
In terms of commercial vehicles, YunRongQiXing has reached a cooperation agreement with Deppon Express to provide a one-year regular autonomous light truck transfer service, which is also the first L4 autonomous light truck commercial project in China.
Transferring technology to freight logistics is a major advantage for L4 autonomous driving companies. As the ODD area for urban distribution is basically the same as that of passenger cars, there is no need for secondary system development to meet the scenario demands.
In addition, as freight transportation is concentrated at night, with less traffic and fewer people, the road conditions are simple, thus enabling faster commercialization.
At 8 p.m. every night, YunRongQiXing’s self-driving light truck begins its duty and works overnight until 6 a.m. the next day, transferring logistics between one warehouse and three stores of Deppon Express in Futian and Longhua districts of Shenzhen, achieving a delivery timeliness rate of 100%.
The head of Deppon Express Shenzhen region stated that during the busy “618” period, YunRongQiXing’s self-driving light truck helped to significantly improve the efficiency of urban logistics transportation and reduce operating costs.
Passenger vehicles are the largest market where self-driving companies are competing to land, and the reason behind this is not difficult to understand. Before the fleet is put into commercial operation, cooperating with automakers to produce autonomous driving devices is the best way to generate cash flow.
In addition, successfully entering the automaker’s supply chain means that self-driving companies can obtain a continuous source of data from vehicle operation, covering various long-tail scenarios such as corner cases to optimize and improve autonomous driving algorithms.
It should be noted that even Waymo, the leader in the industry, has a fleet of less than 1000 vehicles, while a single car model from an automaker can sell tens or even hundreds of thousands of vehicles, the difference is self-evident.
Of course, being selected by automakers is not so simple. With over a century-long history of automobile industry, the high demand for technology goes without saying. In addition, the cost is also a significant consideration.
“The L4 autonomous driving system with low cost is the ‘key’ for self-driving companies to cooperate with car companies for mass production,” Zhou Guang said. YunRongQiXing is promoting the continuous decrease in the price of L4 autonomous driving systems by focusing on the most critical aspects of cost, such as “vehicle-level sensors, vehicle-level chips, and high-precision maps for mass production.”In terms of sensors, based on proprietary perception, localization, planning, and control algorithms, Yunrongqixing can adapt to low-cost, vehicle-level solid-state LiDAR.
On the chip side, the company has developed its own inference engine technology that supports high-level autonomous driving systems to run on low-power, low-computing power, vehicle-level chips, breaking the computing constraints of the chips.
At the same time, Yunrongqixing’s L4 autonomous driving system has been able to adapt to mass-produced high-precision maps, speeding up the production and landing process of autonomous driving vehicles.
In December 2021, Yunrongqixing officially released the L4 autonomous driving mass production plan, DeepRoute-Driver 2.0, with a retrofit cost of less than $10,000 and a mass production cost of less than $3,000, causing a sensation in the industry.
Zhou Guang revealed that Yunrongqixing has already cooperated with automakers to produce autonomous driving cars based on this plan.
Autonomous driving beep to make profits: safety personnel, please step aside
For autonomous driving companies, autonomous driving can only enter profitable practice and complete the self-circulation of the enterprise through consumers’ verification. However, as mentioned earlier, this idea could not really be implemented until the “Management Regulations” were introduced.
In the past, Beijing, Guangzhou, and other regions had issued some regulations that allowed companies to try out autonomous driving operations, but they were all non-commercial pilot demonstrations.
On July 5th, the “Management Regulations” were officially released, clearly stating that they can choose to open roads for testing and demonstration applications and business pilots in administrative regions with relatively complete vehicle-road coordination infrastructure. It was not until this time that China’s commercial exploration of intelligent networked vehicles had a legal basis.
Autohome learned that since July 2021, Yunrongqixing has conducted a continuous year of Robotaxi operations in Futian District, Shenzhen, completing more than 50,000 travel orders and accumulating operational experience in autonomous driving vehicles, including vehicle dispatch and user experience, laying the foundation for the subsequent launch of fee-based services.
It should be noted that regulatory approval is only the first step in the commercialization of autonomous driving, and the next issue is whether it can be profitable.
“It’s like allowing you to set up a stall now, but whether you can keep the business going depends on yourself. It’s not okay to lose money and make a lot of noise.” A person in the industry vividly compared.
As one of the biggest expenses for autonomous driving vehicles, retrofitting costs have been continuously reduced as domestic auto parts companies have risen. Now, the need to “reduce costs” is the opponent of autonomous driving, human drivers, or more accurately, safety personnel.According to data, ride-hailing drivers account for about 70% of the cost of traditional taxi services, and safety personnel also cost nearly the same amount. Including hardware modification costs and autonomous driving program costs, the total expenditure far exceeds the former, so it is easy to draw the conclusion: to make a profit in autonomous driving, safety personnel must be removed.
Prior to this, due to regulatory factors, autonomous vehicles were not allowed to be tested on the road without safety personnel.
Now, this obstacle is about to be eliminated. According to the “Regulations”, from August 1, Shenzhen will allow autonomous vehicles without safety personnel on board to hit the road. Zhou Guang expressed slightly excitedly that soon, we will be able to see Etrong’s unmanned Robotaxis driving on the streets of Shenzhen.
More and more players are accelerating into this “unmanned” movement. For example, at the just-concluded 2022 Baidu World Congress, Baidu’s independently developed Apollo RT6 made its debut, providing optional configurations for unmanned driving, including the main driverless mode without a steering wheel.
It is not difficult to see that the production “hot war” among autonomous driving companies has already begun.
With the release of this “Regulations”, autonomous driving companies based in Shenzhen have taken the lead and will be the first to seize the opportunity.
“Next, Etrong will fully cooperate with relevant standards, specifications and implementation rules, as well as upstream and downstream companies, relying on its technology cooperation with automakers and Robotaxi operation experience in Shenzhen’s CBD and light truck delivery experience to jointly promote the commercialization of autonomous driving.” Zhou Guang confidently said.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
