Author: Zhu Yulong
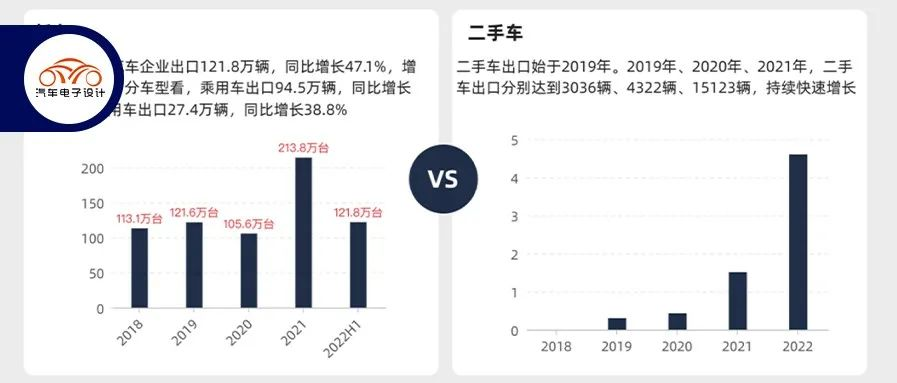
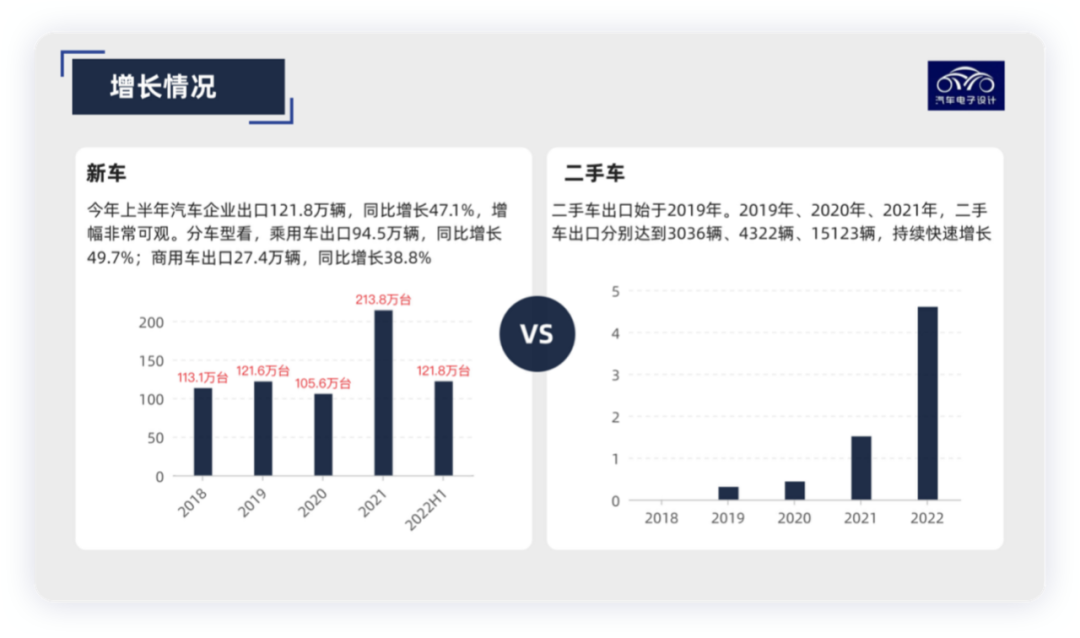
Today we mainly talk about the overseas map of China’s automotive industry. According to the data from China Association of Automobile Manufacturers, in June, the export volume of automobile companies reached a record high of 249,000 vehicles, a year-on-year increase of 57.4%. In the first half of the year, China’s total export volume of automobiles was 1.218 million vehicles (accounting for about 10% of the total sales volume), a year-on-year increase of 47.1%, including 945,000 passenger cars (a year-on-year increase of 49.7%) and 274,000 commercial vehicles (a year-on-year increase of 38.8%). With the intensification of domestic competition, Chinese automakers have focused on electrification and intelligence, and have become the characteristics of expanding overseas markets through these two differentiations, which is actually changing the image of Chinese automobiles.
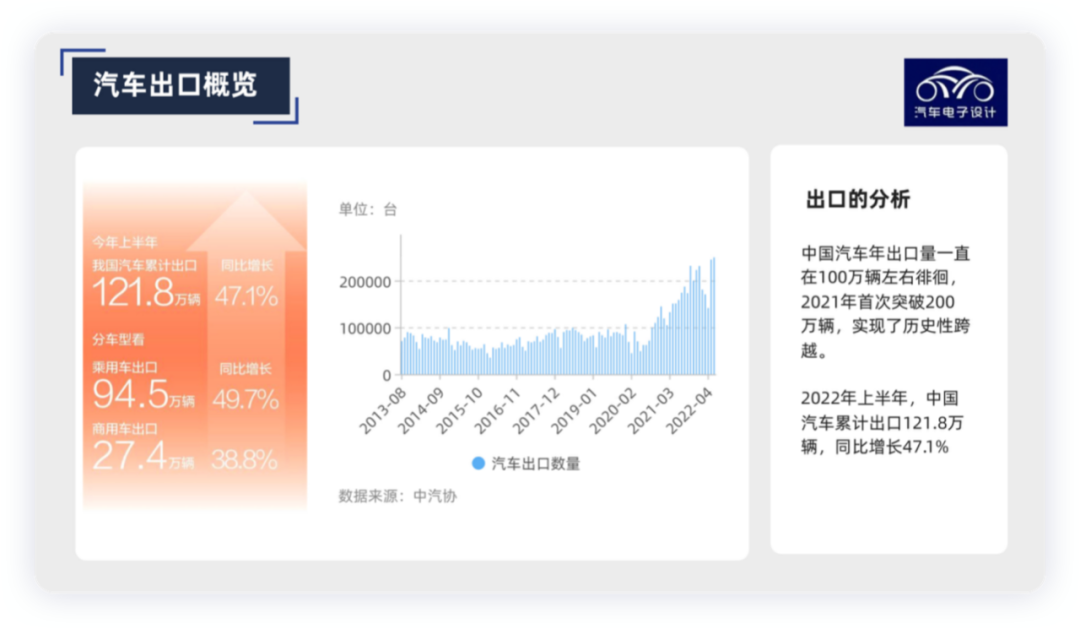
The annual export volume of Chinese cars has been hovering around 1 million vehicles, and it exceeded 2 million vehicles (2.138 million) for the first time in 2021, and second-hand cars have also been exported overseas since 2019.
Export destinations of Chinese cars
From the export structure, China exports to Asia, Europe, South America, North America, and Africa. Among them, Asia is the largest market for exports, mainly including Southeast Asia (230,000), West Asia (228,600), and South Asia (190,000), classified by 2021.
-
Asia: The main export countries are Saudi Arabia, Bangladesh, and the Philippines.
-
Europe: It mainly includes Russia, Belgium (which seems to be a hub), and the United Kingdom.
-
South America: It mainly includes Chile (the largest single-country export destination of China), Peru, and Brazil.
-
North America: It mainly includes Mexico and the United States.
In terms of coverage, it mainly enters markets where local brand strength is weak, foreign giants have withdrawn, and the overall market competition is slack. We can see that in 2021, none of us had chips. From the perspective of supply, there is a priority issue.
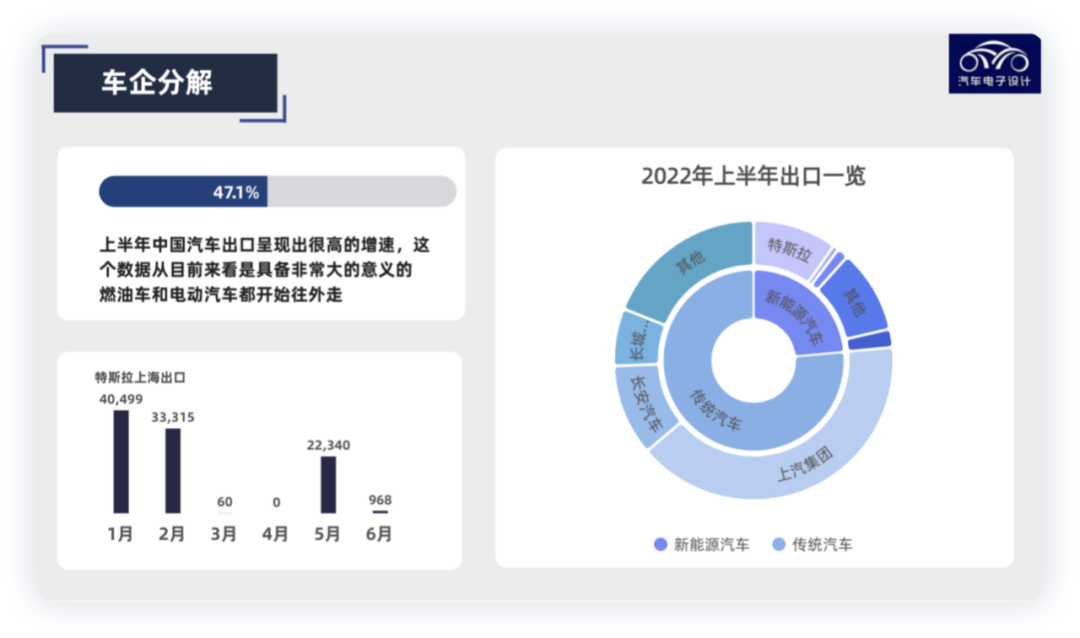
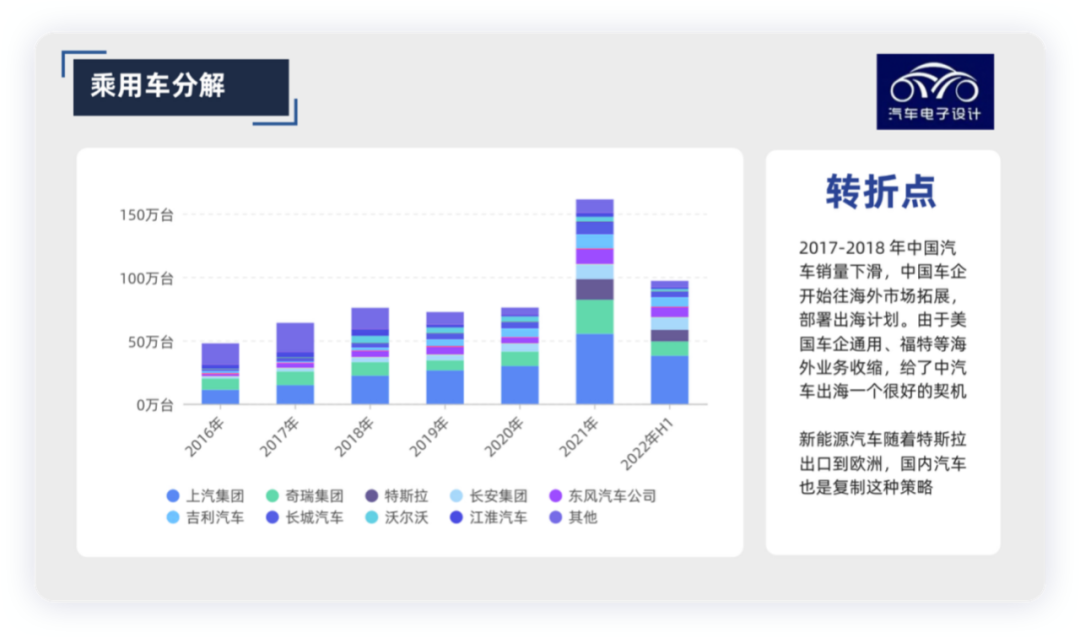
 In the first half of 2022, the auto industry exported 1.218 million vehicles, an increase of 47.1% year-on-year. New energy vehicles exported 202,000 vehicles, an increase of 1.3 times year-on-year, accounting for 16.6% of the total automotive exports. Tesla exported approximately 100,000 vehicles in just three months, accounting for about half of China’s new energy vehicles. Among traditional car manufacturers, SAIC, Changan Automobile and Great Wall Motors are the main players in overseas markets.
In the first half of 2022, the auto industry exported 1.218 million vehicles, an increase of 47.1% year-on-year. New energy vehicles exported 202,000 vehicles, an increase of 1.3 times year-on-year, accounting for 16.6% of the total automotive exports. Tesla exported approximately 100,000 vehicles in just three months, accounting for about half of China’s new energy vehicles. Among traditional car manufacturers, SAIC, Changan Automobile and Great Wall Motors are the main players in overseas markets.
As China’s auto sales declined in 2017-2018, Chinese car companies began to expand into overseas markets with their “going out” plan. The shrinking of overseas businesses such as General Motors and Ford provided a good opportunity for Chinese auto companies to expand into overseas markets. As Tesla exported to Europe, Chinese carmakers copied this strategy, and China’s growth strategy for new energy vehicles was also driven by Tesla. China’s overseas expansion of new energy vehicles is therefore closely tied to Tesla.
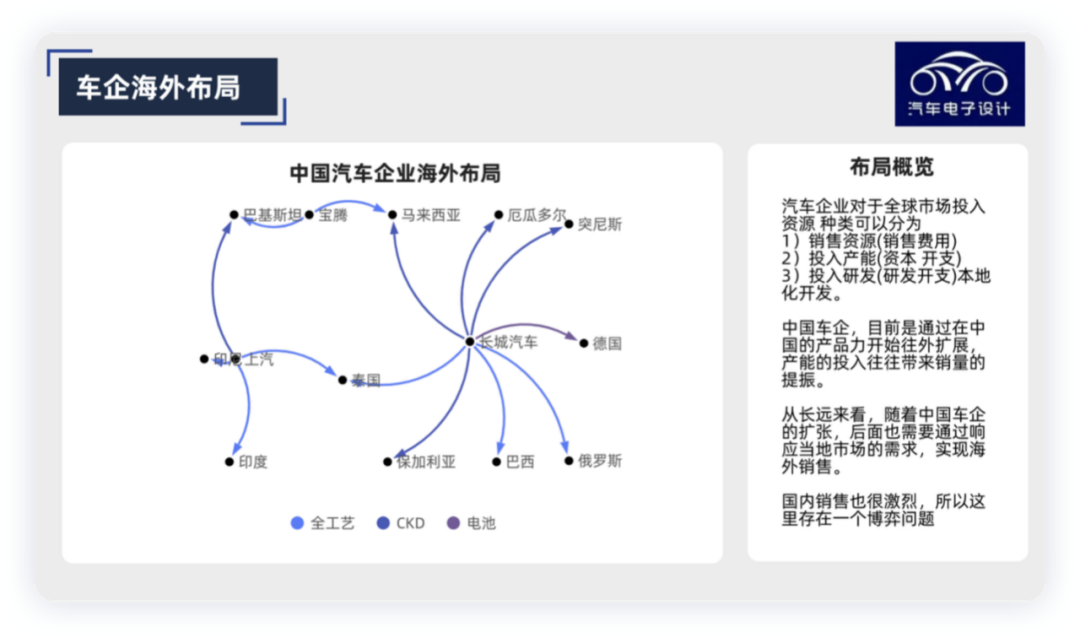
From a global perspective, the types of resources that auto companies invest in global markets can be divided into:
-
Sales resources (sales expenses): to help other markets accept our products and brands.
-
Investment in production capacity (capital expenditures): to expand output.
-
Investment in R&D (R&D expenses): to develop localization, increase viscosity, and integrate into local cultures.
Currently, Chinese car companies are expanding outward based on their product strength in China. Investment in production capacity often leads to an increase in sales. In the long run, as Chinese car companies expand, they will also need to respond to local market demands to achieve overseas sales. The domestic market is also very competitive, so there is a game theory problem here. We have also seen that relying too much on traditional car companies may look good in the short term in overseas markets, but not in the long term.
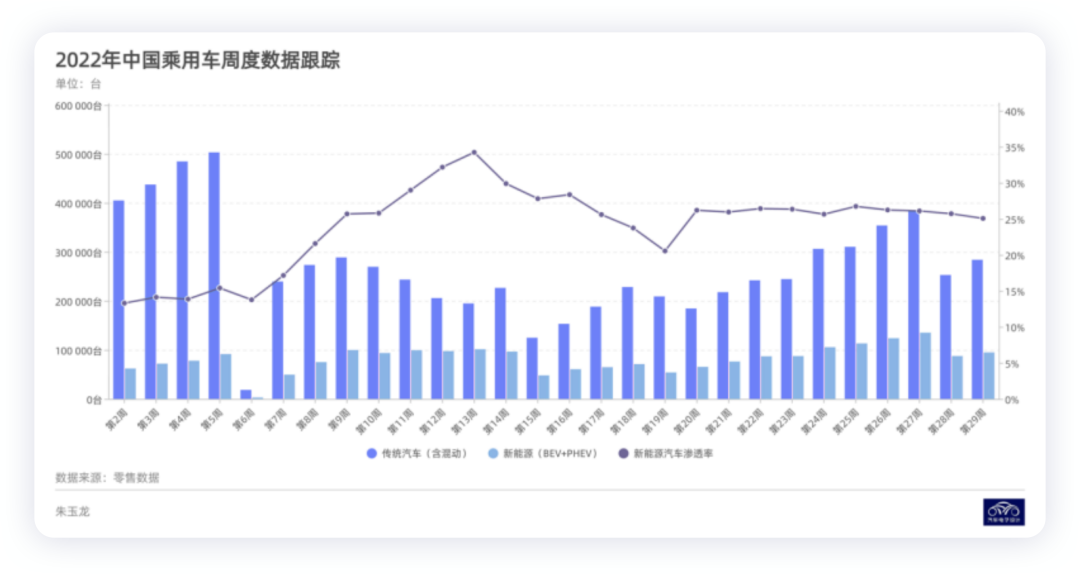
In terms of fuel vehicles, the Chinese market is the most competitive, with a market penetration rate of over 25%.
 Therefore, in order to win over a limited number of consumers, the introduction of new fuel-saving automotive technologies will be the fastest and consumer acceptance of new configurations will be the quickest. China has the strongest comprehensive ability in terms of product power, cost-effectiveness, and so on, and car models that can compete overseas throughout their entire lifecycle can be extended and overall scale can be expanded.
Therefore, in order to win over a limited number of consumers, the introduction of new fuel-saving automotive technologies will be the fastest and consumer acceptance of new configurations will be the quickest. China has the strongest comprehensive ability in terms of product power, cost-effectiveness, and so on, and car models that can compete overseas throughout their entire lifecycle can be extended and overall scale can be expanded.

Summary: I believe that the Chinese automotive industry still has great potential. With the start of a new round of eliminations, resources in the Chinese automotive industry are beginning to converge and consolidate.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.