Author: Zhu Yulong
Today, a friend talked to me about the Ideal L9, which currently requires a one-week wait for a test drive. During the promotion process, Ideal’s self-developed suspension control system had an issue, which has now become a public relations event. I specifically came to the iyiche community to discuss air suspension with everyone:
-
What is air suspension and what are the benefits? Why is it used on the Ideal L9 but not on the Ideal One?
-
Is air suspension prone to failure? What is its failure mode?
-
What are the possible situations with the air suspension on the Ideal L9, and should owners be concerned?
In fact, what everyone cares about is whether the air suspension configuration on the Ideal L9, the best SUV under five million RMB, truly lives up to its name.

Air Suspension
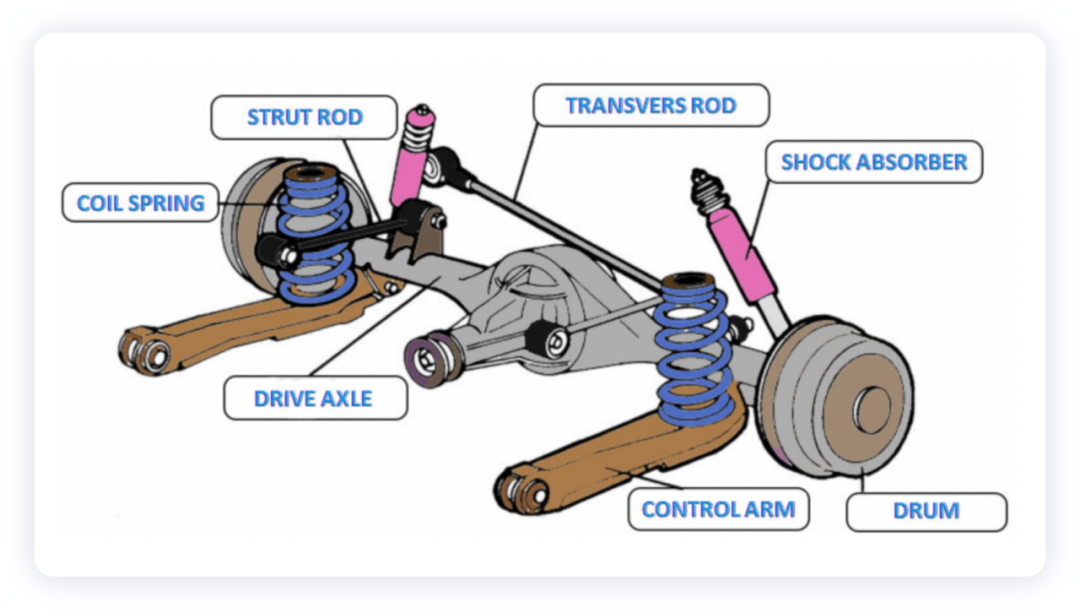
First, let’s talk about air suspension. First, let’s take a look at the main function of suspension, which is to transmit various reactions and moments acting on the wheels to the body and frame, and cushion the impact of the road surface. The suspension of a car is usually divided into independent and non-independent suspension.
-
Independent suspension means that each side of the wheel is individually suspended under the body or frame by elastic elements.
-
Non-independent suspension, on the other hand, has both wheels on one solid axle.
The difference between independent and non-independent suspension is that when one side of the wheel encounters a bump on the road, an independent suspension only makes the wheel on the bumpy side jump, while the wheel on the other side is unaffected, whereas a non-independent suspension causes both wheels to jump when one encounters a bump. Therefore, suspension is the core module of a car’s chassis system, determining both the comfort of the ride and the control of the driving experience.
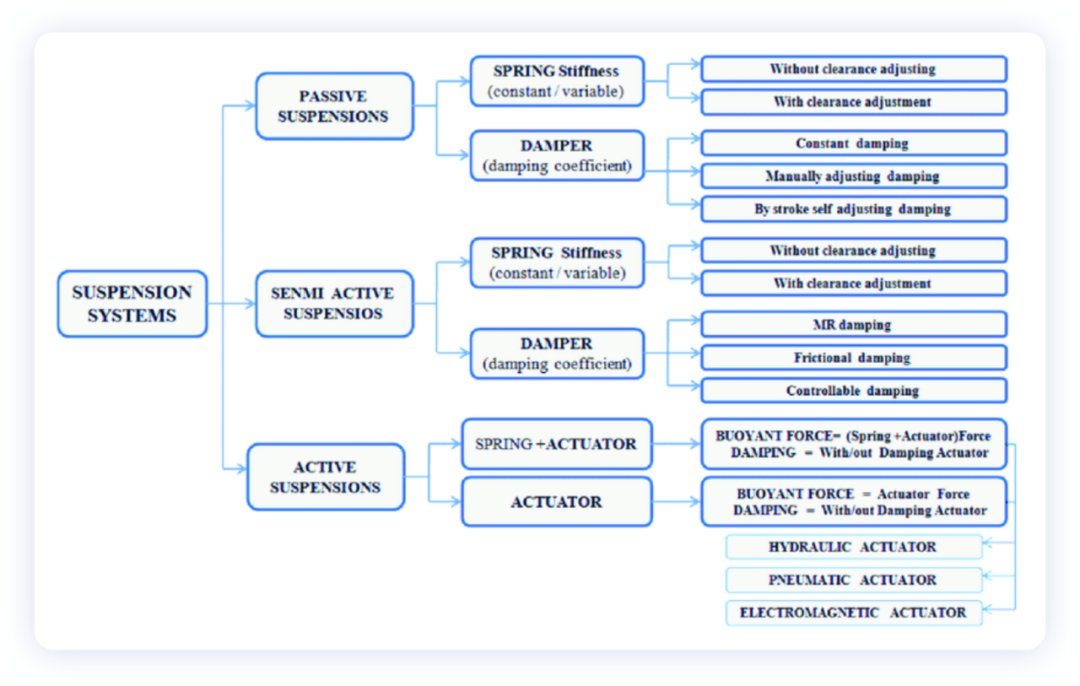
The basic components of a suspension system are:
-
Elastic elements (various springs for cushioning)
-
Shock absorbers (damping effect)
-
Guiding mechanism (control arms, etc. for transmitting force)
-
Lateral stabilizer (lateral anti-roll bar, etc. to reduce excessive body sway)
 Designing a car suspension system should first meet the requirements of safety and durability. In terms of performance, it is necessary to solve the contradiction between comfort and handling. Here, a balance is needed to make the driving feel either more comfortable or more sporty (like the choice between fish and bear’s paws, it is difficult to have both). The biggest difference lies in the springs and shock absorbers.
Designing a car suspension system should first meet the requirements of safety and durability. In terms of performance, it is necessary to solve the contradiction between comfort and handling. Here, a balance is needed to make the driving feel either more comfortable or more sporty (like the choice between fish and bear’s paws, it is difficult to have both). The biggest difference lies in the springs and shock absorbers.
If the spring stiffness is high and shock absorber damping is large, the suspension system will be “hard,” which is conducive to maintaining the vehicle posture and supporting the entire vehicle during cornering, thus improving the overall handling, but sacrificing comfort. The more comfortable the driver, the less comfortable the passengers will feel.
If the spring stiffness is low and shock absorber damping is small, and the natural frequency of the spring is close to 1Hz, the resonance caused by road impacts during vehicle travel will be reduced, making the suspension system feel “soft” in terms of sensory feedback, and improving the overall ride comfort. However, the sensitivity of the road feedback decreases, and the overall stability decreases. Too low stiffness can make it difficult to maintain vehicle posture, resulting in serious problems such as high-speed cornering.
Active suspension systems allow drivers to freely adjust stiffness and damping according to their needs at different times. Air suspension replaces metal coil springs with air springs. An electronic control system adjusts the amount of air and pressure in the air spring cylinder through an air pump and electromagnetic valve, changes the hardness and elasticity coefficient of the air spring, and adjusts the softness and hardness of the suspension as desired. By adjusting the amount of air injected, the travel and length of the air spring cylinder piston can be adjusted, and the vehicle’s chassis can be raised or lowered to achieve adjustable vehicle height, balancing comfort and handling. We see that luxury cars generally use air suspension, which effectively improves the characteristics of the vehicle.
The air spring is filled with air and has compressibility. When encountering bumpy road impacts, many small vibrations are not easily transmitted to the vehicle interior through the air spring, thereby improving ride comfort.
With the increase of the load, the air inside the air spring is continuously compressed, and the stiffness continuously changes, which can achieve a nonlinear stiffness curve, thereby improving the comfort of the ride.
Therefore, passive suspension system parameters are fixed, while active suspension system parameters are adjustable. Most family cars use passive suspension systems, and the balance between comfort and handling must be achieved when designing the vehicle. Different brands will make trade-offs in suspension suspension for cost considerations to create a style that matches their own brand. When one parameter of the spring stiffness or shock absorber damping coefficient is adjustable, it is called a semi-active suspension (damping coefficient adjustable), which includes the CDC damping continuous variable system and the MRC electromagnetic induction suspension system.If the spring stiffness, damping coefficient and length can be adjusted, it is called an active suspension system. The air suspension system is composed of a variable-damping shock absorber and a variable-length air spring based on the variable damping shock absorber, which replaces the original mechanical coil spring and passive damper with an air spring and an electronic control damping mechanism. The air spring can effectively change the body height and stiffness by adjusting the pressure inside the spring. The electronic control damping mechanism adjusts the softness and hardness of the suspension by changing the damping coefficient. The two work together to improve the comfort and agility of the driving experience.
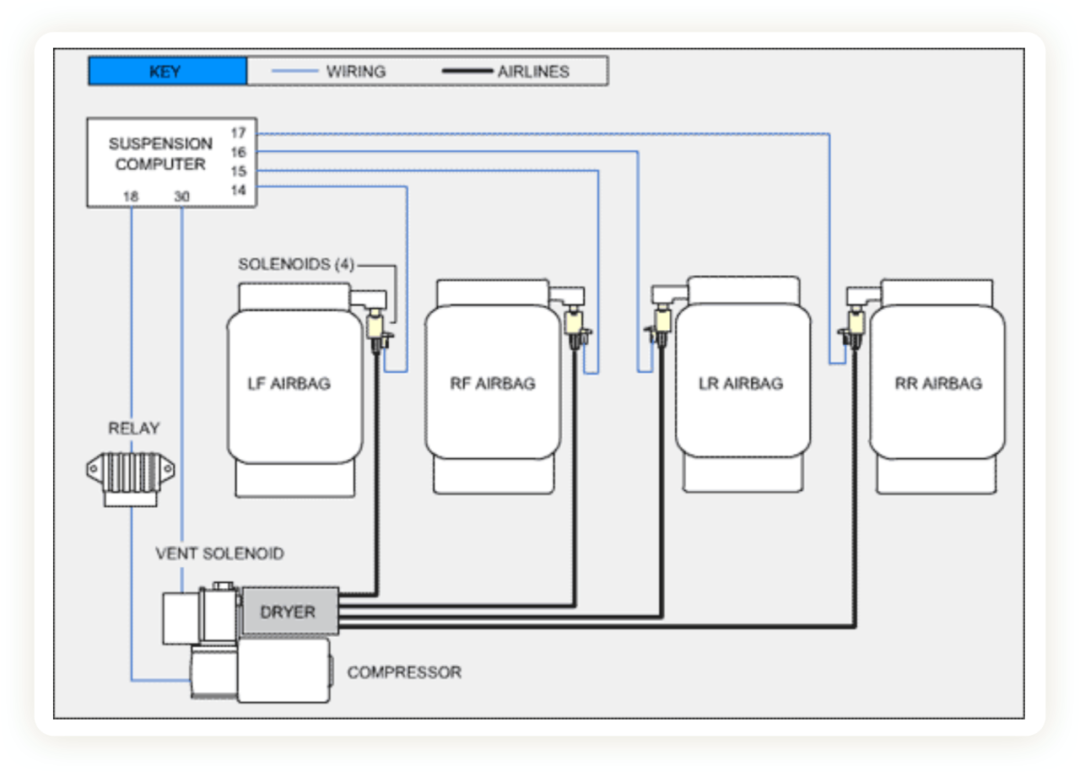
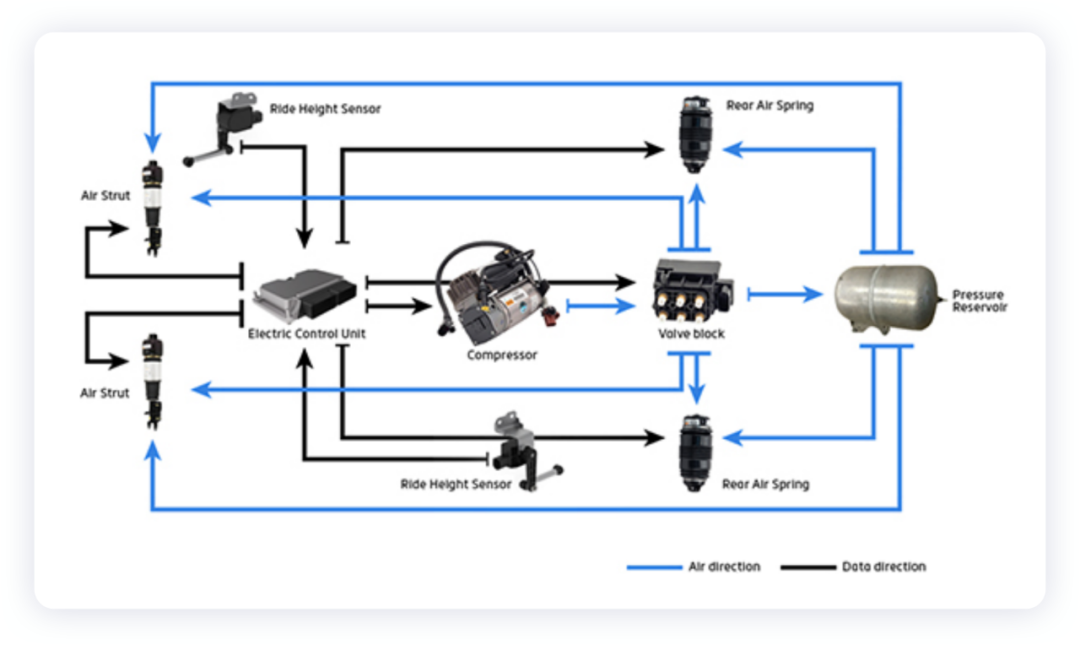
As shown in the figure above, the main components of the air suspension system consist of an air supply system (compressor, air tank, distribution valve), ECU, air spring, CDC damper, various sensors, and related piping. The ECU receives signals from various sensors to determine the body’s motion status (speed, acceleration, road impact, etc.), and adjusts the chassis accordingly. The compressor provides a source of pressurized air, which adjusts the stiffness of the air spring and the height of the body by inflating and deflating the airbag through the distribution valve. By adjusting the damping coefficient of the CDC damper, the parameters of the suspension are adjusted in real-time.
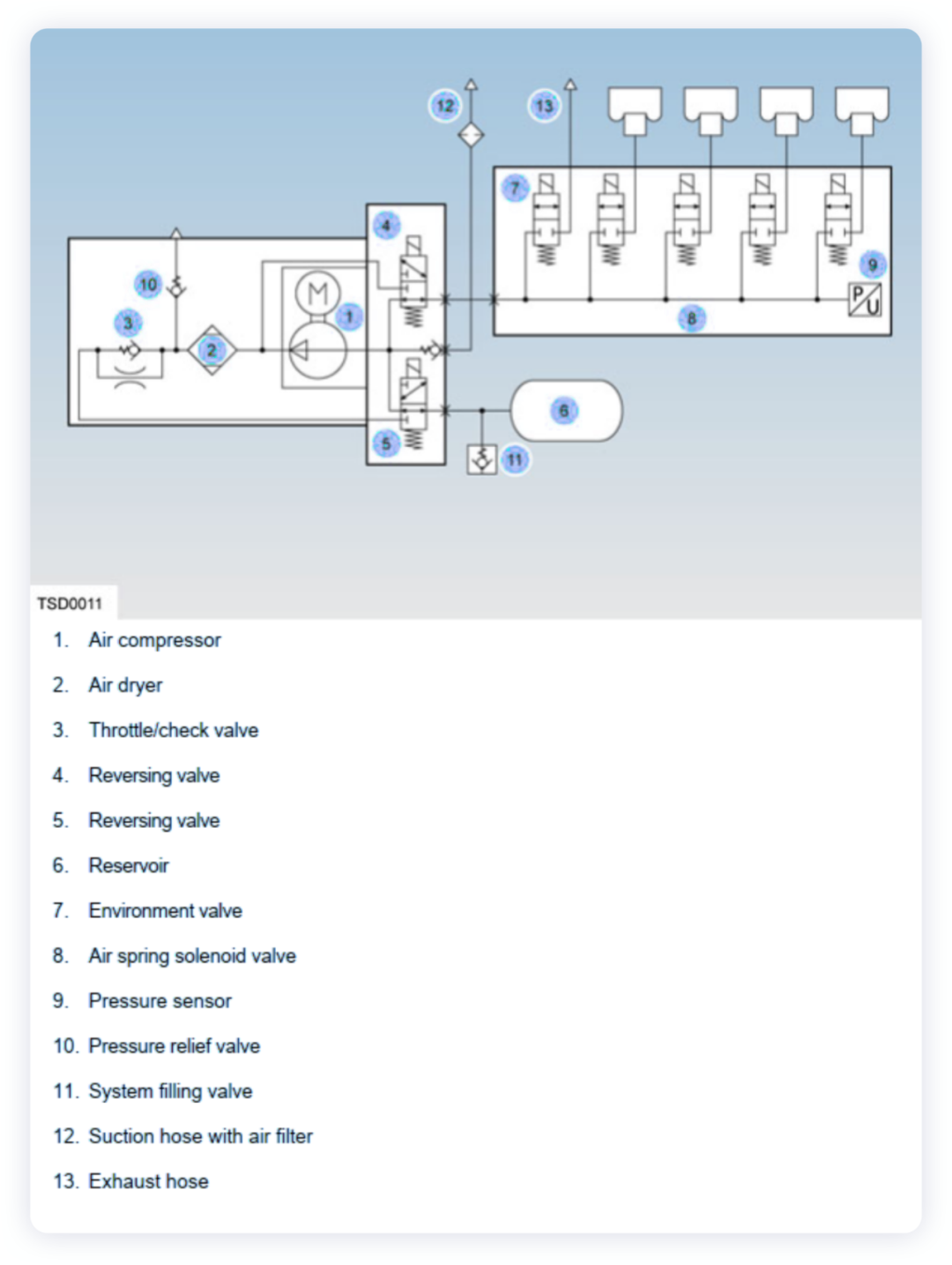
There are two main types of air springs: bladder-type and diaphragm-type, depending on their structure.
-
Bladder-type air spring: The bladder-type air spring (single, three, or four sections) consists of a closed compressed gas in an airbag and a rubber bladder with curtain cords. As the number of nodes increases, the elasticity of the spring becomes better and better, but the sealing becomes worse. The steel waistband surrounds the middle part between the joints to prevent the middle part from expanding radially outward. The upper and lower cover plates seal the airbag, and it is used more in commercial vehicles.
-
Diaphragm-type air spring: The sealed airbag is composed of a rubber diaphragm and a metal pressing piece, which is more commonly used in passenger cars.
-
Sleeve-type air spring has a simple structure and can reduce weight and assembly complexity.
When the rubber air spring is in operation, the inner cavity is filled with compressed air to form a compressed air column. As the vibration load increases, the height of the spring decreases, the volume of the inner cavity decreases, the stiffness of the rubber spring increases, and the effective bearing area of the inner cavity air column increases. At this time, the bearing capacity of the rubber spring increases. When the vibration load decreases, the height of the rubber spring increases, the volume of the inner cavity increases, the stiffness of the rubber spring decreases, and the effective bearing area of the inner cavity air column decreases. At this time, the bearing capacity of the rubber spring decreases.
Within the effective stroke, air springs have stable and flexible transmission, efficient control of amplitude and vibrating load with the increase and decrease of vibrating load, as well as adjustable stiffness and carrying capacity by increasing or decreasing the inflation volume, and the ability to attach auxiliary air chambers for self-control regulation.
Are Air Suspensions Easy to Break?
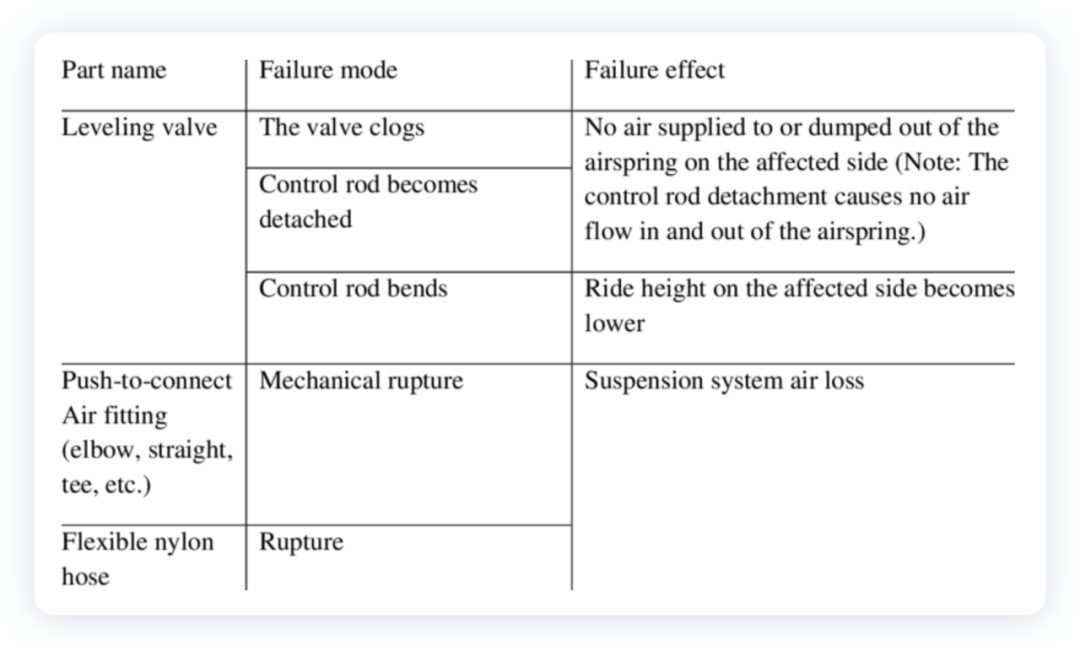
In fact, air suspensions come with high cost as well as high-end feeling. Compared with traditional suspensions, air-adjustable suspensions have a more complex structure, and the probability and frequency of failure are higher than those of the coil spring suspension system.
Over time, it is easy for water in the air to attach to the rubber layer and cause cracking, which tests the wear resistance of joints and rubber membranes and other components. In addition, exposed rubber is easily affected by the environment and becomes aged. At this time, the entire air suspension system will fail. If pebbles puncture the air bags while driving, the system may also fail. Air suspensions are parts that are easy to break. If the system fails, the air spring will leak, and the terrible experience of the body sinking will make consumers very frustrated.
Ideal Air Suspension for L9
On the ideal ONE, because of the problem of soft suspension tuning and strong acceleration, passengers are relatively prone to motion sickness. The ideal L9 air suspension solves the problem caused by the soft suspension tuning of ideal ONE, but there are indeed accidents such as air suspension electronic adjustment failure and airbag explosion. Currently, what problems this vehicle has still need detailed investigation by the Ideal official. It is necessary to reproduce the location and road conditions through the working data of that day. We, as spectators, still need Ideal to provide detailed investigation results.Summary: I think we need to have more patience. If it is an extremely rare event, this matter can be resolved. Actually, in the improvement process of Ideal One, we can see that what we really want to see is that Ideal Auto can give a persuasive explanation to resolve this PR event successfully. We should be more tolerant of new energy vehicle companies because some mistakes are inevitable in the process of making efforts. Many people mainly pay attention to the previously advertised SUV under 5 million RMB, but cannot afford it. From my understanding, for a young company like Ideal, it is inevitable to be impetuous with an “arrogant scholar” attitude, pointing the country and arousing passion with words, just like “the dung-covered village chieftain of old times”.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.