Xiaomi’s Smart Driving Solution for Cars Becoming Visible
Author: White Pigeon
On June 23, Continental Group announced that it has secured production orders for the 5R1V multi-sensor fusion system solution from a highly anticipated domestic new automaker to help the new automaker create a mass production project for L2 level autonomous driving. However, Continental Group did not disclose which new car manufacturer it is.
According to the timeline for product releases of various car companies, the only company that meets the description of the “highly anticipated new car manufacturer” and the “mass production of the first electric car in 2024” given by Continental Group is Xiaomi.
This means that Xiaomi’s first car model’s smart driving solution is likely to adopt “millimeter-wave radar + intelligent camera” and will have L2 level assisted driving capability.
In addition, based on Xiaomi’s investment layout and developments in the automotive industry since it announced its participation in the car manufacturing industry, it is likely that Xiaomi’s smart driving solutions will not be limited to L2 level assisted driving.
This article attempts to dissect the full picture of Xiaomi’s smart driving solutions in the future, based on Xiaomi’s investment layout and developments in the automotive industry.
Cost-effectiveness is the keynote of Xiaomi’s cars
In April of last year, Xiaomi founder and CEO Lei Jun announced that the price range of the first Xiaomi car would be between 100,000 yuan and 300,000 yuan, and the first car model would either be a sedan or an SUV.
According to the news obtained by “Travel Fans” from sources close to Xiaomi Automotive, Xiaomi’s first car model will be a sedan, directly targeting Tesla’s Model 3.
There are also insiders who have revealed to Automotive Insights that Xiaomi’s cars will primarily be positioned as mid-to-high-end models:
-
Mid-range models, priced between 150,000 and 200,000 yuan for A+ class cars
-
High-end models, priced between 200,000 and 300,000 yuan for B-class cars
Within the price range of 150,000-300,000 yuan, this is similar to the 3,000-5,000 yuan market in the current smartphone market.
This also means that Xiaomi’s cars are more focused on the mass market and will attract a wider range of consumers with cost-effectiveness. After all, Xiaomi’s ability to triumph in the fiercely competitive smartphone market is largely due to its products’ excellent cost-effectiveness.Apart from cost-effectiveness, the smart features of Xiaomi’s cars are what the world is anticipating.
Lei Jun once said, “it will definitely represent cutting-edge technology and highest level of production at the time of launch.”
In March this year, Luo Baojun, general manager of Xiaomi’s Beijing-Tianjin branch, revealed that the engineering sample of Xiaomi’s car would debut in the third quarter of this year, and “it will definitely exceed everyone’s expectations.”
However, Xiaomi’s product system mainly covers models in the range of RMB 150,000 to RMB 300,000, which also means that Xiaomi needs stricter control over the production cost of whole vehicles, including the cost of the overall solution for smart driving.
The 5R1V (5 millimeter-wave radars + 1 8 million pixel camera) plan announced by the mainland this time is also considered to be an economically applicable option.
In the 5R1V plan:
The millimeter-wave radar consists of the 5th generation forward millimeter-wave radar (long-range radar) and angle radar (short-range radar).
The specific model of millimeter-wave radar is not directly disclosed by the official.
Some insiders speculate that the long-range radar may be ARS510 instead of ARS540, which will be produced in 2021.
According to relevant information, ARS540, as the first 4D imaging radar, was designed by the mainland specifically for L5 level autonomous driving. It will be first equipped on BMW’s next-generation autonomous driving vehicle, iNext, and also applied to its high-end models by General Motors.
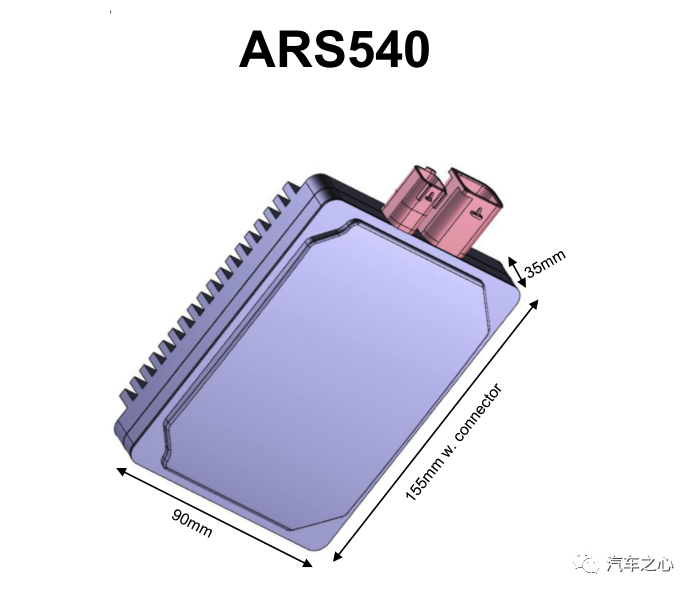
By comparison, ARS510 is cost-effective and can be used for functions such as adaptive cruise control (ACC) and emergency braking assistance (EBA), and can be installed in the front of the car or hidden behind plastic covers, such as the front bumper, grille, etc.
The short-range radar may be SRR510 or SRR520.
Information shows that SRR520 can support 100 meters range-finding, and can detect the surrounding environment of the vehicle more accurately based on 77GHz technology. It is small in size and easier to integrate behind the bumper.

The 8 million pixel camera will be developed and produced by Continental Xinchijia (Shanghai) Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd., a joint venture between mainland group and Horizon based on the Horizon** Journey 3** chip.

It is reported that the camera has been optimized for Chinese road scenarios, and has better object recognition performance.The system relies on high computing power and algorithm to detect unique obstacles and traffic lights in China. It can achieve precise visual perception and intelligent driving decision-making control.
This means that Continental Group can maximize its performance in the development and production of cameras. Meanwhile, Journey 3, as a domestically-produced autonomous driving chip, has more cost advantages.
In addition to hardware, the Continental Group also provides an autonomous driving and driving safety function software package in this order. The function software package will be integrated into the customer’s intelligent driving domain controller.
It is worth noting that in May of this year, Continental announced that it had obtained a mass production order for high-performance computing units from a domestic new car manufacturer.
The high-performance computing unit not only integrates the functions and characteristics of the vehicle body and vehicle control domain but also maintains direct communication with other domains within the vehicle, such as the autonomous driving domain and the intelligent cockpit domain.
It is reported that this solution will also be put into production on the electric vehicle platform of the new car manufacturer in 2024. According to the timing, this mass production order for high-performance computing units may also come from Xiaomi Auto.
At the current time, the 5R1V multi-sensor solution may be more cost-effective, but in 2024, when other automakers all have equipped with several lidar sensors, Xiaomi Auto may lack a competitive advantage.
At the same time, in terms of the realization of autonomous driving functions, advanced driving assistance functions dominated by urban NOA are about to be put into mass production in the next two years. Xiaomi’s first electric vehicle in 2024 only has L2 assisted driving capability and does not match Lei Jun’s aforementioned ambitious statement.
Is Xiaomi Auto going the visual route? Is lidar just a technical reserve?
Currently, automatic driving sensor equipment can roughly be divided into two factions:
- First, Tesla insists on the purely visual route;
- Second, other automakers except for Tesla insist on putting lidar on the vehicle and taking a multi-sensor fusion route.
Judging from Xiaomi’s layout in the automotive field, its first electric vehicle is more likely to adopt a visual solution.
On August 25, last year, Xiaomi officially acquired the autonomous driving technology company DeepMotion.
As early as 2018, DeepMotion’s founder and CEO Cai Rui publicly stated that DeepMotion adopts a multi-sensor fusion strategy mainly based on visual.At that time, Deepmotion’s high-precision positioning technology had achieved a positioning accuracy of about 30-40cm in front and back, and 10-20cm left and right.
Deepmotion integrates perception, positioning, and mapping modules at the algorithm level, with high-precision maps as the core.
For this purpose, Deepmotion also designed a system that implements a solution for 3D perception, high-precision map drawing, and positioning through sensors such as cameras, millimeter-wave radars, ultrasonic radars, GPS, IMU modules.
The hardware modules of this system include:
- A set of GPS systems;
- IMU modules;
- Three cameras;
- A millimeter-wave radar
- 12 ultrasonic radars
- A self-developed FPGA computing platform.
The biggest feature of this hardware architecture is its low cost, and the cameras, millimeter-wave radars, GPS, IMU, and other sensors are synchronously operated, and the self-developed deep learning algorithm can also run on the FPGA computing platform.
Starting from high-precision maps and positioning, DeepMotion began to provide a full-stack autonomous driving solution, including front/surround/360-degree perception systems, and independent valet parking (AVP) solutions.
Based on the acquisition of DeepMotion, we can basically infer that Xiaomi’s autonomous driving solutions will adopt a vision-based approach, with high-precision maps and technologies that support crowd-sourced updates.
It is worth noting that just before the official announcement of the acquisition of DeepMotion, in early August of the same year, Xiaomi also announced an investment in another autonomous driving technology company, Geometric Intelligence (Geohoo).
According to the official website introduction, Geohoo focuses on a self-developed autonomous driving software and hardware integration system based on 4D millimeter-wave imaging radar, supplemented by visible light and infrared imaging multi-sensor fusion perception, to achieve accurate target perception, clustering tracking, accessible space estimation, high-precision positioning and mapping, path planning, decision control, and meet the needs of autonomous driving at various stages.
In other words, Geometric Intelligence can achieve L2-L4 level autonomous driving functions based on the “4D millimeter-wave radar + visible light vision + infrared imaging multi-sensor fusion perception system”.
Currently, Geometric Intelligence has obtained a spot of production cooperation for SAIC Group projects, and the two sides are accelerating the research and development and production of passenger cars with local autonomous driving functions at L3, and commercial trucks with fixed field L4 level functions.The company’s product solutions will achieve functions such as autonomous and unmanned parking in urban areas, parks and highways, automatic following and lane changing on congested city roads and highways, and autonomous detouring.
Of course, choosing a visual route does not mean that Xiaomi has completely abandoned the use of lidar.
Xiaomi has invested in four lidar companies in the field of lidar.
Public information shows that Xiaomi invested in Hesai Technology through Xiaomi Group and Xiaomi Industrial Investments, while Lei Jun’s affiliated Shunwei Capital invested in Innovusion and Beixing Photonics. Xiaomi’s Yangtze River Industry Fund participated in the new round of strategic financing of Suteng Juchuang.
Hesai Technology has won mass production designated projects from car companies such as IDEAL, JIDU, Gordion, and Lotus by launching a long-distance hybrid solid-state lidar AT128.
Suteng Juchuang has won cooperation orders from more than 40 car companies, including XPENG, GAC, WM, and IM, by using MEMS hybrid solid-state lidar.
Innovusion Tuda Tong is currently the lidar supplier on NIO’s first intelligent pure electric sedan ET7.
Beixing Photonics is a non-mechanical solid-state planar array lidar enterprise with an independent technical route, and is expected to release a vehicle-mounted lidar this year.
Based on this, camera + millimeter-wave radar + high-precision map or Xiaomi’s intelligent driving solution is the preferred option.
Of course, the possibility of Xiaomi’s future cars being equipped with lidar cannot be completely ruled out.
On the one hand, the addition of lidar can make the overall sensors redundant, achieve dimensional increase in vehicle perception, improve the reliability of perception, and effectively identify targets that the camera is currently unable to recognize, such as road bumps, missing manhole covers, scattered debris, and large static obstacles.
On the other hand, one of the reasons why Tesla did not use lidar before was that its cost was very high. But with the advent of hybrid solid-state lidar, its price is now around $1,000.
Industry insiders said that as lidar is put into mass production, its price will eventually drop to $400-500.
The XPeng P5, which has already been launched, has a 550P version equipped with two lidars, priced at 225,900 yuan.
At the same time, the XPeng P5 also provides users with optional services, and the 550E and 550G are both versions without lidar.
By comparison, for Xiaomi’s cars positioning at the 150,000-300,000 yuan level, the price of lidar can be completely covered, and the addition of lidar can help achieve higher-level autonomous driving, so the probability of Xiaomi completely abandoning lidar is not high.
Self-developed software algorithms, integrated supply chain, achieving L4 level autonomous driving.The advantage of Xiaomi in the field of IoT lies in the huge hardware system built by its ecosystem companies. With the core software system of IoT, based on the hardware devices of the ecosystem companies, Xiaomi can achieve interconnectivity among all things.
Nowadays, Xiaomi is quickly copying its ecosystem strategy in the fields of mobile phones and consumer electronics to the automotive industry.
In the development of autonomous driving technology, Xiaomi’s approach is also to develop its core software algorithm and integrate ecosystem resources to ultimately achieve L4 level autonomous driving technology.
Previously, Lei Jun posted a recruitment poster on Weibo, inviting 500 self-driving technology elites to work on Xiaomi’s self-developed L4 autonomous driving technology.
In addition, Deepmotion, which was acquired by Xiaomi, has its co-founder and CEO Cai Rui, CTO Li Zhiwei, chief scientist Yang Kuiyuan, and R&D director Zhang Chi, all of whom come from Microsoft Research Asia.
Insiders say that DeepMotion has strong algorithm capabilities, and will complement Xiaomi in terms of engineering capabilities and commercialization.
This also means that through the acquisition of Deepmotion, Xiaomi will make up for its shortcomings in autonomous driving software algorithms, thereby achieving positive development iterations of autonomous driving software algorithms.
Beyond the core software algorithm, Xiaomi’s intelligent driving system can rely entirely on its investment in ecosystem companies for product integration and development.
-
Self-driving big computing chip: Xiaomi has invested in Heizhima Intelligent Technology;
-
Lidar: Xiaomi has invested in Hesai, Beixin Photonics, Tudatong, and Suteng Juchuang;
-
Autonomous driving solutions: Xiaomi has invested in ZongMu Technology, GeometryAutohuzhu, ZhiXingZhe, and Momenta.
ZongMu Technology is a leading domestic enterprise in the automatic parking solution field, with mass customers including Changan Auto, Dongfeng Integra, FAW Hongqi, etc.
Momenta is currently one of the most popular self-driving software companies in China, with mass customers including SAIC IM, Great Wall Salon, Lotus, BYD, etc.
Combining the official announcement of the mainland group, it is easy to see that Xiaomi’s autonomous driving sensor hardware is based on supply chain procurement. The autonomous driving function, including L4-level functions such as automatic parking, may also integrate solutions from ZongMu Technology or Momenta, etc.
Ultimately, the core of Xiaomi’s intelligent driving solution lies in its self-developed software algorithm capabilities.
2024 will mark the beginning of the decisive and elimination battles for the entire automotive industry.
For Xiaomi, which has hit the ceiling in the smartphone race, and Lei Jun, who is embarking on what may be his last entrepreneurial venture, this battle must not be lost.
In the face of new forces in the automotive industry that have already taken root, as well as traditional automakers that have transformed themselves, the quality of Xiaomi’s intelligent driving will also affect its ultimate development.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
