Author: Zhu Yulong
In an attempt to sort out the transition from Volkswagen’s MEB platform to SSP, we can identify this process from some details, especially things like lighting control and thermal management, which can easily be found from the system classification.
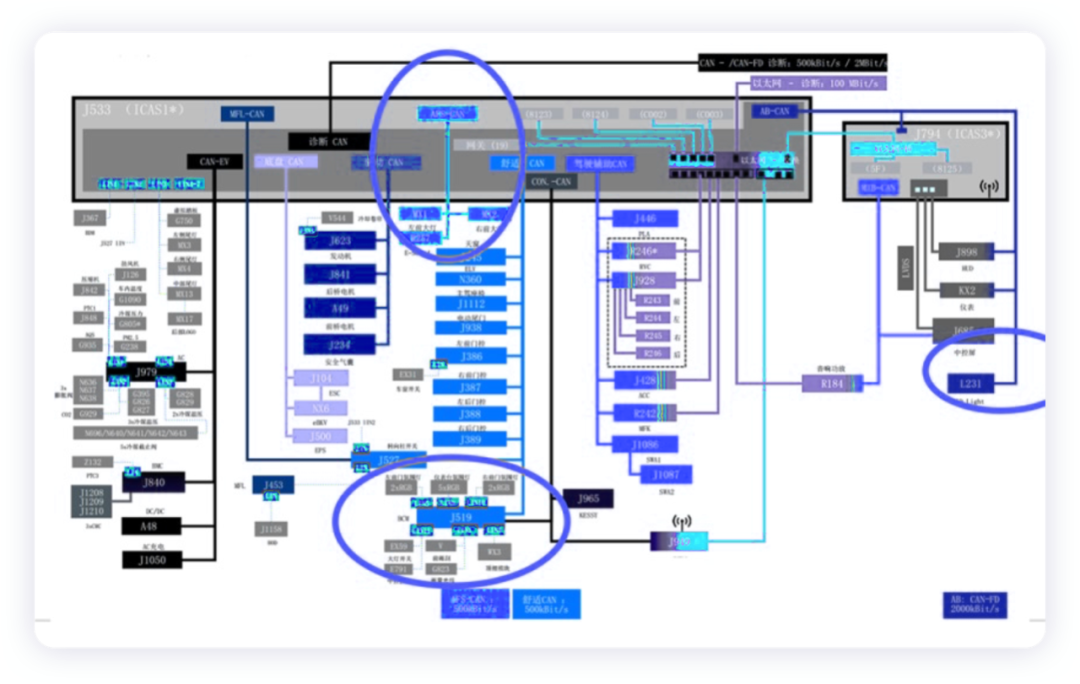
These lighting controls mainly include ICAS1, ICAS3 (IQ Light), and BCM. The controller inside the headlight completes the control logic inside the headlight. The overall communication process includes:
-
AFS CAN ICAS1 communicates with the headlight at a rate of 500k/s.
-
BCM: communicate on the comfort CAN, control 3 lighting circuits through LIN communication, and realize the response of the headlight switch.
-
AB CAN-FD: between ICAS1 and ICAS3, control the ID Light at a rate of 2M/s.
Then the overall lighting control appeared, ICAS1 completed the overall logic to implement control of external lighting, headlight internal execution function, BCM implemented control of ambient lighting, and finally ICAS3 controlled IQ Light.
Lighting Drive
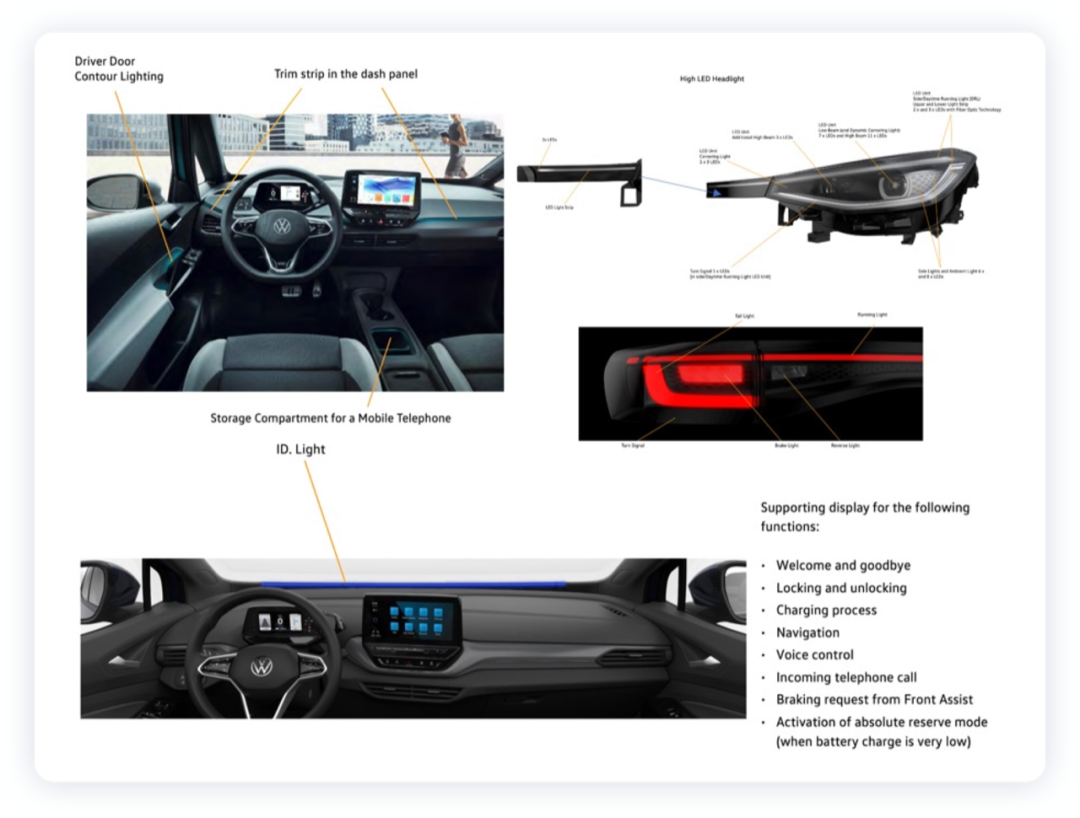
From the perspective of lighting control, the headlight is a typical example, and the lighting controller mainly includes the driving of LEDs and the control of two motors. From Volkswagen’s design perspective, this is a typical modular design, centered around IQ.light safety lighting technology, and includes four main parts: matrix LED front headlights, full LED taillights, exterior ambient lighting and interior ambient lighting. This means that communication on MEB needs to be compatible with the previous MQB communication system.
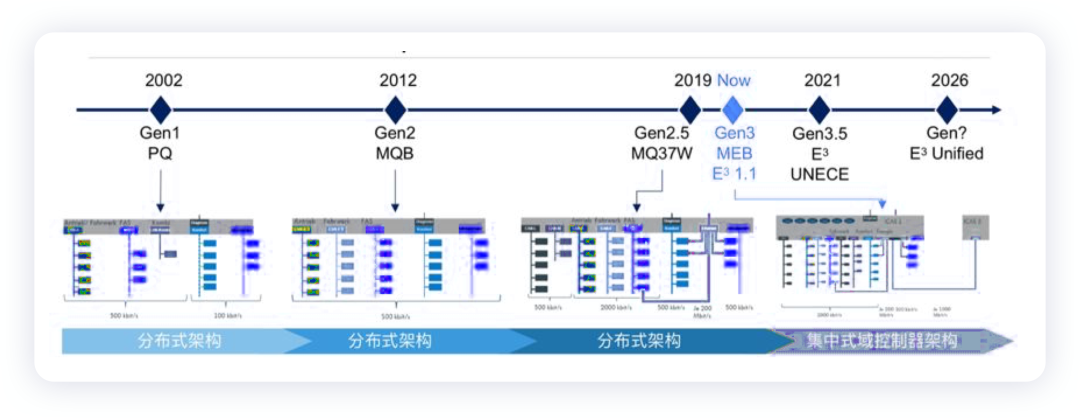
Note: Now it seems that the ability of intelligent devices mainly lies in the ability to control small motors, which is almost in the car body, seats, lighting, thermal management, etc.
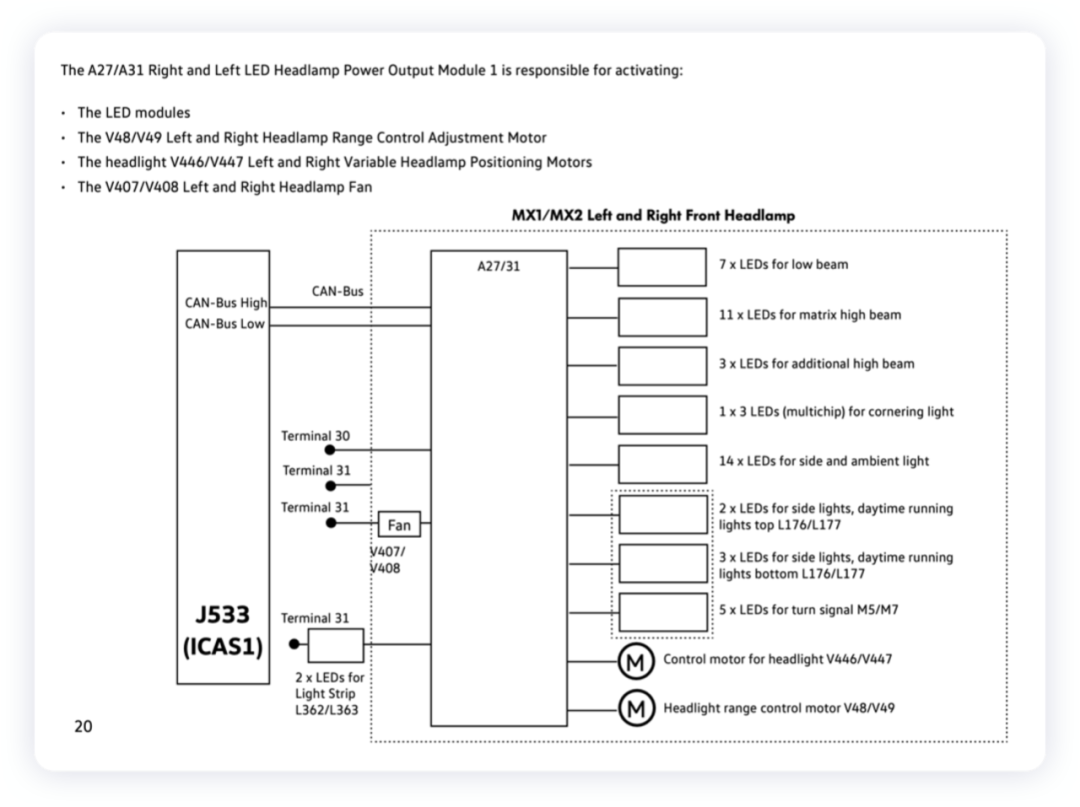
The controller extension includes additional LED chips.
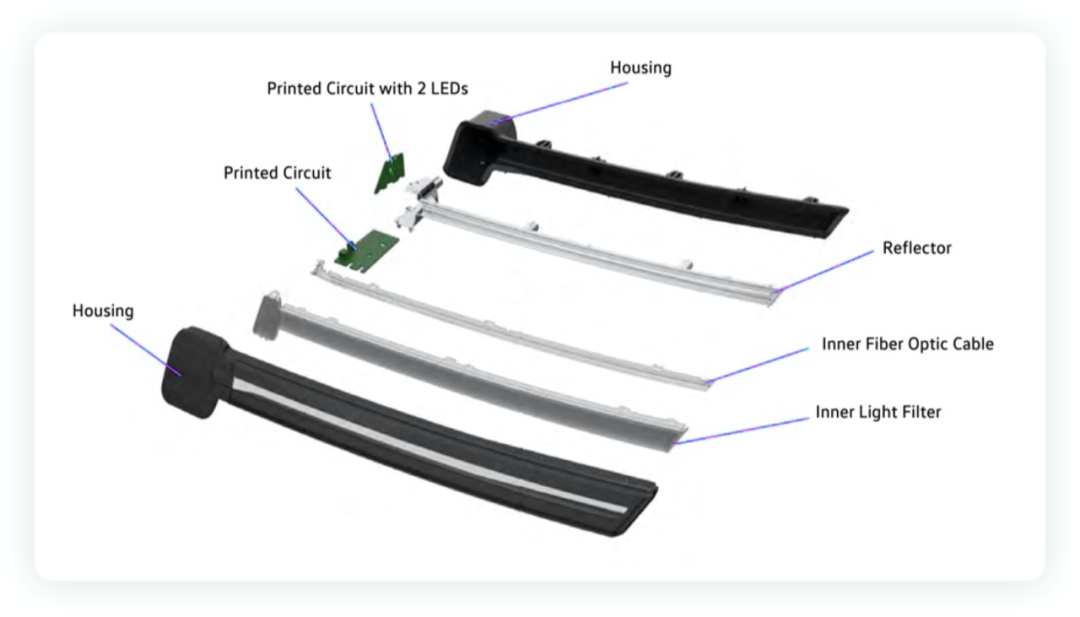
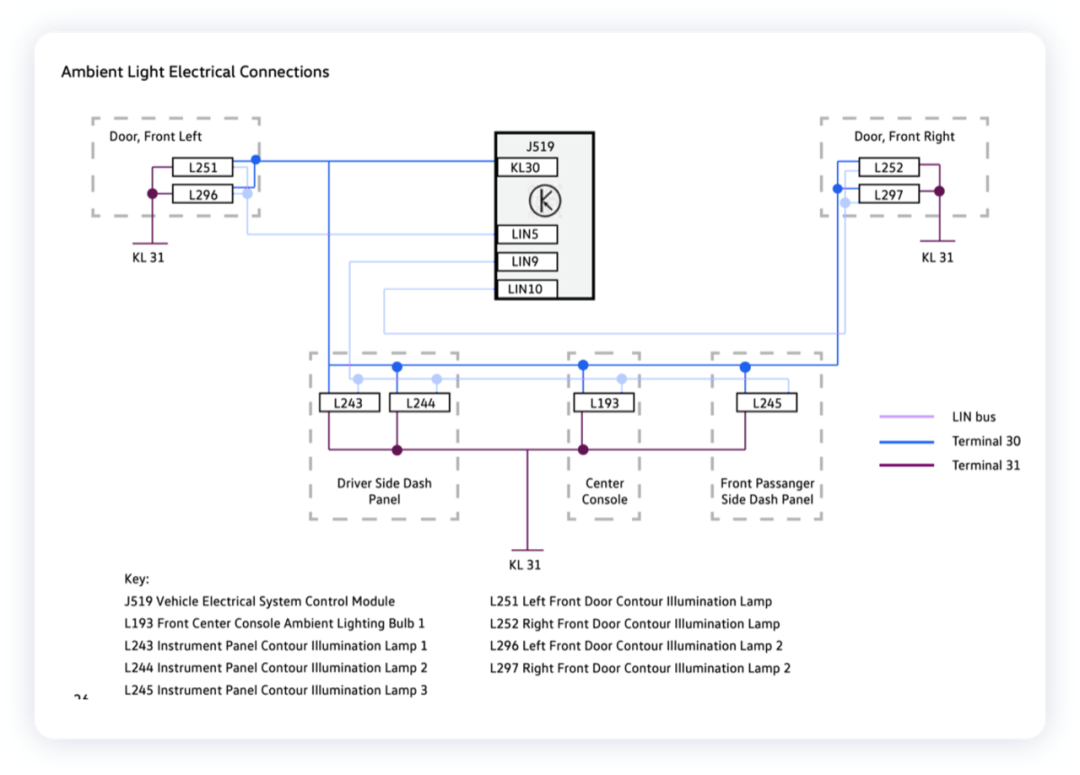
In the logic of the entire interior light, J519 body is a signal transmitter, and the entire electronic driving part is decentralized into the light, and then controls the left and right door lights and the left, middle and right three ambient lights through three-way LIN communication.
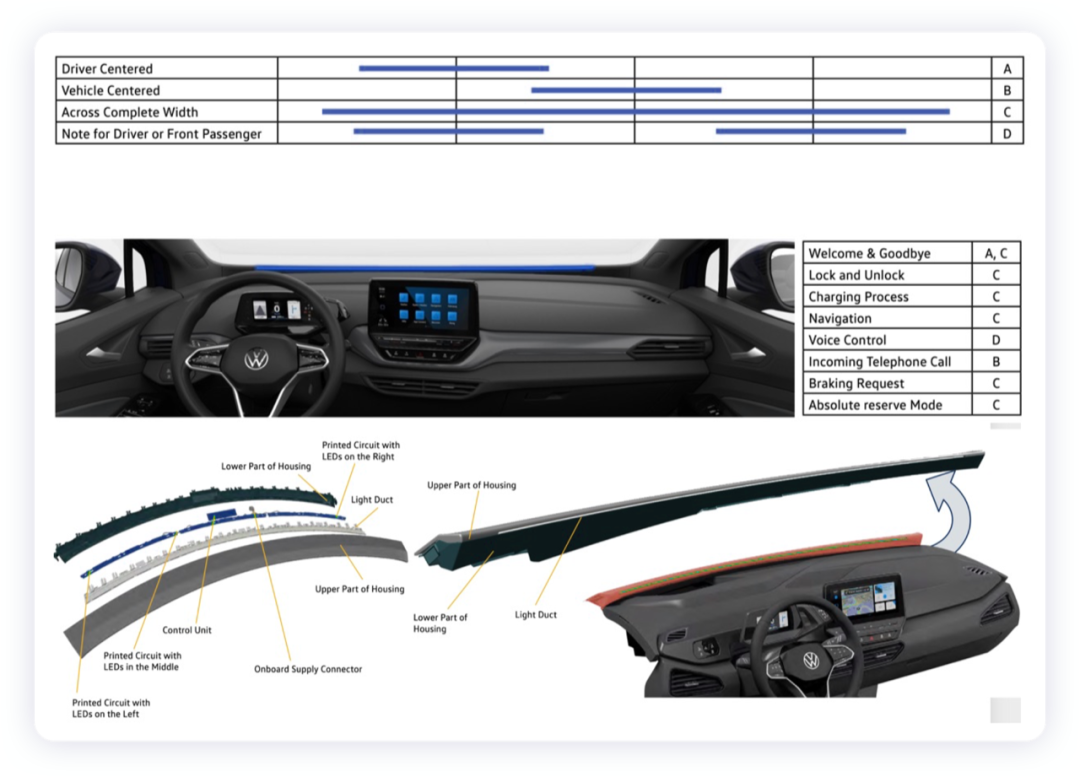
Here, 54 RGB LEDs are used, divided into three PCB circuit boards, and the main control driving module has also been made into a separate board. It is controlled by CAN communication. According to the instructions, the animation effect of the LED is fixed, and then the animation effect is started by ICAS3, and ICAS1 is used to determine the light effect of the control locking and unlocking.
Light control logic
In this aspect, we actually trace back to the fact that MEB is somewhat scattered in the overall logical design, that is, the original framework remains unchanged, and the front light module, BCM control light are all modular components before MQB. The real logic change and direct control on MEB are only the 54 light chips on the instrument panel.
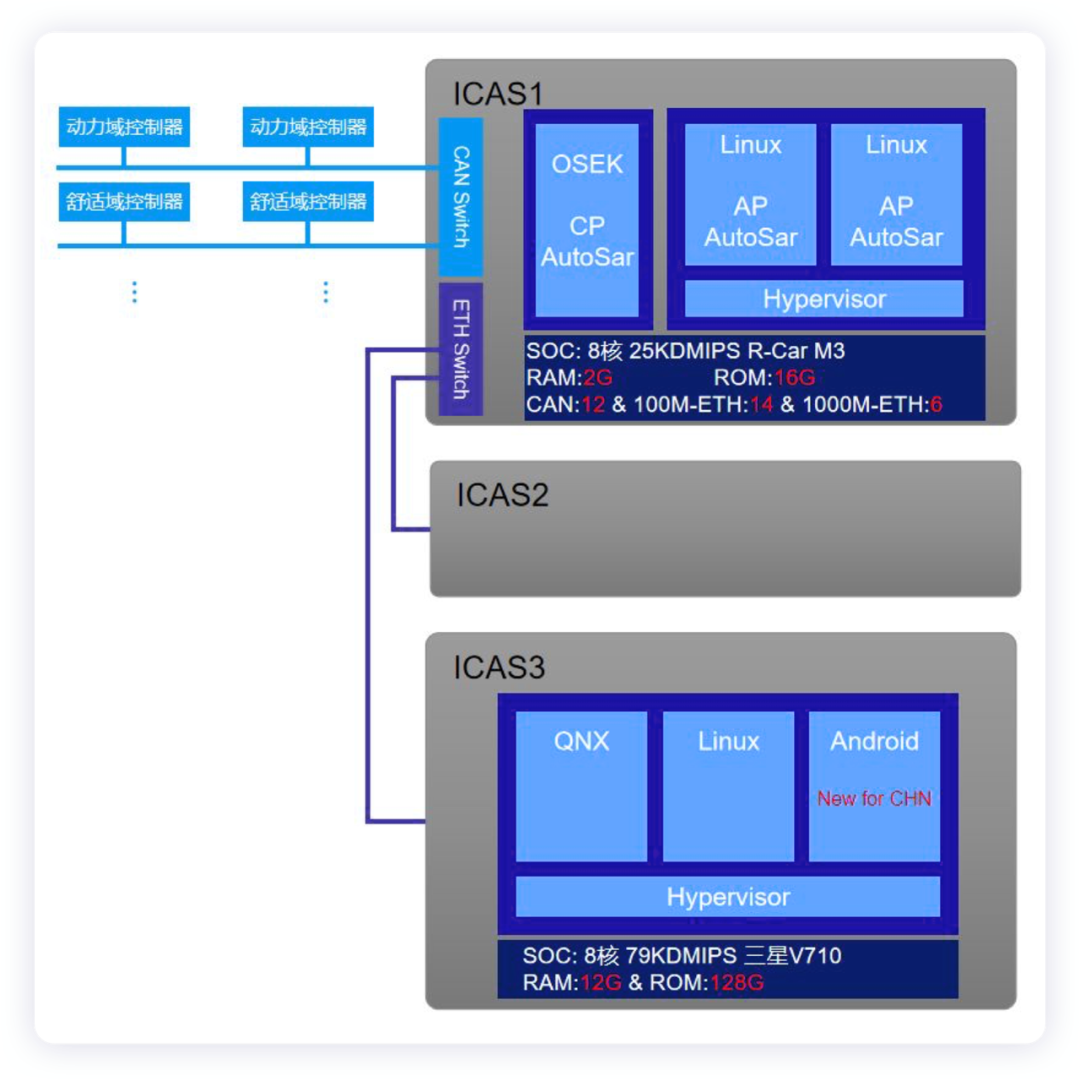
The processor of ICAS1 includes the application server of Adaptive Autosar, Java application server, embedded software cluster and software cluster internal affairs, which are realized on R-CAR M3. In the embedded software, a complex car light system (including the entire set of light logic for locking and unlocking), dynamic car light assistance system, and matrix headlight control are implemented.
ICAS3 includes QNX, Linux, and Android, mainly controlling the ID Light for lighting.
 Summary: In my personal opinion, because the overall lighting needs to be forward compatible with various components, the main logic of the iteration is the light language control. To put it simply, there is still room for improvement in this train of thought.
Summary: In my personal opinion, because the overall lighting needs to be forward compatible with various components, the main logic of the iteration is the light language control. To put it simply, there is still room for improvement in this train of thought.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
