Translation
Author: Zhu Yulong
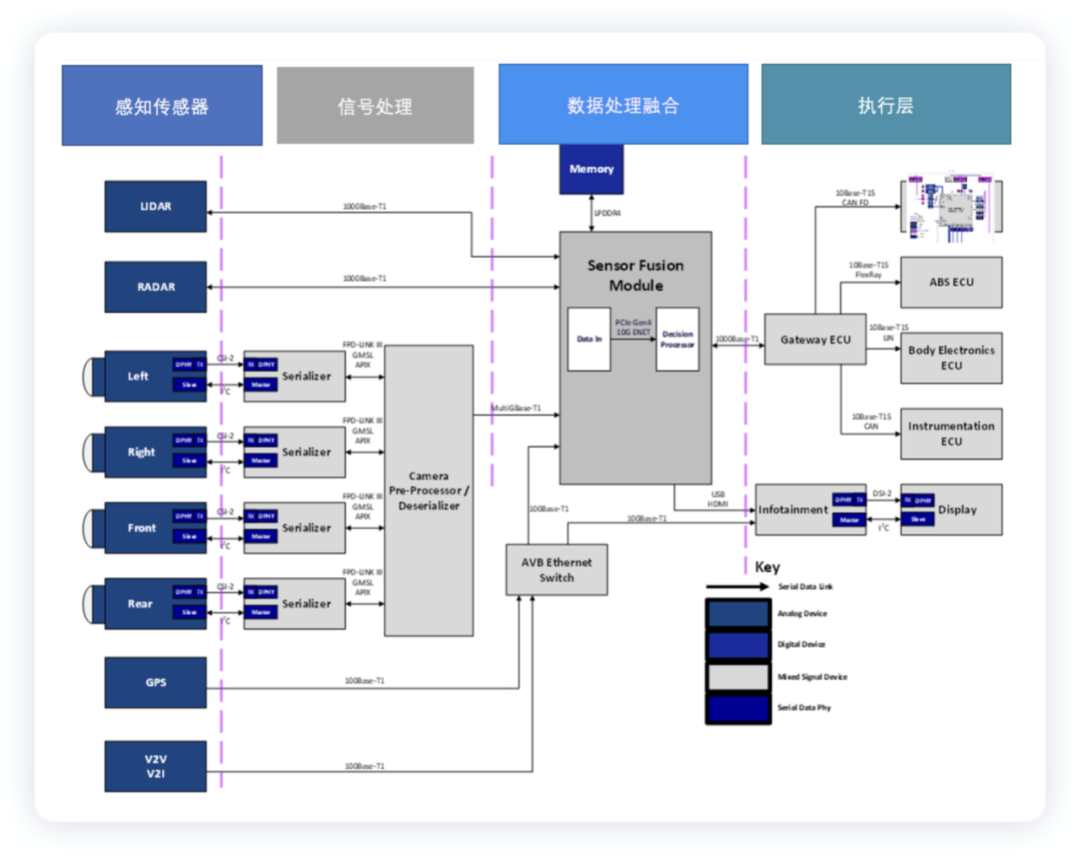
Due to the large number of perception sensors (such as cameras, LiDAR, and mmWave radar) used in cars, these sensors need to meet both high-speed data transmission and signal integrity, as well as low cost and low weight requirements. Considering how to iterate the entire sensor plan has become an interesting consideration element for wiring harnesses and connectors.
In particular, switching from traditional coaxial cables to Ethernet transmission – let’s explore this important topic for future wiring harness and connector design.
Automotive Ethernet technology uses single-twisted-pair (T1) and point-to-point network topology, with the main difference being data rate and coding method.
Traditional Processing
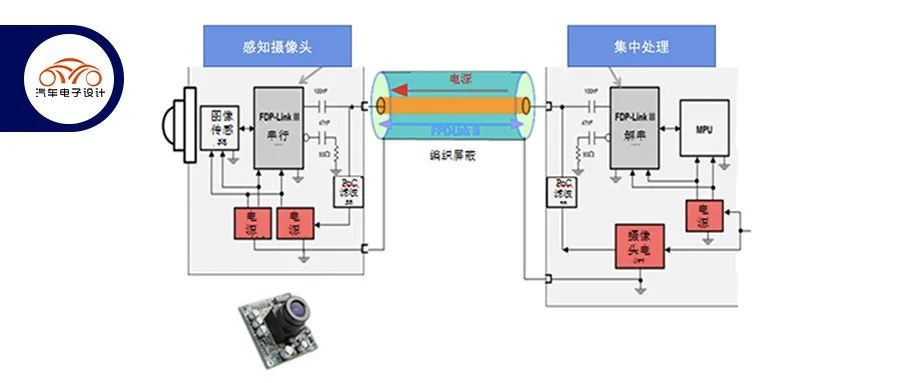
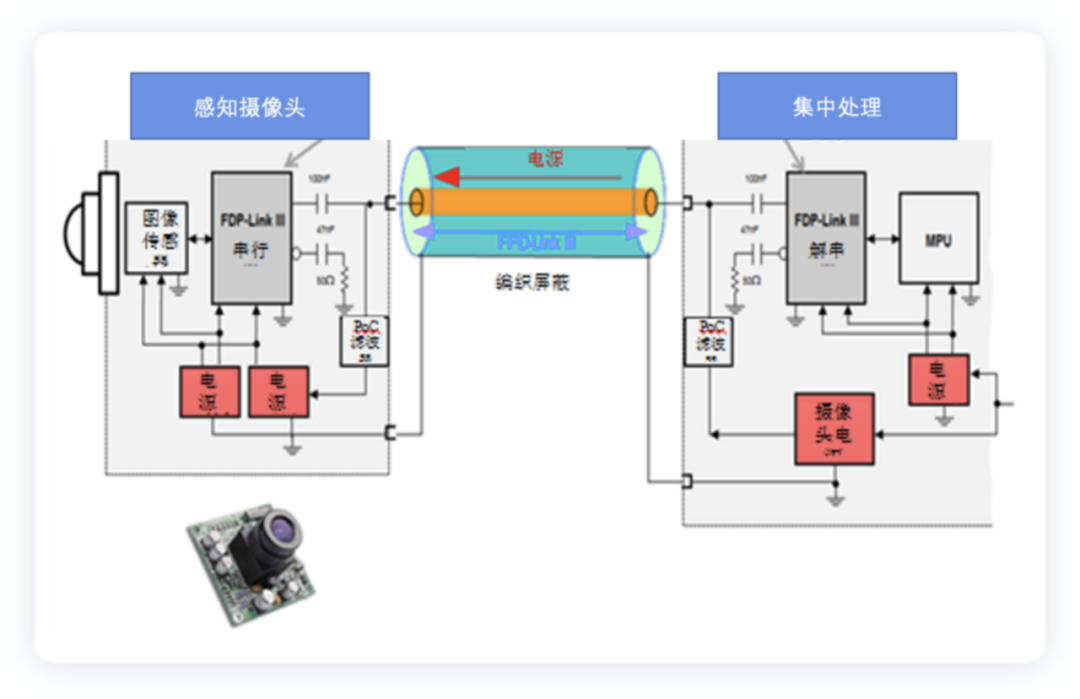
In the car, the Power over Coaxial Cable (PoC) provides a compact solution equipped with a widely used Flat Panel Display (FPD) Link III digital video interface. The deserializer transmits power and control signals through the coaxial cable, and the serializer sends back the video signal through the same cable.
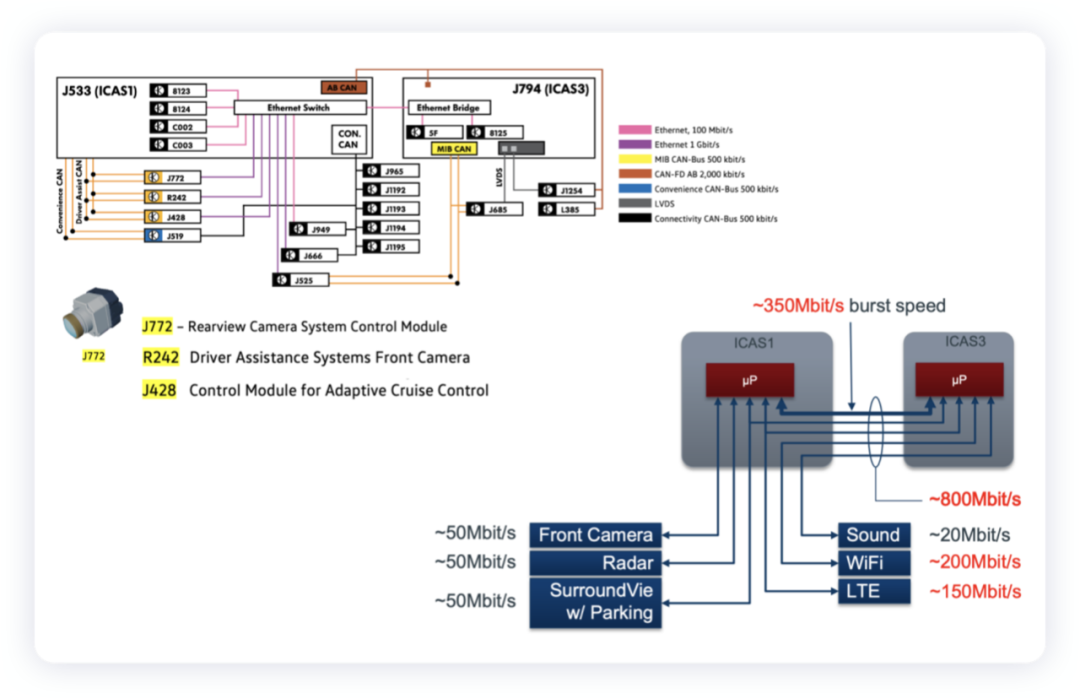
In Volkswagen’s original triple-domain control, the ICAS1 gateway is connected to the front and rear view control modules. That is, car companies began to try to use 100Base-T1 Ethernet (IEEE 802.3bw standard for 100Mb/s Ethernet), originally Broadcom BroadR-Reach, using PAM3 coding, full-duplex communication, and point-to-point topology. 100Base-T1 is used for applications that require medium-high data rates. Its main purpose is to replace existing technology (heavier and more expensive cables such as MOST and LVDS), and currently, several cameras in the ADAS field can be used for replacement.
Comparison of Cost Differences
In the previous parking analysis, there was actually an alternative consideration, which was to switch to Ethernet connections in the previous generation Taycan J1 platform, replacing the coaxial cable. Adjustments were mainly made in the aspects of cameras, wiring harnesses, and main control modules.
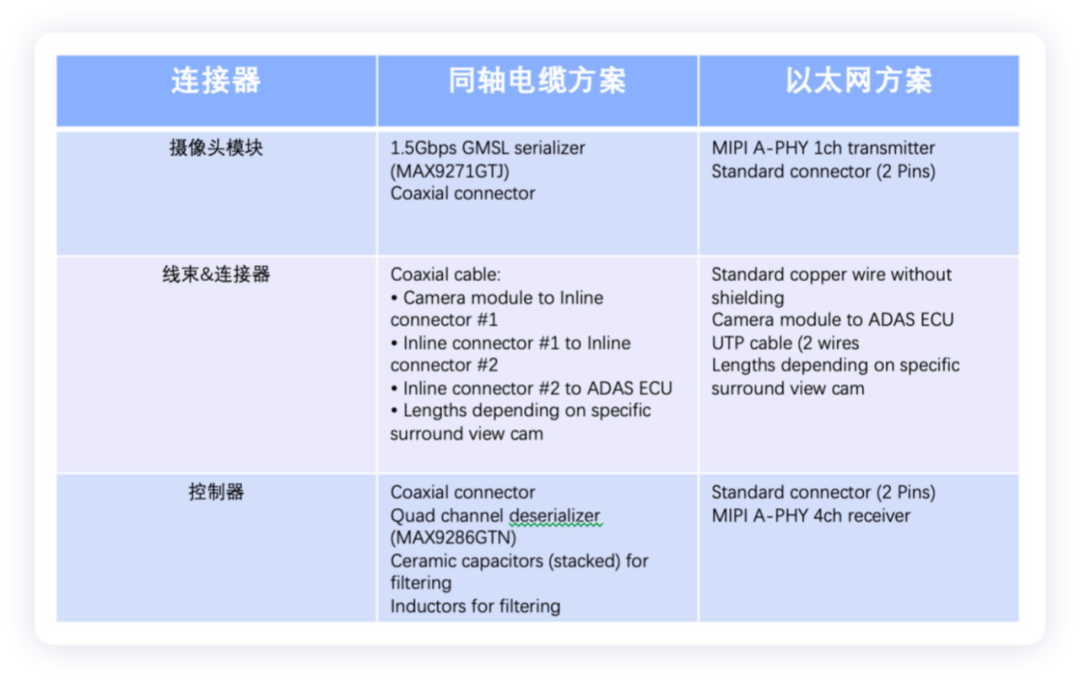 As mentioned above, in the coaxial cable scheme, the wire harness mainly uses LEONI Dacar® 462 KOAX, which corresponds to 3.96 US dollars. The cost of the whole connector set is about 24 US dollars, of which the cost of the connector is around 11 US dollars.
As mentioned above, in the coaxial cable scheme, the wire harness mainly uses LEONI Dacar® 462 KOAX, which corresponds to 3.96 US dollars. The cost of the whole connector set is about 24 US dollars, of which the cost of the connector is around 11 US dollars.
If it is changed to Ethernet connection, the change of the connector is shown in the figure above. The total cost of the connector can be controlled at 2.89 US dollars, the largest decrease. The cost of twisted pair LEONI Dacar® 546 2×0.35 is 0.17 US dollars/m. The total cost of the wiring harness system is 10 US dollars, which is reduced by 14 US dollars.
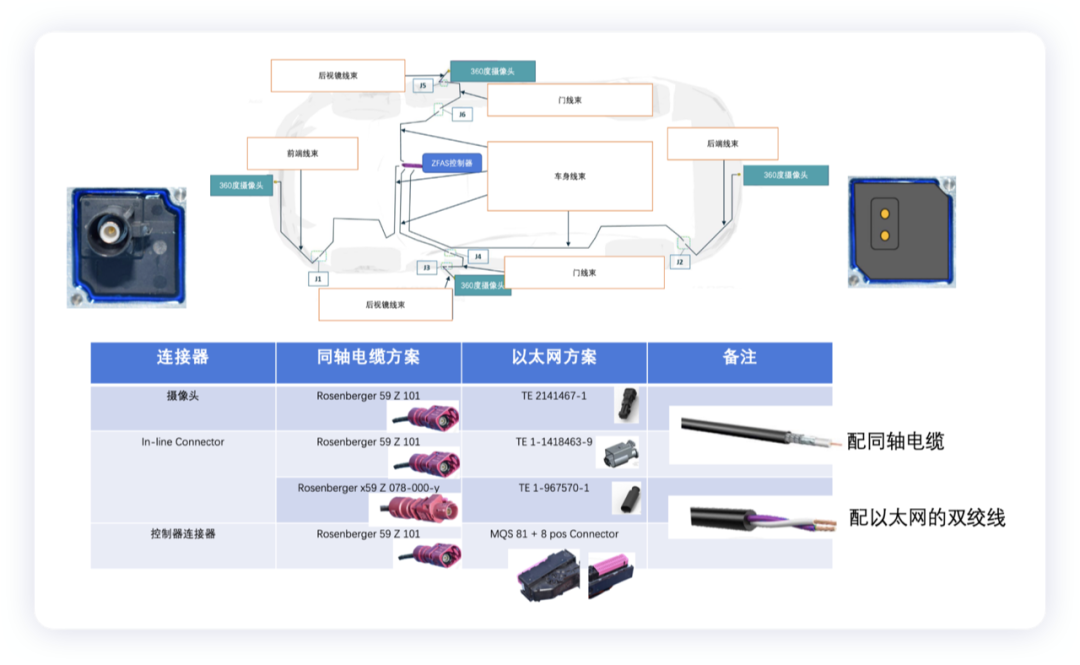
In summary, of course, many details can be obtained in the subsequent investigation. I think that in the process of advancing towards autonomous driving, the substitution of technical costs is the most important driving force.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.