Manbetx, sent from the copilot temple\
Intelligent car reference| WeChat official account AI4Auto
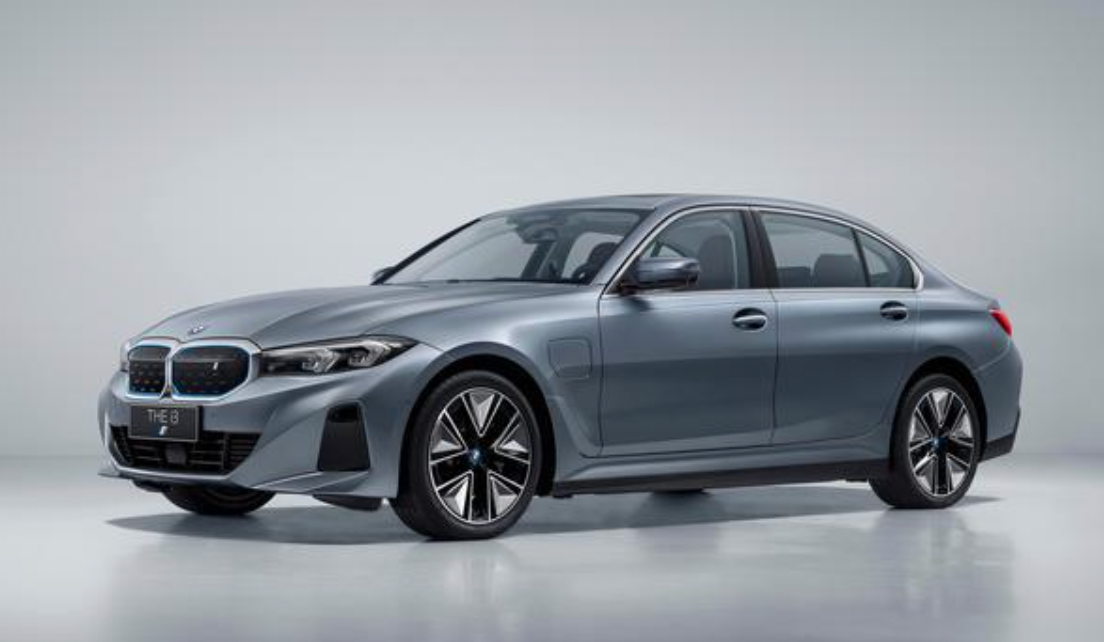
The BMW i3 has officially rolled off the production line at the Shenyang factory. Note that this is not the recently announced discontinued microcar i3, but the electric version of the classicBMW 3 series.
In terms of price, it is slightly more expensive than the fuel version of the 3 series, starting at 349,900 yuan. It directly competes with its rivals, NIO ET5 and Tesla Model 3.
In terms of intelligent driving, it is equipped with the Mobileye EyeQ4 chip, with a computing power of 2TOPS, and uses a solution of 3 front cameras and 5 mm-wave radar sensors.
The biggest highlight in terms of functionality is the hands-free driving in traffic congestion scenes, which is very similar to the L3 level intelligent driving system, Drive Pilot, installed in the Mercedes-Benz EQS. The only difference is that BMW i3 still requires the driver to maintain attentiveness.
On the three-electricity level, it adopts BMW’s fifth-generation eDrive electric drive technology, single-rear-mounted rear-wheel drive magnet synchronous motor, with a maximum output power of 210 kW and a peak torque of 400Nm.
The battery uses a 70 kWh high-nickel ternary lithium battery pack, with a maximum range of 526 kilometers and a fast charging time of more than half an hour.
In addition to inheriting the 3 Series, there is another major controversy about this car:
Is it gas-to-electric?
What Kind of Car Is It?
First, let’s take a look at the smart configuration.
In terms of intelligent driving hardware, the BMW i3 uses Mobileye’s EyeQ4 intelligent driving chip with a comprehensive computing power of 2TOPS.
The sensor solution selected by the BMW i3 includes 3 front cameras and 1 forward long-range mm-wave radar and 4 short-range mm-wave radars.
In terms of function implementation, in addition to basic driving assistance functions, BMW i3 is also equipped with the Pro automatic driving assistance system, the biggest highlight of this intelligent driving system is that it allows hands-free driving when the speed is below 60 kilometers per hour.
The usage conditions are similar to the Benz Drive Pilot intelligent driving system, but the difference is that the driver is allowed to do other things when driving hands-free under the Benz Drive Pilot system, such as watching dramas.But BMW i3 strictly requires drivers to keep their eyes on the road and pay attention to the driving status of the vehicle.
In addition, the BMW i3 can also achieve the function of shift lever lane change when driving at a speed of over 70 kilometers per hour.
However, all these functions require additional options at a price of 5,900 yuan. In addition, for an extra 8,600 yuan, automatic parking can also be selected.
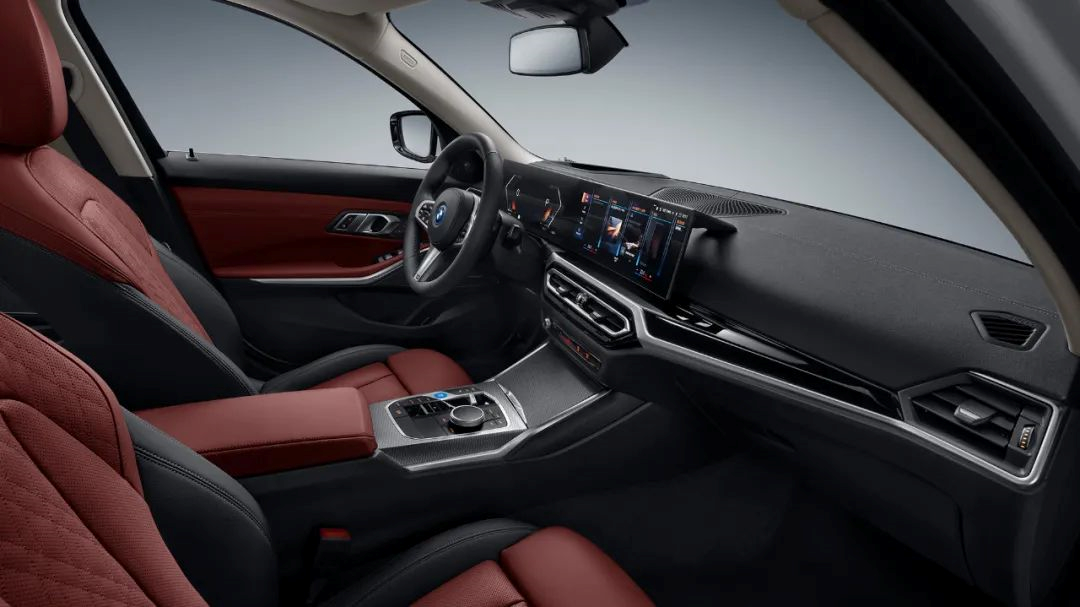

At the level of intelligent cockpit, BMW i3 is equipped with BMW iDrive operating system 8.0. The entire cockpit ecosystem is in deep cooperation with Tencent. Tencent’s applications, such as WeChat and QQ Music, are built into the cockpit system.
In addition, the BMW i3 also supports wireless Apple CarPlay, which is more familiar to Apple users.

At the interactive level, a curved dual-screen composed of a 12.3-inch digital instrument panel and a 14.9-inch touch screen replaces a large number of physical buttons.
Now let’s take a look at the three-electric system.
Based on the CLAR platform architecture, the BMW i3 adopts a single rear-mounted rear-drive motor layout, with a maximum output power of 210 kW and a peak torque of 400 N·m.
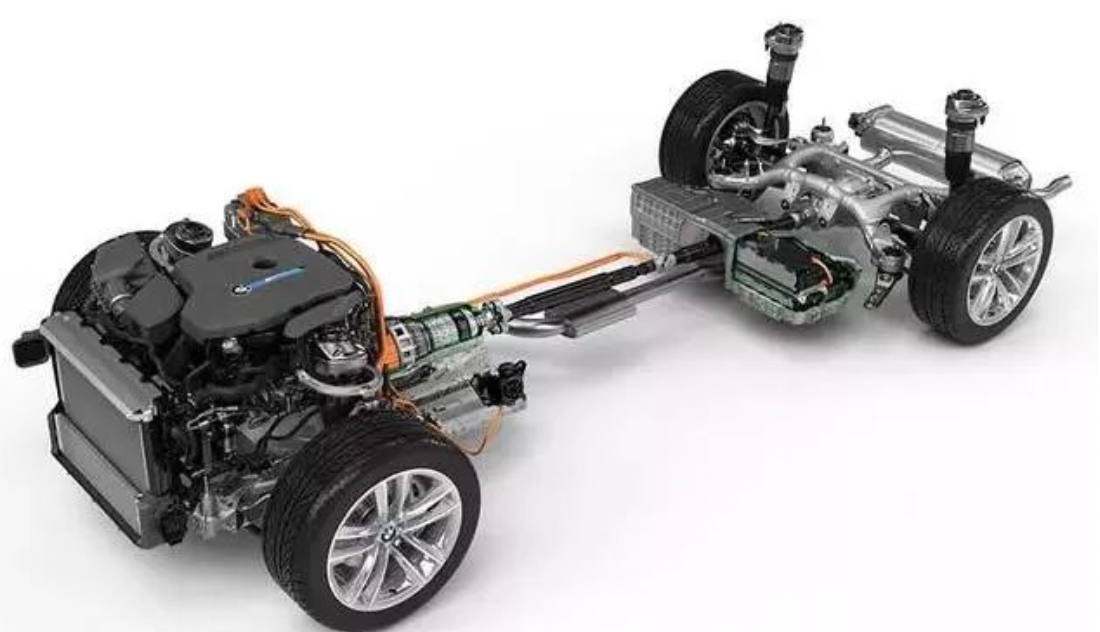

According to official data, the acceleration from zero to 100 kilometers per hour is 6.2 seconds.
As for the battery, the BMW i3 is equipped with a 70 kWh high-nickel 811 ternary lithium battery pack, which can achieve a maximum range of 526 kilometers. The time to fast charge 80% of the electricity is over half an hour, and the time for slow charging is 6.75 hours.
In terms of size, it is 4,872 mm long, 1,846 mm wide, 1,481 mm high, and has a wheelbase of 2,966 mm, which is relatively larger than the fuel version of the 3 Series.

Regarding the exterior and interior, since it inherits the BMW 3 Series, the BMW i3 has not changed much in appearance, and the difference is that the front grille is fully enclosed, while still retaining the traditional BMW grille style.
Lastly, the price.
The BMW i3 is priced from CNY 349,900, which is about CNY 50,000 higher than the starting price of the 3 Series.
Within this price range, there are two competitors targeting the same market segment as a mid-sized pure electric sports sedan, NIO’s ET5 and Tesla’s slightly cheaper Model 3, both of which are scheduled to be delivered in the second half of this year.
Can the ET5 and Model 3 compete with each other?
When it comes to pure electric vehicles, the first thing to compare is intelligence, followed by electrification, while brand attributes such as cultural soft power are subjective.
Therefore, let’s make a head-to-head comparison in terms of intelligence, three-electric technology, and price, based on paper data.
Let’s first discuss intelligent driving. What is Tesla’s greatest claim to fame?

Full Self-Driving (FSD) system, from algorithm to chip, is a completely self-developed technology that functions entirely on a visual-based approach. Currently, extensive full-automated driving tests are being carried out in North America.
Although FSD full automatic driving function cannot be used in China yet, the upgraded version of autonomous assisted driving function is already available. Highway assisted driving function such as Autosteer, automatic entrance and exit ramps and automatic lane switching, as well as automatic parking, are already supported.
Now with the NIO ET5. It is equipped with the NIO Autonomous Driving (NAD) system, which boasts an impressive computing power of 1016 TOPS, equivalent to four NVIDIA Orin chips, putting it in a completely different class than the BMW i3 in terms of computing capability.

According to NIO’s official website, the company’s Aquila perception system and Adam computing platform is gradually achieving “autonomous driving” in four major scenarios: highways, urban areas, parking, and battery swapping.
Of course, it should be emphasized that it is a gradual implementation. However, it is certain that high speed autonomous driving capability, such as the capability of Autosteer, will be achieved in mass production. This is because all of NIO’s older models are already equipped with this technology.
In terms of capability, it is similar to Tesla. Basic functions such as automatic ramp entry and exit, automatic lane switching, and automatic obstacle avoidance can all be achieved.

Compared to the two models mentioned above, the only competitive advantage the BMW i3 has is the function of allowing hands-free driving. However, its computational power of 2 TOPS is nowhere near the level of the Model 3 and ET5.The BMW i3 is severely constrained by the chip’s computing power in achieving more intelligent driving functions through OTA updates in the future, which means that it has completely lost this battle. As for the intelligent cockpit aspect, each of the three models has its own characteristics, with features such as digital keys and voice interaction. However, the NIO VR glasses remain unique for the “metaverse” cabin in the mass-produced cars. In terms of the “three electric” aspects, the low-end version of the Tesla Model 3 is equipped with a rear permanent magnet synchronous motor with a maximum output power of 194kW, peak torque of 340N·m, and acceleration of 6.1 seconds per hundred kilometers. As for the battery and range, the low-end Model 3 is equipped with a 60kWh lithium iron phosphate battery with a maximum range of 556 kilometers and a quick charging time of one hour. Overall, the “three electric” data of the BMW i3 is slightly better than the low-end Model 3, but it is still inferior to the 3.3-second 0-100 acceleration and 675-kilometer range of the high-end version of the Model 3. On the other hand, the NIO ET5 adopts a front and rear dual motor layout with a maximum output power of 360kW, peak torque up to 700N·m, and acceleration of 4.3 seconds per hundred kilometers. As for the battery and range, the three versions of the ET5 are equipped with standard range battery packs (75kWh) with a range exceeding 550 kilometers, long-range battery packs (100kWh) with a range exceeding 700 kilometers, and ultra-long-range battery packs (150kWh) with a range over 1000 kilometers. The BMW i3 is still at the bottom. Finally, let’s talk about the price. The Model 3 starts at 290,000 yuan, making it the cheapest of the three cars. The NIO ET5 starts at 325,000 yuan, but it also has a BaaS plan (battery rental), with a pre-subsidy starting price of 258,000 yuan. The more expensive BMW i3 has a starting price of 349,900 yuan. So, in terms of overall price and other paper data, the most expensive BMW i3 is actually the least attractive. Its only advantage is the traditional luxury brand tone of BMW, and not to mention the backing of the classic 3 Series. What do you think?
One more thing
After discussing this car itself, let’s talk about the controversy around the BMW i3 and other pure electric vehicle models based on the BMW CLAR platform architecture:
Is it really a conversion from gasoline to electricity?
Let’s first take a look at what the netizens have to say:
And as buyers ourselves, we consulted a BMW 4S dealership in Beijing not long ago and got the following answer:
The BMW i3 cabin has two large screens, which are different from the gasoline version of the 3 Series, so it is not considered a conversion from gasoline to electricity. As for the three electric characteristics of the chassis, it is not a standard for distinguishing between conversions from gasoline to electricity.
This answer…is quite interesting.
Any PR jargon would suffice, but from a technical point of view, whether it is a conversion from gasoline to electricity ultimately depends on the design concept of the chassis architecture, which is the essence of the controversy, and whether the CLAR platform is a platform for converting from gasoline to electricity.

Official information shows that the CLAR platform was launched in 2015, and during its development, the underlying architecture design for pure electric vehicle models, 48V light hybrid vehicle models, plug-in hybrid vehicle models, and gasoline vehicle models were comprehensively considered.
In other words, the difference between the CLAR platform and the platform for converting from gasoline to electricity is that the latter is based on the transformation from gasoline vehicles to electric vehicles, while the CLAR platform ensures that it is adaptable to both gasoline and electricity from the outset of the development process.
Therefore, the CLAR platform may not necessarily be a platform for converting from gasoline to electricity, but it certainly is not a pure electric platform.
However, this type of development concept that wants both fish and bear paws is less likely to have greater expansion in the future compared to a true pure electric platform.

At this point, the controversy over whether the CLAR platform is a platform for converting from gasoline to electricity is not very significant. What is more worthy of attention is BMW’s conservatism and helplessness in the process of electrification transformation, which lies behind the CLAR platform.
After all, BMW’s real pure electric platform, NEUE KLASSE (New Generation), will not be launched until 2025.
Before this, if BMW wants to lay out in the electric vehicle market ahead of time, it can only make do with the CLAR platform for now.
— Done —
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
