WM 发自 副驾寺
Smart Car Reference | AI4Auto WeChat Account
Growth, growth, and more growth. In the latest quarter financial report, Xpeng’s revenue, delivery, and loss situation all improved significantly.
Looking at the trend, high growth has become a norm for Xpeng’s performance. However, Xpeng’s long-term vision and current challenges are also further exposed under high growth.
Affected by the rise in raw material prices, Xpeng’s overall gross profit margin is 12%, a decrease of 2.4 percentage points month-on-month, and the automotive sales gross profit margin is 10.9%, a decrease of nearly 2.7 percentage points month-on-month.
However, Xpeng’s profitability has not substantially improved for the entire previous year.
What is the reason?
Xpeng’s Long-term Vision and Current Challenges
The long-term vision and current challenges are both reflected in Xpeng’s profitability.
According to the latest quarterly financial report released by Xpeng, as of Q4 2021, Xpeng’s overall gross profit margin was 12%, a decrease of 2.4 percentage points from the previous quarter. Automotive sales gross profit margin is 10.9%, a decrease of 2.7 percentage points compared to the previous quarter.
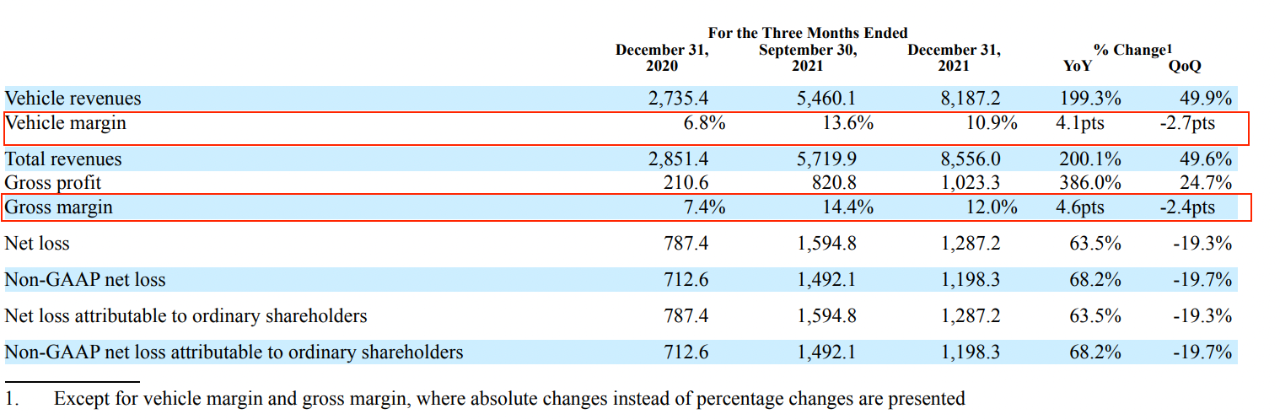
Xpeng’s official explanation for the decline in gross margin involves the rising prices of battery raw materials during Q4, which led to an increase in the production cost of complete vehicles.
At the same time, He XPeng, the CEO of Xpeng, indicated that Xpeng will work with suppliers to enhance the prevention and control of battery shortages this year. He believes that there will be some changes in material prices in the next one to three quarters, and ultimately the company is capable of better controlling battery costs.
Therefore, the rise in battery raw material prices has become the current challenge impacting Xpeng’s current profit level.
But in the long run, far-sightedness is a deeper issue that Xpeng must face.
Historical data shows that Xpeng’s gross profit margin for each quarter in 2021 was 11.2%, 11.9%, 14.4%, and 12%, respectively, and the automotive gross profit margin was 10.1%, 11%, 13.6%, and 10.9%, respectively.
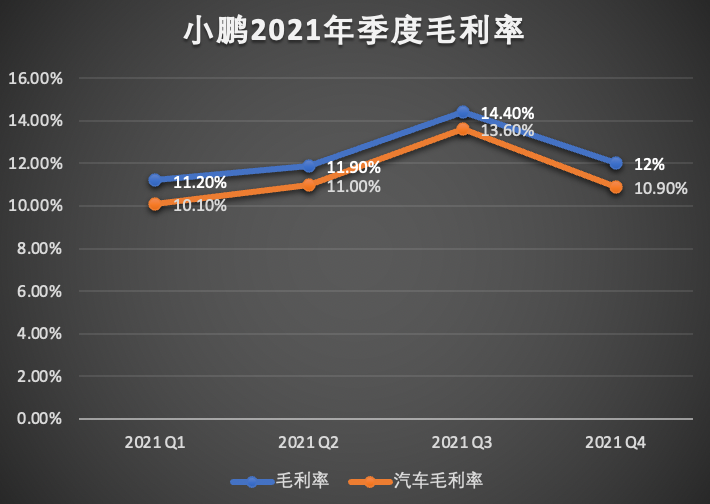
In other words, Xpeng’s financial performance steadily increased in 2021, except for gross margin, which stagnated, and profitability did not improve substantially.
At the same time, such a gross margin performance is even more prominent when compared to its peers, such as NIO and Li Auto. In Q4 2021, the gross margin of NIO and Li Auto was 17.2% and 22.4%, respectively. In the long run, NIO’s annual gross margin for last year was 18.9%, while Li Auto’s was 21.3%.
In contrast, Xpeng’s overall gross profit margin for 2021 was 12.5%, which is a clear disadvantage in comparison.If there are differences in business strategies between NIO and Li Auto and XPeng, a horizontal comparison is not representative. In this case, Tesla can be used as a reference point for XPeng.
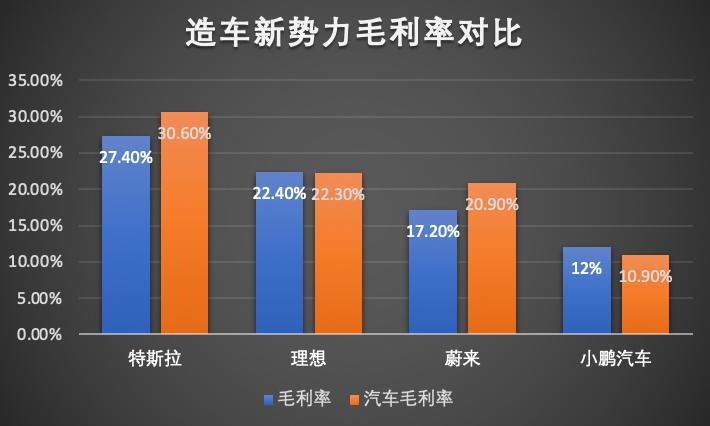
Tesla’s latest financial report shows that in the fourth quarter of last year, its overall gross profit margin was 27.4%, and the gross profit margin of cars was as high as 30.6%. The annual gross profit margin was 25.3%, and the gross profit margin of cars was 29.3%.
In terms of growth, XPeng’s gross profit margin in the first quarter of last year was roughly equivalent to that of Tesla in the first quarter of 2019, which was 12.5%. However, different from XPeng, Tesla’s gross profit margin had reached 18.8% by the end of that year, and it had achieved profitability in the second half of that year.
In the same one-year period, XPeng’s quarterly gross profit margin remained basically unchanged.
Therefore, the question can be further explored:
Why can’t XPeng’s profit level be increased?
The product is still the most crucial factor. Regardless of whether it is NIO, Li Auto, or XPeng benchmarking Tesla, they all have a common feature: the high-end nature of the product.
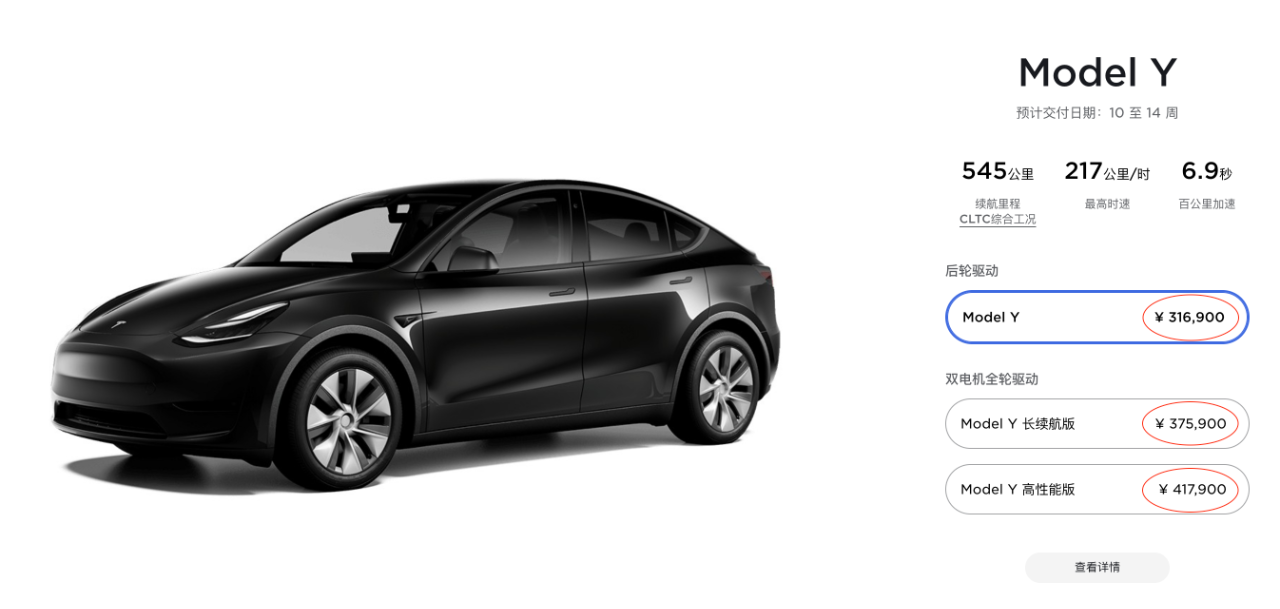

The price range of Tesla’s main model, Model 3, is between RMB 290,000 and RMB 360,000, while Model Y is priced at RMB 310,000 to RMB 410,000. The main models of NIO and Li Auto are also priced at more than RMB 300,000, and the price of NIO ES8 even reaches up to RMB 600,000.
However, the prices of XPeng’s current three main models are all lower than those of the above-mentioned competitors. This is certainly following the “mass” route and taking the lead in firmly establishing its foothold in the largest consumer area of the market. But at the same time, XPeng also has to bear the other side of the coin: insufficient brand strength.
What does the high-end product nature bring? Advantages in pricing and profit margins.
Taking Tesla as an example, in the fourth quarter of last year, its automotive sales revenue was US$15.96 billion, with 308,700 deliveries. By extrapolation, Tesla’s average revenue per car was as high as US$51,700 (equivalent to RMB 330,000), while the automotive sales cost of Tesla in the same period was US$10.689 billion, with an average cost per vehicle of US$34,600 (equivalent to RMB 220,000).

In other words, Tesla’s gross profit margin per vehicle is as high as RMB 130,000.At XPeng, the automotive sales revenue for Q4 2020 was RMB 8.187 billion, delivering 41,751 vehicles at an average unit revenue of only RMB 196,000. During the same quarter, total automotive sales costs were RMB 7.297 billion, with the average cost of each vehicle being RMB 175,000. As a result, XPeng’s gross profit margin per vehicle was left with only RMB 21,000.
Therefore, the answer to the problem of core profitability seems to be evident: the unequal pricing power brought by brand tonality is the main reason for XPeng’s weak profitability, which is exactly where XPeng’s foresight lies.
How much does high-end models affect XPeng’s profitability? One set of data can illustrate the issue.
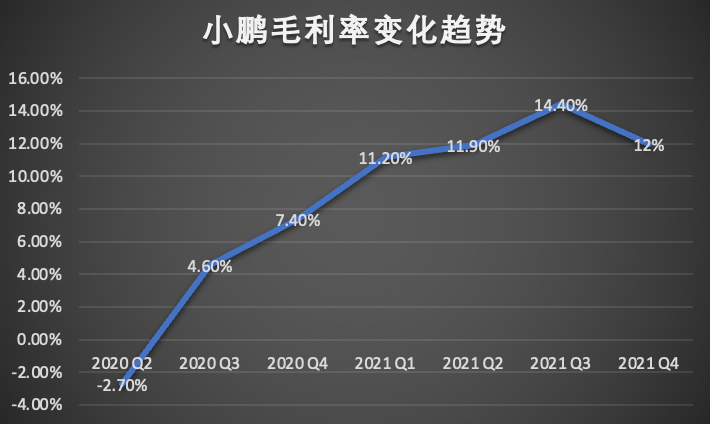
From the growth trend of XPeng’s gross profit margin, in Q3 2020, XPeng’s gross profit margin finally turned positive and then sharply increased to 11.2% in Q1 2021, which then maintained at over 10%.
The takeoff time of XPeng’s gross profit margin happened to coincide with the large-scale delivery of XPeng’s high-end model P7.
However, now, the growth of the gross profit margin has basically stalled, which also reflects that the single-engine of XPeng P7 is no longer powerful enough to improve the gross profit margin.
What Will XPeng Do?
Previously, He XPeng rarely mentioned the gross profit margin target. But this time, this issue was finally brought up in the analyst conference room:
“The company’s medium- to long-term goal is to increase the overall gross profit margin to over 25%.”
The goal has been set, so what’s left is how to achieve it.
In this regard, Tesla, which has already paved the way, has provided XPeng with a good template. To broaden its pricing power, focusing on the mid to high-end markets may be the best way out and choice for XPeng.
XPeng is actually doing just that.

According to XPeng’s product plan, XPeng G9, a high-end pure electric SUV, will be launched in June this year and start delivery in the second half of the year, which will be responsible for another gross profit margin growth engine.
From the latest official information released, G9 is based on XPeng’s latest intelligent electric platform, including X-EEA 3.0 electronic and electrical architecture, XPower 3.0 power system, high-performance chassis, and a higher-level intelligent cockpit system. It supports 800V high-voltage fast charging, and the 5-minute charge can achieve a range of 200 kilometers.On the intelligent configuration side, He XPeng revealed during an analyst conference that the latest XPILOT 4.0 intelligent driving system from XPeng will be installed, enabling intelligent driving fusion between highway and urban open road scenes.
As for the most important aspect, pricing, XPeng hasn’t made any public announcements yet; however, compared to the same level models of ES6 and Ideal ONE, and considering the software and hardware configurations, the market generally guesses that the price will be between 300,000 and 4 million yuan.
In addition, He XPeng also revealed that a C-level car and a B-level car will be launched next year based on XPeng’s two new platforms. The prices are unknown.
He XPeng stated that the main task of these two cars is to help XPeng gain cost control ability, so as to cover a wider range of user groups in the rapidly growing mid-to-high-end market.
Of course, the P7, which truly establishes XPeng as a flagship, will also be upgraded in the mid-term with the addition of “laser radar,” as the current P7 cannot be iterated to the stage of intelligent driving on urban open roads.
Although XPeng’s core profitability has not increased, the benefit is that the investment in intelligence is starting to transition from potential energy to kinetic energy.
Starting from the P5, XPeng’s intelligent sensor scheme has stabilized, and the ability of intelligent driving will continuously shift from offense to defense, with the company’s focus further tilting towards product line, brand, and user services.
Finally, we will briefly summarize the main points of XPeng’s financial report this time:
What does the financial report say?
First, let’s look at the overall operating performance:
In Q4 last year, XPeng Automobile’s revenue scale reached RMB 8.556 billion, a year-on-year increase of 200.1% and a sequential increase of 49.6%, with automobile sales revenue reaching RMB 8.187 billion, a year-on-year increase of 199.3% and a sequential increase of 49.9%.
Sales costs were RMB 7.532 billion, an increase of 185% YoY and an increase of 53% QoQ.
Three expense items were RMB 2.015 billion, up 60% YoY and down 28% QoQ, and R&D expenses were RMB 1.451 billion, up 215.43% YoY and up 15% QoQ.
In terms of deliveries, XPeng Automobile delivered a total of 41,751 vehicles in Q4, a year-on-year increase of 222.1% and a sequential increase of 63%, ranking first among local new forces in the same period.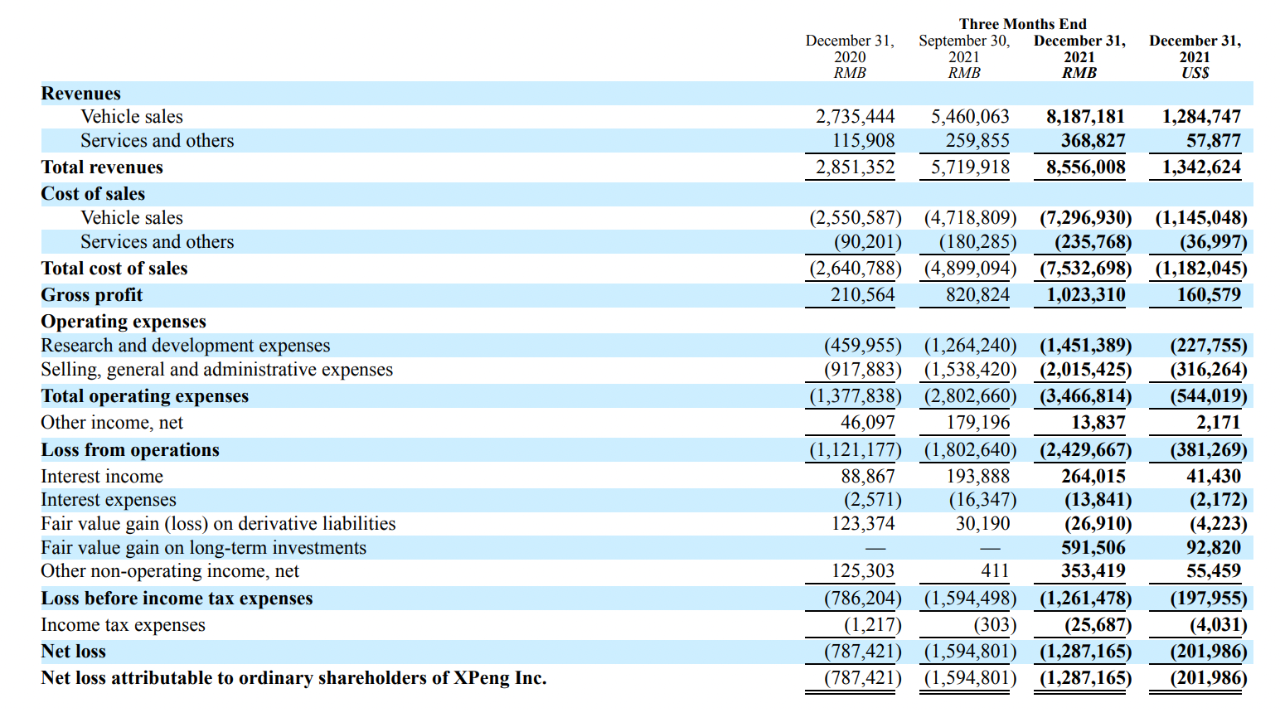
On an annual basis, XPeng’s revenue for the entire year reached CNY 20.988 billion last year, an increase of 259.1% compared to the previous year. Among them, the revenue from car sales was CNY 20.042 billion, an increase of 261.3% compared to the previous year.
Sales costs were CNY 18.366 billion, an increase of 229% compared to the previous year. The three expenses totaled CNY 5.305 billion, an increase of 81.6% compared to the previous year, and research and development expenses were CNY 4.114 billion, an increase of 138% compared to the previous year.
The gross profit margin was 12.5%, an increase of 8.1 percentage points compared to the previous year. The gross profit margin of car sales was 11.5%, an increase of 8 percentage points compared to the previous year. The net loss was CNY 4.863 billion, an increase of 49.8% compared to the previous year.
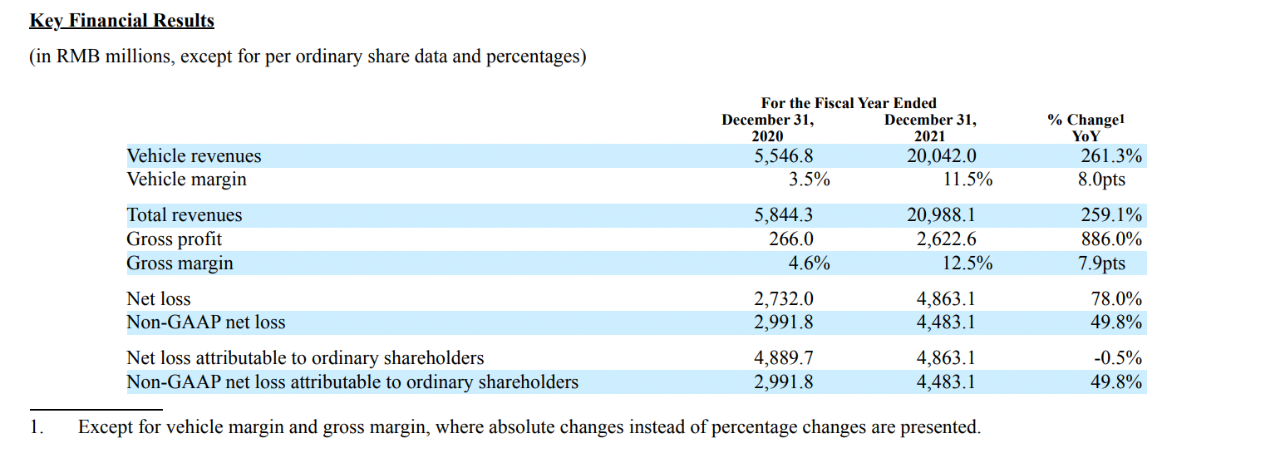
In terms of deliveries, XPeng delivered a total of 98,155 vehicles last year, an increase of 263% compared to the previous year, ranking first among new car makers.
Regarding intelligence, He XPeng spoke about the entire industry:
XPILOT 4.0 will have a technological advantage over mainstream automakers’ intelligent driving systems, while also being able to comprehensively catch up with and even surpass some (capabilities of) domestic RoboTaxi players.
Head RoboTaxi players? It goes without saying who they are.
XPILOT 4.0 is currently in the testing and research phase and is expected to be launched next year. It is planned to be installed on four models, including XPeng P5, XPeng G9, and two new models to be launched next year.

In terms of autonomous driving capabilities, XPeng will integrate highway navigation assistance and city open road intelligent driving.
XPILOT 3.0, which is currently in mass production, has a penetration rate of 20%, and the latest iterative version of XPILOT 3.5 is expected to complete city open road intelligent driving function NGP in the second quarter of this year.
It is expected to be pushed after obtaining approval for high-precision maps of cities in the second half of this year.
In addition, He XPeng also revealed information about RoboTaxi:
Starting in the fourth quarter of this year, RoboTaxi testing will begin, and the testing platform will be XPeng’s newest G9.
The RoboTaxi plan will officially begin in 2026. He XPeng said that according to the current situation, the timing and effectiveness may come earlier than this point.
one more thing
Although XPeng has prepared to launch an attack on the high-end market, Tesla has already set an example in front. But their paths are opposite:
Tesla’s route is to establish itself in the market with the luxury cars Model S and Model X, costing over 700,000 yuan, and then release cheaper cars around 300,000 yuan to increase sales, moving down the high-end brand to capture the market, which consumers buy this.

On the other hand, we have mainly taken the cost-effective route in the previous stage, and now we want to move our brand up to pursue the high-end market. The difficulty level of this path is enough to make countless domestic car companies cry blood and tears.
At least in the short term, it is not easy to support a high-end car model costing over 300,000 yuan.
However, for XPeng, or other car-making new forces that rely on cars costing less than 100,000 yuan to seize the low-end market, this is a difficult path. But, to survive and thrive, moving the brand up is almost the only and best way out.
This high-end road has also happened in the smart-phone market. Huawei has succeeded, but Lei Jun, XPeng’s big brother, is still struggling with Xiaomi.
As for car manufacturers, is there any reference for the previous paths?
Annual Report Link:
https://d18rn0p25nwr6d.cloudfront.net/CIK-0001810997/08b0622b-984f-4027-ad55-05befacb3bf4.pdf
— The End —
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
