Author: Zhu Yulong
At the Electric Vehicle Hundred People Convention, Xin Guobin, Vice Minister of Industry and Information Technology, proposed to “improve regulations and standards, and enhance quality and safety levels”. He particularly mentioned “releasing and implementing guidance on safety system construction for new energy vehicle enterprises, improving power battery thermal runaway alarm and safety protection levels, making consumers more willing to buy and more confident in use”.
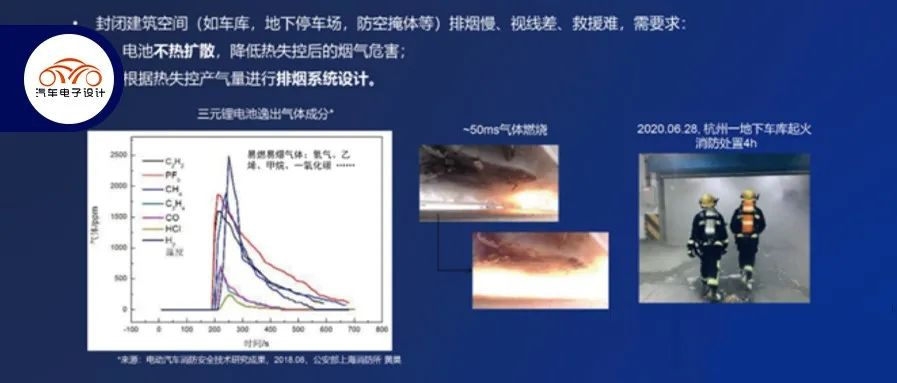
As electric vehicles have developed, user demands have mainly focused on range and fast charging, with safety being the bottom line. Power battery safety is an important component of new energy vehicle safety, and solving the safety issues of power batteries can greatly alleviate user concerns about the safety of new energy vehicles. Especially since electric vehicles are appearing more frequently in closed building spaces such as garages, underground parking lots, and bomb shelters, these closed spaces have slow smoke evacuation, poor vision, and difficult rescue operations, posing higher requirements for the safety of electric vehicles.
An Inventory of Power Battery Safety Technologies
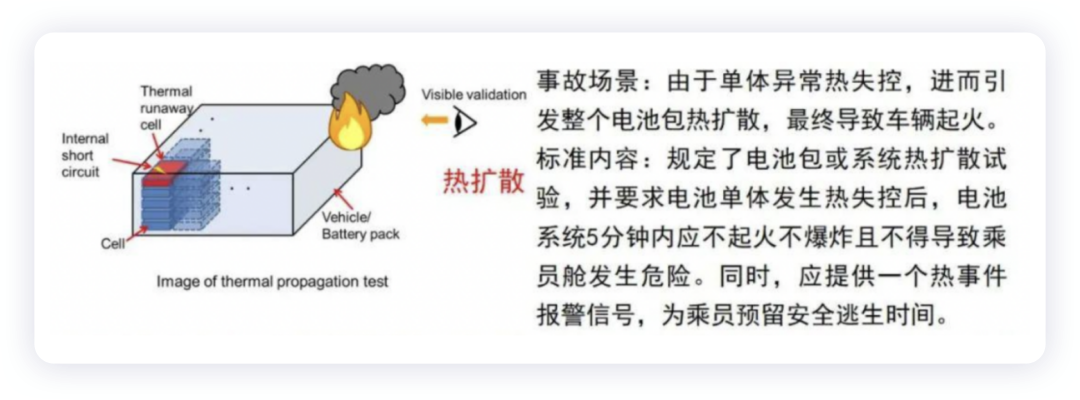
If the system does not undergo thermal diffusion in the event of single battery cell failure, it can significantly reduce the smoke hazard after thermal runaway; within a building, if only individual battery cell thermal runaway gas production occurs locally, the range of smoke control is relatively easy to manage. This way, the public will have more confidence in owning new energy vehicles in the next stage, and their understanding of the safety of new energy vehicles will be more comprehensive, thus protecting lives and property to the greatest extent possible.
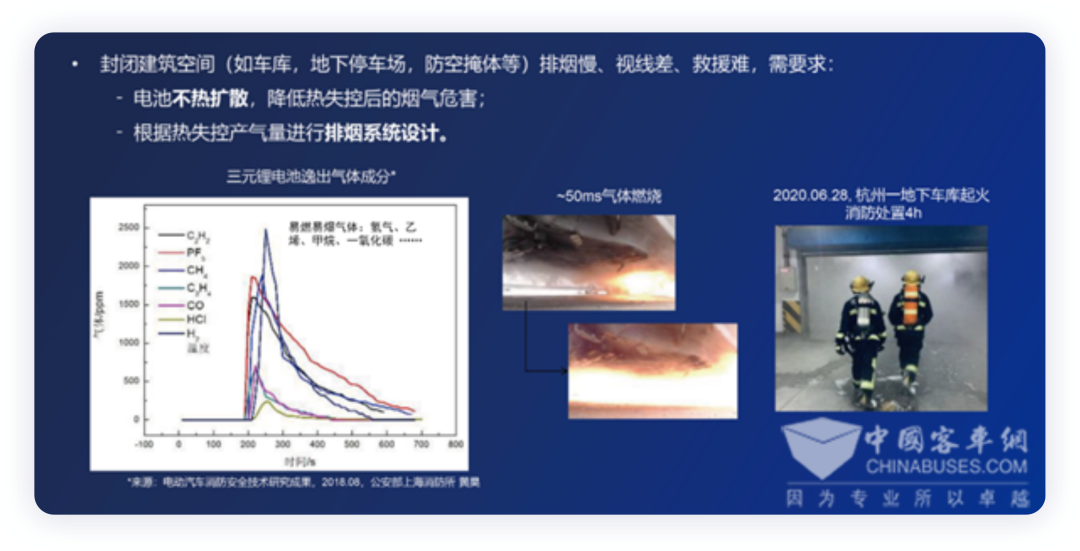
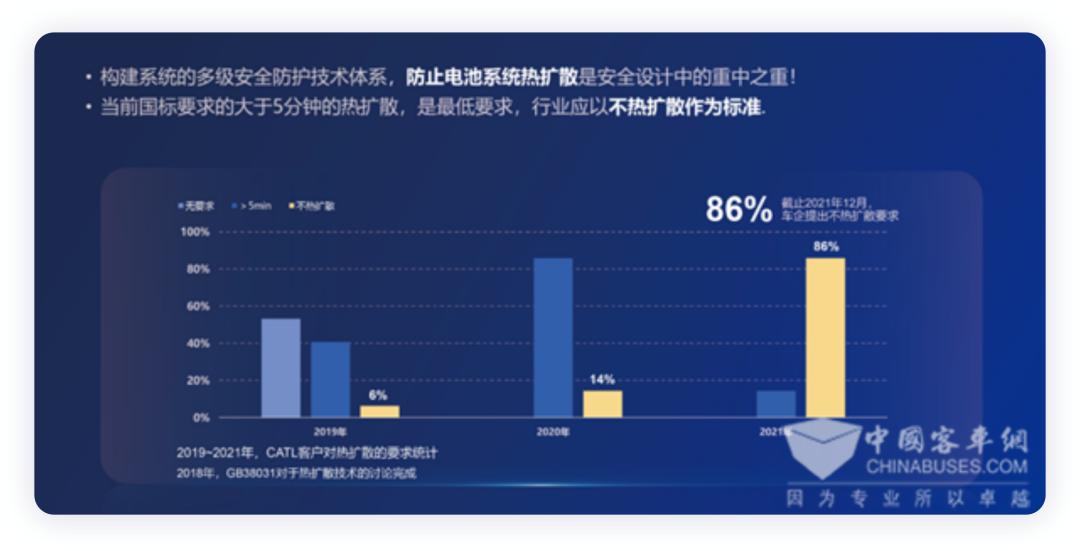
First, let’s take a look at the requirements of China’s power battery safety regulations. In May 2020, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology announced that the mandatory national standard GB 30381-2020 “Safety Requirements for Power Battery of Electric Vehicles” organized by it has been approved and issued by the State Administration for Market Regulation and the National Standardization Administration, and will be implemented from January 1, 2021. “Safety Requirements for Power Battery of Electric Vehicles” specifically adds a battery system thermal diffusion test, requiring that after a battery cell undergoes thermal runaway, the battery system should not catch fire or explode within 5 minutes, leaving safe evacuation time for passengers.
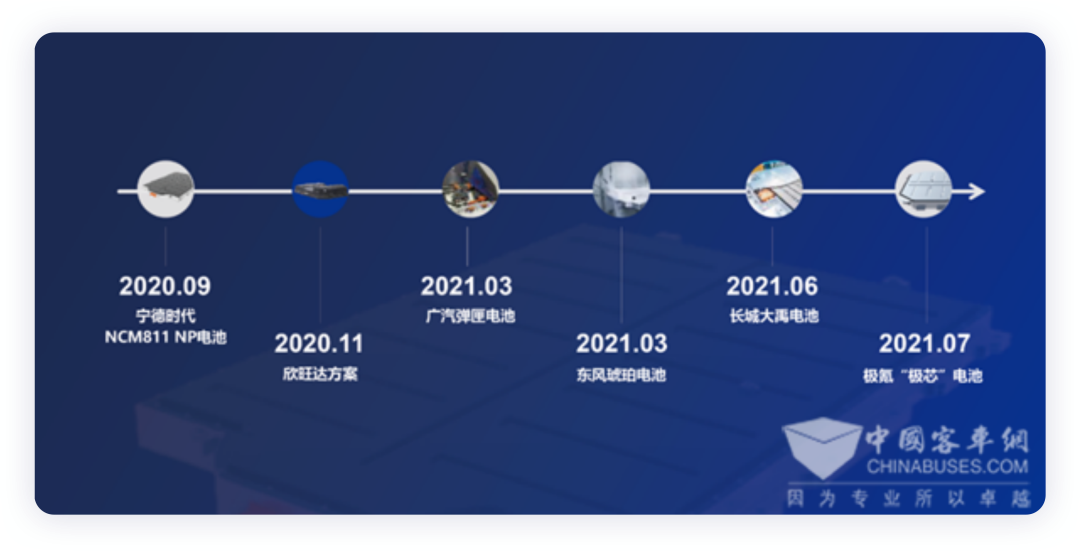
With the progress of 2021, Chinese battery companies and vehicle manufacturers have begun to continuously release technologies related to battery safety, mainly including:
 – Battery Manufacturers
– Battery Manufacturers
CATL, BYD Battery, Amperex Technology Limited, Farasis Energy
- Automakers
BYD, JAC Motors, GAC Motor, Dongfeng Aeolus, Great Wall Motors, Geely Geometry
Timeline of Mainstream Automakers and Battery Manufacturers’ Technology
- Jan 2020
BYD’s Blade Battery
- Mar 2020
JAC Motors’ Honeycomb Battery
- Sep 2020
CATL introduces NCM811 NP battery
- Dec 2020
Farasis Energy’s Gel Polymer Battery
- Dec 2020
Amperex Technology Limited introduces non-flammable battery
- Mar 2021
GAC Motor introduces Magazine Battery
- Mar 2021
Dongfeng Aeolus introduces Amber Battery
- Jun 2021
Great Wall Motors introduces Dyad Battery
- Jul 2021
Geely Geometry introduces Geely Core Battery
These battery systems are able to achieve non-propagation of thermal runaway for five minutes, based on the experiment. However, the safety measures of battery manufacturers are questioned by some people. As suggested by Wang Fengying, NPC Representative and CEO of Great Wall Motors, during the Two Sessions in 2022, many automakers are currently working on safety technology for preventing thermal runaway for power batteries, but the promotion of new technologies has not met expected results due to insufficient awareness in the industry.
Therefore, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) has released the 2022 Work Plan for Automotive Standardization, emphasizing the revision of safety standards for power batteries to improve the warning and protection against thermal runaway. In future revisions of safety standards, it is possible that requirements for thermal diffusion may be raised to a mandatory level, thereby increasing safety threshold.
In conclusion, safety is of the utmost importance in the electric vehicle industry, and problems should be solved from the source. Non-propagation of thermal runaway should be a standard feature at this stage.
Safeguards for Vehicle Owners by Automarkers
As indicated in a speech by CATL at a China Hunderd People’s Club, only 14% of enterprises had “high requirements” in 2020, believing that batteries should have the requirement of single-cell thermal runaway without the propagation of the system. The vast majority of enterprises have since increased their design requirements for non-propagation technology to 86% in 2021, indicating that automakers are also quickly increasing the design requirements in order to prevent vehicle combustion. This is a common technology requirement for automakers, allowing for faults in the battery cell yet preventing accidents.
Current technical means and data are as follows:- The difference in chemical systems makes it more challenging to develop 811 ternary batteries than ternary 5 series and phosphate-based lithium-ion batteries. The main difficulty lies in the high-nickel cathode materials.
-
For the thermal insulation material between battery cells, aerogels are an example. The first layer of insulation material is used to separate the batteries according to the space requirements of different chemical systems, to prevent thermal runaway between them.
-
Heat insulation materials should be used regularly between battery cell compartments. High-temperature insulated composite materials are also used, and directional explosion-proof outlets are designed, which directs the high-temperature gas and flame outwards.
-
Pressure relief and gas discharge: multiple flow channels are designed to control the flow of heat sources according to the predetermined trajectory, minimizing thermal impact on adjacent battery blocks. The thermal runaway of battery cells is also efficiently expelled through these channels, which prevents sudden thermal impacts on adjacent battery cells and the occurrence of secondary thermal runaway.
-
Insulation design: High-voltage components inside the battery pack require insulation protection. Both high-voltage connections and high-temperature safety zones inside the battery pack must also have insulation design.
At the 100-People Conference, Ningde Times introduced its 8 series products that have achieved non-thermal diffusion. The new generation of high specific energy NP products, which can travel 1000 km, will soon be manufactured in bulk.
In 2022, the transition from low-range safety to high-range safety is crucial. As the low-range version of LFP (lithium iron phosphate) penetrates the market more extensively, the safety of ternary batteries, which are capable of super-fast charging, must be improved. Once these conditions are met, the safety of China’s battery systems will fully cover the global market. China was the first to introduce the experiment of detecting thermal runaway transmission in five minutes to the safety field of power batteries. The establishment of standards for battery safety should boost China’s confidence. GTR (Global Technical Regulation) should not be the only criterion for regulating the safety of electric vehicles. China’s new energy vehicles rank at the forefront of the world, and aim to set the international standards.
Personally, I believe that with the upgrade of the safety standards of electric batteries by the Department of Industry and Information Technology, the revision of safety standards should consider the stages of industry technological development and the rigid demands of Chinese consumers. Thus, I suggest the inclusion of non-thermal diffusion technology in the new national standard for new energy vehicles, which aligns with the original purpose of developing new energy automobiles.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.