2021, the dust has settled. The power battery market experienced a rollercoaster year.
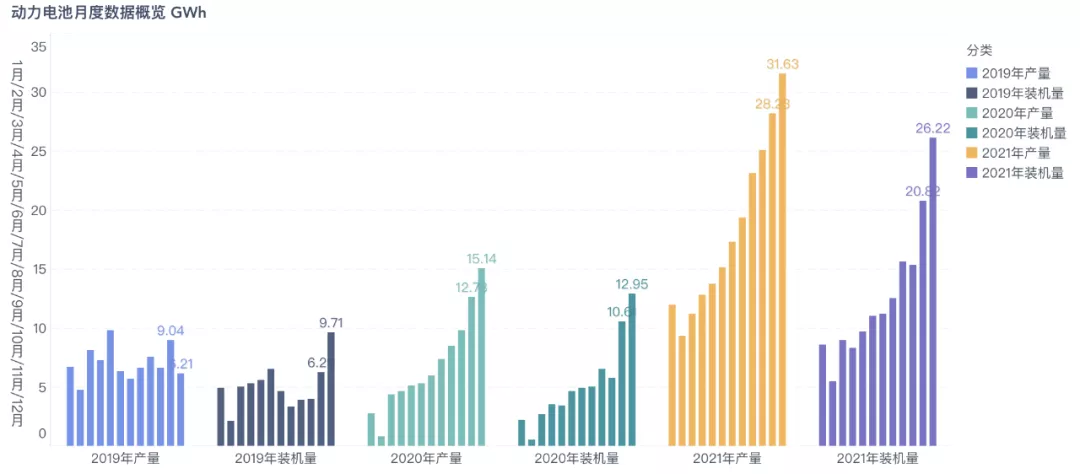
A few days ago, the Power Battery Innovation Alliance released the monthly data for December 2021:
- December: production of 31.6 GWh, sales of 35.5 GWh, and installation volume of 26.2 GWh
- 2021: production of 219.7 GWh, sales of 186.0 GWh, and installation volume of 154.5 GWh
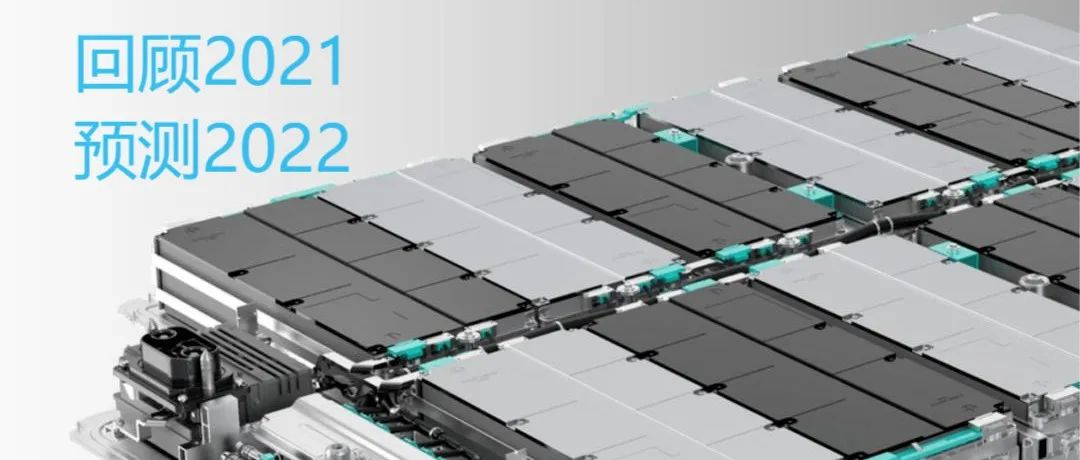
The following figure shows that in 2020 and 2019, the power battery market was still in a state of stagnation, but in 2021, the demand for power batteries suddenly surged.
In 2021, the production of power batteries exceeded 219.7 GWh, a year-on-year increase of 163.4%. The production of ternary batteries did not exceed 100 GWh, but remained at a high level of 93.9 GWh. The production of lithium iron phosphate batteries accumulated to 125.4 GWh, accounting for 57.1%, and the year-on-year cumulative growth reached 262.9%. Lithium iron phosphate batteries surpassed ternary batteries, which is very clear and distinct.
Market Specification Overview
- The main demand
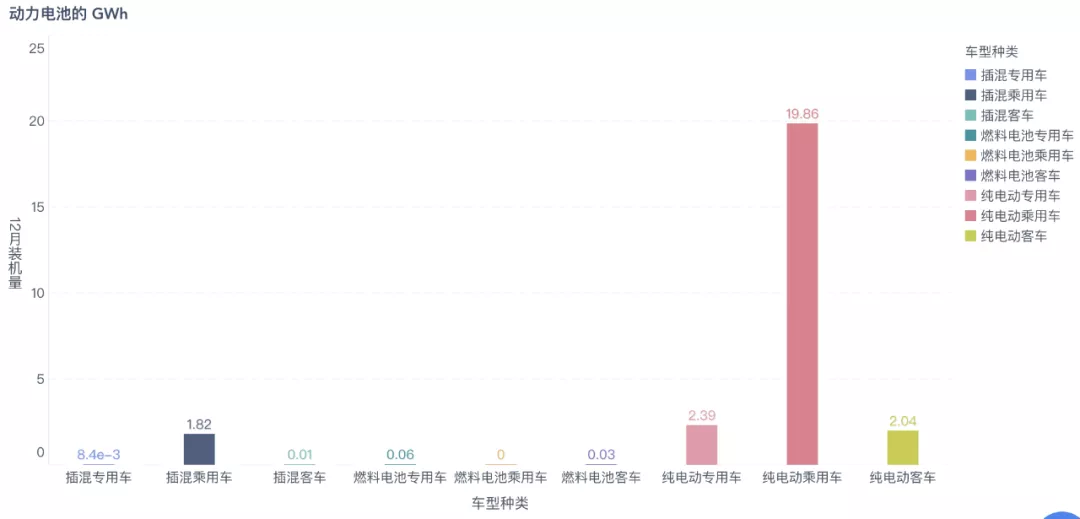
In December, plug-in hybrid passenger vehicles used 1.82 GWh of power batteries, pure electric commercial vehicles used 4.43 GWh (2.04 GWh for pure electric buses and 2.39 GWh for pure electric trucks), and pure electric passenger vehicles still lead far ahead with 19.86 GWh.
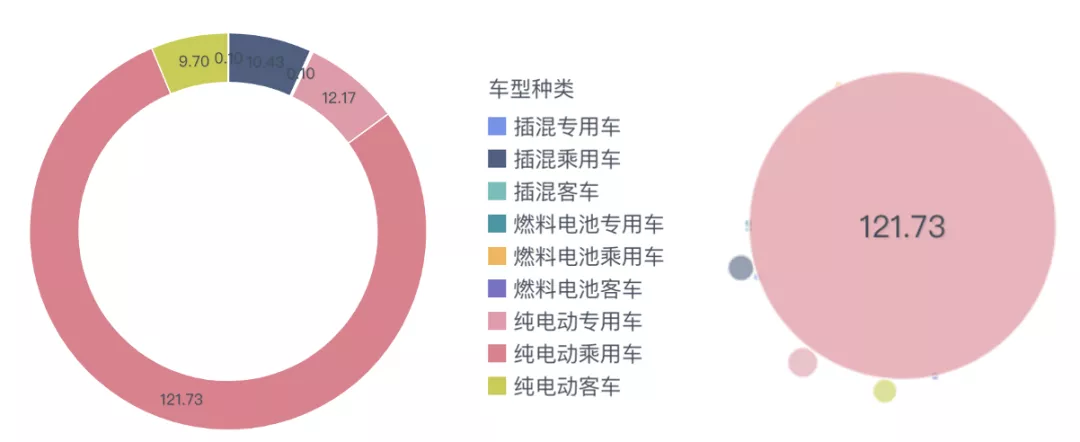
Looking at the whole year of 2021, pure electric passenger vehicles used 121.73 GWh of batteries, accounting for 78.7%. The annual demand for pure electric buses, pure electric special-purpose vehicles, and plug-in hybrid passenger vehicles ranged from 10-12 GWh each, which means that the power battery industry is highly concentrated in the passenger car market. Objectively speaking, this confirms that the current demand growth is driven by the demand for new energy vehicles in the consumer market (C-end). The consumer market is many times larger than the commercial market (B-end). As the penetration rate continues to increase, the gap between the C-end and the B-end will continue to widen.
- The situation of power battery suppliersBy the end of 2021, there will be only 58 power battery enterprises left in China as suppliers are further aggregated. In December 2021, the market share of the top 3, top 5, and top 10 power battery enterprises was 75.8%, 84.5%, and 93.4%, respectively. In terms of the annual ranking, the power battery installed capacity of the top 3, top 5, and top 10 power battery enterprises was 114.6 GWh, 128.9 GWh, and 142.5 GWh, with a market share of 74.2%, 83.4%, and 92.3%, respectively.
However, the following figure provides a more intuitive view: CATL accounts for more than 52%, BYD’s market share is 16%, and CTE’s share is 6%. The concentration effect in this market is very thorough and obvious.

Regarding the penetration of iron phosphate batteries in December, the installed capacity of ternary batteries and iron phosphate batteries was 11.1 GWh and 15.1 GWh, respectively, with a year-on-year increase of 84.7% and 118.5%. The installed capacity of iron phosphate batteries is rapidly surpassing that of ternary batteries. In terms of various auto companies, who is leading the way?
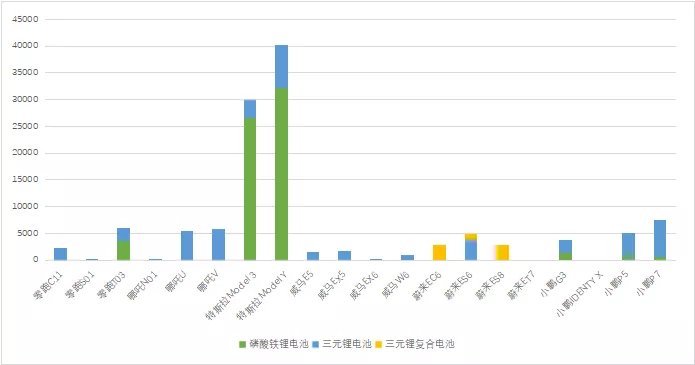
The following is classified based on the matching of vehicle models. From the vehicles delivered in December, Tesla, BYD, and Wuling have rapidly switched to iron phosphate batteries (over 75%), followed by Changan and Ora (over 40%). However, most other automakers are still in the planning phase, mainly limited by the production capacity of iron phosphate batteries and the switch speed of the whole vehicle.
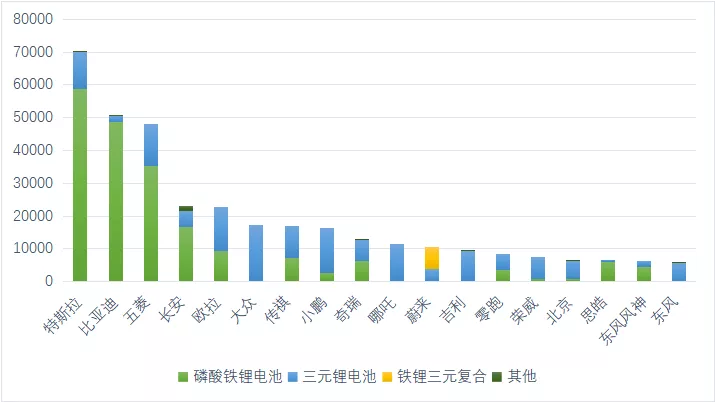
Tesla’s application speed and proportion in iron phosphate batteries are the fastest, accounting for the vast majority of new vehicle manufacturing, as shown in the figure below.
Based on an estimated 60,000 units, Tesla alone used 3.6 GWh of iron phosphate batteries. NIO uses the latest technology of iron phosphate and ternary composite, and the 75 kWh ternary composite battery currently accounts for more than half of NIO’s overall production. XPeng has not been able to obtain sufficient production capacity of iron phosphate cells effectively; therefore, the majority of its cells are currently based on ternary cells. Leading Ideal’s T03, LI has obtained a large number of iron phosphate cells, so the speed of iron phosphate battery adoption is also relatively fast.
 ## The Evolution of Technology and Demand Pattern
## The Evolution of Technology and Demand Pattern
To gain a deeper understanding of the technology trends in 2022, it is necessary to carefully compare the actual situations of lithium iron phosphate and ternary battery systems.
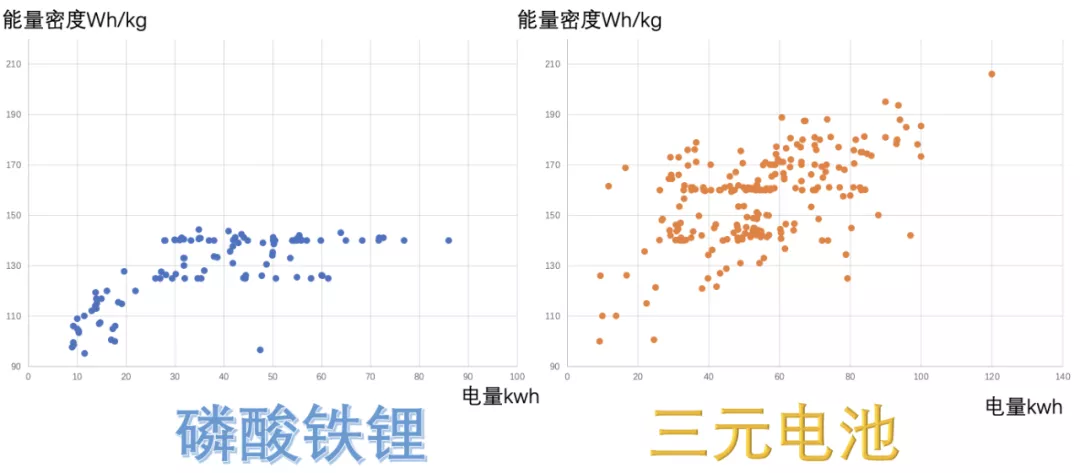
According to the data, currently, the energy density of most lithium iron phosphate battery systems is below 140Wh/kg, which still has some gaps compared to ternary batteries.
In other words, the difference in the whole-package energy density of lithium iron phosphate and ternary batteries mentioned before does exist. Part of the ternary battery energy density has exceeded 200Wh/kg and is moving towards even higher data. In the era where subsidies are essential, energy density is indeed crucial, but subsidies have begun to be gradually phased out of long-term consideration.
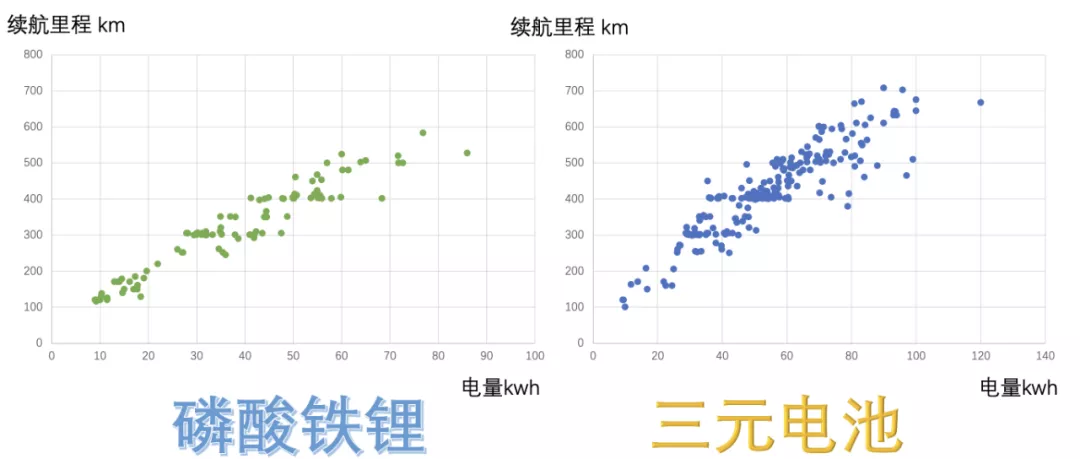
In December 2021, the lithium iron phosphate battery system can support a range of 600 kilometers for pure electric vehicles.
Ternary battery systems do have some advantages in terms of energy density, but the biggest problem is still that comprehensive comparison puts it at a disadvantage. Pure electric cars equipped with ternary batteries can reach 700 kilometers in range, but it is mainly relying on 100kWh or so battery products. Under the condition of no subsidies for below 20kWh, the cost is hard to bear compared to lithium iron phosphate. The products with a range of around 300 kilometers, 400 kilometers, 500 kilometers, and 600 kilometers are more intensive for ternary batteries.
In terms of the comparison of core parameters, currently, lithium iron phosphate has advantages in safety and cost and can meet the needs of consumers for the range of electric cars. With the increasing cost pressure in 2022, automakers need to switch to lithium iron phosphate on a large scale to effectively address cost issues.
In 2022, possible technological changes include:
1) Ternary high-end batteries starting to launch the first generation of fast-charging batteries based on a 2C standard, which marks the first differentiation in high-end product lines in 2022.
2) The fast-charging speed of lithium iron phosphate is also improving, and according to the current situation, 2C lithium iron phosphate batteries will gradually be promoted in 2022.
3) In 2022, second-line battery companies that previously focused on the development of ternary batteries will also begin to launch their lithium iron phosphate products.
Starting from 2017, safety issues have plagued the Chinese electric vehicle industry for a long time. Therefore, lithium iron phosphate staged a magnificent comeback in 2021. However, from the perspective of product characteristics, I personally believe that the ternary technology route has the potential for long-term evolution.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
