Author: Da Yan
At the 2022 CES in Las Vegas, Volvo, which had just achieved successful market debut in 2021, also released a series of heavyweight messages one after another, demonstrating its latest achievements in the field of pure electric and intelligent interconnected.
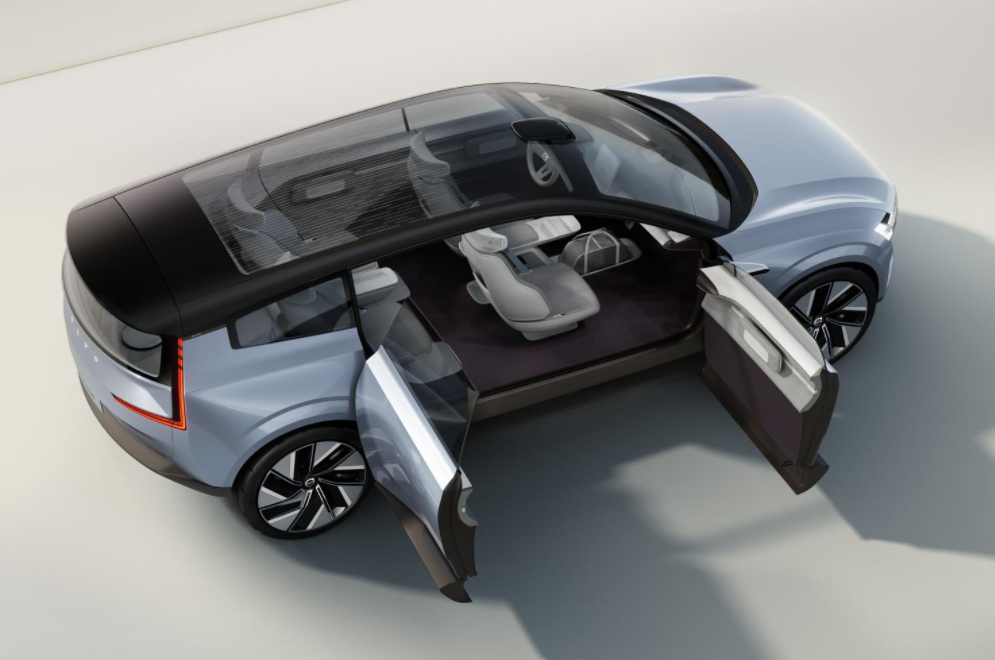
Based on Volvo’s brand-new pure electric platform, the Concept Recharge, along with a series of strategies such as the introduction of the Qualcomm Snapdragon digital cockpit platform, deep integration with Google Assistant, and the highly autonomous driving function – Ride Pilot, declared the strongest smart interconnected technology for this northern European luxury brand.
Ride Pilot is the biggest highlight of Volvo’s CES
Volvo started research on autonomous driving / driving assistance functions very early in the luxury brand market, and is one of the few brands to popularize the City Safety function.
As early as 2016, Volvo cruised at 70km/h on the 6th Ring Road in Beijing to test the Drive Me autonomous driving test project. For Volvo, the most important goal in promoting autonomous driving is to maximize the reduction of various accidents that may occur during the driving process, in addition to bringing people a better driving experience.
Therefore, in recent years, Volvo has been polishing its own autonomous driving system until the latest achievements were revealed to the outside world this time.
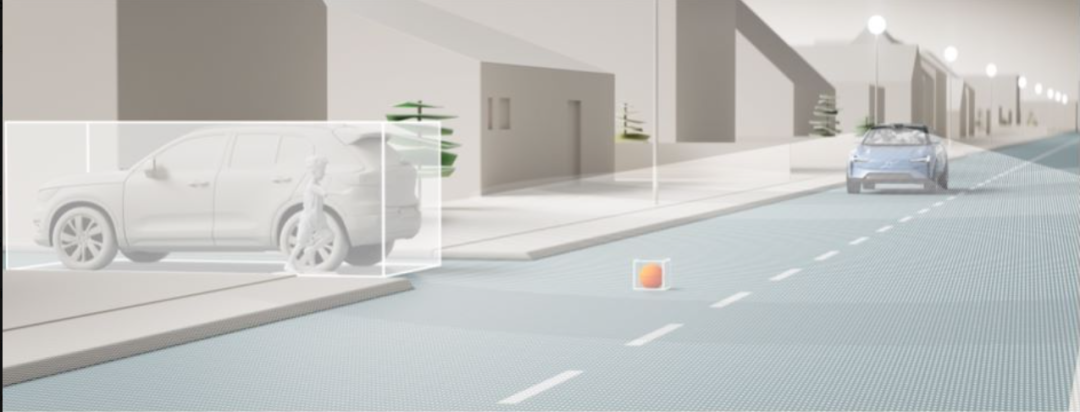
At CES, Volvo officially announced that it will launch the highly autonomous driving function – Ride Pilot to users in California, USA. Once Ride Pilot is enabled, the driver can delegate all driving-related work to Volvo, which not only means that drivers can be freed from the heavy burden of driving, but also can spend more driving time engaging in activities such as reading, writing, office work, and socializing. This highly advanced autonomous driving system created by Volvo, which is based on vision safety, will naturally be highly anticipated by people.

To achieve highly autonomous driving, preparation must be made in both software and hardware.
In terms of hardware, Ride Pilot will be equipped with more than 20 sensors, among which Luminar’s Iris laser radar sensor will become the biggest highlight. In addition to Luminar’s laser radar sensor, it will also be equipped with 5 radars, 8 cameras, and 16 ultrasonic sensors.In terms of software, Ride Pilot relies on Zenseact, an autonomous driving software development company under Volvo, and the development team from Luminar, a technology company within Volvo. They aim to create a software platform that can maximize hardware capabilities and achieve automatic driving functions.
After the high-speed road safety test of Ride Pilot passed, Volvo will also follow the example of other OEMs such as Tesla, and offer subscription services to owners of their new pure electric flagship SUV, which will be launched later this year. This provides Volvo with a new source of income, in addition to total vehicle sales revenue. Of course, the relevant autonomous driving software can also be continuously upgraded through OTA functions to gradually unlock more autonomous driving scenarios for consumers.
Qualcomm and Google collaborate with Volvo to enable intelligent cockpit
In addition to autonomous driving technology, intelligent cockpits are also an important area of competition among major OEMs in the era of intelligent connectivity. In terms of intelligent cockpits, Qualcomm and Google have become Volvo’s biggest reliance for maintaining technological leadership.
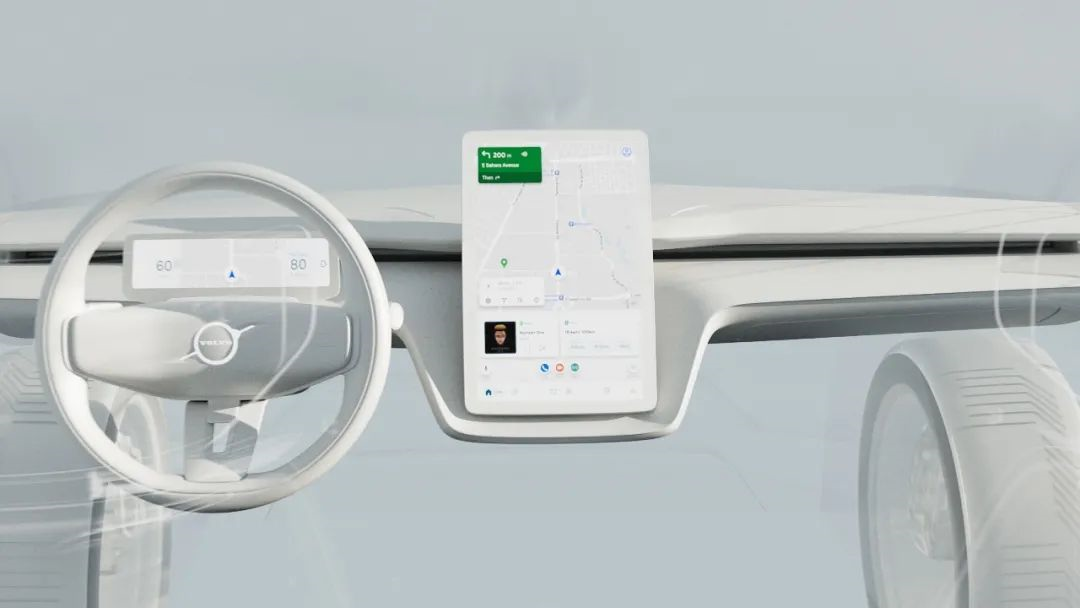

At CES 2022, Volvo announced its collaboration with Qualcomm. In the future, Volvo’s pure electric SUV will be equipped with the Snapdragon digital cockpit platform as a high-performance central hub. With the support of this platform, the operating speed of Volvo’s next-generation in-vehicle infotainment system will be doubled, and the image generation speed will be increased by 10 times to meet customers’ continuous demands for images, audio, and artificial intelligence.
In addition, Volvo will further deepen its collaboration with Google on its next-generation intelligent in-vehicle communication system. It will become the first car company to directly integrate with Google Assistant devices.
With the support of Google Assistant devices, the Volvo in-vehicle system can be deeply integrated with the Google smart home ecosystem. Volvo owners can remotely control various functions on their cars via voice commands on the Google system on the car or any mobile device that supports Google Assistant after the vehicle is synced with their personal Google accounts. With Google Assistant, users can not only access various information of the car at any time but also unlock many new features, including charging preset functions, to set a specific time for the car to begin charging, providing more convenient operations.

Meanwhile, Volvo has also paid attention to the exclusive needs of Chinese users.The built-in native Android automotive system co-developed by Volvo and Google not only leads the way in adaptation, stability, and fluency in the segmented market, but also provides a more open automotive intelligent ecosystem. Domestically leading technology giants such as Gaode Map, iFlytek, Huawei, Tencent, and Alibaba can embed their services and applications in Volvo’s set of automotive systems, enabling seamless connection between daily life and driving life for Chinese consumers.

The Urgent Need to Accelerate Forward-looking Technologies in China
Currently, the driving assistance/autonomous driving capability will be an important reference indicator for domestic consumers when purchasing a car, especially when buying a new generation of smart electric vehicles. Better driving assistance/autonomous driving functions can not only greatly improve driving safety but also reduce driver fatigue.
As Volvo’s largest single market globally, when Ride Pilot can be introduced to the Chinese market will have a direct impact on Volvo’s future sales in the country. However, the landing of Ride Pilot is not just about the completion of hardware installation and the importation of Zenseact algorithms. Similar to the large number of tests it has conducted in Europe and the United States, Volvo also needs to conduct a large number of road tests in China to achieve the deployment of Ride Pilot technology in the country. This requires a considerable amount of time and accumulation and cannot be achieved overnight. Currently, Volvo has set a midterm goal of selling 1.2 million vehicles annually, and the pivotal position in the Chinese market is self-evident. In the face of domestic competitors’ continuous updates of driving assistance/autonomous driving functions, Volvo needs to accelerate the deployment of Ride Pilot in the Chinese market.
Models on the SPA2 platform will gradually be revealed in 2022, and Volvo’s existing models will usher in a new round of updates and replacements. The launch of more competitive new generations of electric vehicles will help Volvo achieve its strategic transformation into a pure electric luxury brand car company. Throughout this process, whether it is relying on its own Zenseact self-developed autonomous driving software platform or software and hardware products from top partners such as Google, Luminar, and Qualcomm, Volvo seeks to maximize the synergies and work hard to achieve its strategic goals.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
