Introduction
With the rapid development of autonomous driving technology, the commercialization process is gradually accelerating. The last three kilometers of urban end-to-end delivery, as a huge market, is one of the scenes where autonomous driving technology is most likely to land first, and has also become the focus of attention for major manufacturers and start-ups.
At present, the main scene of end-to-end unmanned delivery is express delivery and instant delivery, the latter including take-out, fresh food, supermarkets, and retail. According to the “End-to-End Unmanned Delivery Track Research Report” by Chentao Capital, the market size of China’s end-to-end delivery market will exceed 300 billion yuan in 2021, and no matter which scene it is, it contains huge market value.
At this stage, the commercial model of unmanned delivery has initially formed, the technology can support part of the scene demand, and major manufacturers have also come up with their own physical unmanned delivery vehicle solutions, such as Meituan’s Magic Bag 20, Alibaba’s Small Donkey, JD.com’s fourth-generation unmanned delivery vehicle, and so on. This article will take readers to review the development of the unmanned delivery industry and the improvements and performance of various vehicle products in this year.

Latest Development of Unmanned Delivery Industry
With the rise of industries such as express delivery and take-out in recent years, the market demand for logistics and distribution in China is huge, and the demand for express delivery and instant delivery business is also growing at a high speed. In promoting this market, major internet companies have also keenly smelled the huge business value and introduced unmanned delivery-related products early. With the further maturity of autonomous driving technology this year, unmanned delivery has also been commercialized in many scenes, and unmanned delivery vehicles from major companies have taken a big step forward from testing to normal operation. Meituan’s automatic delivery vehicle, Magic Bag 20, has achieved normal trial operation on public testing roads in Beijing. Alibaba’s Small Donkey has also successfully entered more than 200 universities in the country for delivery operations, and JD.com has launched a brand-new fourth-generation unmanned delivery vehicle this year for its end-to-end logistics and delivery business. It can be said that as one of the scenes where autonomous driving technology is most likely to land first, unmanned delivery has attracted the attention of many internet companies and startups, and its market prospects have also been recognized, which has prompted companies to update and iterate their own unmanned delivery vehicle products.

At the same time, rapid breakthroughs in technology, policies, and commercialization have also made the future of unmanned delivery bright.### Technical Aspects
In terms of technology, the low-speed autonomous driving technology has gradually matured at present, and the related industrial chain has gradually improved. Costs of key upstream components such as LiDAR and chip computing platforms have gradually decreased, and the technology of wired control chassis has become mature and gradually been put into production. The technical limitations and barriers to unmanned delivery have been gradually cleared in the technology field.
Policy Aspects
Various regions in China have issued relevant policy standards for unmanned delivery. In May 2021, the Beijing high-level autonomous driving demonstration zone adopted a double review and certification system similar to that of Germany. It first awarded the domestic first batch of unmanned delivery vehicle codes to three companies, Meituan, JD.com, and XSK, and opened up Beijing Yizhuang’s 225 square kilometers of road rights. In October 2021, Shenzhen released the first domestic commercial application standard for autonomous driving low-speed unmanned vehicles, focusing on the construction of autonomous driving demonstration cities. It emphasized the introduction of low-speed unmanned vehicles to enrich city service scenarios. Cities led by Beijing have opened up road rights for unmanned delivery vehicles, providing regulatory models for the industry. As the safety of unmanned delivery vehicles gradually improves, the ecosystem expands, and the model is verified, more cities will open up road rights for unmanned delivery vehicles in the future.
Commercialization Aspects
In the unmanned delivery industry, multiple companies, including Internet enterprises and start-up companies, have explored commercialization in their respective application scenario fields and made rapid progress. The consensus among various companies is to gradually drive the selected direction of unmanned delivery enterprises in terms of scenarios and business needs. These enterprises also underwent a full sprint this year.
Unmanned Delivery Application Scenarios
Currently, the application scenarios of unmanned delivery are mainly divided into three categories: express delivery, food delivery, and supermarket retail. Among them, the transportation scenarios for express delivery are relatively simple, and the immediacy requirement is not high, and the collection capability is also strong. The food delivery scenario has the highest immediacy requirements, and due to the unique features of food delivery products, such as fresh products, the requirements for storage environment and transportation conditions are also the highest. The immediacy of supermarket retail is lower than that of the food delivery scenario and usually serves a single or fixed vendor, and the driving route is also relatively simple. Compared with these scenarios, each company has also chosen the most suitable track for themselves, and launched relevant self-developed vehicle products.
Meituan’s unmanned delivery service hopes to cover end-to-end instant delivery in outdoor scenarios, including public roads, parks, and semi-closed parks. The initial design of Meituan’s newly released self-developed automatic delivery vehicle “MoBag20” was used to cope with the most complex traffic conditions and the most challenging vehicle capabilities for public road operations. It has now been put into normal delivery of fresh food and takeaway on public roads in Beijing.
Alibaba’s “Little Mule” is dedicated to its own express delivery service, providing daily delivery services at Cainiao post stations on campuses and in communities.
JD.com has also focused on its own express delivery business from the company’s own business needs. The route is fixed, the traffic participants are fewer, and the road conditions are relatively simple, similar to Alibaba.## Global Inventory of Autonomous Delivery Vehicles
The choice of deployment scenarios is crucial for enterprises, as it not only determines their layout in the industry but also affects the design and selection of hardware for autonomous delivery vehicles, as well as the overall product design concept. Designing products based on the most complex scenarios is undoubtedly the safest and most reliable approach, as can be seen from the autonomous delivery vehicle products of various enterprises. Therefore, we can conduct an inventory and horizontal comparison of several well-known autonomous delivery vehicle enterprises on the market.
Comparison of Autonomous Delivery Vehicle Products
Internet enterprises have a significant advantage in the autonomous delivery industry, whether from the leading position of autonomous driving technology at present, the demand for autonomous delivery derived from platforms, or the expansion of business. Currently, domestic internet enterprises represented by Meituan, Alibaba, and JD.com, and foreign internet enterprises represented by NURO have relatively mature autonomous delivery vehicle products in operation. This section compares various enterprises from several aspects, such as vehicle hardware capabilities, safety, and commercialization, which can also reveal the current development status of engineering technology in the industry.
Vehicle Hardware Capabilities
The above table shows the parameter information of several leading autonomous delivery vehicle products in China. As they are used for daily delivery purposes, the size and endurance of each enterprise’s autonomous delivery vehicles are relatively similar.
In terms of design speed, since Meituan hopes to explore autonomous delivery services that cover the entire outdoor scenario, their design speed can reach up to 45 km/h. In actual operation on public roads, the maximum speed is controlled at 20 km/h to ensure safety. JD.com, Alibaba, New Stone Age, and White Rhino all focus on closed or semi-closed scenarios such as campuses and parks, and the design speed is controlled within 30 km/h. Overall, each enterprise’s autonomous delivery vehicle is developing towards a direction of being smarter, more stable, safer, able to carry greater loads, and with longer endurance.
In terms of critical hardware configuration such as sensors, almost all enterprises use a multi-sensor fusion solution, including LiDAR, millimeter-wave radar, cameras, ultrasonic radar, and other sensors. This is essential at present since related technologies for autonomous driving aren’t stable or mature enough. Thus, multiple sensors provide redundancy to enhance the overall safety and stability of the autonomous driving and operation process.Meituan’s autonomous delivery vehicle, Mobike20, has significant advantages in terms of sensor quantity and performance. The vehicle is equipped with over 30 sensors, capable of obstacle recognition within a range of 5cm-150m, 360-degree real-time perception with no blind spots, and outstanding autonomous driving perception capability. Meituan has also accumulated rich autonomous driving technologies to date. Alibaba’s little donkey integrates the most advanced artificial intelligence and autonomous driving technologies from DAMO Academy, with human-like cognitive decision-making ability. It can navigate freely and safely in complex last-mile scenarios, smoothly handling turns, sudden stops, and encountering other vehicles. JD Logistics’ unmanned delivery vehicle has developed a world-leading L4 level, vehicle-standard fourth-generation product, with autonomous driving, intelligent obstacle avoidance, traffic light recognition and intelligent pick-up functions without the need for human intervention. NURO’s autonomous delivery vehicle also comes equipped with 360-degree panoramic cameras, lidar, long-range and short-range radar, and ultrasound sensors. The rich and redundant hardware configuration ensures there are no blind spots in the whole vehicle.
It can be seen that in the intelligent field of unmanned delivery vehicles, internet enterprises have taken the lead due to their early accumulation. Whether in the richness of sensor equipment or the maturity of autonomous driving technology, they have an advantage. In the era where data is king, the earlier the large-scale practical landing testing is carried out, the more likely they are to win in the fierce competition.

Safety design
As an industry that has not yet been widely implemented at present, the unmanned delivery industry may still raise doubts and concerns in people’s minds. Safety is a necessary prerequisite for the large-scale implementation of unmanned delivery. In order to achieve reliability in the safety field, unmanned delivery vehicle products launched by various companies have all considered perception redundancy, hardware redundancy, algorithm redundancy, etc. to ensure the safety of driving. Moreover, as a vehicle that actually operates on the road, whether it meets vehicle-standard regulation is also an important indicator for evaluating the safety of unmanned delivery vehicles.
Public information shows that Meituan’s Mobike20 has gone through 31 sub-tests in three major aspects, including whole vehicle performance testing, comprehensive vehicle durability testing, and low-temperature adaptability testing. A safety system covering the entire process of pre-event prevention, in-event supervision and post-event treatment is built across five dimensions of design safety. It can detect obstacles from 150 meters away and automatically slow down.

Business implementation
The final scenario for unmanned delivery vehicles to enter commercial operation has emerged, and currently there are several categories of unmanned delivery vehicles that have landed on the market: those with internal service needs, those providing software and hardware solutions, and those providing unmanned delivery capabilities. For the main domestic and foreign enterprises, we have summarized their research and development and landing situations in the unmanned delivery vehicle field as shown in the following table:
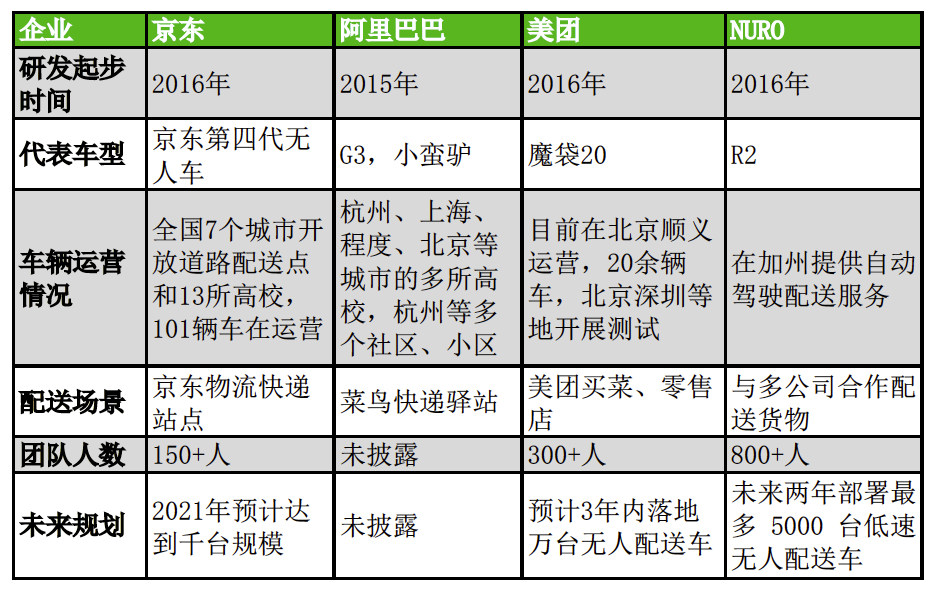
Taking self-owned platforms and business needs as the starting point to create a commercial landing direction has become a common idea of Internet companies at this stage. The scenario for unmanned delivery vehicles is simpler than that of autonomous driving, and it is easier to achieve commercial landing in the commercial industry. However, at the same time, if complex scenarios can be used to promote commercial landing and design their own unmanned delivery vehicle products, it will be more conducive to establishing safer and more complete unmanned vehicle solutions. The domestic Meituan is ahead in this regard.
Abroad, represented by NURO, it is the first and only enterprise to obtain the federal government’s approval license from the DOT and NHTSA in the United States. It has also begun testing fully autonomous vehicles R2 on public roads in cities in California, Texas, and Arizona, without drivers, passengers or tracking vehicles. Currently, it has also obtained a total of 1.5 billion U.S. dollars in financing, including Google, and has started commercial operations.
Future prospects of unmanned delivery
In summary, the future of commercialization of unmanned delivery is very clear, which is also why many Internet giants are willing to spend a lot of energy, invest in manpower and materials, and enter the field of unmanned delivery. There are three trends regarding the future prospects of unmanned delivery:
First of all, driving technology development through scenarios will become the industry’s grand direction. For example, Meituan quickly iterated and improved its capabilities through practical combat in the most difficult complex scenarios on city public roads, and then fed back the vehicle product technology. This model may be widely borrowed from in the future, and Meituan’s first-mover advantage may enable it to occupy an advantage in fierce commercial competition.

Secondly, mass production is an absolute must for the future of unmanned delivery vehicles. To truly achieve commercial landing and profitability for unmanned delivery, unmanned delivery vehicles must eventually move towards mass production. Whether it is a wired chassis or a sensor, only when the cost can be reduced to tens of thousands or hundreds of thousands, can profitability and normalized operations really be achieved.Finally, the unmanned delivery industry is about to witness large-scale commercial applications, and companies that identify scenarios and leverage their strengths will have an advantage in the market. Companies such as Meituan, which represent self-operated delivery scenarios, have added momentum to the commercialization of China’s unmanned delivery industry. Meituan, which has occupied scenario and technological advantages, is expected to become China’s NURO, obtaining government approval for normalized commercial operations and taking the initiative in the development of the unmanned delivery industry in the future.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
