The Most Impressive Thing after Driving Was Braking
Recently, I experienced the pre-launch Ford Mustang at Tianma.

It was not the V8, nor the V6, nor the 4-cylinder Mustang. Some people call the Mustang with a 2.3T engine the “wild donkey,” so I’ll call the electric Mustang I drove the “electric donkey,” and it was the “electric donkey GT,” haha.
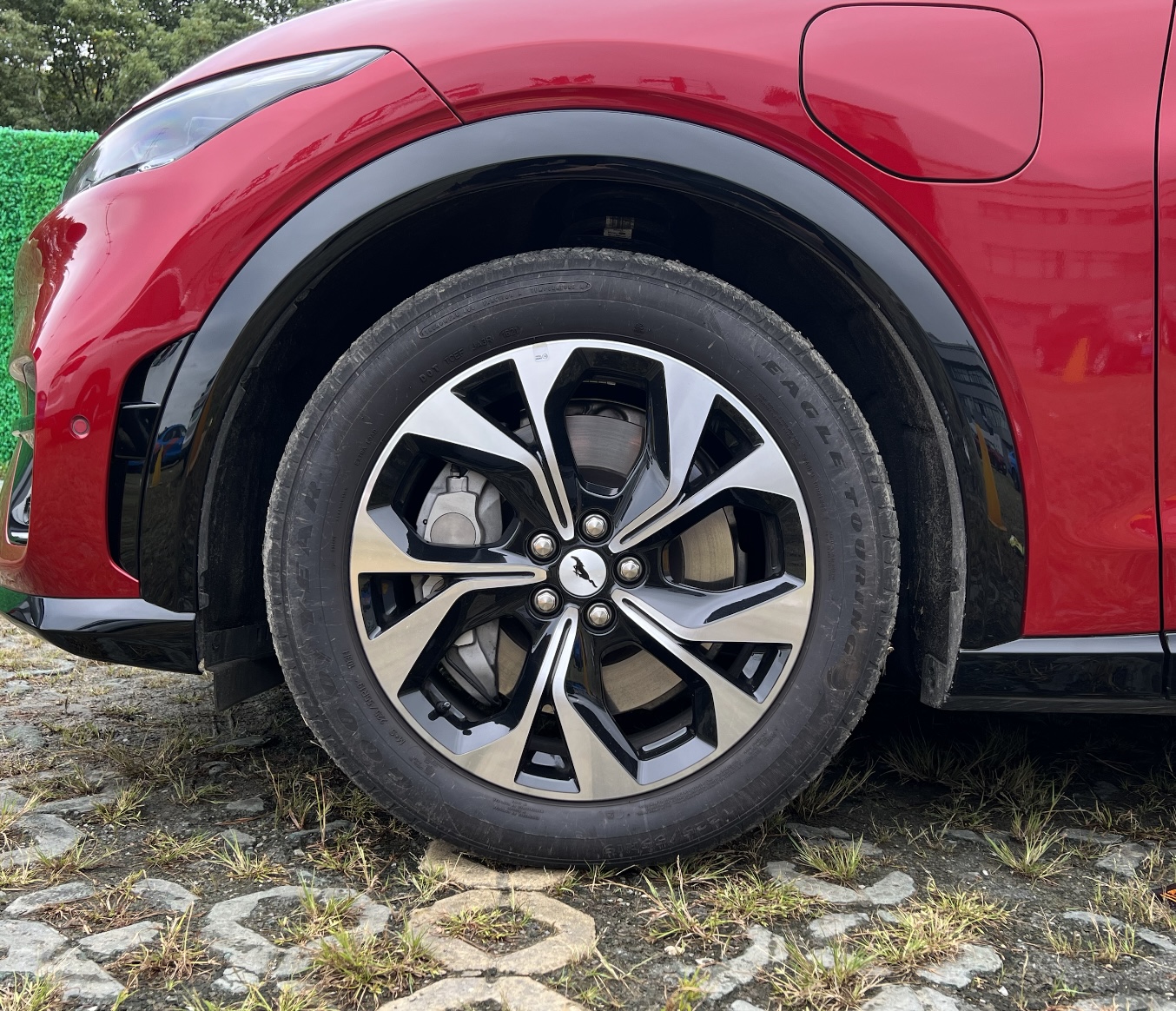
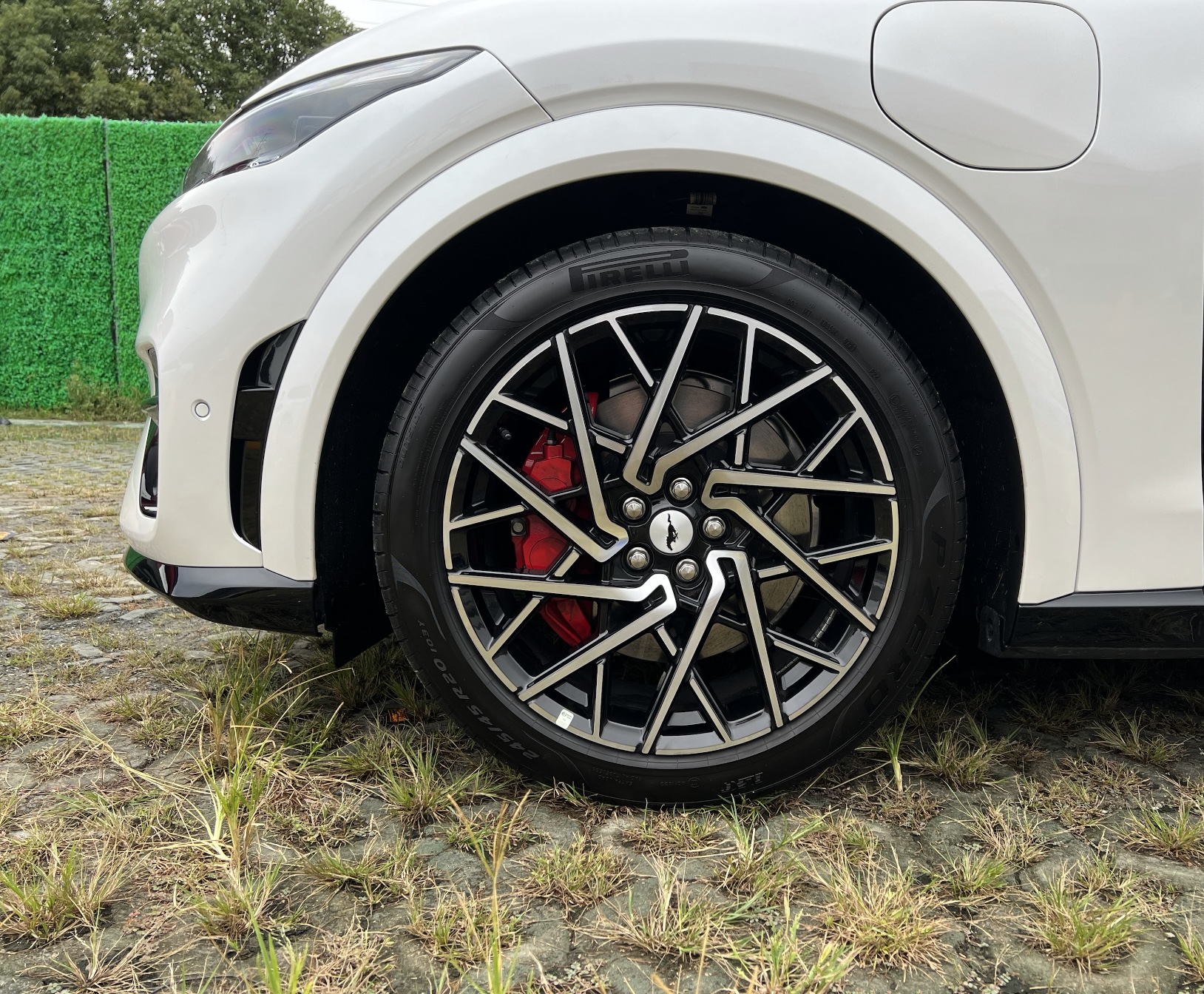


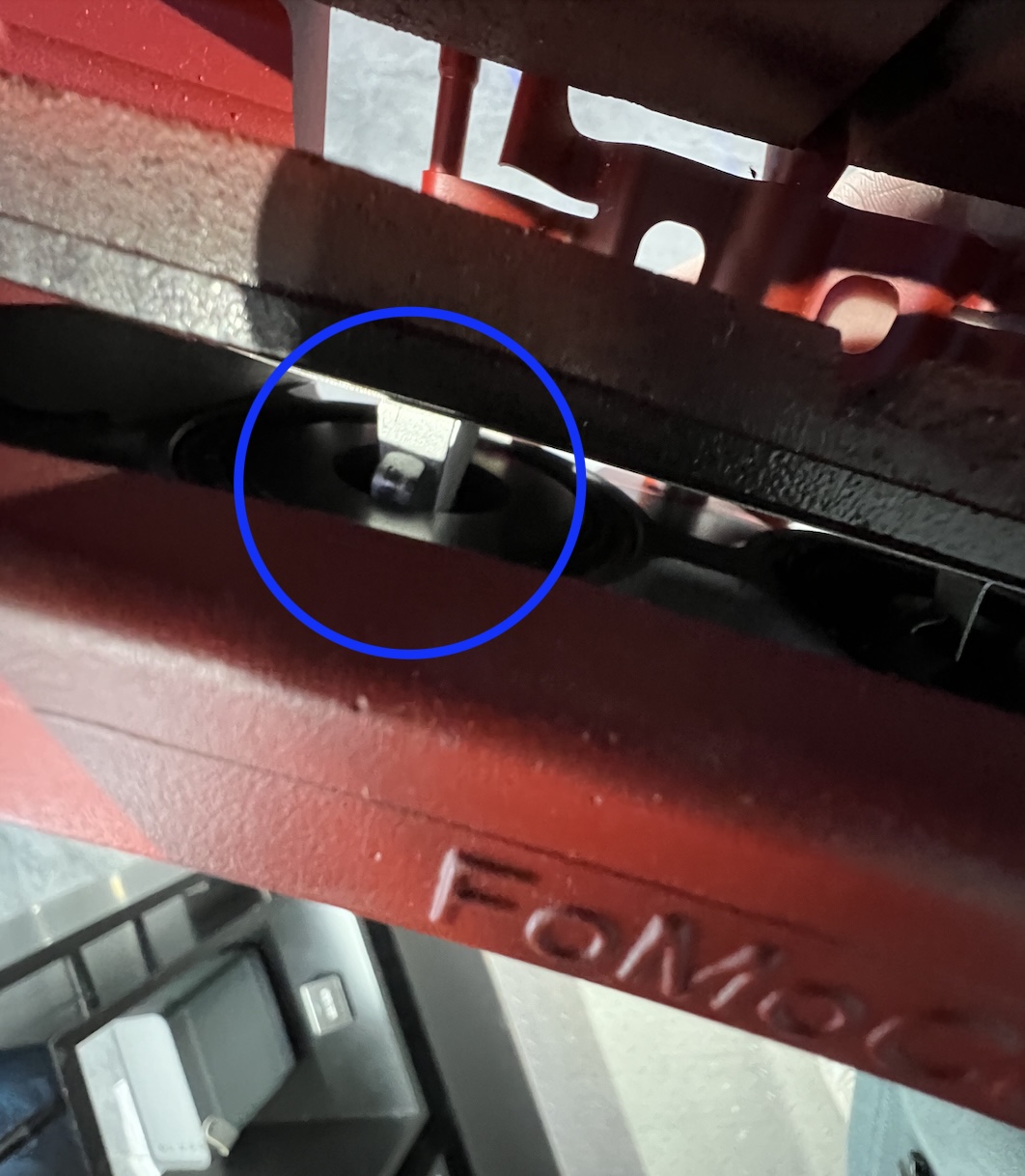
The pure electric acceleration and lively tail made me feel like the Mustang in the electric era was no longer an endangered species. I noticed that both the GT version and the lower versions of the car had two rings on the caliper, and after close observation, there was no difference between the braking system of these two cars except for the red paint. However, this does not mean that this braking system lacks sincerity. In fact, it is very interesting and has a lot of technological content.
Let’s Learn About Brake System
Before we get into the topic, let’s start with some (not so) hardcore background knowledge to help you quickly understand the braking system of a car.

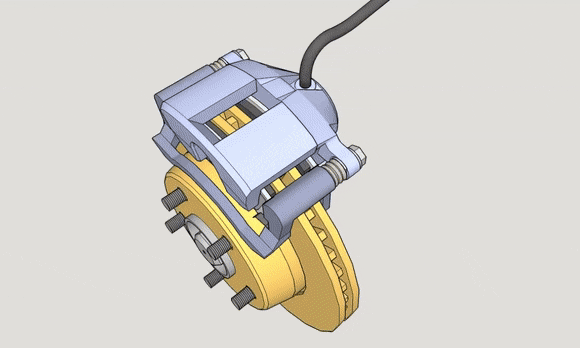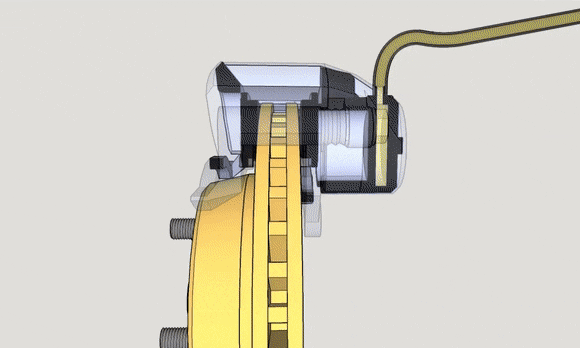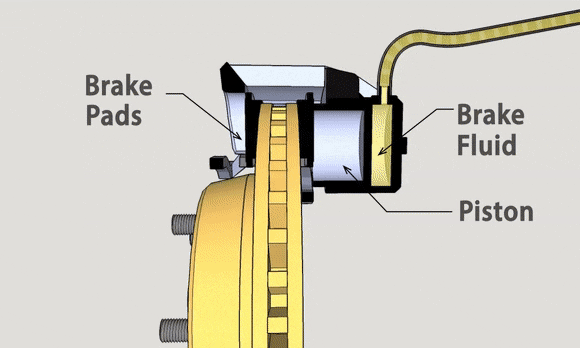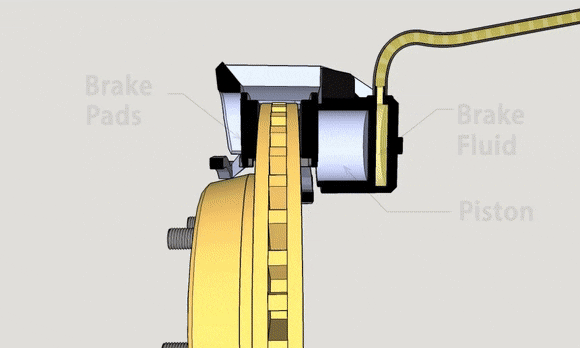
The brake pedal is the second pedal counted from the right. By stepping on it, the driver pushes the brake fluid through the brake master cylinder, which is linked by a lever structure, and then the brake fluid is transmitted through the brake fluid pipe to the brake sub-pump to exert force to prevent the car tires from rotating.
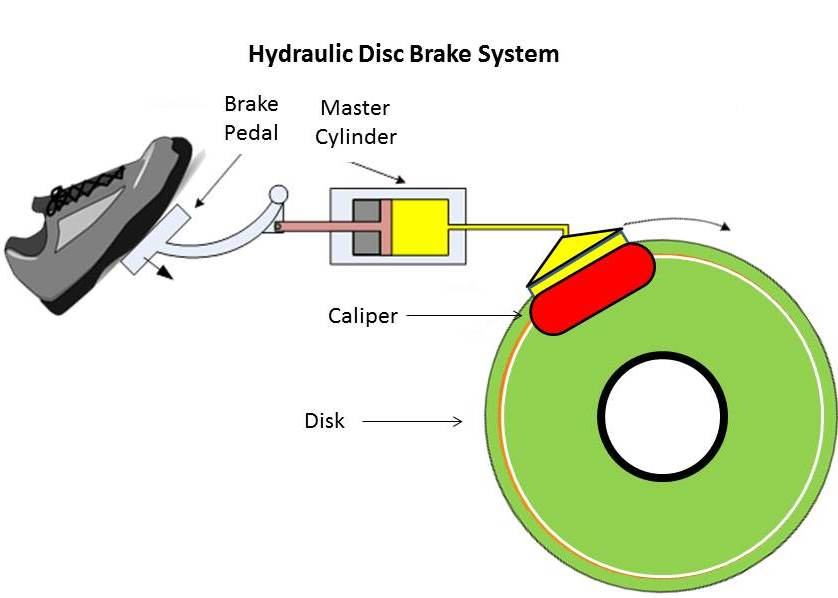
Because the car brake is essentially an energy conversion device that converts kinetic energy into heat to reduce speed, as long as it can provide friction, it can take many forms. The mainstream types are as follows.### Outdated Drum Brakes
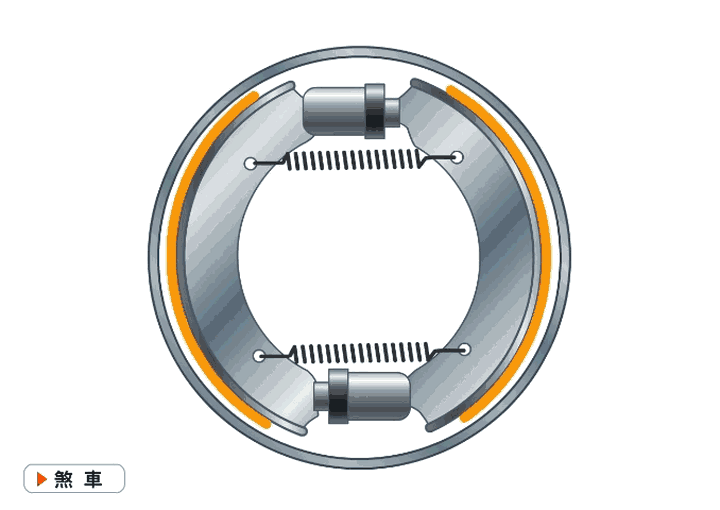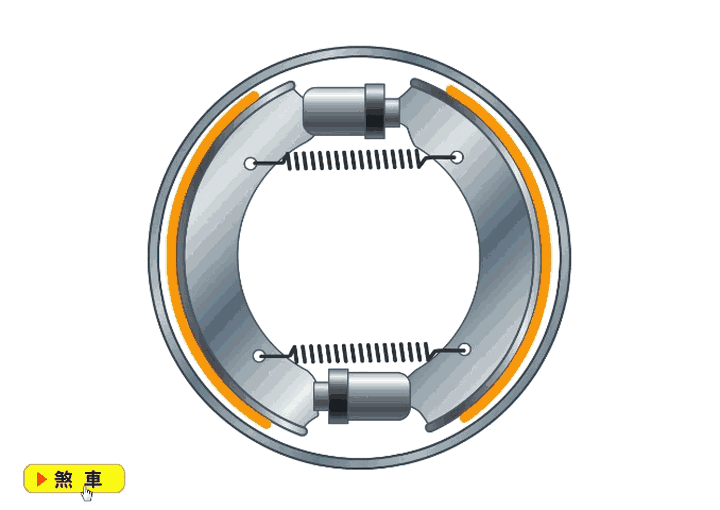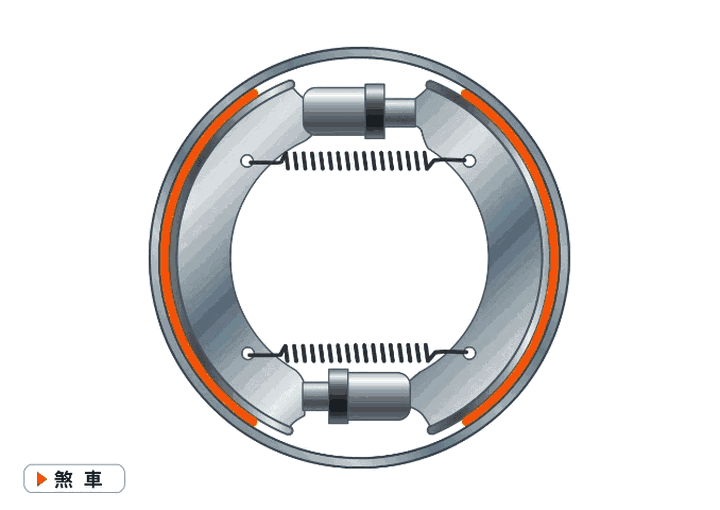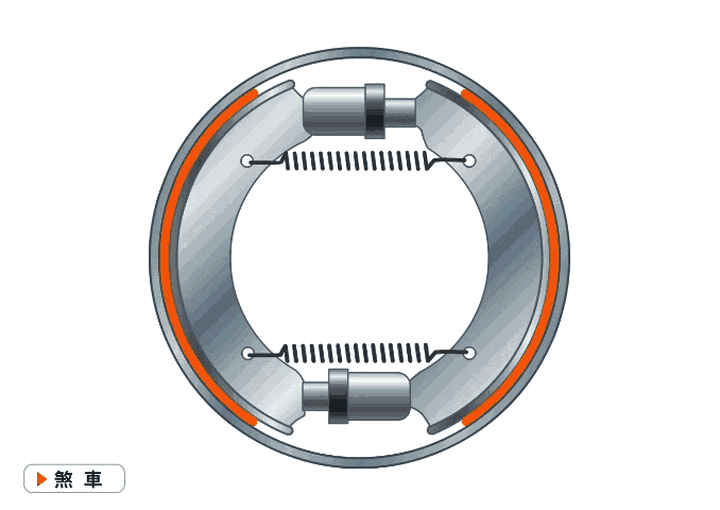
Drum brakes, commonly known as drum brakes, work just like squeezing a cup with your hand. They work by using brake shoes on both sides of the brake drum to create friction and slow down or stop the vehicle.
The advantages of drum brakes are their low cost and large friction area, which means less force is needed to achieve the same braking force. Drum brakes are commonly found on large trucks. The disadvantages are that, due to their enclosed structure, they are not suitable for high-frequency braking and have slower response times. They also add weight to the vehicle.

Because of their low cost, if you see them on the rear wheels of a car, it means that the car is relatively inexpensive.
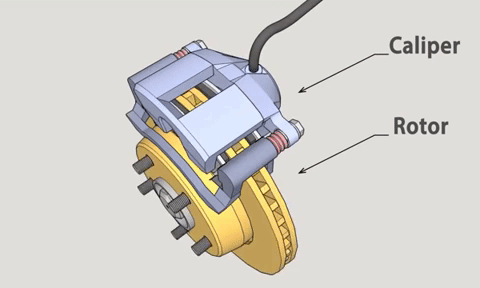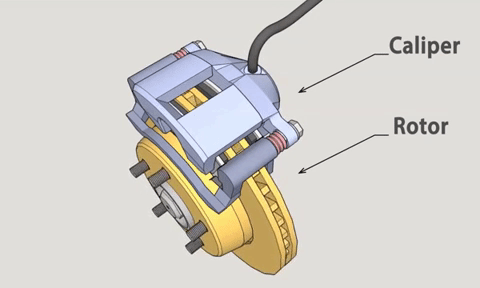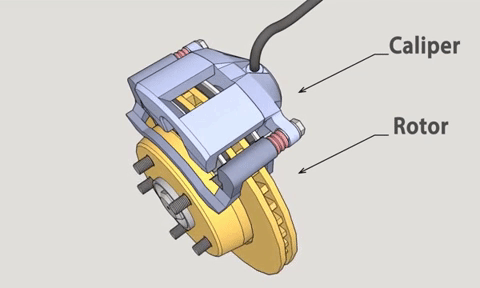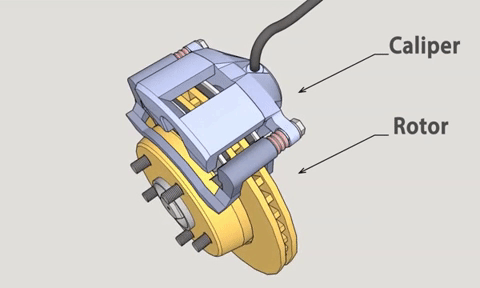
More Mainstream Disc Brakes
Disc brakes, also known as disk brakes, work by pushing brake pads against a rotor with hydraulic pressure, creating friction and slowing down or stopping the vehicle.
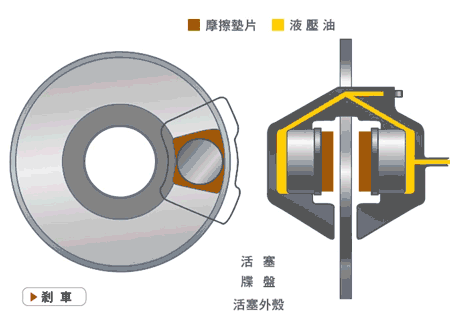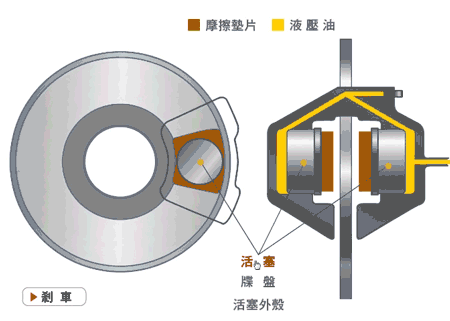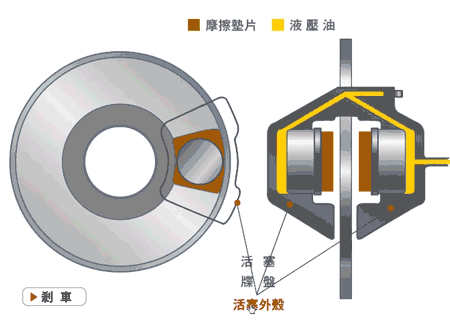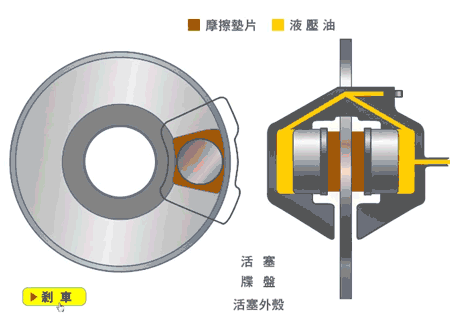
Disc brakes are an external braking system. The advantages are good ventilation and heat dissipation, linear braking, good control, and less chance of locking up. The main disadvantage is their cost.
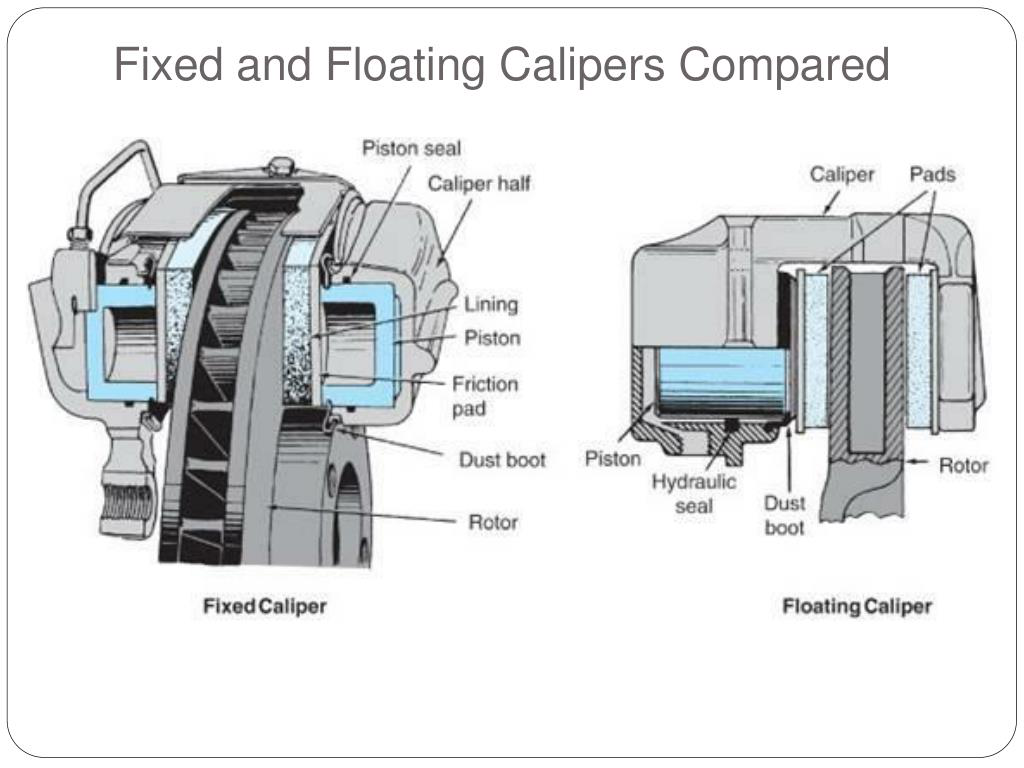
There are many types of disc brakes. Starting with the caliper that provides the clamping force, they can be divided into two types: floating and fixed calipers.
The floating caliper is the cheaper and lower-performance option.
This type of caliper can move in the direction perpendicular to the brake disc, thanks to two guide pins (the parts covered by the red dust boots), which is where it gets its name.
Because of this design, this type of caliper can lock the brake disc from front to back when the piston is pushed, using the reaction force, with a piston located only on one side. These calipers are cheap but have no other advantages.Due to the floating structure, all brake systems are subjected to reactive forces, which are borne by the guide pins that also fulfill the function of floating front and rear. As a result of a higher degree of deformation, it cannot provide better brake “feel,” and it is also heavier and has worse heat dissipation performance than its steel counterpart.
In comparison, the fixed brake caliper, also known as the opposed piston or multi-piston caliper, is more advanced and has superior performance.
It works by “clamping” the brake disc from both sides at the same time. This type of caliper structure is simpler than the floating caliper, with the exception of the piston, which is all fixed. Therefore, it has higher strength, more precise action, and better braking feel.
This type of caliper is usually made of aluminum alloy and has a larger volume, so it can provide better heat dissipation performance. Good heat dissipation means that it can support continuous braking without generating thermal decay. Almost all vehicles participating in international famous races use this type of caliper.
The number of pistons in a multi-piston caliper ranges from 2 to 10 or more. It is actually a misconception that the more pistons, the more braking force. This depends on multiple factors such as:
- Total piston area (pressure);
- Brake pad size and material (area and friction coefficient);
- Brake disc size and material (moment arm and friction coefficient), etc.

The main purpose of multi-pistons is to make the braking force more uniform. As we can see from the Japanese top brand Endless’s 12 piston product image, there are different sizes of pistons in this caliper to apply balanced force to the brake pads as much as possible, thereby ensuring no uneven wear on the brake pads that affects their service life.

Fixed brake calipers can be made of cast iron, aluminum alloy, or even titanium alloy. The structure can also be divided into two-piece or monoblock design, while the manufacturing process includes casting, forging, CNC machining, and even 3D printing, which offers various options to choose from.

As for brake discs, they are not always steel discs. High-performance production cars can also choose carbon ceramic brake discs that are more heat tolerant and lighter.The fixing methods of brake discs include integrated cast iron, joint casting, floating type, and other different forms.


Mileage anxiety forces the evolution of brakes
One big problem with disc brakes is that:
They keep braking even when you don’t use them.
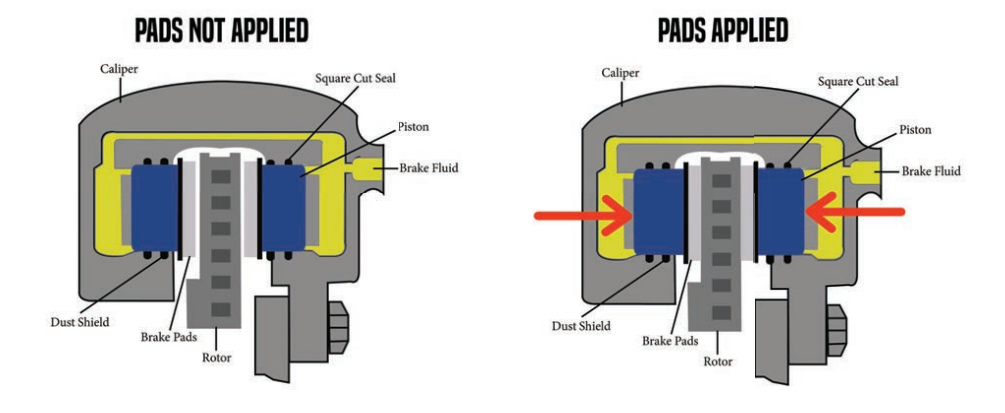
Compared to drum brakes, which have springs to retract the brake shoes, the calipers of disc brakes rely at best on the return force of the oil seal and dust cover on the pistons, which leaves only a small amount of clearance. Even if your pistons return, the brake pads will still rub against the rotor.
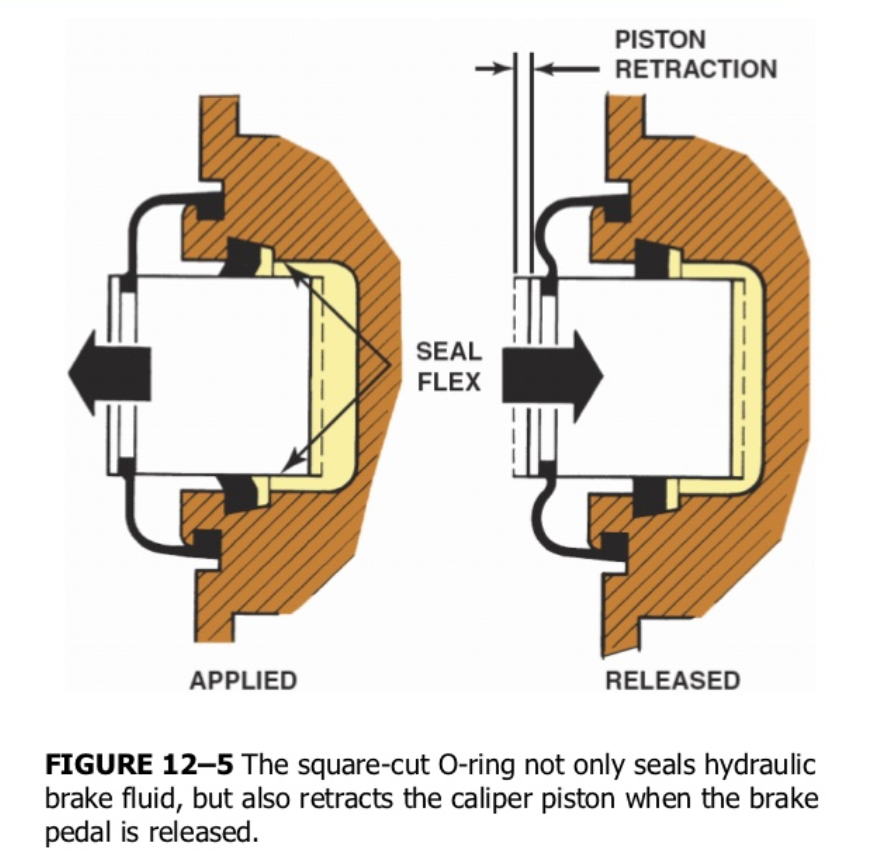
This frictional loss is also called stiction, which is insignificant for gasoline-powered cars that can recuperate energy, but for electric cars with higher drive efficiency but lower energy density, the frictional loss means a significant reduction in range, and the reduced range and inefficient regeneration bring about range anxiety.
So, what can we do as electric car drivers?
Revert to the past?
Didn’t drum brakes also have stiction? Why not use them again?
Therefore, FAW-Volkswagen Group has developed a drum brake to solve this problem. This drum brake is standard on all MEB platform models under the Volkswagen Group, such as the Q4 e-tron and ID.4.

So how did FAW-Volkswagen change people’s prejudices against drum brakes? The answer is high technology.
- The composite structure of aluminum alloy and steel enables this drum brake to achieve 30% weight reduction compared to previous products;
- The protrusions on the aluminum alloy shell can help dissipate heat and are corrosion-resistant, making the car more fashionable.3. Equipped with a built-in brake torque sensor to real-time monitor braking force, ensuring seamless and comfortable collaboration between the mechanical brake system and energy recovery system.
So, the reasoning behind using drum brakes, which do not play a major role in braking and have a longer lifespan, for the rear wheels in the presence of regenerative braking is simply that, according to mainland China and Volkswagen. However, this does not stop people from pursuing disc brakes!
So, what about disc brakes?
The answer is low-drag calipers.
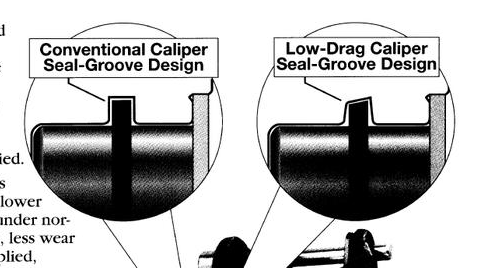
In fact, techniques such as using oil seal cross-sectional shapes to optimize piston return have been around for a long time. But through studying the brake calipers of the Mustang, I found more ways to reduce drag.
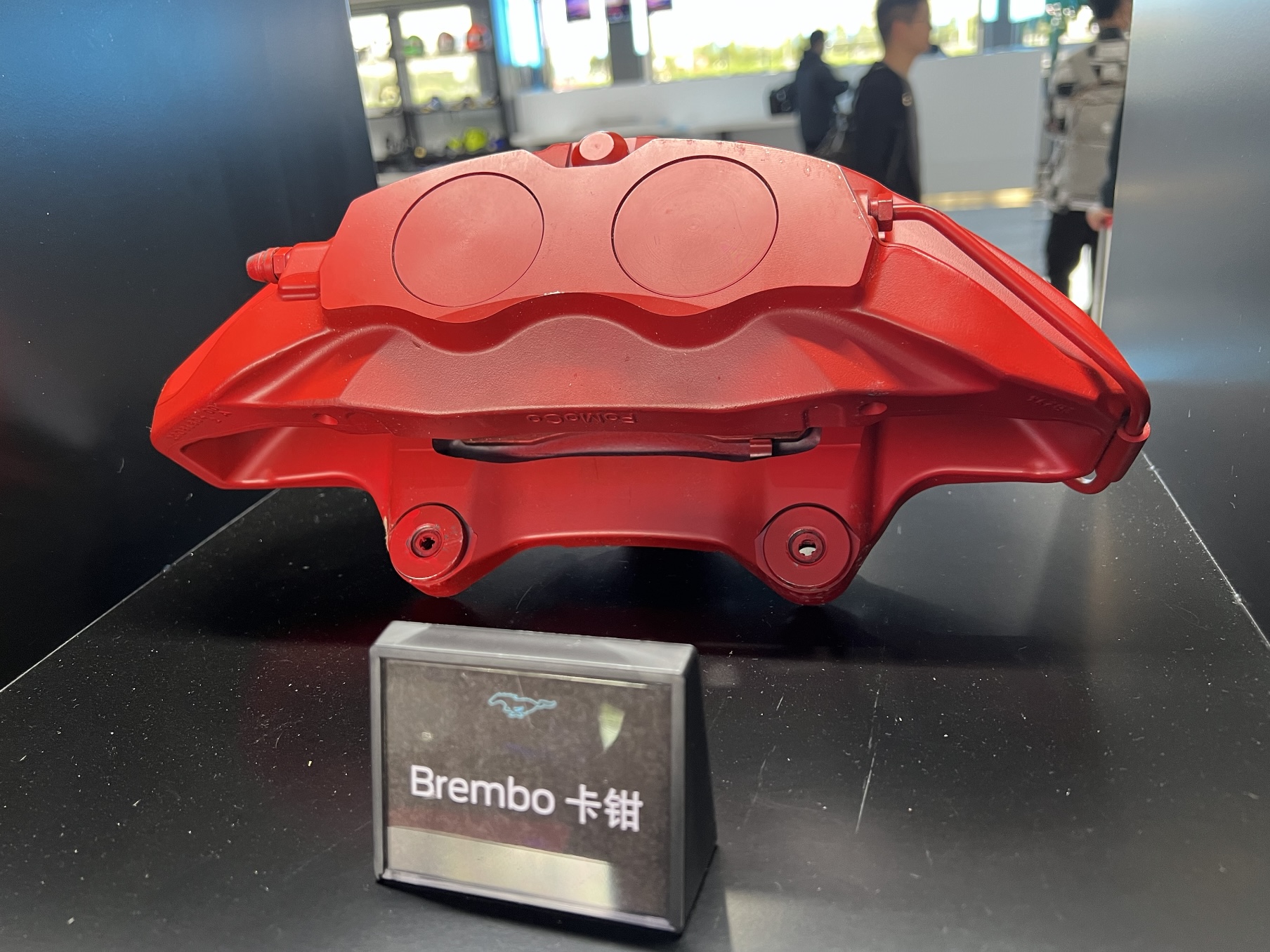

Taking this “Brembo caliper” from the event, I found that it was not as simple as Ford claimed.
As mentioned earlier, piston return in the caliper is the first step, but the key is to prevent the brake pads from contacting the brake disc in order to reduce unnecessary drag. This caliper solves this problem with two very simple tricks.

- The spring behind the brake pad can be embedded in the piston recess, allowing the brake pad to return together with the piston.
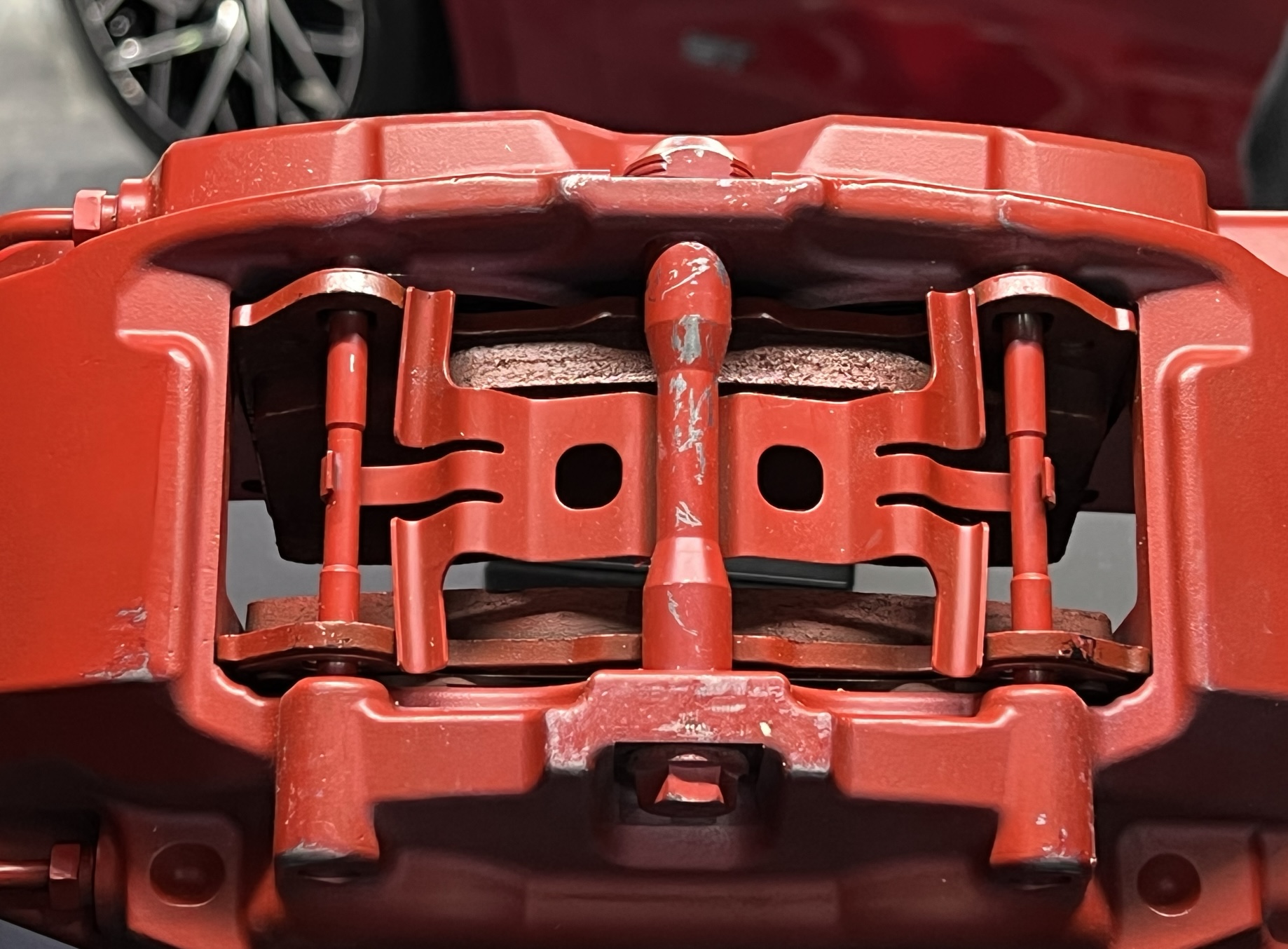

- The caliper spring plate is not bent, but is designed to provide outward force to assist in the brake pad’s return.
 The official name of this Brembo caliper that is mounted on Ford vehicles is called Flexira, according to Brembo.
The official name of this Brembo caliper that is mounted on Ford vehicles is called Flexira, according to Brembo.
The Flexira® brake caliper is specifically designed for vehicles with smaller wheel hubs, such as compact sedans and SUVs (especially electric cars), to improve rolling resistance. This caliper is designed for limited space, while ensuring the same function and high performance as Brembo fixed calipers.
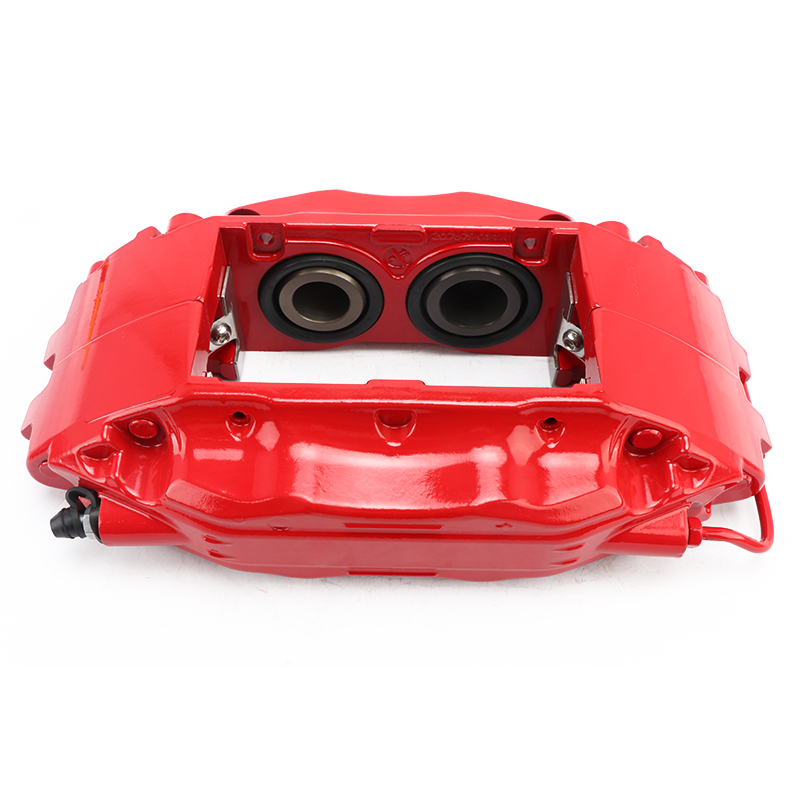

Compared to the Brembo F50 calipers used by Tesla, NIO, and XPeng, the advantage of Flexira is that it has a smaller width, which is suitable for smaller and narrower wheel hubs, and allows for more patterns to be carved into the wheel hub spokes. You might think that calipers have been slimmed down, which may result in lower strength.
No, not at all. The two circles mentioned earlier will come into play here.

Compared to cast iron engines, all-aluminum engines have advantages in weight reduction and heat dissipation. However, if pursuing power, especially by squeezing power through high-pressure turbocharging, the strength of the cylinder body will become a bottleneck.
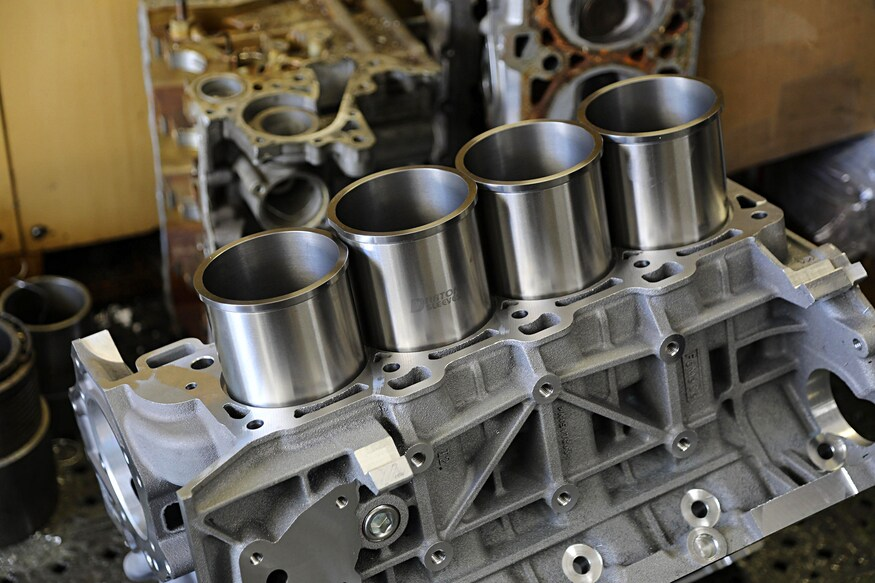

At this point, we need stronger cast iron cylinder liners to strengthen the internal structure of the engine and prevent the entire engine from exploding due to excessive pressure.
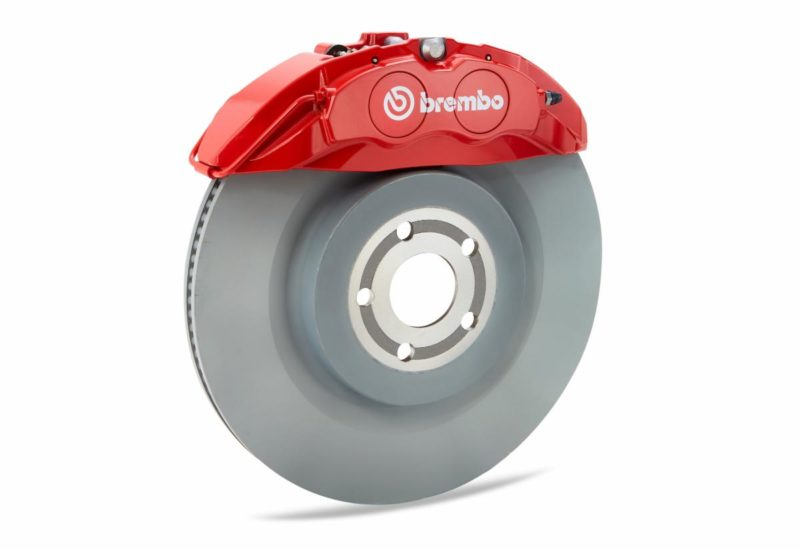

The logic behind Ford’s calipers and cast iron liners is the same, according to Brembo.
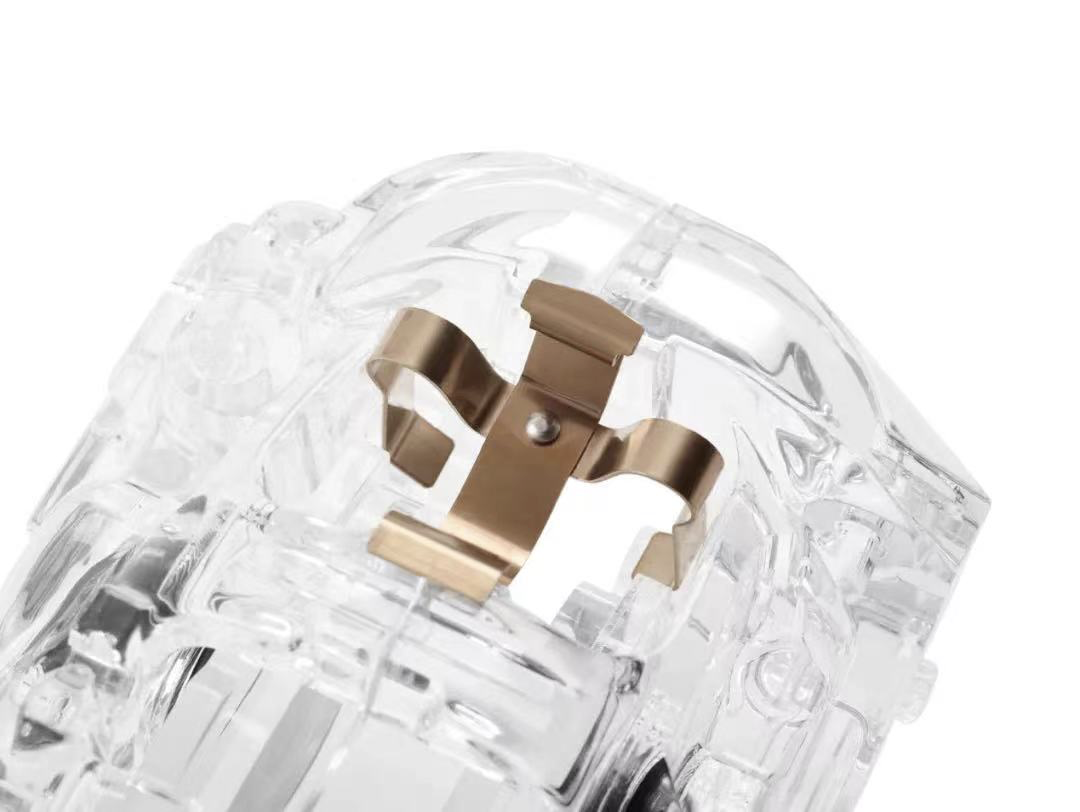
The aluminum Flexira® brake caliper is manufactured using Brembo’s gravity casting technology. After the aluminum “shell” is cast, steel inserts or “sleeves” are added to increase the overall mechanical strength of the component and reduce the caliper’s axial volume. These cylindrical inserts can be seen on the front surface of the caliper, and the logo is also printed on top.
It has the strength of an aluminum opposed piston caliper and the small size of a steel floating caliper, making it a two-in-one solution.
Environmental protection needs to be thoroughly addressed.
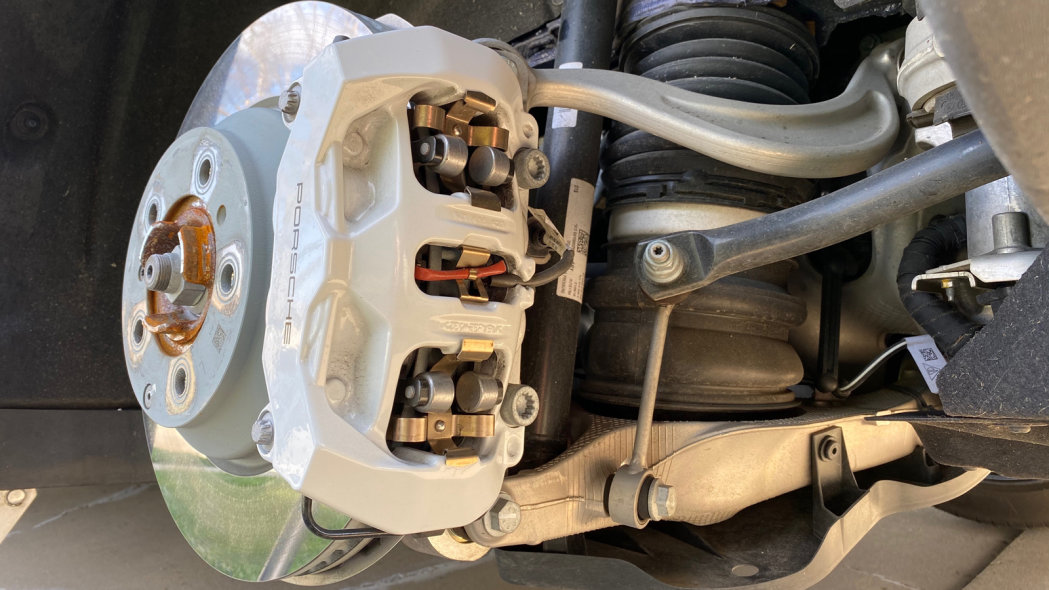
 Actually, Porsche has adopted the spring structure similar to that of the Flexira caliper in its hybrid and pure electric calipers for assisting the brake pad to return to its original position.
Actually, Porsche has adopted the spring structure similar to that of the Flexira caliper in its hybrid and pure electric calipers for assisting the brake pad to return to its original position.
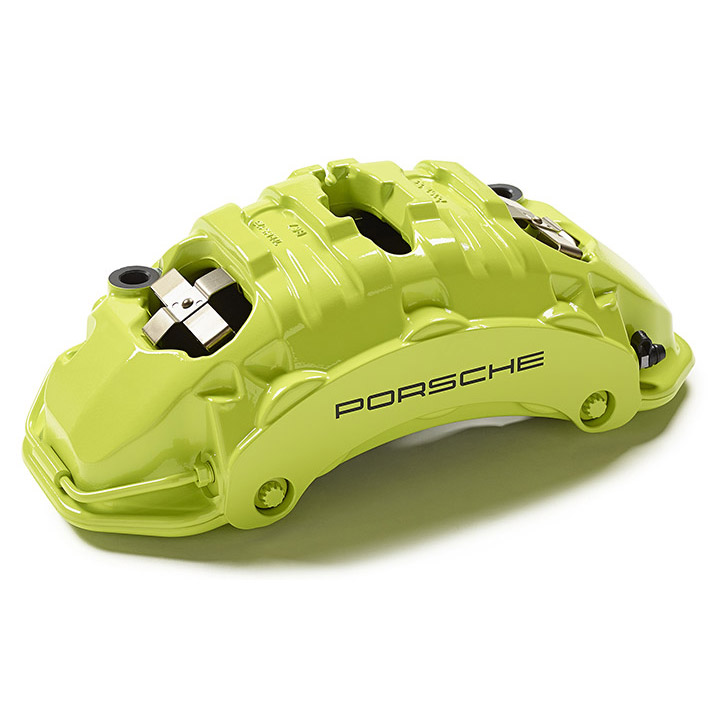


However, in addition to energy efficiency, we should also pay attention to the environmental performance of a vehicle throughout its entire lifecycle. Among them, the brakes are still a significant part.
In 2021, California and Washington state have banned the use of copper in brake pads, and will do so in 2025 respectively. The reason is that harmful substances such as copper in brake dust and other heavy metals will cause serious harm to aquatic animals, thereby causing unnecessary damage to ecology. And the caliper on Mach-E also complies with the latest environmental regulations in the local area and adopts a copper-free formula.
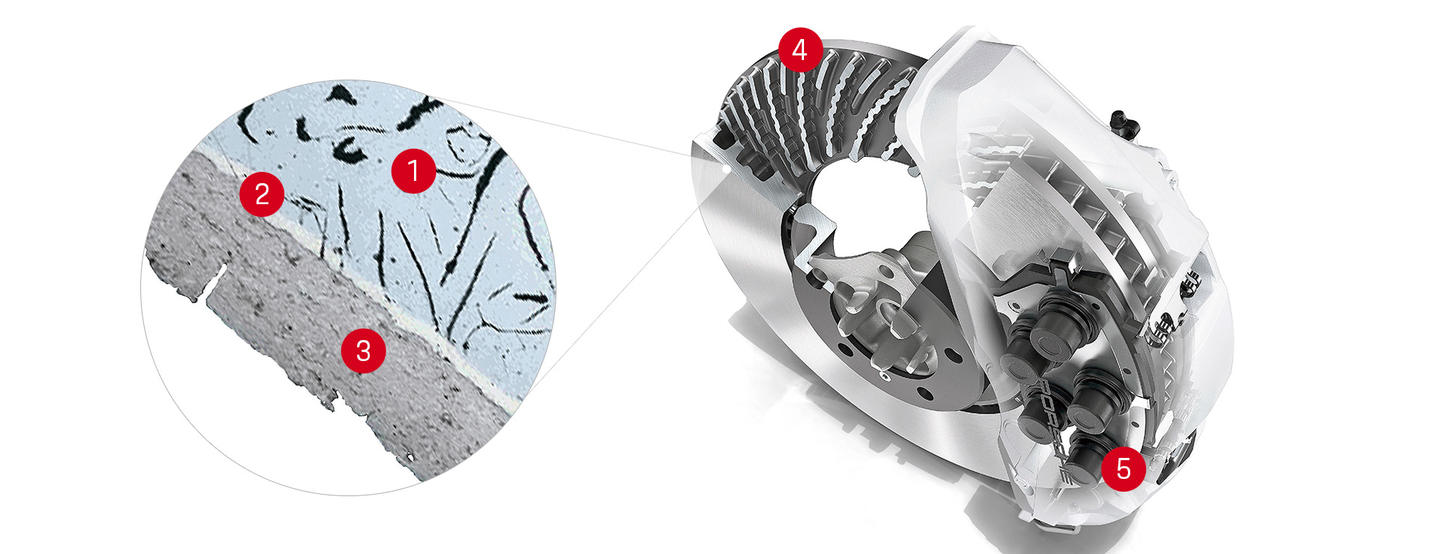
Porsche collaborated with Bosch and its affiliated company/brand Buderus to launch the tungsten carbide supersonic spray-coated brake discs under the name of PSCB (Porsche Surface Coated Brake), which achieved high-temperature performance close to that of carbon ceramic brake discs by using a tungsten carbide coating of 100 microns, or 0.1 millimeters, on steel brake discs, and increased 30% in service life.
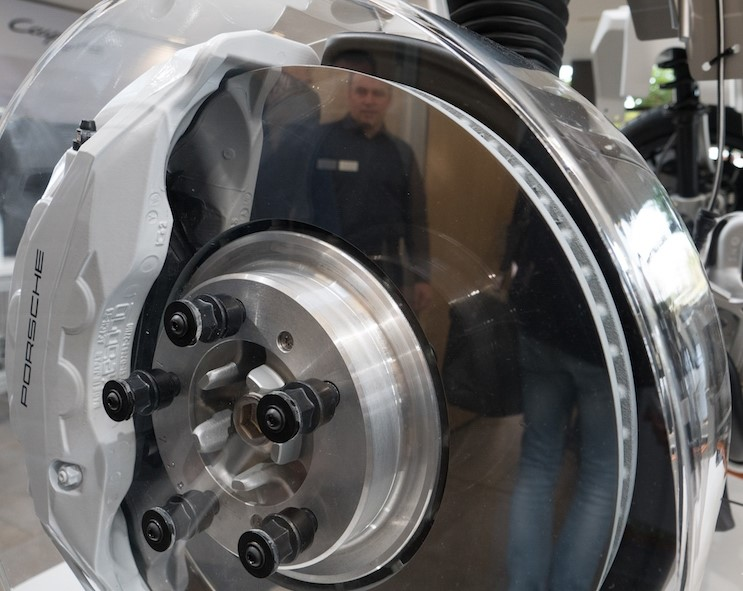

The brake pad used in conjunction with the super-hard braking disc surface is also specially formulated, reducing brake dust by a total of 90%. This not only contributes to the environment, but also allows it to show off its exclusive white caliper color. It is worth knowing that the reason why no one uses white is because it is afraid of getting dirty and looking bad. What’s cooler is that after driving 6,000 kilometers, the brake disc will present an amazing mirror effect due to the hard material in the brake pad grinding it.
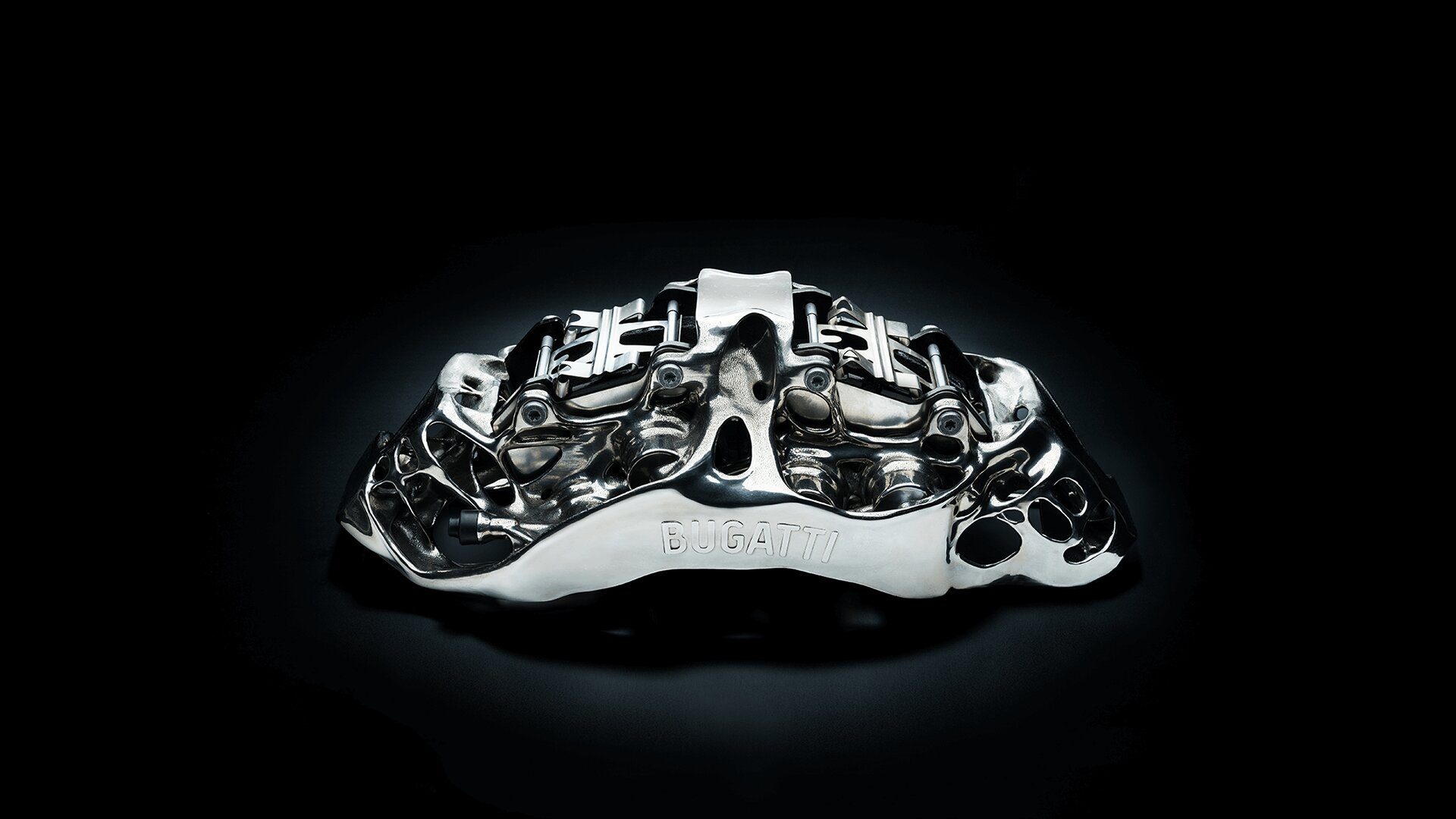
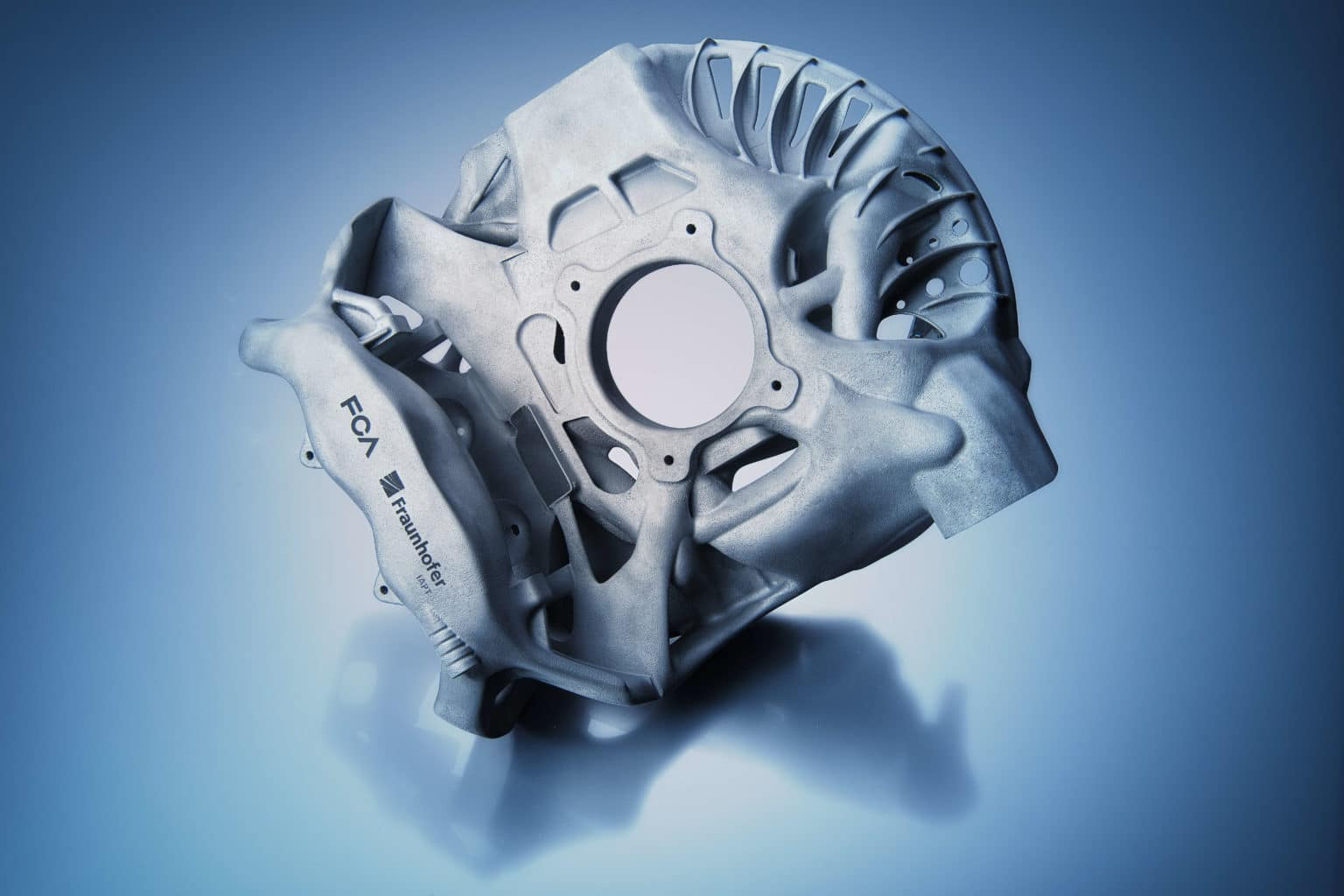 The product launched by FCA Group and 3D printing technology company Fraunhofer last year is even more creative. Through excellent topological structure optimization, the product combines the brake caliper and steering knuckle in an organic way, bringing lightweight, reducing processes, and material waste. However, the efficiency of 3D printing itself still needs to be improved, and we won’t be able to see this type of product on the market in the short term.
The product launched by FCA Group and 3D printing technology company Fraunhofer last year is even more creative. Through excellent topological structure optimization, the product combines the brake caliper and steering knuckle in an organic way, bringing lightweight, reducing processes, and material waste. However, the efficiency of 3D printing itself still needs to be improved, and we won’t be able to see this type of product on the market in the short term.

As a brake industry leader, Brembo not only does not have drum brake products, but also does not involve drum brake products in its product planning. Drum brakes can solve the problem of rust caused by low frequency of use of the rear brakes, but Brembo can also solve this problem through brake discs with special formulas. After all, they believe that the market acceptance of drum brakes is really not good.
After writing this popular science post, I just want to say that carbon neutrality is really meticulous.
In the details of automobile braking, we also see a microcosm of the times. The future blue sky and green water are also the golden mountains and silver mountains. The investment philosophy of ESG is slowly permeating our consumer behavior… it’s good.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
