In recent months, the topic of “cobalt-free” power batteries has become increasingly popular. In February 2020, it was reported that Tesla and CATL were in talks about possible use of cobalt-free batteries. On May 11, 2020, CATL stated during a briefing that, in addition to lithium iron phosphate batteries, they had also been developing technology reserves for “cobalt-free batteries.” On May 18, 2020, SVOLT Energy Technology (formerly the power battery division of Great Wall Motors) released the first cobalt-free battery product based on a new NMx cathode material. On July 16, 2021, SVOLT Energy Technology held a ceremony in Jiangsu to mark the start of production of the world’s first cobalt-free battery. This means that the world’s first cobalt-free battery has officially entered mass production, making SVOLT Energy Technology the first power battery enterprise in the world to overcome the technical difficulties of cobalt-free batteries and achieve mass production of products. On August 29, 2021, the 24th Chengdu International Auto Show opened. At the exhibition, SVOLT Energy Technology held a press conference, announcing that the world’s first cobalt-free battery pack had been officially installed in the Great Wall Euler Cherry Cat, the first SUV model of Great Wall’s Euler brand. This sparked strong industry attention.

Does the popularity of cobalt-free batteries indicate that the power battery industry has entered a cobalt-free era? Can cobalt-free batteries occupy the dominant position in the power battery market? Will lithium iron phosphate batteries and ternary lithium batteries lose their dominant positions?
To understand these questions, we need to analyze the following aspects:
What exactly is a cobalt-free battery?
As the name suggests, a cobalt-free battery is a battery that does not contain cobalt elements. The key materials for lithium batteries are positive and negative electrodes, separators, and electrolytes. The critical element that determines battery performance is the material used in the positive and negative electrodes. At present, over 95% of battery negative electrodes are made of graphite, with little difference. However, there are many types of positive electrode materials, such as lithium cobalt oxide (LCO), lithium manganese oxide (LMO), lithium iron phosphate (LFP), ternary lithium (nickel-cobalt-manganese lithium NCM, nickel cobalt aluminum lithium NCA), etc. Different positive electrode materials not only affect battery performance but also directly determine the name of the lithium battery.
Therefore, any lithium battery with a positive electrode material that does not contain cobalt can be called a cobalt-free battery. Although lithium iron phosphate batteries do not contain cobalt and are classified as cobalt-free batteries, cobalt-free batteries are not limited to lithium iron phosphate. If the cobalt (Co) element in the positive electrode (NCM, NCA) of a ternary lithium battery is completely replaced, it can also be called a cobalt-free battery.
Why develop cobalt-free batteries?Cobalt is an important component of the ternary lithium-ion positive electrode material and does not participate in electrochemical reactions. Its role is to provide a stable layered structure for the material and improve its cycling and rate performance. Due to limited reserves and production, cobalt has become a strategic rare metal resource. As the most expensive element material, the international market price of cobalt is extremely unstable and has remained high for a long time. Cobalt in the positive electrode material accounts for about half of the total battery cost, which is more expensive than nickel, manganese, and aluminum combined.
According to data from the US Geological Survey in 2020, the currently proven global cobalt reserves are only 6.92 million tons and are non-renewable resources. Global cobalt resources are highly concentrated, mainly distributed in three countries: Congo (Kinshasa), Australia, and Cuba. Congo (Kinshasa) has a cobalt reserve of 3.6 million metal tons, accounting for 52% of the world’s cobalt reserves and ranking first in the world. The rare metal mining and armed conflict in Congo (Kinshasa) have caused long-term instability in the region, resulting in large fluctuations in cobalt prices. In the past 20 years, the price of cobalt has surged to about $48 per pound (about RMB 860,000/t), and fallen to as low as $8 per pound (about RMB 150,000/t), with a price difference of up to 6 times and multiple occurrences of sharp rises and falls. Since the beginning of 2021, under the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, global wide-scale economic stimulus plans, and unexpected global demand for electric vehicles, the price has risen rapidly again.
As the global process of electric vehicle electrification continues to accelerate, it can be imagined that if a raw material has limited reserves, its price will continue to rise. Based on this background, in order to get rid of resource constraints and reduce costs, global battery suppliers and automakers are trying to reduce the cobalt content in ternary lithium-ion batteries by all means. Zero cobalt is the ultimate goal pursued by automakers. Increasing the proportion of nickel in the positive electrode while reducing the cobalt content is a good method to improve battery energy density and reduce costs. “High nickel, low cobalt” has become the trend of the current stage.
Currently, BYD plans to adjust the nickel-cobalt-manganese ratio to 8:1:1 by the end of this year. The head of Panasonic’s automotive battery department states that the cobalt content in its ternary battery has been reduced to 3%, and they hope to reduce the cobalt content in ternary batteries to zero, which is already under development. In early May, Tesla announced that the battery installed in the Model 3 has greatly reduced the cobalt content while increasing the nickel content, achieving the highest energy density ever and super heat resistance. Recently, Tesla CEO Musk stated on social media that the cobalt content in the Model3 battery has been reduced to less than 3%. They will continue to improve their technology and strive to completely abandon cobalt in the next generation of batteries, changing the reputation of “blood batteries”.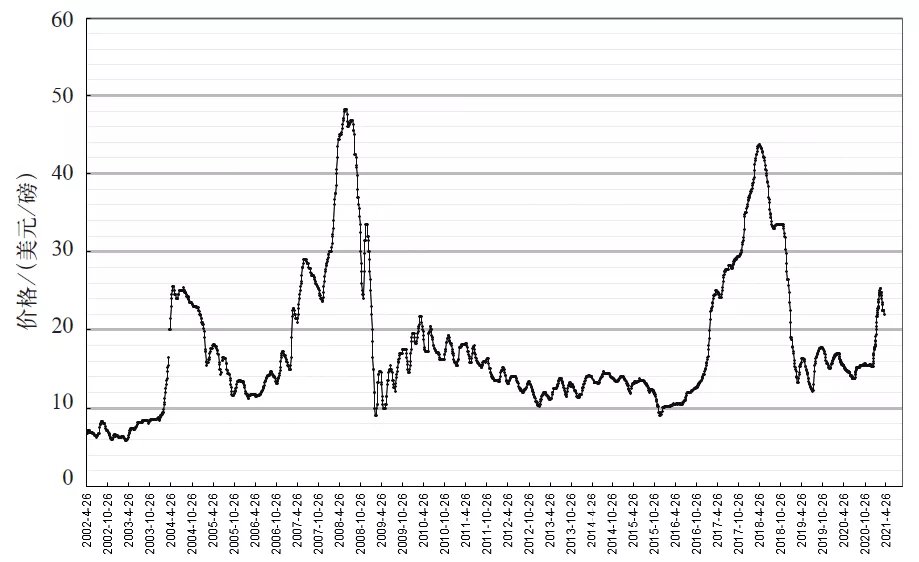
What is Cobalt-Free Battery Released by Honeycomb Energy?
Different from other battery companies’ “low-cobalt” batteries, Honeycomb Energy officially launched a “0” cobalt new product: 115 Ah and L6 thin cobalt-free long battery cores, which are the world’s first companies to successfully develop cobalt-free batteries. Cobalt-free technology needs to face many scientific research difficulties, and it is not simply a matter of removing cobalt elements. The cobalt-free battery released by Honeycomb Energy has three key technologies. One of them uses ion doping technology, that is, two elements with larger chemical bonds are doped into the material to replace cobalt. The other two technologies are single crystal technology and nano-network encapsulation.
Compared with the same level of high-nickel ternary batteries, Honeycomb cobalt-free battery cores have the core advantages of high safety, high energy density, high cycle life, and low cost. The energy density of 115 Ah reaches 245 Wh/kg, and it can achieve a quality assurance of 1.2 million kilometers in 15 years. The capacity of L6 thin cobalt-free long battery core is 226 Ah, and it is expected to achieve a range of 880 kilometers. The cycle life can exceed 3000 times, and it can easily pass the 150℃ hot box test and the 140% SOC overcharge test, and has multiple international standard certifications.
Outlook
As the world’s largest consumer market for new energy vehicles and the largest consumer of cobalt products, China’s proven cobalt reserves are only 80,000 tons, accounting for 1.14% of the world’s total reserves. This means that if we want to vigorously develop the new energy industry, if we do not have an effective solution to the cobalt resources, we can only rely on imports, which is also the biggest bottleneck problem facing China’s lithium battery industry at present.The launch of cobalt-free batteries will indeed bring significant changes to the industry chain. This does not mean that the technical route of power batteries will be greatly affected, it is only the beginning. The technical route of lithium iron phosphate and ternary lithium batteries is still mainstream. With the support of new technologies developed by leading companies such as CATL and BYD, the energy density of lithium iron phosphate and ternary lithium batteries will gradually increase. However, cobalt-free batteries are a huge advancement in technology for the new energy vehicle industry and the power battery industry. This will also create positive pressure for domestic and foreign industry competitors. Especially for Chinese battery companies, as we all know, for a long time, the basic innovation of battery materials and core patents have been basically controlled in the hands of European, American, Japanese, and South Korean countries. Although China’s lithium-ion battery industry is leading globally in terms of scale, it has long been “lagging behind” in basic material innovation. China urgently needs some original innovation, because the current market competition is a patent war. If we are doing traditional battery technology, the patents are also owned by the United States. However, with our own developed cobalt-free battery technology, we have broken through the US patent.
As China is the leading market for new energy vehicles, with the complete withdrawal of subsidies, the impact of policies on technical routes will become smaller and the market mechanism will eventually return to itself, such as technology and cost. Cobalt-free batteries for power batteries have become a global industry consensus. Under the trend of rapid global electrification, the scarcity of cobalt resources will seriously threaten the supply chain security of electric vehicles. Cobalt-free technology allows the industry to get rid of cobalt as a rare resource facing the risks of high prices, scarce resources, and constraints. It can also help significantly reduce the cost of power batteries. Ferret Energy has courageously put forward a targeted new cobalt-free battery product solution, which is commendable. It is believed that with the continuous improvement of China’s new energy research and development capabilities, more head-to-head technologies will be overcome one by one!
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.