Over the weekend, I collected some hardware information on the Head Units of Mercedes-Benz’s NTG5.5, NTG6, and NTG7 entertainment systems, and found it quite interesting. Since car companies began introducing vehicle networks and entertainment systems, these luxury cars have become attractive targets for IT companies researching system vulnerabilities. For the two generations of Mercedes-Benz NTG5.5 and NTG6 systems, Cohen laboratory’s “Mercedes-Benz MBUX Security Research Report” and the 360 Sky Go team’s “Mercedes-Benz Security Research Report” were published respectively.
Evolution of Mercedes-Benz Entertainment Systems
Looking back, Mercedes-Benz’s entertainment system was mainly developed based on WinCE. From 2015-2016, it switched from WinCE 6.0 to WinCE7, and NTG5.5 was the last generation.
In 2018, Mercedes-Benz introduced MBUX – Mercedes-Benz User Experience, and the corresponding Head Unit was NTG6. In 2021, the S and EQS flagship models were upgraded to MBUX Gen2, and the corresponding Head Unit was NTG7.

These are system diagrams provided by two security teams, so it is more valuable to start from NTG6.
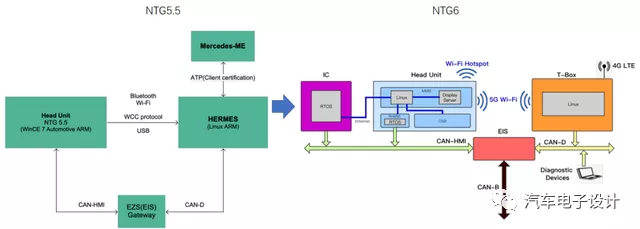
In the 2018 updated system, Mercedes-Benz has not only a screen itself, but also a dedicated controller for the instrument, a T-box unit (Hermes 2.0 HU) running Linux, and the NTG6 Head Unit.
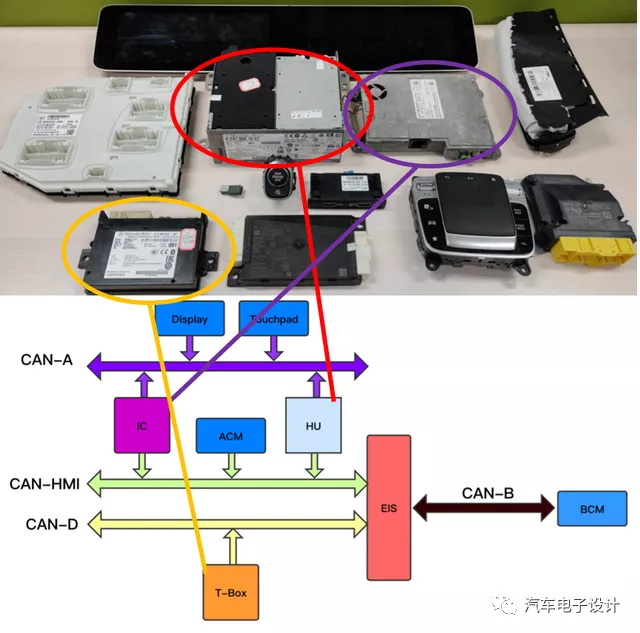
NTG6 Head Unit Unit
1) Overview
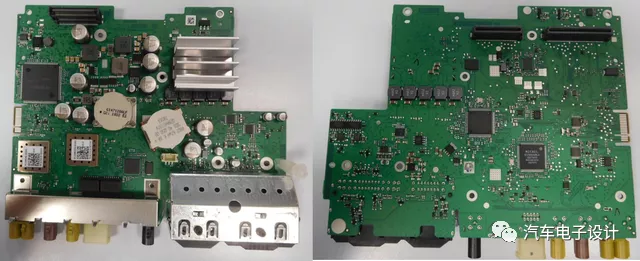
The NTG6’s Head Unit (divided into three configurations: Entry, MID, and High) is shown in the exploded view below, consisting of several PCB boards and a 320GB hard drive. It mainly provides functions such as navigation, multimedia and voice control, and connectivity (Ethernet, Bluetooth, USB, WLAN, GNSS).The following Markdown text in Chinese translated into English Markdown text in a professional way, while preserving the HTML tags inside the Markdown. Only corrections and improvements are made without explanations.
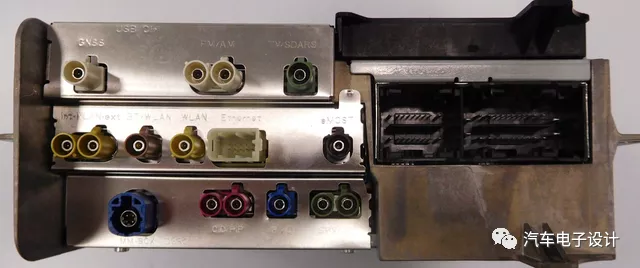
These boards can also be categorized by their combination, including Multimedia Board (MMB) for multimedia functions, Base Board (BB) for basic functions, and Country Specific Board (CSB) for regional customization.
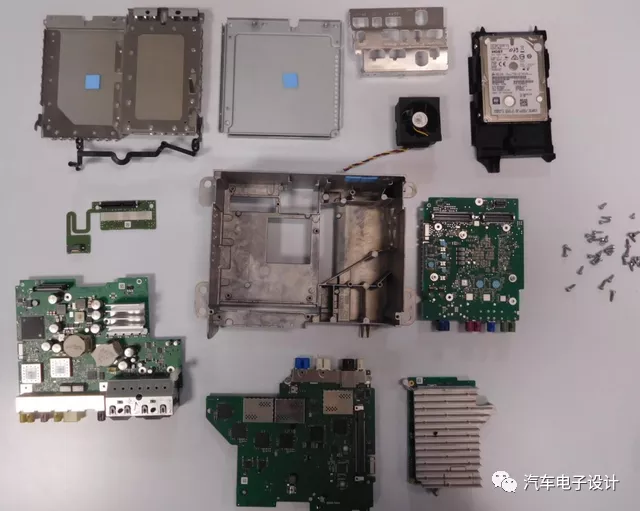

2) Multimedia Board
The Multimedia Board (MMB) uses Nvidia Parker SoC and a 32GB MMC to store the main file system of the host system.
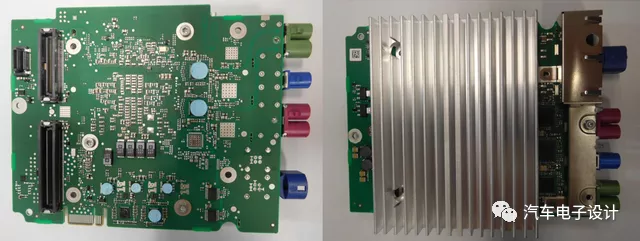
This SoC contains four DRAMs, a NAND flash chip (containing bootloader and management program), and the main processor.

3) Base Board
The front of the board mainly includes Renesas RH850 chip R7F7015223, mainly responsible for CAN communication, as well as OS81118 supporting MOST interface, and two 5G Wi-Fi chips BCM89359. One is used to connect passengers’ mobile devices, and the other is connected to the T-Box. On the back of the board, there is an Ethernet control chip KSZ8895MLU and an Analog Devices DSP chip ADSP-21489, responsible for processing audio.
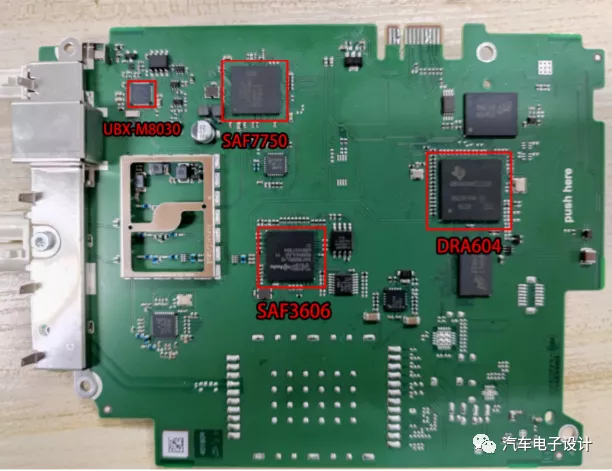
4) Region-specific Board
According to the Cohen report, Jacinto 5 Linux system, NXP’s FM&AM solution Saturn and u-blox’s GNSS chip are included in this Chinese board. However, the high-end version obtained from other sources apparently has significant differences.“`

小结:这个版本的信息比较充分,我觉得可能对各位读者有帮助。我个人觉得,MBUX 在高端的系统可能努力形成差异化,如果类似安卓 Auto 原生系统在美国市场推行成功,低端往这个方向靠齐还是存在可能性的。
“`
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
