On June 17th, at the Apollo Park in Beijing’s Yizhuang district, Baidu unveiled its latest fifth-generation driverless Robotaxi, the Apollo Moon.

Over the past eight years, Baidu’s Apollo Robotaxi has undergone four iterations. The third-generation Robotaxi, launched in 2017, employed various perception hardware, including a self-developed computing platform, LiDAR, millimeter-wave, and cameras. The fourth-generation Robotaxi, launched in 2019, abandoned the retrofitting of mass-produced vehicles and instead adopted front-load mass production.
The newly released fifth-generation, called the Apollo Moon, is a driverless Robotaxi platform that has partnered with the brand ARCFOXxing, and employs the Alpha T (ARCFOX αT) model for deployment. At the event, Baidu proudly announced the cost of the fifth-generation Apollo shared driverless vehicle at 480,000 RMB.
What is Robotaxi
Today, we released images of the Alpha T of the Robotaxi edition on Weibo, and many users asked in the comments section, “Why does the car have such a large radar on the roof, and why does it not look like the car we buy?”
So first, let’s answer the question, what is a Robotaxi?
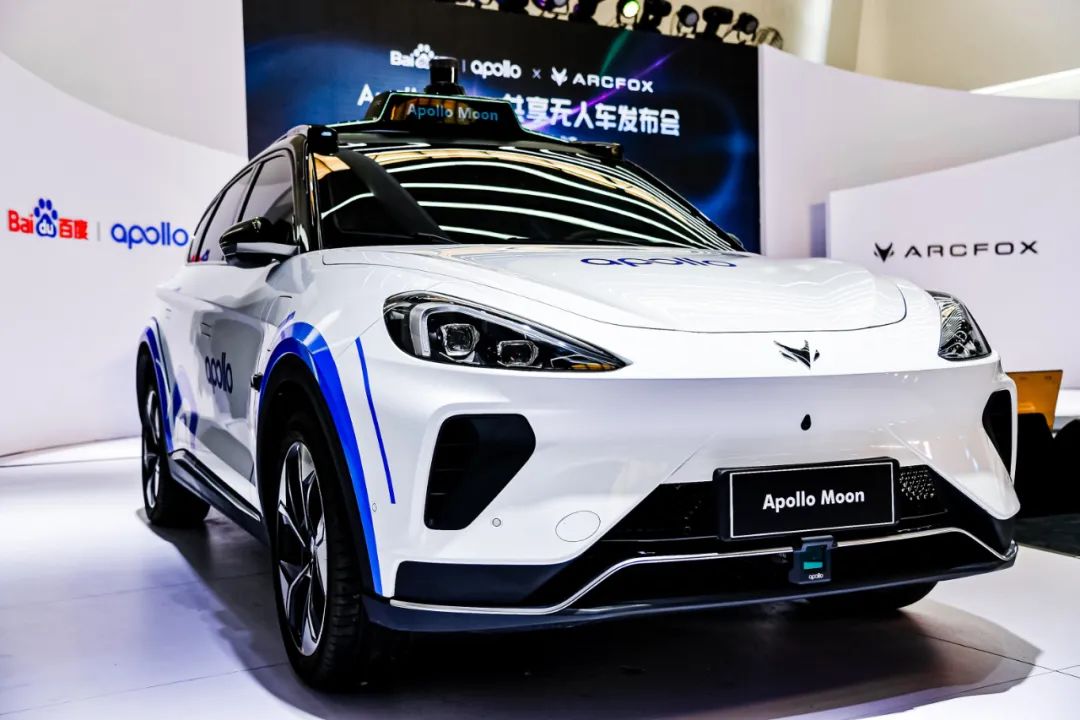

Robotaxi is literally an “autonomous driving taxi” or “driverless taxi.” The ultimate vision is to offer on-demand driverless taxi services when vehicles are fully automated.
These vehicles can be understood as taxis, without human drivers, and are purchased directly from the manufacturers. So, you don’t have to worry about how the car looks.
The reason why Robotaxis have such horn-shaped roofs is that it allows for a better detection of the surrounding environment with the LiDAR that is necessary for automated driving.
As Robotaxis will eventually operate without human intervention, they have cost and efficiency advantages over human-driven cars. Autonomous vehicles do not get distracted like their human driver counterparts and through cloud-based data management, they can significantly improve road safety and reduce traffic congestion.
However, commercializing Robotaxis is still relatively difficult, as fully scalable autonomous driving technology is yet to be achieved, and there are governmental restrictions related to policy implementation and testing licenses due to safety reasons.The autonomous driving companies often stack a large number of expensive cameras on the car to achieve better safety redundancy. Therefore, the unit cost of Robotaxi can reach RMB 1-2 million.
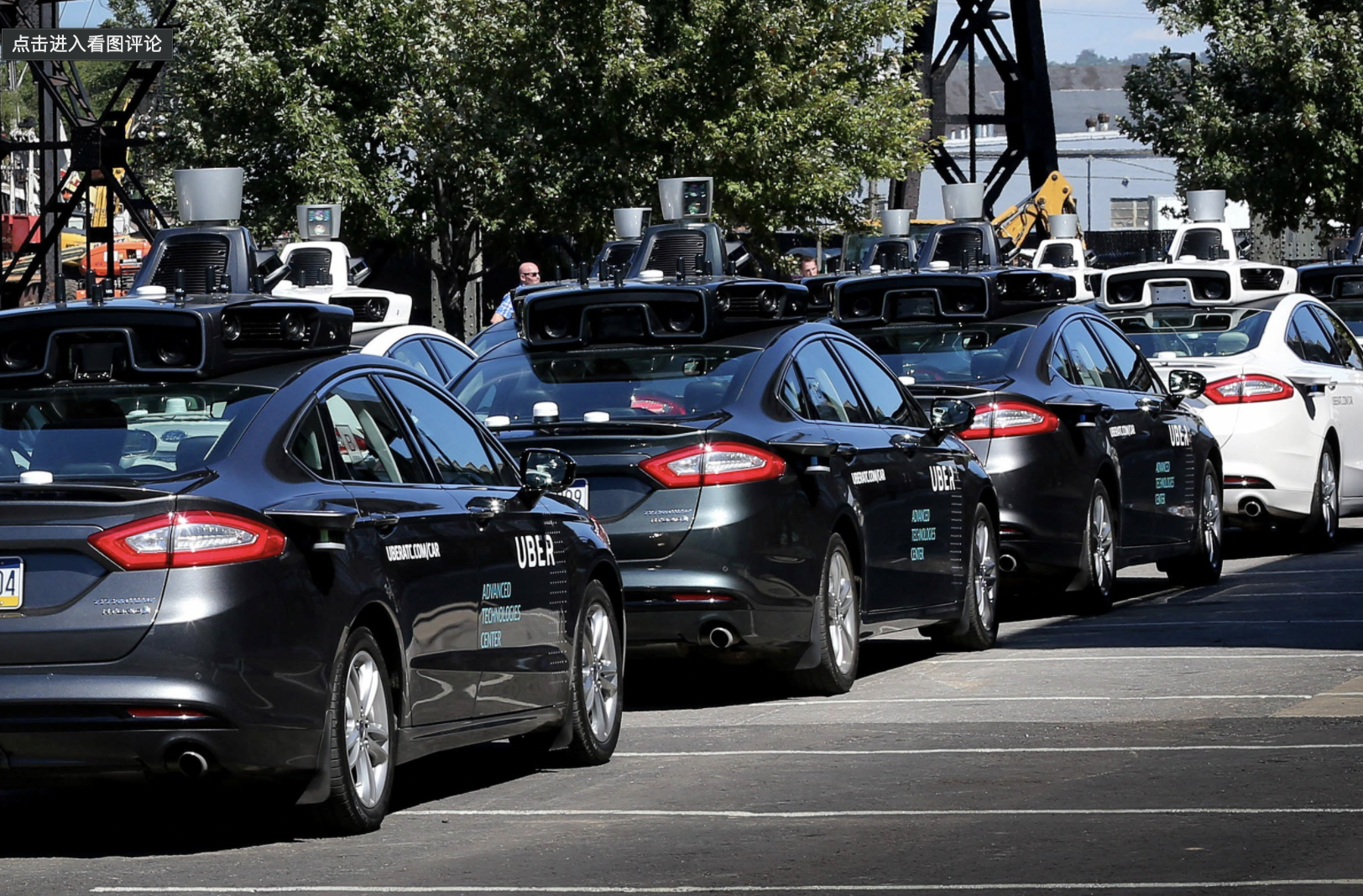

Each vehicle needs at least 2-3 safety personnel to work in shifts during the day. According to ZipRecruiter, the average annual salary of taxi drivers in the United States is about USD 31,000. The annual cost of a single safety staff member per car in the United States can reach up to approximately USD 100,000.
As a result, the high cost of autonomous driving Robotaxi, as well as the corresponding demand for the number of safety personnel, has made it impossible for the initial test fleet to expand and commercial applications to become distant.
Baidu Apollo’s Three-pronged Approach to Commercialization
“Hell no, I’m not going to do Robotaxi. Companies that are doing Robotaxi right now are done for. Robotaxi is a result, not a business target. The taxi experience in the Chinese market is already good, and autonomous driving will not make it better.”
Su Qing, chief architect of Huawei’s BU, pronounced the death of Robotaxi companies during a media communication meeting.
However, Wang Yunpeng, general manager of Baidu’s Autonomous Driving Technology Department, believes that Robotaxi is an important part of Apollo’s overall technological commercialization, and it can form a good strategic synergy with the intelligent driving business for mass production cars.
“After several years of exploration, we found that the two businesses have strong strategic synergies, which we summarize as “technological downgrade and data backfeeding.” Applying Robotaxi’s L4 level technology to mass-produced cars can provide better autonomous driving capabilities and user experience. At the same time, mass-produced cars can also provide Robotaxi with massive high-quality data for technology improvement. This is a highly synergistic positive feedback loop that will greatly promote the rapid development of technology and products, forming a unique competitive advantage.”
Baidu’s Chairman and CEO, Robin Li, also summarized Apollo’s three business models.
“In the field of intelligent driving and other growth businesses, autonomous driving is about to reach a breaking point. Apollo has developed three business models: First, provide Apollo’s autonomous driving technology solutions to host manufacturers; secondly, integrate Baidu’s autonomous driving innovations end-to-end and push the most advanced technology to the market at the first time through “Baidu Made” car making; thirdly, share unmanned autonomous vehicles.”
Regarding the first point, Baidu provides technical services to host factories, which Baidu has been implementing for a long time, such as Baidu CarLife, Baidu Map-Vehicle Edition, and Xiaodu Car OS.

The promotion of AVP and ANP autonomous driving technologies is also underway, such as the recent WM W6. Baidu plans to launch one new vehicle per month that integrates the Apollo suite in the second half of this year. Baidu expects that in the next 3-5 years, the number of vehicles produced with front-end integration of autonomous driving systems will reach 1 million.

In the second point, the founding of Jidu Auto is Baidu’s attempt to enter the automobile manufacturing industry, with a plan to invest 50 billion yuan in five years. The first car will be launched at the 2022 Beijing Auto Show. The purpose is to showcase Baidu’s strength in software and hardware to fully demonstrate its autonomous driving capabilities and various technical advantages in smart cars.
In summary, the goal is to showcase the various highlights of Apollo to most effectively attract host factories to cooperate with Baidu.
At Jidu Auto’s recent first media communication event, they claimed that Apollo has “Lego-like abilities,” allowing manufacturers to arbitrarily build their own highlights according to their needs.
The third point is Apollo’s shared autonomous vehicle, which mainly refers to Robotaxi.
Apollo Moon
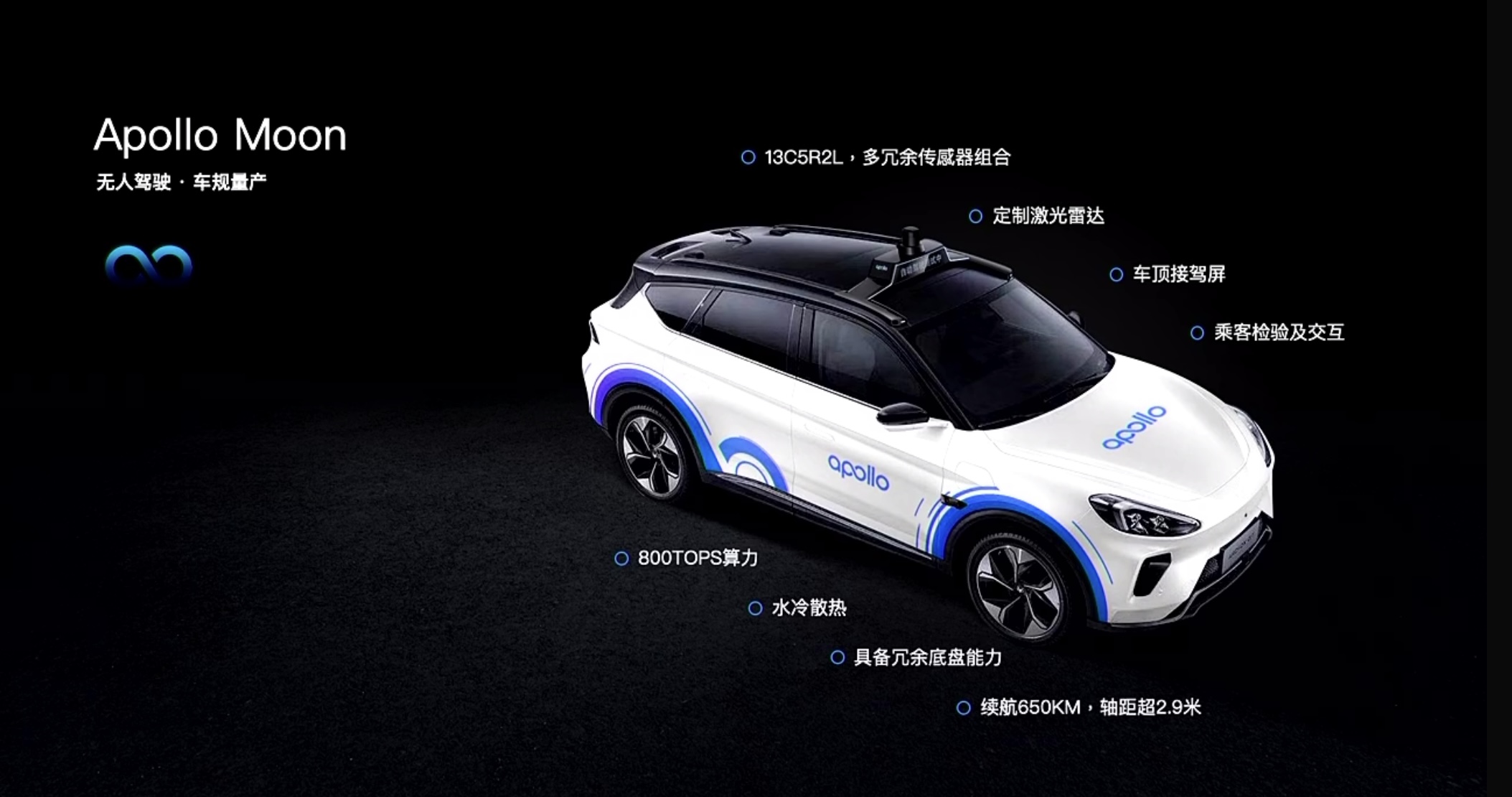
Since Baidu’s autonomous vehicle technology has already iterated to the fifth generation with Apollo Moon, let’s take a look at the advantages of the Alpha T (ARCFOX αT) that serves as its carrier.
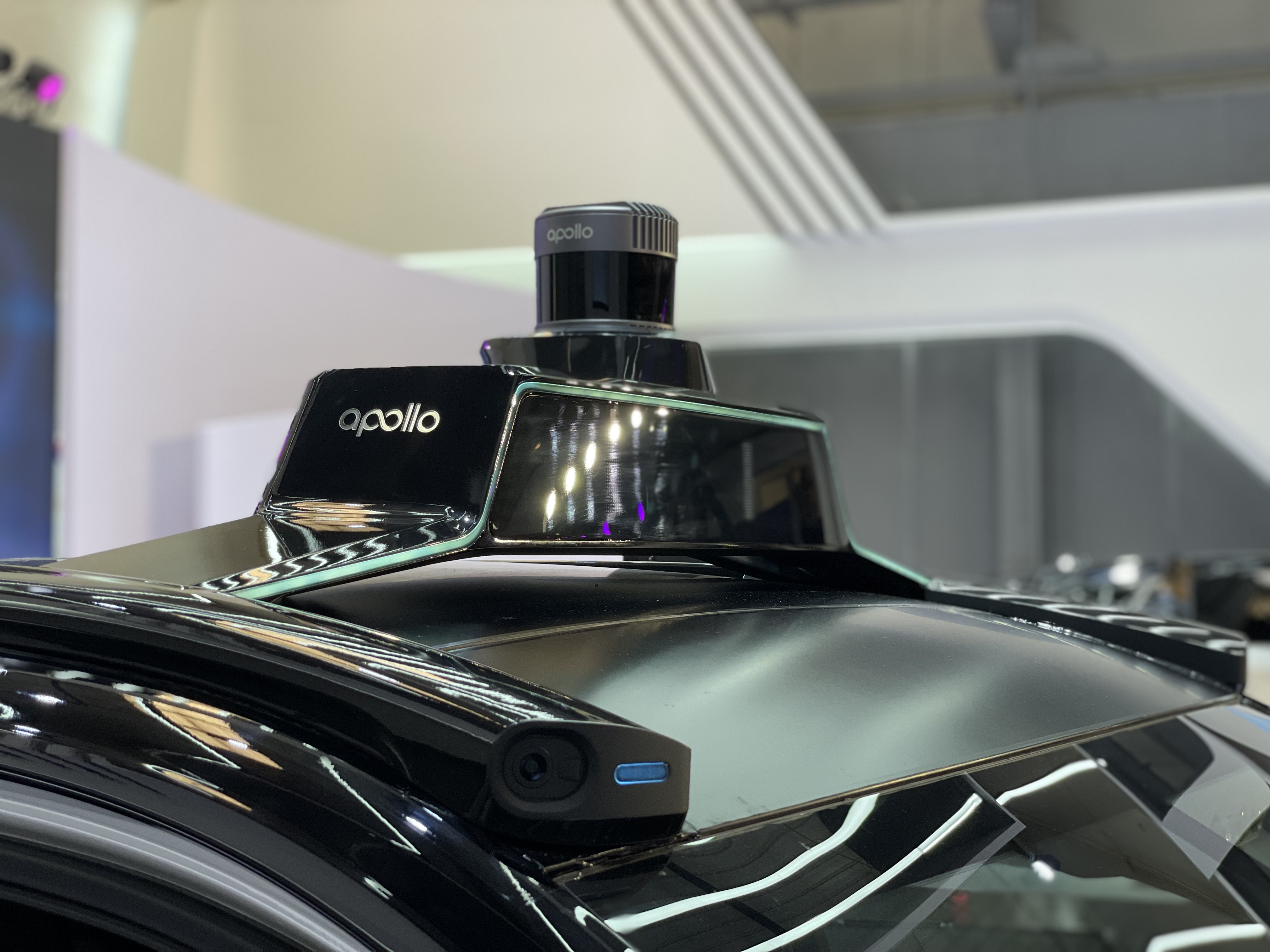
Perception Hardware
-
Two LiDARs
-
Thirteen cameras
-
Five millimeter-wave radars
-
Twelve ultrasonic sensors
 # Apollo Moon: A Vision-Based Autonomous Driving Route
# Apollo Moon: A Vision-Based Autonomous Driving Route
Apollo, developed by Baidu, is a vision-based autonomous driving route that utilizes a laser radar jointly developed with Velodyne, a global leader in LiDAR technology. However, the number of lines used by the LiDAR is low, resulting in a relatively low cost.
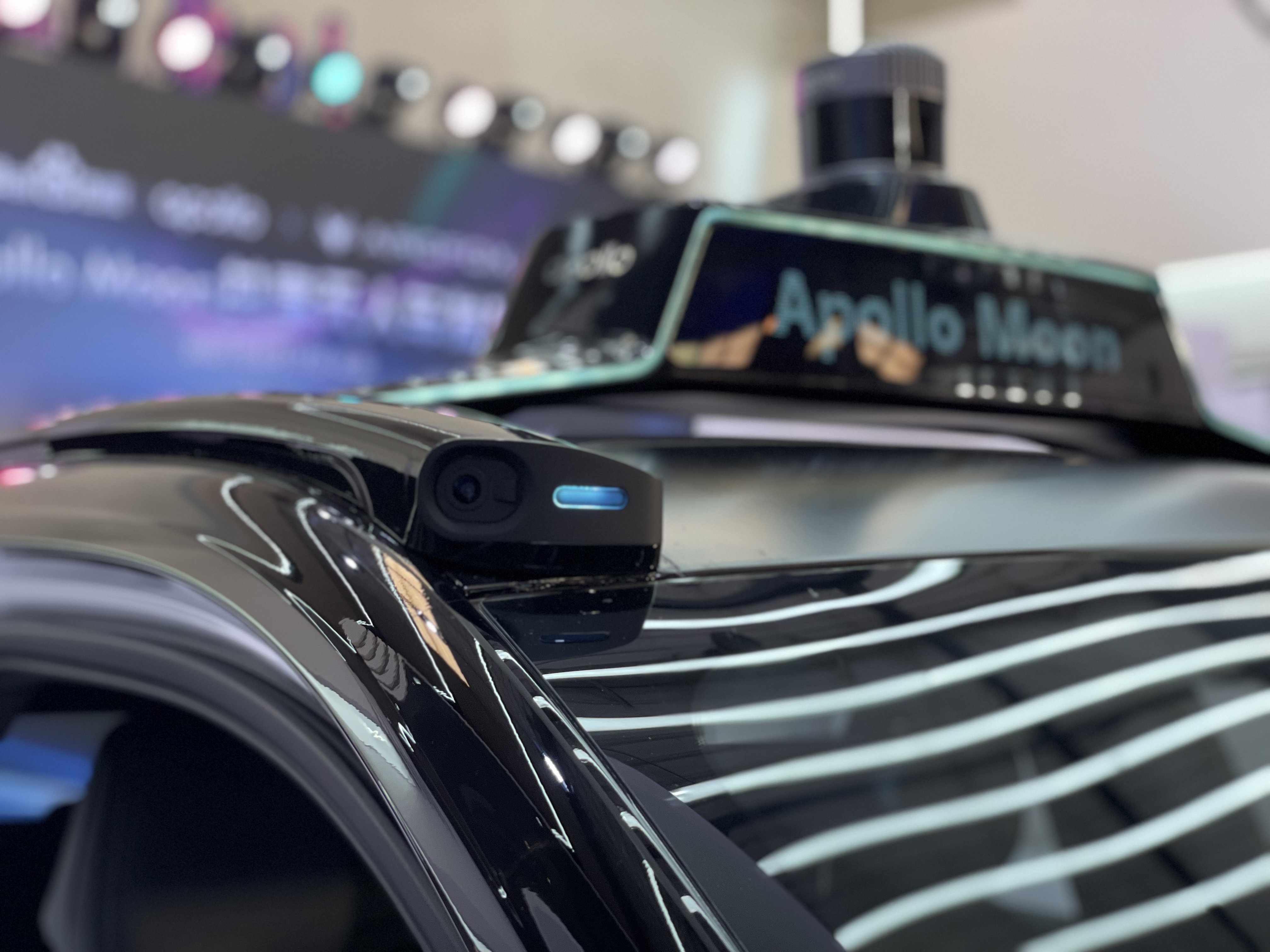

In contrast, the camera has significantly improved the resolution and frame rate to enhance visual perception. The vehicle is equipped with a self-cleaning camera system, similar to headlight cleaning.
Of course, this requires high communication speed and computing power. The Alpha T (ARCFOX αT) itself carries a gigabit Ethernet network, and the platform’s computing power is increased to 800 TOPS in this upgrade.
Apollo Moon has a complete failure detection and downgrading strategy and supports 5G cloud driving and V2X functions. According to the official statement, compared with the previous generation, the vehicle’s overall ability has increased tenfold, and the successful delivery rate on complex urban roads has reached 4 nines (99.99%).
Finally, the cost for a robotaxi capable of autonomous driving is 480,000 RMB.
Wang Yunpeng, Vice President of Baidu and General Manager of the Autonomous Driving Technology Department, confidently states that as a commercially available unmanned vehicle, including the total cost of the vehicle and all components installed later, Apollo Moon costs only 480,000 RMB, which is one-third of the average cost of the industry’s autonomous driving models.
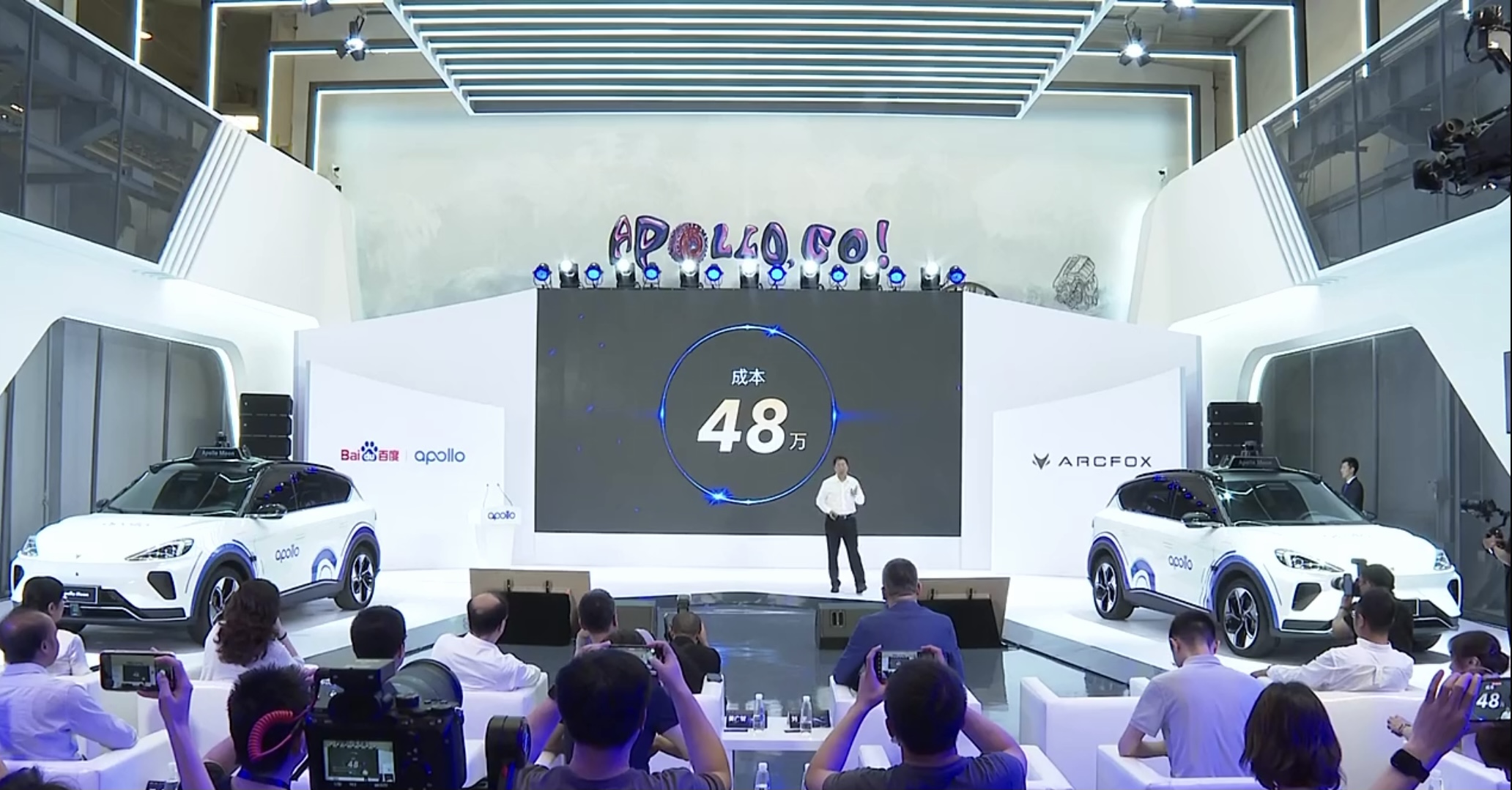

Wang Yunpeng also claimed that Apollo’s fifth-generation unmanned robotaxi can guarantee no failures within 20,000 hours. According to a usage time of 5 years, the cost of this robot amounts to around 8,000 RMB per month, which already reaches the monthly operational cost of online car-hailing services in first-tier cities. However, this is all based on the premise of having no safety personnel.
In fact, from the appearance of this fifth-generation Apollo Moon’s unmanned robotaxi, it is evident that the vehicle’s front end is highly integrated, with almost all the perception hardware integrated into the vehicle’s body. This not only makes it look good but also maximizes scalability and reduces retrofitting costs.

Wang Yunpeng proposed even more ambitious goals: to achieve product upgrades in two years, increase the ability tenfold, reduce the cost by half, and reach a testing mileage of 40,000 kilometers per day.
Unmanned Operation of Apollo MoonIn the Robotaxi autonomous operation and interaction, Baidu has also made many innovations.

On the top of the vehicle, Baidu has made an interactive “roof boarding screen” that displays vehicle status and facilitates identification of people and vehicles. In the demonstration screen, pedestrians can be alerted externally, and users are also supported to customize.
The 650 km range and more than 2.9 m wheelbase both suggest that this vehicle can work continuously for long distances and has decent seating space.
For more convenient services, this vehicle supports independent control of four-door locks, dynamic identification of passengers getting on and off, detection of rear-passenger status, and even automatic door closing.
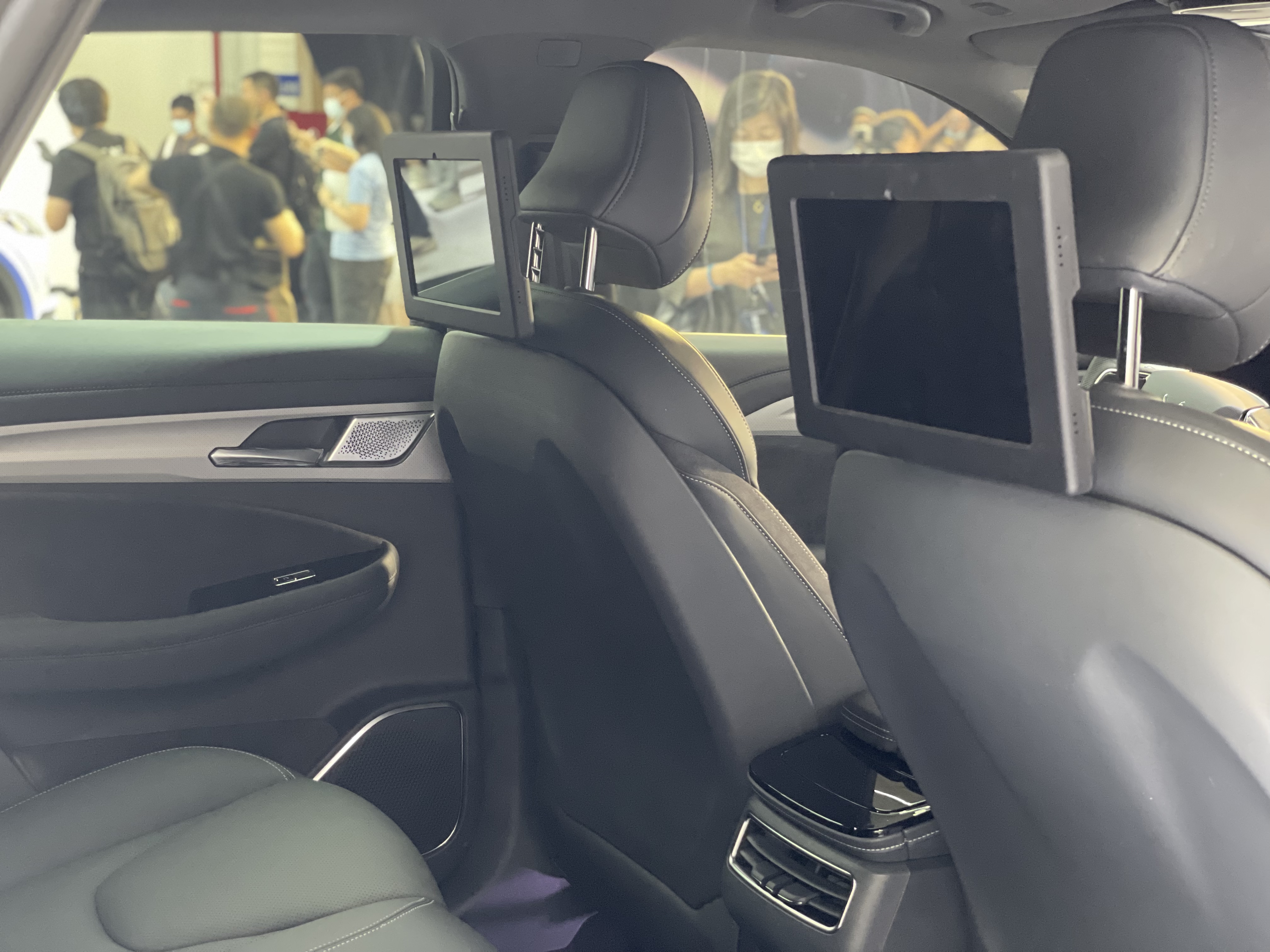

Rear passengers can also perform voice interactions, app control air conditioning, and window functions.
ARCFOX and Baidu
ARCFOX’s deep cooperation with Huawei in the field of autonomous driving is well known to the public, and the Alpha S (ARCFOX αS) HI version, a crystallization model, will be delivered in Q4 of this year. The release of unmanned vehicles by Baidu and ARCFOX has made outsiders speculate on ARCFOX’s brand business model and technological direction.
At the media communication meeting, the vice president of ARCFOX Automobile said that Huawei, like Bosch, is just a supplier for ARCFOX.
The cooperation between ARCFOX and Baidu will not be limited to the Apollo Moon, which will be unveiled in September. Dai Kangwei, the general manager of BAIC New Energy Corporation, said that next year there will be models equipped with the AVP automatic parking technology that can also achieve wireless charging.
During the event, Baidu and ARCFOX also signed a new strategic cooperation agreement, and it is expected to produce 1,000 shared unmanned vehicles in the next 3 years.

ARCFOX’s party secretary Liu Yu said that based on ARCFOX’s Gigabit Ethernet, he hopes to build ARCFOX into a platform and welcomes various manufacturers to try to develop on this platform.
This is the ultimate vision of ARCFOX’s business model, which also perfectly explains why ARCFOX chose to cooperate deeply with Baidu and Huawei, two autonomous driving companies with completely different technological routes.
ConclusionCurrently, Baidu Apollo has achieved 2,900 patents in the field of intelligent driving and has 244 testing licenses, with over 12 million kilometers of autonomous driving test mileage. Baidu Apollo has conducted autonomous vehicle testing in cities such as Changsha, Beijing, and Cangzhou in China. In January of this year, it was granted an autonomous driving test license on open roads in California by the Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV).
In April, Baidu was listed as the “Leader” in the Guidehouse Autonomous Driving Competitive Ranking for the second consecutive year, affirming its autonomous driving capabilities.
Despite Baidu Apollo’s prestige in the industry, various domestic automakers in China have chosen to use solutions from suppliers such as Mobileye and Bosch, or have developed their own technologies. This has forced Baidu to accelerate the commercialization of Apollo Robotaxi and to build its own vehicles to showcase its capabilities to automakers.
Baidu is not satisfied with its leading position in China’s autonomous driving industry. In the next three years, it plans to expand Apollo to 30 cities, realize a scale of 3,000 unmanned vehicles, and provide services to 3 million people, achieving commercialization on a regional level.
Baidu Apollo’s “three-legged” commercialization model is being unfolded. The synergy of these three elements in promoting each other will directly reflect the rapid updating of Baidu’s autonomous driving capabilities.
Regarding Baidu’s bold bet on autonomous driving, I believe that Li Yanhong’s determination may be even greater than that of Xiaomi’s Lei Jun for his entrepreneurial endeavors.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
