Author: Qiukaijun
Compared to electrification, BYD’s achievements in intelligence are not as outstanding. Some even argue that this is BYD’s biggest shortcoming compared to Tesla.
Some people say that BYD has fallen behind in intelligence and can only join forces with Huawei to use Huawei’s intelligent driving solutions to compete with Tesla…
Does BYD not attach importance to this? In fact, Wang Chuanfu has said long ago that electrification is the first half, and intelligence is the second half. BYD also started exploring intelligence very early. However, BYD emphasizes the openness of intelligent network-connected automotive ecology. For example, in 2018, BYD launched the intelligent network-connected system, opened 341 sensors and 66 control rights on the car, and entered into 3 million applications in the mobile phone ecosystem.
Consumers are certainly not satisfied with this. Regarding the intelligent driving part, how does BYD plan to do in other parts of the intelligent cabin?
On May 19th, after the 1 million new energy vehicles offline ceremony, BYD held a smart car forum in Shenzhen.
Yang Dongsheng, Vice President of BYD Group and Dean of Product Planning and Automotive New Technology Research Institute, comprehensively introduced BYD’s intelligent strategy. Based on this, we can roughly evaluate how BYD develops smart cars and what level of intelligence BYD will achieve in the short term.

Definition of BYD Smart Car
“The only judgment standard to measure whether a car is truly intelligent,” Yang Dongsheng said, “is whether the car’s network-connected system can take over or replace all functions of a smart phone after entering the vehicle.”
“Currently only BYD DiLink can do this.” He added.
BYD’s definition and exploration of smart cars emphasize the functions of the intelligent cabin, especially the replacement of mobile phones.
-
BYD Car Machine Evolution Milestones
-
In 2008, the first multimedia system was launched on F6;
-
In 2009, the first electronic key system was launched;
-
In 2011, the self-developed BYD cloud service, an automotive network-connected product, was launched, and functions such as remote start of air conditioning and remote opening of car doors were realized;
-
In 2012, the world’s first remote driving key was created, allowing the owner to remotely control the vehicle at short distances and in narrow spaces;
-
In 2013, the Android system car platform was developed;
-
In 2014, the first open Android system car machine CarPad was installed on G5;
-
In April 2018, the intelligent network-connected system DiLink compatible with the mobile phone ecosystem with unique car ecosystem was launched.The evolution from BYD car infotainment system to intelligent networking system demonstrates that BYD, taking advantage of the rich ecosystem of Android system on mobile, has integrated it into the automotive ecosystem, naturally possessing a vast resource. “BYD’s DiLink application market supports millions of mobile ecosystems.”
It doesn’t stop there, as Yang Dongsheng stated, “We see that the car has unique independence and convenience, fixed usage duration, exclusive system and the best imaging system, thereby truly becoming the third space. Therefore, while supporting the mobile ecosystem, we also look at which ecosystems can have better applications on the technical end. We have seen music, video, games… these usage scenarios have an experience in-car that far surpasses that of a mobile device.”
Based on this, BYD has led the trend of openness in the industry, launching DiLink 1.0 in 2018, which opened up 341 sensors and 66 control rights for the entire vehicle. They hope to use a standardized and open platform, leveraging the internet and the entire industry to create an internet-connected intelligent car.
“The mobile ecosystem is very prosperous in our car infotainment system,” Yang Dongsheng explained. According to the statistics of BYD car infotainment system, WeChat is most frequently used by car owners in-car, followed by Gaode Map and TikTok. “This is different from our traditional cars that focus on music listening.”
BYD also connects the mobile ecosystem ID and the car ID, allowing consumers to seamlessly connect the inside and outside of the car.
Increasing investment in intelligent driving
BYD has actually been researching and developing intelligent driving for a long time.
In early 2013, BYD collaborated with the Beijing Institute of Technology to jointly develop the experimental vehicle for automatic driving with cable remote control (pictured below). This vehicle won first place in the National Autonomous Driving Car Competition in the second half of that year.

In 2014, BYD and the Institute for Infocomm Research in Singapore jointly carried out research and development in automatic driving and intelligent transportation.
In 2016, Wang Chuanfu revealed that in addition to its own research on automatic driving technology, BYD also cooperated with Baidu in autonomous driving research, mainly to obtain high-precision maps. In September 2018, BYD released the D++ open ecosystem platform, which includes autonomous driving platforms and car application parts.
On March 28, 2019, at the BYD spring new product launch conference, one of the first batch of autonomous driving partners of BYD’s D++ Smart Open Ecosystem, AutoX, demonstrated product upgrades for the unmanned version of automotives, utilizing BYD Qin Pro Developer Edition autonomous driving vehicle platform (pictured below).
 In the same year, BYD started to equip L2 level autonomous driving on its Tang EV and DM models.
In the same year, BYD started to equip L2 level autonomous driving on its Tang EV and DM models.
However, BYD’s intelligent driving capability is fully presented in the Han model, which was launched in July 2020 and has attracted much attention in the industry. This model is equipped with the BYD DiPilot intelligent driving assistance system.
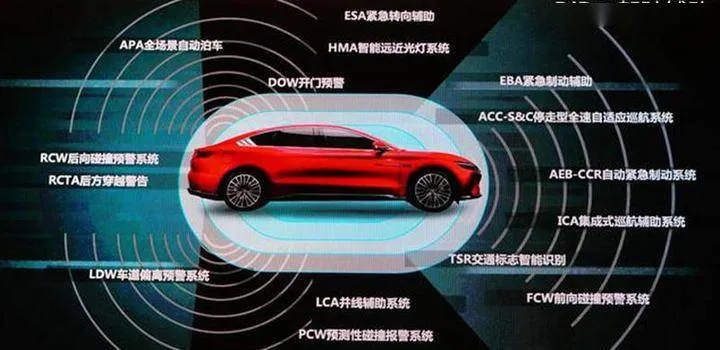
The DiPilot system has automatic emergency braking assistance, forward collision warning system, adaptive cruise control, single lane integrated cruise control, traffic congestion assistance, lane departure warning system, lane keeping system, blind spot detection, automatic parking, panoramic imaging, remote driving and other functions. It is a standardized advanced driving system.
Later, DiLink will upgrade to ICC intelligent navigation system, ICA integrated adaptive cruise control system, TJA traffic congestion assistance system, RCTA rear cross-traffic alert system, RCW rear collision warning system and other higher-level functions.
What sets DiPilot apart is its unique “coach” mode. By “observing” and “understanding” the driver’s behavior, it can combine the user’s personalized driving habits with the driving scenarios, and it has self-learning and self-evolving capabilities. Moreover, BYD integrates the DiPilot system with the previous DiLink intelligent network system, which is applied to the Han model to further improve personalized interaction experience and intelligent driving assistance performance.
According to the industry-standard definition, the DiPilot system is a relatively standard L2 level autonomous driving. The leading intelligent driving systems in the industry have been extended to lane change assistance (generally determined as L2.5) and navigation-assisted driving (partial scene L3).
From this perspective, many people think that BYD’s intelligent driving capability is relatively ordinary.
“We will increase investment in intelligent driving in the future,” said Yang Dongsheng.
Intelligent driving: from concept to development.
Yang Dongsheng introduced BYD’s intelligent driving concept.
He believes that solving the safety issue is the primary task of intelligent driving, and thus intelligent driving can be divided into three stages: assistance, companion, and rescue. In terms of application strategy, BYD will adopt advanced hardware deployment and software iteration to gradually introduce some intelligent driving functions.
Yang Dongsheng believes that assistance will significantly improve safety on highways, such as ACC+AEB+LKA… In the future of intelligent driving, “we must introduce functions similar to these three functions to assist drivers…to make every driver a skilled driver.”The so-called companion defines the intelligent driving function in the mode of living scene. “For example, in coach mode, how can we help a novice become a competent driver during the process, by assisting and accompanying them gradually, making the process more progressive and leveled?”
The so-called rescue refers to saving lives beyond the limits of human driving in extreme situations. The logic is that electric vehicles respond in milliseconds and can quickly adjust the vehicle attitude with the help of intelligent driving algorithm and high-performance chip processing platforms, along with some safety designs, making the vehicle safer.
During the Q&A session, Yang Dongsheng stated that BYD would focus on the first stage, making sure to do well in the safety assistance function.
When Tesla and XPeng Motors proposed their full-stack self-research concept, how can BYD achieve these intelligent driving functions?
Yang Dongsheng explained during the DiPilot introduction that “BYD is more about integrating these functions and making them automatically adapt to the owner’s requirements.”
What about the future?
At the same event, BYD invited Horizon Robotics’ founder and CEO Yu Kai and Momenta’s founder and CEO Cao Xudong to participate.
Yang Dongsheng said, “We will also work vigorously with ecosystem partners. With high-performance chips and strong control algorithms, together we will create a strong and unified ecosystem to develop leading intelligent electric vehicles.”
Of course, as a provider of self-supply, BYD definitely has its own areas of expertise. At least, according to Chen Gang, the general manager of BYD Semiconductor, in the ADAS vehicle rule-based semiconductor components, BYD can self-supply for MCU, DMS, night vision systems, and 360-degree panoramic parts. For many sensors and chip components, BYD is also self-researching and self-supplying.
In addition, during the Shanghai Auto Show, BYD introduced the intelligent features of the E-platform 3.0.
E-platform 3.0 has four domain controllers under a new electronic and electrical architecture and independently developed BYD OS for vehicle operation. Based on this electronic and electrical architecture and BYD OS, electric vehicles will achieve stronger autonomous driving capabilities, and the iteration speed of new features can be shortened from two months to two weeks, reducing the functional iteration cycle by more than 70%.
Although people are full of imagination about BYD + Huawei, Huawei did not have a representative on stage at this forum. In the past, the news of cooperation has emerged, but is limited to Huawei Cloud, Huawei Hicar, and Huawei 5G vehicle communication. As for Huawei’s recommended intelligent driving solution, it has some overlap with BYD’s own electronics and electrical architecture in terms of hardware, and in terms of computing chips and algorithms, it competes with Horizon Robotics and Momenta.
Of course, a car company is not limited to just one supplier, and BYD and Huawei certainly have collaborations.Overall, in the second half of the competition in the automotive industry – intelligence, BYD has not yet shown the same strength in electrification as it did. It needs to work harder relative to the expectations of fans of Dyson.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.