*Author: Dayan
On April 30th, NIO released its 2021 Q1 financial report. Similar to its stable performance in the domestic market, NIO’s financial data has also been continuously improving.
Overall, the company’s Q1 revenue reached 7.98 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 481.8% and a quarter-on-quarter increase of 20.2%; the gross profit margin of vehicle sales continued to climb to 21.2%, and the comprehensive gross profit margin was 19.5%. In terms of profits, the company’s net loss for the first quarter was 451 million yuan, but compared with the loss of 1.723 billion yuan in the same period last year, there has been a significant improvement.
In addition, NIO has cash reserves of 47.55 billion yuan, which provides sufficient ammunition for NIO’s continued new car and core technology research and development.
Continuous Sales Growth: Promising Prospect of ET7
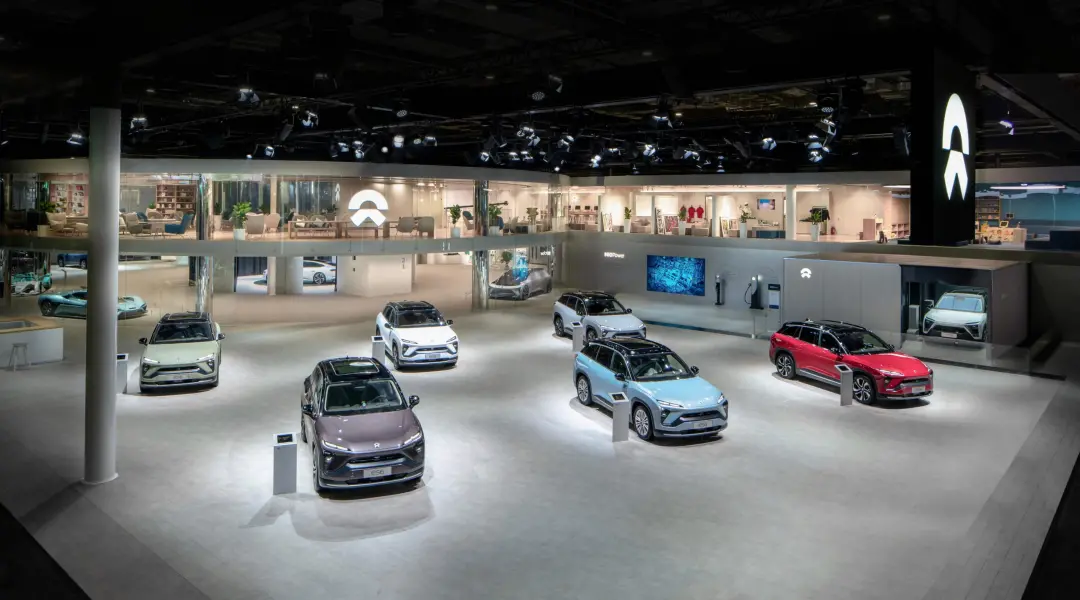
Good financial data certainly relies on the steadily rising sales volume for a car company. NIO is currently selling three models in the domestic market: large and medium-sized SUVs ES8 and ES6, and the coupé SUV EC6. The sales volume of the three models is relatively balanced.
Overall, in Q1 2021, NIO delivered a total of 20,060 new vehicles, a year-on-year increase of 422.7% and a quarter-on-quarter increase of 15.6% from Q4 in 2020. Among them, NIO ES8 sold 4,516 vehicles, NIO ES6 sold 8,088 vehicles, and NIO EC6 sold 7,456 vehicles. Li Bin, the founder, chairman, and CEO of NIO, stated that due to the semiconductor shortage, it is expected that 21,000-22,000 vehicles will be delivered in Q2 of 2021.

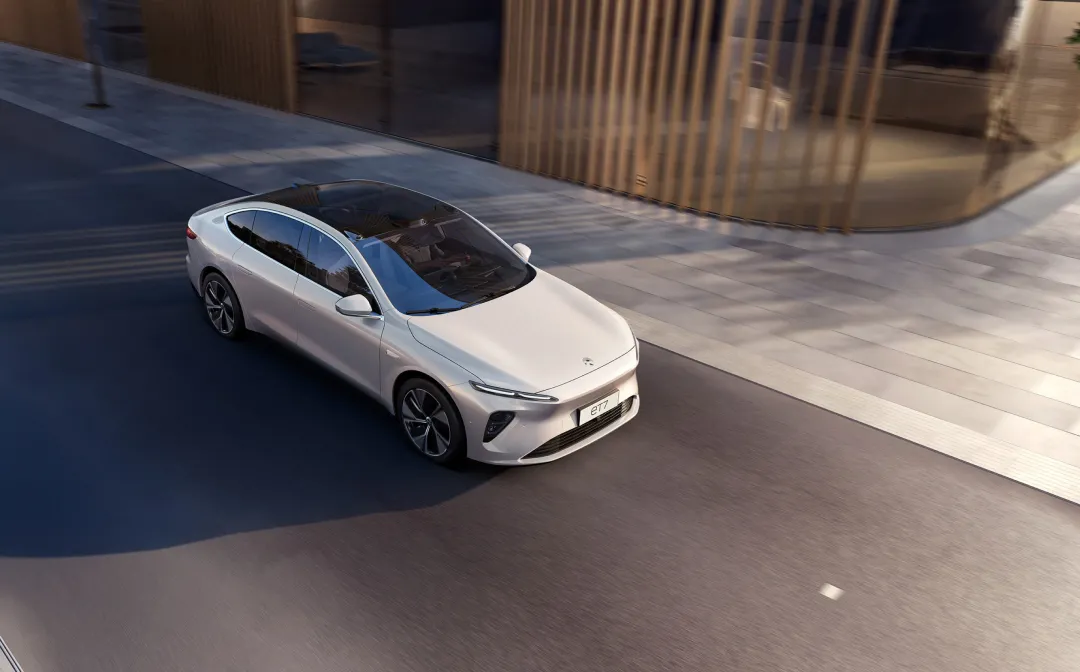
One of the vehicles that cannot be ignored by NIO is its latest flagship sedan, the ET7. The production of this model is already in full swing and it is expected to begin delivery in the first quarter of 2022.
In terms of range, NIO ET7 will be equipped with a 70 kWh and 100 kWh battery pack, with a range of 500+ km and 700+ km respectively. In the future, it will also use a 150 kWh battery pack to achieve a range of more than 1000 km.

However, the biggest highlight of this model is its autonomous driving system, which is composed of a hardware system consisting of 11 8-million-pixel cameras, 1 ultra-long-distance high-precision LIDAR, 5 millimeter-wave radars, 12 ultrasonic radars, 2 high-precision positioning units, 1 vehicle-to-road collaborative perception, and 1 enhanced driver monitoring system (DMS).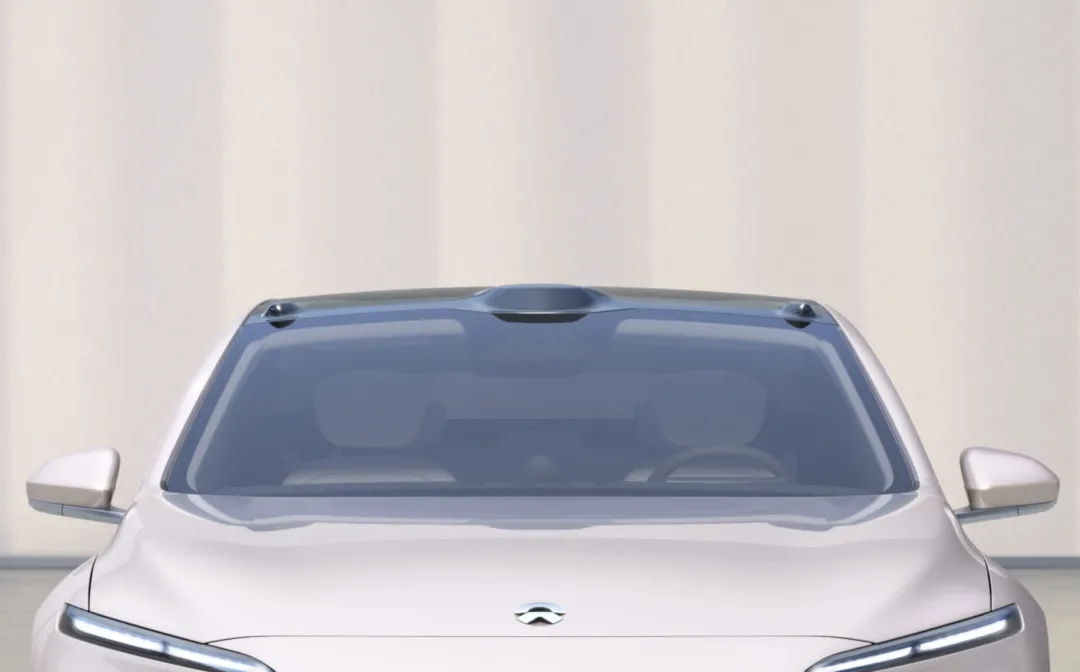
In addition, equipped with four NVIDIA Drive Orin chips, the total computing power of NIO Adam’s supercomputing platform is as high as 1016 TOPS, far exceeding Tesla FSD HW 3.0’s computing power of only 144 TOPS.

Rising Sales of High Value-Added Components Bring Double Rewards to NIO
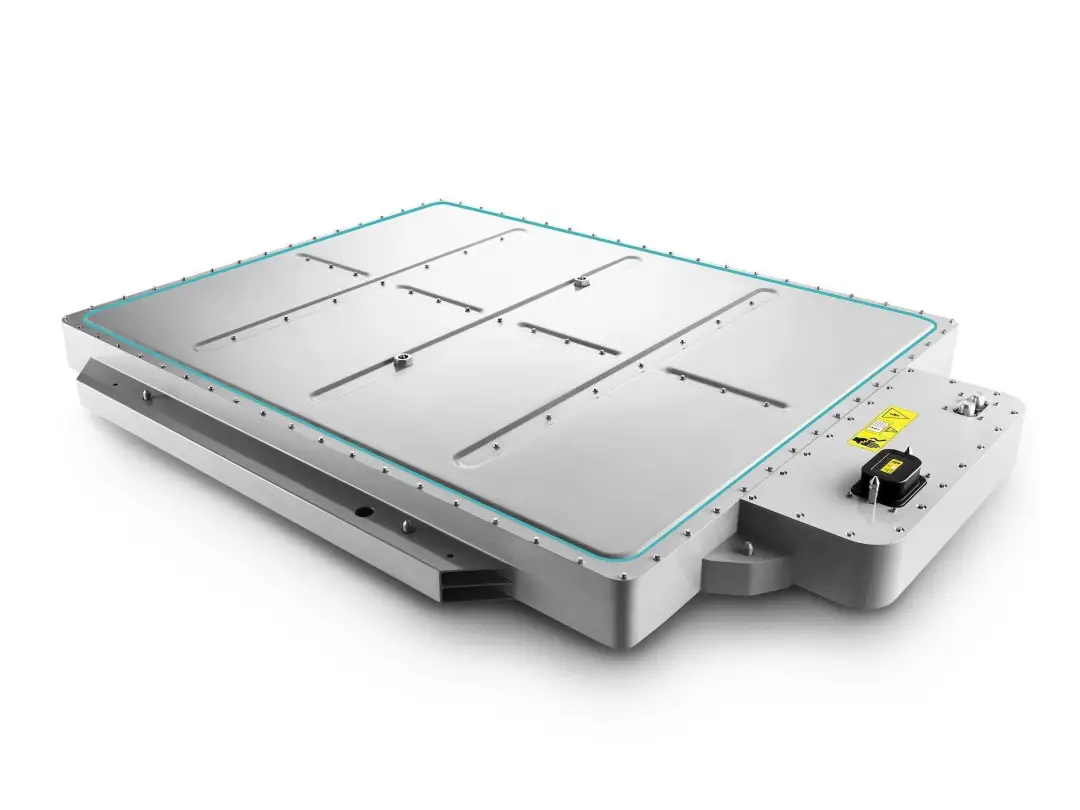
In addition to the continuous increase in sales volume, the rising sales of high value-added components and the increasing adoption rate of NIO Pilot have brought sustained benefits to NIO’s financial data and increased the gross profit margin per vehicle. Especially with the 25% increase in the utilization rate of the 100 kW battery pack, which not only benefits NIO’s profitability, but is also an important reflection of NIO’s technology being recognized by consumers.
For smart connected cars, software will also become an important source of income for automakers in the future. With the continuous iteration and update of NIO Pilot, it is gradually approaching L4 level of self-driving capability, and NIO’s software income is also promising.

For NIO, its terminal price has already successfully stood firm in the luxury brand market, and with its current performance, it does not need to offer discounts in order to maintain its reputation. A firm terminal price can play an important role in maintaining NIO’s brand reputation.
With such confidence, NIO can provide customers with more cost-effective products and more valuable services. In the situation where customers are willing to pay luxury car prices to choose NIO cars, NIO should focus more on reducing its costs to obtain greater profits while maintaining the same level of customer experience.
It is also worth mentioning that NIO’s second-generation battery swapping stations have already begun deployment. The battery compartment of the second-generation battery swapping station can hold up to 13 batteries, and the daily service capacity of a single station is 312 times, further shortening the battery swapping time. Battery swapping is a development direction encouraged by national policies. Deploying battery swapping stations and achieving profitability of the stations will be the next important issue for NIO.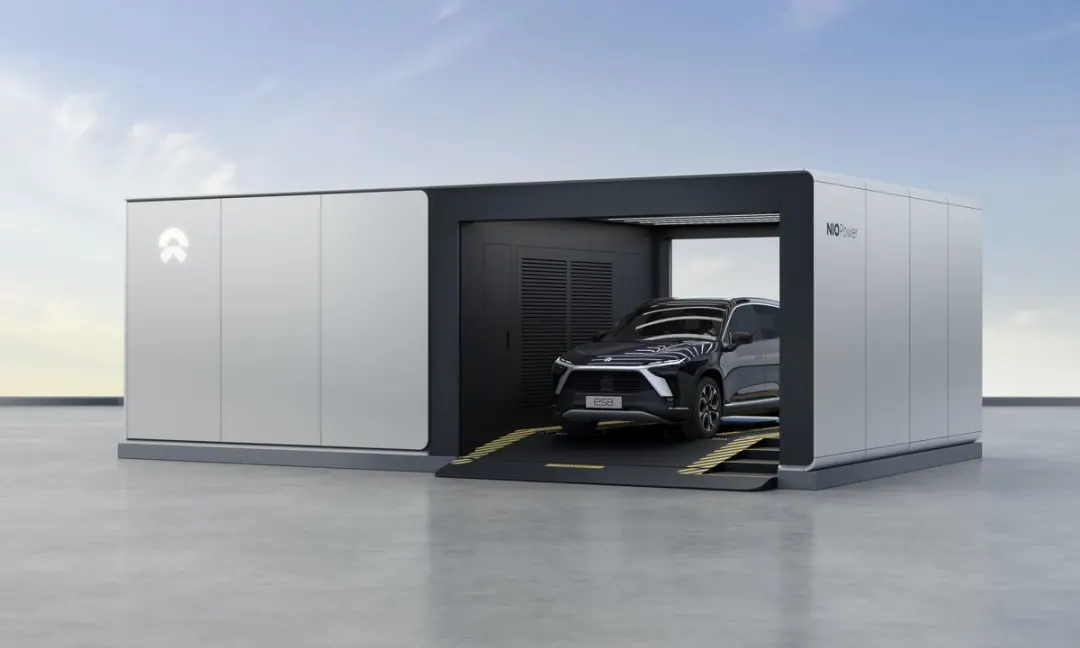
Concerns for the “Future”
A lack of long-term planning will result in short-term concerns. In the short-term, the biggest challenge for NIO will be the issue of chip shortages. Like other major manufacturers, NIO stopped production for five days due to chip problems at the end of March. The fire at the Japanese Renesas factory and subsequent production stoppages will also present challenges for global automotive chip suppliers, with the effects expected to become apparent in May. In the short term, NIO hopes to maintain monthly deliveries at around 7000-7500 units.
However, due to NIO’s relatively small size, the impact of chips on NIO’s financial data will be far less than that of larger traditional automakers.
In addition, as NIO’s delivery volume continues to climb, there may be a significant impact on NIO’s financial data. Whether NIO can maintain its previously high level of customer service operation, which is highly regarded by NIO customers, is also subject to some uncertainty. In order to maintain the current level where a dozen employees serve a single customer, NIO will need to invest more resources into customer service.
When NIO completes a 20% gross margin on their vehicles and bumps against ceilings for future growth, finding a sustainable customer service operation is also a challenge that they urgently need to resolve.

In the long run, another challenging issue Li Bin will face is how to further increase terminal sales volume for NIO.
In March alone, the Model 3 sold over 25,000 units, while the recently launched domestic Model Y also exceeded 10,000 units. Surpassing Tesla should be an unquestionable responsibility and obligation for new domestic automakers such as NIO.
As internet giants like IM, Jidu, Xiaomi, and Didi enter the market, competition for NIO will only become increasingly fierce. This includes Baidu, a traditional automotive giant that has solid in-vehicle engineering expertise and is entering the smart connected vehicle industry with high-level autonomous driving, intelligent cockpit systems, and internet ecology. This will undoubtedly have an impact on NIO.
 Currently, NIO is in a relatively stable state of development, with financial and sales data trending towards a positive direction. With the launch of the ET7, as well as the increased adoption rates of high value-added subsystems like the 100 kW battery pack and NIO Pilot, NIO’s gross margin per vehicle will continue to increase.
Currently, NIO is in a relatively stable state of development, with financial and sales data trending towards a positive direction. With the launch of the ET7, as well as the increased adoption rates of high value-added subsystems like the 100 kW battery pack and NIO Pilot, NIO’s gross margin per vehicle will continue to increase.
However, NIO will also need to address challenges such as the high costs of customer operation and maintenance, and the increasingly competitive domestic NEV market in its development process. This is especially true with the entry of technology giants such as Alibaba, Baidu, Huawei, and Didi into the intelligent connected vehicle market. As a first-mover in this market, NIO’s ability to consolidate its leading position will depend on its ability to play to its strengths and minimize its weaknesses.
The global market for intelligent connected vehicles is enormous, but the road to success will undoubtedly become narrower. Under this huge market trend, NIO will need to continually strive for breakthroughs, such as by seeking exclusive technology like autonomous driving chips, intelligent cabins, and next-generation battery swapping technology in order to secure its position in the market and claim a piece of the pie.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
