Introduction
Since the birth of the automobile over 130 years ago, with the continuous development of traditional cars, the entire automotive industry and consumer market have reached some basic consensus on the main indicators for describing cars.
It is customary to classify cars by wheelbase and engine displacement, and to evaluate vehicles based on comfort, driving performance, safety, etc.
However, with Tesla’s breakthrough in electric vehicles and the entrance of IT and electronic companies such as Huawei, Xiaomi, and Apple into the field of smart cars, not only Tencent, Alibaba, Baidu, and Meituan have entered the field through investment in new car manufacturing companies.
Xiaomi’s $10 Billion Investment

I think there are several directions:
1) The initial investment of $10 billion is mainly used to build products, that is, around product development. Compared to Huawei’s positioning as a Tier 1 smart car manufacturer, Xiaomi’s focus is definitely on the whole vehicle. The whole vehicle is actually system integration, load various technologies in platforms, and then sell them out in different areas. Faced with revolutionary changes in smart cars, only the definition of the whole vehicle can achieve immediate success and pull the whole lever.
2) Will there be OEM production? From the current perspective, whether it is a joint venture or OEM production, technology companies entering the automotive industry must focus on the part that consumers perceive in cars, such as autonomous driving, intelligent cockpits, software systems that connect cars and mobile phones, and other interaction-priority parts. Xiaomi will most likely find partners to do the heavy asset part.
3) How to understand and revolutionize smart cars? From what we’ve seen this year, all electric car companies are talking about product strength and intelligence, competing with each other to occupy the commanding heights of the gasoline car market, and enhancing product strength with technology features that consumers are willing to pay for. Xiaomi’s strategy is not just about cost-effectiveness, but presenting its own intelligent software part in the car.
Note: Mr. Lei Jun has earned quite a bit of money from personal investment in new car manufacturing forces, which is a bit like investing first and then entering the field of smart cars in a big way when the inflection point arrives.
What is a Smart Car?
Currently, consumers, automotive industry practitioners, and planning units have different understandings of smart cars.
However, from a broad perspective, everyone’s ideas on the ultimate evolution of smart cars are similar: the functions and performance of smart cars mainly depend on the “driving robot” that serves as the vehicle’s brain.
Unlike traditional cars that we currently see, smart cars are no longer rigid driving execution mechanisms controlled by car owners, but intelligent robots that can expand vehicle functions and improve performance through software upgrades. What we can be sure of is that the development path of smart cars is similar to that of smart phones, full of iteration and development.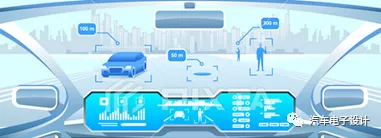
From a macro perspective, intelligent vehicles need to possess the following basic properties:
1) Equipped with advanced sensors and other devices, which includes various sensors for detecting road traffic, as well as a corresponding data processing and computing platform. By using new technologies such as artificial intelligence, the vehicle can calculate and judge the driving status and road environment status, ultimately resulting in a fully autonomous driving function.
Of course, according to the definition of standard institutions, vehicles above L3 will also be included in the field of intelligent vehicles, and the transition time here will gradually evolve with software and hardware.
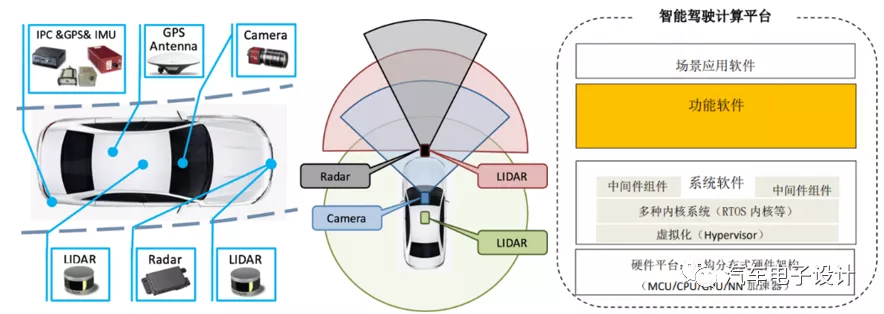
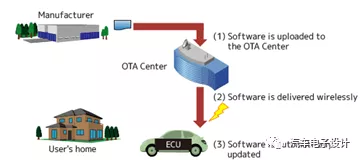
2) Equipped with an advanced software system that can update most of the core software functions through fast network interconnection, gradually becoming an intelligent mobile space and application terminal.
Due to the development requirements of intelligent vehicles, the companies that produce them need to control all software updates inside the vehicle, especially those relating to core functions. Through continuous development and iteration, these updates are pushed to consumers. The evolution itself requires a complete software system.
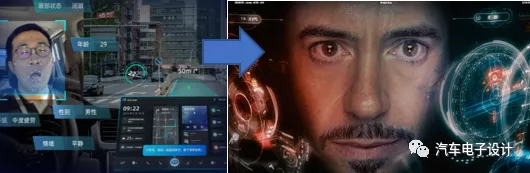
3) Equipped with an interaction system that can continuously recognize and manipulate consumer needs, able to support both manual and automatic driving modes.
Currently, intelligent vehicles need to have the ability to independently perceive the state and needs of passengers inside the vehicle. They must also possess “perception” and “understanding” of humans, and by analyzing data such as visual data (optical), speech (acoustic), and chassis and body data such as steering wheels, brakes, accelerators, gears, seat belts, etc., they can use biometric technology (mainly facial recognition and sound recognition within the passenger compartment) to comprehensively judge the driver’s (or other passengers’) physiological (portrait, facial features, etc.) and behavioral (driving behavior, sound, body movements) states. In order to provide feedback on human needs, intelligent vehicles need to provide multi-modal interaction capabilities, by integrating visual and speech perception data-ultimately evolving into an intelligent assistant in the vehicle.
ConclusionLet’s write some more. I think there is a lot to explore in this field. The automotive industry has become more dynamic and challenging since entering the year 2021!
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
