Introduction
After the news of Volkswagen’s production shutdown due to chip shortages in the domestic media came out, the issue of idle automobile production caused by the shortage of chips worth several US dollars has indeed aroused much discussion. This article aims to explore two aspects, one is the current status of the shortage of automotive chips, and the other is what causes the mismatch between chip supply and automotive demand.
Automotive Semiconductor Supply Status
1) Situation of major OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers
According to Automotive News, Volkswagen Group, Continental, and Bosch warned last Friday that the production of automotive chips required for automobile production has been disrupted globally due to the impact of the pandemic. As automobile manufacturing relies on core components such as engine ECUs and ESPs (which is the reason for the production shutdown reported in the domestic media, but in reality, it is only an example and not the actual cause of the shortage).
The pandemic in 2020 has greatly disrupted the entire automotive industry chain, slowing down automobile production at the beginning of the year. With the gradual recovery of demand in China and other markets since July, some local shortages of automotive spare parts have emerged.
In fact, according to Conti’s statement, the production capacity provided by the automakers was sufficient, but the additional capacity required them to order automotive semiconductor products from chip manufacturers, and the cycle was 6-9 months. It may take about 26 weeks to confirm with semiconductor manufacturers.
Therefore, this shortage problem mainly occurred from December 2020 and has extended to the first half of 2021, causing bottlenecks in delivery. This impact may have varying degrees of influence on all automakers, and it is difficult to keep up with demand-driven production.
2) Channel side
I consulted friends in the channel and found that the shortage of automotive electronic chips is due to seasonal squeezing, channel panic, and pessimistic expectations of the semiconductor industry in the first half of the year, as forecasted by McKinsey and IDC in April and May.
According to McKinsey’s prediction, sales of semiconductors for automotive applications mainly depend on car sales volume and the level of vehicle digitization and electrification.Since global automotive demand has already fallen sharply this year and will likely decline further over coming months, the automotive semiconductor market is expected to decrease by 10 to 27 percent in 2020. Semiconductor companies will likely not feel any effect until late in the second quarter, however, due to the long lead times of automotive semiconductors.
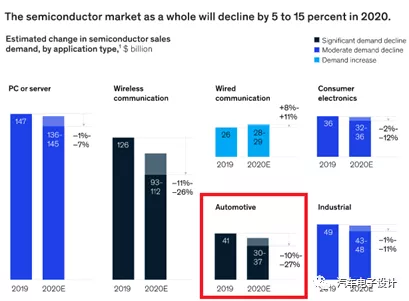
IDC predicts that the automotive and industrial semiconductor markets, which in the past were projected to outperform the other segments, have been particularly hard hit by COVID-19 mandates.
Automobile sales, including light commercial vehicles, declined 5.6% to 81.4 million vehicles in 2019, resulting in a decline in automotive semiconductor growth by 2.7% to $38.4 billion.
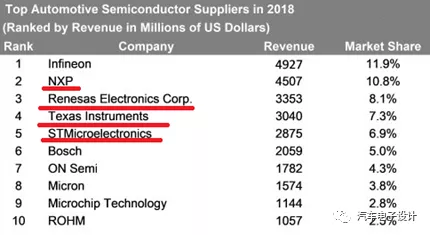
These predictions have led upstream producers to artificially shut down some 6-inch wafer lines, which first affects the supply of high-reliability automotive devices. This adjustment has led to price adjustments by automotive electronics chip companies such as NXP and Renesas.
Based on the current situation, this shortage exists for several companies, and the impact may be minimal for companies such as Bosch because the chip demand is more quickly reflected in their manufacturing departments.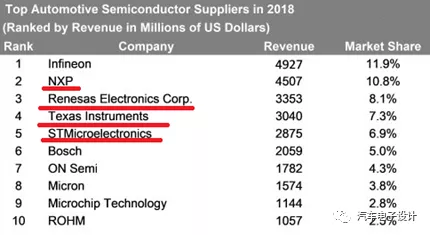
The Long-term Impact of Shortage of Automotive Chips
According to this trend, it may be reflected in two phases.
1) Large Tier 1: These companies are the first to feel the change in demand, as the demand is indeed very high, they can feel these changes first. In fact, the demand for recent cameras and radars of the large Tier 1 companies is increasing, and the overall manufacturing load is increasing. Therefore, within 3-5 months, they can gradually solve the problem.
2) Small Tier 1 and Tier 2: There are still many domestic automotive electronics projects in China. According to the current trend, it may cause hoarding among channel vendors. Due to their long purchase cycle, the response to small demand is not obvious at present; but as the pool of channel vendors gradually dries up, the chip supply problems they face will become more prominent.
These two aspects will slowly affect China’s joint venture OEMs and independent OEMs. If they want to increase production, they may encounter bottlenecks in the first half of 2021, and the status of the economy in the second half of 2021 is still uncertain.
Conclusion
The shortage of automotive chips right now may create an impression that localizing automotive chips is necessary in the long run. Indeed, the value of automotive chips is linked to huge losses in recalls and production stoppages. You can imagine how difficult it is for this industry.
This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.