In mid-April we had the opportunity to try out a Cadillac CT6 equipped with Super Cruise on the Shanghai Circuit. This is the world’s first hands-free driving model and the first assisted driving model equipped with high-precision maps and GPS!
As we enter 2019, competition in the field of assisted driving is becoming increasingly fierce. Almost all new car manufacturers introduce their achievements in the field of assisted driving in a few pages of PPT. Although Super Cruise under General Motors was officially launched in China as early as CES Asia in June 2018, few people know about it. Even those who have heard of it probably only know it from a promotional photo with hands off the steering wheel.
One reason why Super Cruise is not well known is that it has done a lot of software/hardware redundancy, greatly increasing the cost. Therefore, this system only appears in the top-spec version of the Cadillac CT6, which is the CT6 40T Platinum Edition with a price of 699,900 yuan, and the top-spec CT6 also sold for a very short period of time, so very few people have experienced Super Cruise. The other more important reason is left to everyone to guess.
Assisted driving that can give you a sense of security but with limited use
Since Super Cruise is little known, let me first talk about the experience. Super Cruise is positioned as a highway autopilot system, where “highway” can be understood as relatively closed loops and expressways.
There are two conditions for activating the Super Cruise continuous cruising system: First, it must be in a high-precision map coverage area of AutoNavi (a Chinese map service provider). Currently, high-precision maps only cover closed sections such as loops, elevated roads, and expressways, which means that Super Cruise cannot be used on urban roads. In addition, Super Cruise cannot be used on road sections with missing curvature data, such as the Nanpu Bridge in Shanghai. The second is that there must be clear lane lines and the car must be driven within the lane lines.
If the above two conditions are met, a gray steering wheel logo will appear on the top right of the instrument panel.
Press the button located in the middle of the left side of the steering wheel to activate Super Cruise.

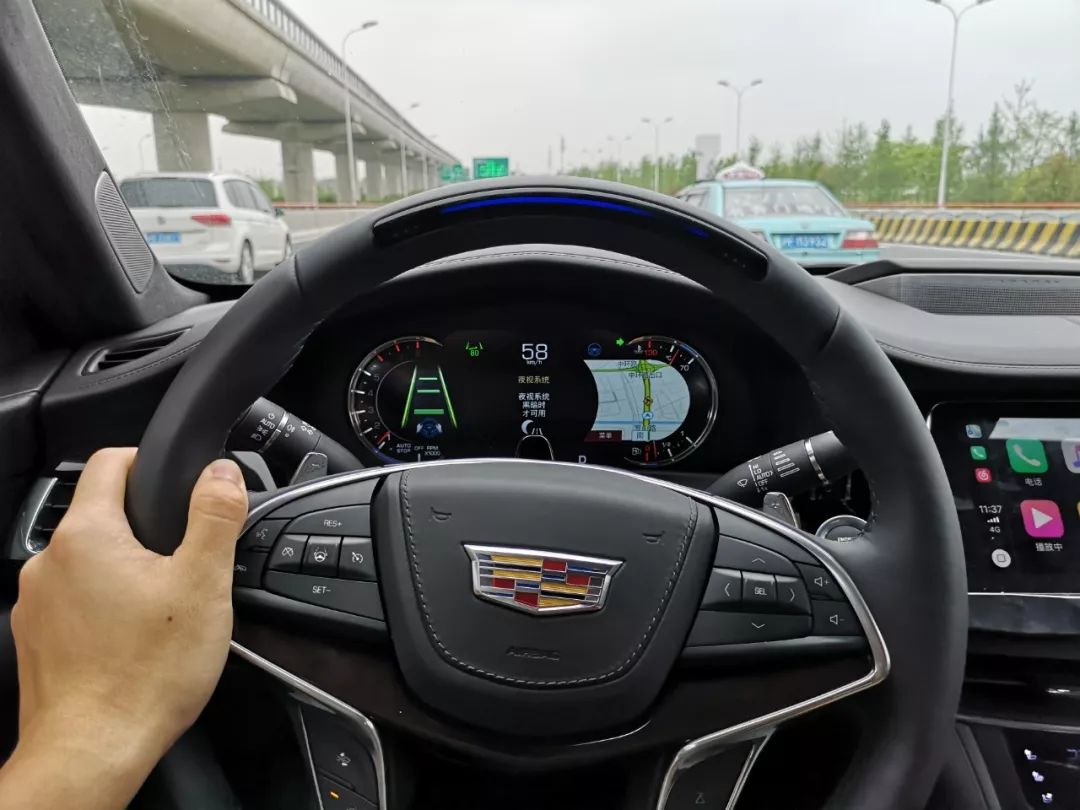
Once Super Cruise is enabled, the gray logo on the dashboard turns green, and a green light above the steering wheel indicates the status. At this point, the vehicle takes control of acceleration, braking, and steering, and you can take your hands and feet off the wheel, yes it’s hands-free L2.

What sets Super Cruise apart from other driver assistance systems is that it uses infrared emitters above the steering wheel and cameras above the steering column to detect your visual focus and eye state, and determine whether you’re distracted. It doesn’t rely on pressure sensors on the steering wheel to determine whether your hands are on the wheel, although Super Cruise does have such sensors.

The system will flash a light above the steering wheel to prompt you to take control if you look away for more than 5 seconds. If you look back at the road, Super Cruise will automatically resume.
If you continue to look away, the light on the steering wheel will start flashing red and the seat will vibrate, requiring you to take over control. If you take over, Super Cruise will automatically disengage and you will need to press the central left button again to turn it back on (ACC remains active).

If you still don’t take over control, the system will assume you are unconscious and the vehicle will slow down and move to the side of the road, while automatically alerting OnStar for assistance.In addition, when the vehicle is approaching a ramp or an area not covered by high-precision maps, the system will flash red and prompt the driver to take over the vehicle in advance.
What should I do if I want to change lanes while driving?
Currently, Super Cruise does not support automatic lane changing. When you want to change lanes, you do not need to exit the cruise function. The driver can directly intervene and turn the steering wheel to change lanes. During the lane changing process, the indicator light on the steering wheel will turn blue. After completing the lane change and staying in the center of the lane for a while, Super Cruise will re-engage and the indicator light will turn green.

This is also different from Tesla Autopilot. When Autopilot takes control, you need to overcome a certain degree of resistance to turn the steering wheel, giving you a feeling of fighting with the system. If you win, Autopilot will disengage. Super Cruise does not give you this kind of feeling at all. When you turn the steering wheel, you only need to overcome a very small resistance, which can be basically ignored.
Does traffic have any impact on Super Cruise?
No, as long as you are in an area covered by high-precision maps, Super Cruise can engage regardless of the speed.
Can I rely on Super Cruise to drive on the entire high-speed road covered by high-precision maps?
No, although high-precision maps cover the entire high-speed road, the system will prompt the driver to take over the vehicle when approaching a ramp. In addition, Super Cruise cannot work on road sections without curve and curvature data, so the use range of Super Cruise is still relatively limited.
What is the feeling of automatic steering?
It is linear. This linearity comes from its auxiliary steering logic. Because Super Cruise has redundant high-precision maps and high-precision positioning, the system knows whether there are any curves ahead, and what the curvature is, so it can achieve very linearity.
Although relying on visual recognition is passive, with the support of excellent algorithms, the turning process can also be very linear. At least Autopilot and Super Cruise have no significant difference in perceived experience.
How is the acceleration and deceleration control?
After talking about the core steering function, the rest of the function is actually the full-speed range adaptive cruise control (ACC) function, relying on 5 millimeter-wave radars to detect surrounding vehicles.The system’s acceleration and deceleration controls are comfortable enough when driving behind another vehicle, but occasionally the system might brake abruptly due to someone cutting in. The distance between vehicles can be adjusted in three levels, but generally the distance is kept quite large.
High-precision Map Redundancy
After discussing the driving experience, it is necessary to talk about the working logic of Super Cruise, starting with its hardware.
The CT6 is equipped with five cameras, five millimeter-wave radars, twelve ultrasound radars, one Mobileye EyeQ3 visual information processor, one high-precision map database, and high-precision GPS.
What sets Super Cruise apart from other driver assistance technologies is that it has an additional complete set of high-precision maps for redundancy, and interestingly, its sensing hardware design layout.
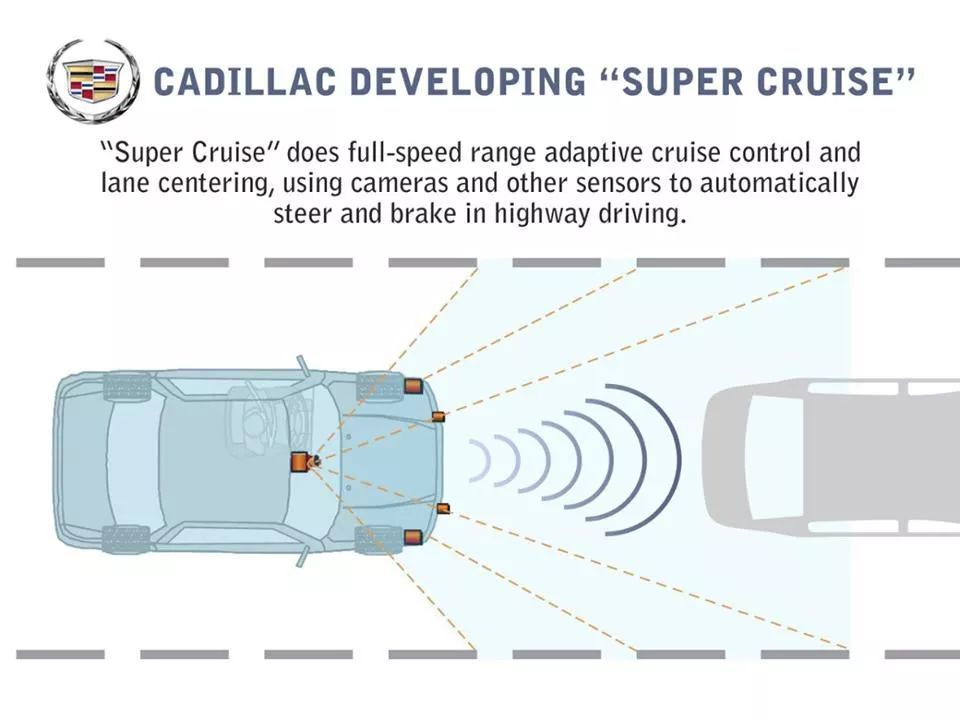
Four of the five cameras are panoramic cameras, with one high-definition front camera. Two of the three cameras, located below the rearview mirror, and the high-definition front camera are involved in driver assistance. They are used to determine the position and orientation of lane markings, recognize road signs on both the left and right, and send the collected image data to the Mobileye EyeQ3 chip for processing, which is then transmitted to the central processor.
Four of the five millimeter-wave radars are located at the front of the vehicle, two for short-range radar and two for long-range radar. They are used to perceive vehicles and obstacles ahead, transmitting the information obtained to the central processor, which makes acceleration or deceleration decisions, determines whether to travel straight or around curves based on data from the cameras and millimeter-wave radars, and realizes the vehicle’s lateral and longitudinal control.
So what is the use of high-precision maps and high-precision GPS?
Currently, Super Cruise is only available in three countries: China, the United States, and Canada. In the United States and Canada, Super Cruise uses high-precision maps provided by Ushr, while in China, Super Cruise uses high-precision maps provided by Amap. Firstly, only when driving in areas covered by high-precision maps can Super Cruise be activated, so the first function of high-precision maps is to determine the region.
In addition, high-precision maps will provide data on road curvature, lane numbers, as well as information on overpasses, exits, and other road attributes. This can provide curvature data for larger turns and make turning smoother. High-precision GPS can also determine the longitudinal distance between the vehicle and its lane based on its position.## What are the Differences between Super Cruise and Autopilot?
Let’s start with a figure:
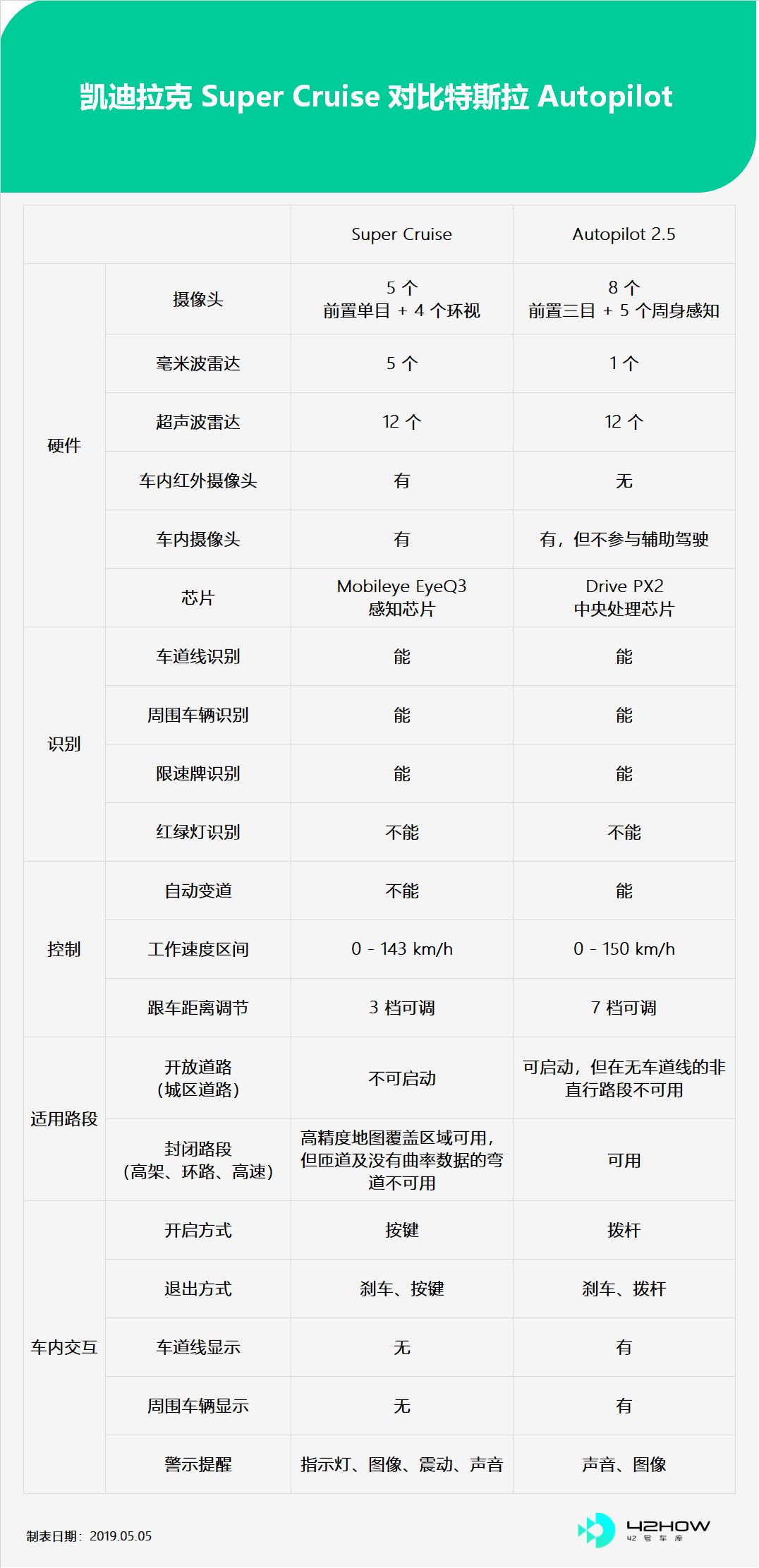
1. The hardware differences are mainly the differences in quantity and layout. Autopilot is mainly based on cameras, while Super Cruise is cameras + millimeter-wave radars. Additionally, there are high-precision maps and high-precision GPS redundancies.
2. The working area differences are that Super Cruise is limited to the area covered by high-precision maps, while Autopilot can work in any area with lane lines.
3. The driver state detection differences – as mentioned earlier, Super Cruise identifies the driver’s visual direction through the camera to determine if the driver is distracted, while Autopilot uses torque sensors on the steering wheel to detect whether the driver’s hands are on the steering wheel to determine if the driver is distracted, with two different methods.
4. Lane change differences – When Super Cruise is engaged, the driver can directly turn the steering wheel to change lanes, while Autopilot needs to be disengaged before changing lanes. If forced to change lanes when in Autopilot mode, the system will exit directly from the assisted steering.
- Decision-making and execution differences – Super Cruise has high-precision map information and clearly defines usable and unusable areas. The system will ask the driver to take over in advance when approaching an unavailable road section. Autopilot will first make its own decisions until the system is unable to process, then will hand over the control to the driver.
6. System update and iteration differences – Super Cruise has fixed OTA updates for high-precision map data every three months, while Autopilot does not have a regular schedule but is much more frequent. Additionally, Super Cruise does not collect information and upload data through cameras to provide feedback to the host factory, while Tesla will use cameras to collect real-time road information and enrich the database.
Super Cruise is worth looking forward to.Let’s summarize: Super Cruise is currently the only assisted driving system that uses high-precision maps. When Super Cruise is active, it gives me strong feelings of safety due to its limited use cases and full perception redundancy. When it comes to selecting routes, Super Cruise doesn’t require too much system decision-making, as there is not much uncertainty and it already knows all the curve information by heart. However, when approaching freeway junctions or sections without high-precision map coverage, the system promptly hands control back to me.
On the other hand, the drawbacks are quite obvious: its use cases are quite limited, as Super Cruise cannot be activated on roads in urban areas, in areas without high-precision map coverage or on roads without curve radius data. Therefore, drivers need to take over frequently.
Additionally, according to foreign media, all Cadillac models are expected to be equipped with the Super Cruise system by the end of 2020, with the CT5 being the second model. Moreover, it will also support automatic lane change function, which is why Super Cruise should not be overlooked!

- Tesla’s autopilot chips in mass production: a long-planned attack* In-depth Analysis: Tesla’s Autopilot and Automated Driving Architecture VS Laser-based Systems


This article is a translation by ChatGPT of a Chinese report from 42HOW. If you have any questions about it, please email bd@42how.com.
